Bridge Crane Crane System, Custom Bridge Crane, Good Crane Price
Overview on types of bridge crane systems, i.e, Top Running, Ceiling Mounted & Freestanding Bridge Crane Systems, hot sale 3 ton to 80 ton bridge cranes.
Category: Bridge Crane
Your Trusted Bridge Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Bridge Crane Crane System, Custom Bridge Crane, Good Crane Price
Top Running, Ceiling Mounted & Freestanding Bridge Crane Systems, hot sale 3 ton to 80 ton
Overview on types of bridge crane systems, i.e, Top Running, Ceiling Mounted & Freestanding Bridge Crane Systems, hot sale 3 ton to 80 ton bridge cranes.
Bridge Crane System, Top Running, Ceiling Mounted & Freestanding Bridge Crane Systems
Exploring Bridge Crane Systems: The Ultimate Guide
The world of material handling and heavy lifting would be significantly different without the presence of bridge crane systems. These engineering marvels serve as the backbone of countless industries, providing the muscle and precision required to move heavy loads efficiently and safely. In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the realm of bridge crane systems, unlocking their potential and shedding light on the key aspects that make them indispensable in various applications.
Bridge crane systems are more than just tools; they are the drivers of productivity, the guardians of safety, and the enablers of seamless material flow. This guide is your compass to navigate the intricate landscape of bridge cranes, whether you are a prospective buyer or an experienced user looking to enhance your knowledge.
Types of Bridge Crane Systems
When it comes to material handling and heavy lifting, versatility and precision are paramount. Overhead bridge crane systems stand out as the true workhorses, offering unmatched capabilities for various material handling tasks.
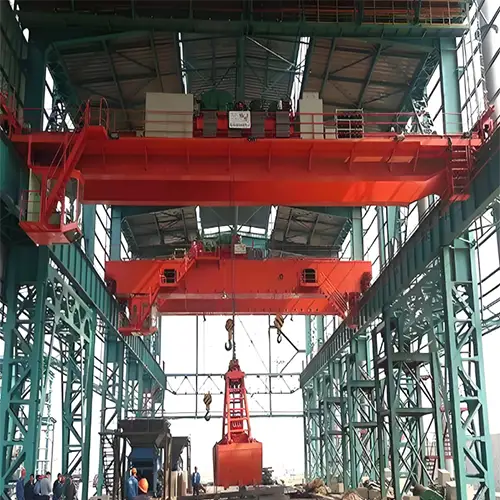
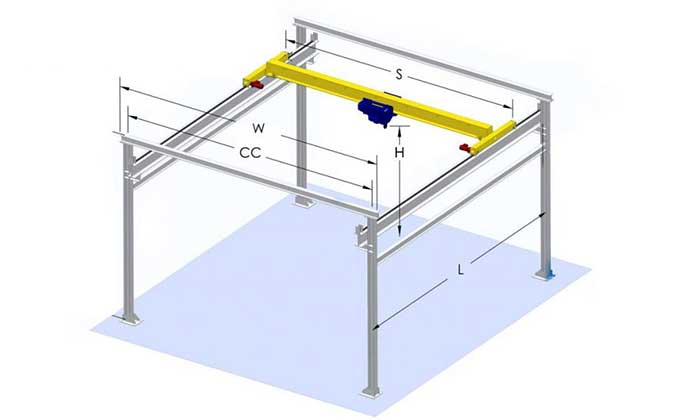
An overhead bridge crane system is a powerhouse of material handling. At its core, it consists of a bridge, trolley, and hoist. The bridge runs along elevated runways, supported by the building structure or framework, allowing for horizontal movement. The trolley, situated on the bridge, moves the load horizontally, and the hoist, which is attached to the trolley, performs the vertical lifting. This combination of components provides a seamless solution for transporting heavy loads with precision and efficiency.
Highlighting Versatility
Overhead bridge cranes are renowned for their versatility. They are suitable for a wide range of material handling tasks, making them indispensable in industries like manufacturing, construction, warehousing, and more. Whether you need to transport raw materials, assemble heavy machinery, or load and unload materials, overhead bridge cranes can do it all.
These cranes can be customized to suit specific requirements, and their load-bearing capacities can vary from a few tons to several tons, ensuring they are adaptable to different scenarios. Additionally, their ability to move loads horizontally and vertically with great accuracy allows for efficient and safe material handling operations.
In the following sections, we will explore other types of bridge crane systems, each with its unique features and benefits, catering to various applications and industries.
Types of Bridge Crane Systems
In the world of material handling, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Different tasks demand different tools. Let's explore various types of bridge crane systems, each with its unique strengths and applications.
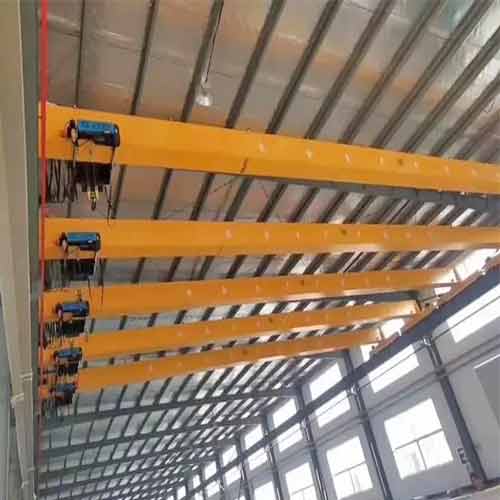

Single Girder Bridge Crane System
Efficiency in Simplicity
Single girder bridge crane systems and single girder overhead cranes are a testament to efficiency in simplicity. They are characterized by having a single bridge girder, the horizontal beam that supports the trolley and hoist. These cranes are excellent for facilities where light to moderate loads need to be handled with precision.
Advantages
- Cost-effective: Single girder cranes are more economical to purchase and install.
- Lightweight: The reduced weight places less stress on the building's structure.
- Versatile: Ideal for maintenance, repair, and light assembly tasks.
Applications
Single girder bridge cranes find their niche in workshops, smaller manufacturing facilities, and warehouses, where they efficiently handle loads that don't require heavy lifting capacity.
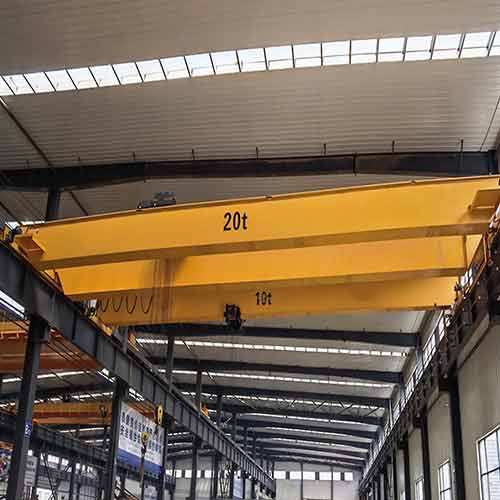

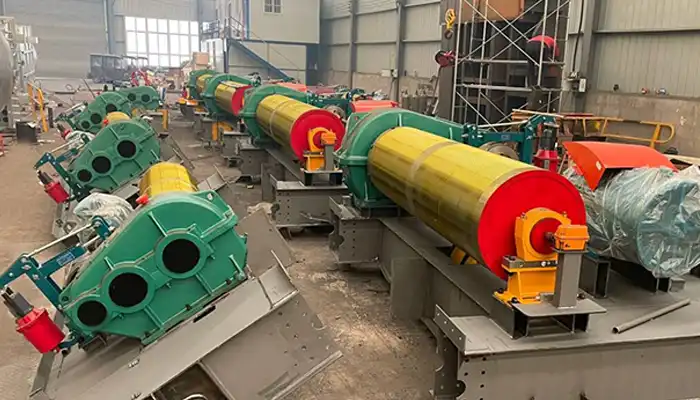
Double Girder Bridge Crane System
Strength and Precision
Double girder bridge crane systems or double girder overhead crane systems , on the other hand, bring a higher level of power and precision to the table. They feature two bridge girders running in parallel, offering increased stability and load-bearing capacity.
Advantages
- Heavy lifting: Double girder cranes can handle significantly heavier loads than their single girder counterparts.
- Durability: Their robust design ensures long-lasting performance.
- Precision: The dual girder configuration allows for accurate load positioning.
Applications
Double girder bridge cranes are the go-to choice for heavy-duty applications. They shine in industries such as steel manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace, where the ability to lift substantial loads with precision is essential.
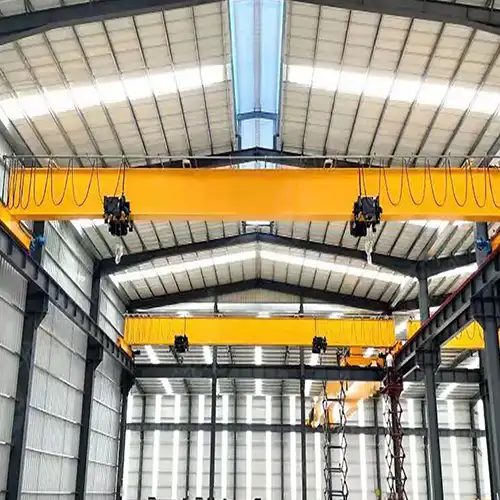

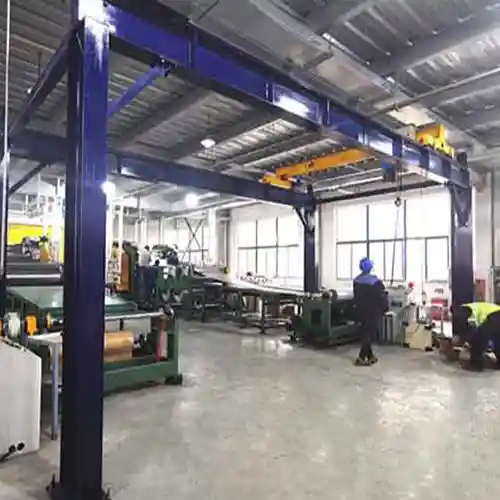
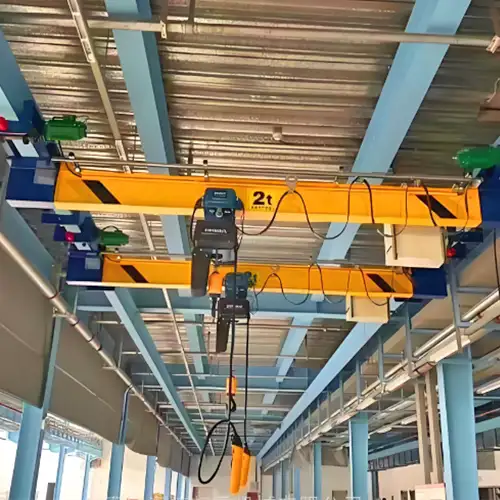
Top Running Bridge Crane System
Up High for Efficiency
Top running bridge crane systems are designed to maximize efficiency by operating on elevated runways. The bridge travels on top of the runway beams, leaving the workspace unobstructed.
Advantages
- Optimal space utilization: The crane's travel path is above, leaving the ground clear for other operations.
- Versatility: Suited for various industries and adaptable to different building structures.
- Precision: Top running cranes offer precise load movement.
Applications
Top running bridge cranes are favored in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and warehousing. Their ability to efficiently transport materials without intruding on valuable floor space makes them a popular choice.
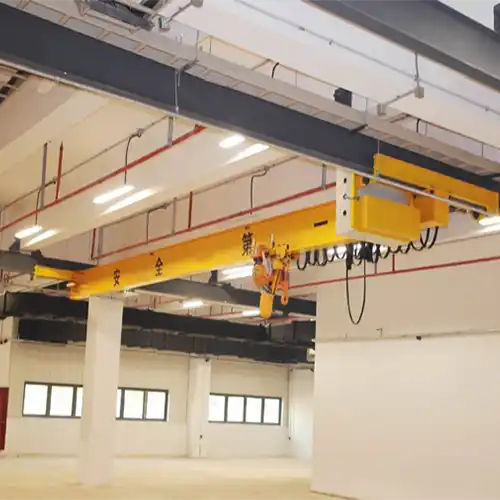

Efficiency from Below
Underhung bridge crane systems operate in a reverse configuration compared to top running cranes. These cranes are suspended from the building structure, allowing them to move loads efficiently beneath the runway.
Advantages
- Cost-effective installation: Underhung cranes are often simpler and more economical to install.
- Ideal for lighter loads: Well-suited for tasks that don't require extreme lifting capacity.
- Space-saving: They make the most of available headroom.
Applications
Underhung bridge cranes are commonly found in workshops, assembly lines, and manufacturing facilities, where they provide efficient and cost-effective material handling solutions for lighter loads.
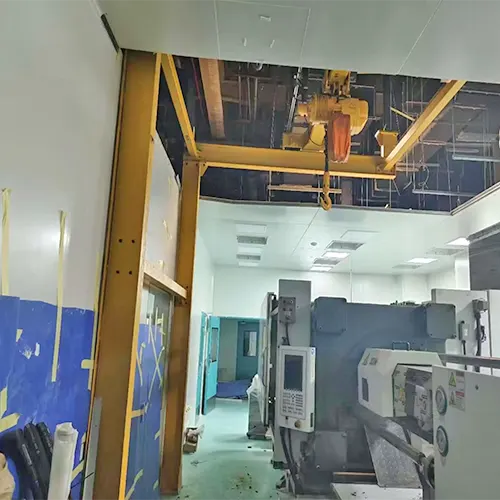
Ceiling Mounted Crane Systems
When it comes to maximizing space and efficiency, ceiling-mounted crane systems are a game-changer. Let's delve into the world of ceiling-mounted cranes and uncover their unique features and ideal applications.
Exploring Ceiling-Mounted Crane Systems
Ceiling-mounted crane systems are designed to make the most of available space. These cranes are attached to the ceiling, allowing them to move loads smoothly and efficiently without taking up precious floor space. They are particularly beneficial in facilities where floor space is at a premium.
Ceiling-mounted crane systems, known for their space-saving and efficient material handling capabilities, come in several types, each designed for specific applications and environments. The main types of ceiling-mounted crane systems include:
- Monorail Crane Systems: Monorail cranes consist of a single rail or track, often mounted on the ceiling, which can be installed in a fixed path. They are suitable for linear material transport in environments with weight restrictions. Monorail systems are commonly used for point-to-point material movement in manufacturing, assembly, and storage facilities.
- Underhung Bridge Crane Systems: Underhung bridge cranes are also ceiling-mounted, but they differ from top-running systems in that the bridge is suspended from the ceiling, allowing for efficient material handling beneath the runway. They are suitable for light to moderate loads and are often used in workstations, assembly lines, and warehouses.
- Ceiling Mounted Workstation Crane System: Ceiling-mounted workstation crane systems are specifically designed for material handling at workstations, assembly lines, and other applications where precise and efficient load movement is required. These systems are mounted to the ceiling, allowing them to cover a defined workspace with ease. They are ideal for tasks that involve repetitive lifting and positioning, contributing to improved productivity and reduced worker fatigue.
- Ceiling Mounted KBK Rail Crane System: KBK (Kranbahnsysteme) rail crane systems are known for their flexibility and adaptability. These ceiling-mounted systems use modular components, such as aluminum profiles and enclosed tracks, to create customized crane solutions. KBK rail crane systems are suitable for a wide range of material handling tasks, including transporting loads of various shapes and sizes. They offer precision and ease of use, making them valuable in manufacturing, logistics, and assembly environments.
Applications Where Ceiling-Mounted Cranes Excel
Ceiling-mounted cranes shine in scenarios where floor space needs to be optimized. They are commonly found in settings like:
- Manufacturing Facilities: Ceiling-mounted cranes are ideal for transporting materials within manufacturing facilities, ensuring that the floor remains clear for other operations.
- Warehouses: These cranes are frequently used in warehouses for efficient storage and retrieval of goods, providing flexibility and quick access to items on high shelves.
- Workstations: In assembly line workstations, ceiling-mounted cranes facilitate the smooth movement of components, enhancing productivity and reducing the risk of accidents.
- Clean Rooms: In environments where cleanliness is crucial, ceiling-mounted cranes help maintain the sterility of the floor area.
By capitalizing on the space above, ceiling-mounted crane systems optimize your facility's layout and material handling capabilities.
Key Components of Bridge Crane Systems
A deep understanding of the key components of bridge crane systems is essential to grasp how these machines operate seamlessly. Let's explore the critical elements that make bridge crane systems tick.
In-Depth Analysis
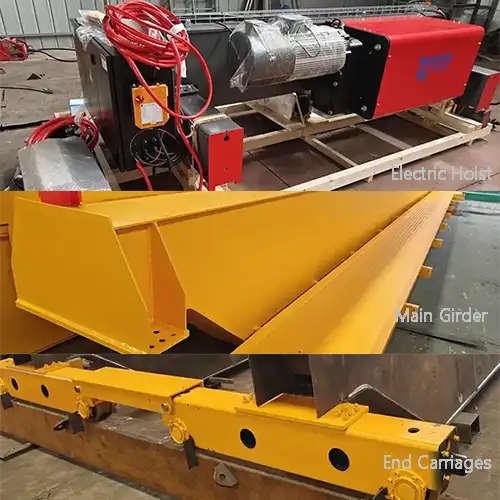
- Trolleys: Trolleys are the mechanisms that facilitate horizontal movement along the crane's runway. They play a crucial role in transporting loads with precision.
- Hoists: Hoists are responsible for the vertical lifting of loads. Different hoist types are available, each tailored to specific applications, whether it's for heavy-duty lifting or delicate positioning.
- Runways: Runways are the horizontal beams that support the crane's movement. They can be top-mounted, underhung, or ceiling-mounted, depending on the crane's design.
- Controls: Control systems are the brains behind the crane's operation. They allow operators to maneuver the crane with accuracy and ensure safe material handling.
Understanding how these components work in harmony is key to optimizing the efficiency and safety of your bridge crane system. In the following sections, we'll dive deeper into the intricacies of bridge crane systems, empowering you to make informed decisions and get the most out of your material handling operations.
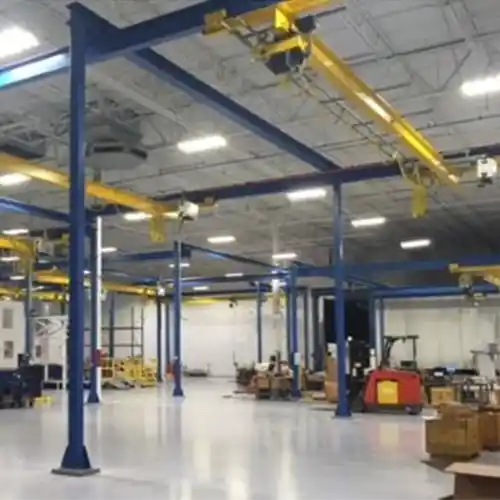
Free Standing Bridge Crane Systems
When it comes to versatility and adaptability, free-standing bridge crane systems are at the forefront. Let's uncover the advantages and applications of these innovative cranes and explore how they stack up against other mounting options.
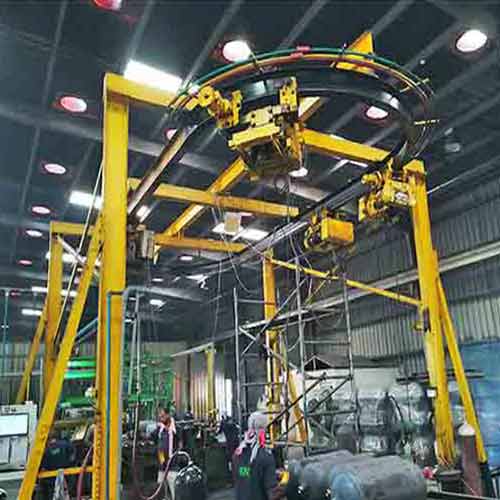

Ceiling mounted monorail rail system
Free-standing bridge crane systems, also known as free-standing overhead cranes, come in several types, each designed to meet specific material handling needs. The main types of free-standing bridge crane systems include:
- Single Girder Free-Standing Bridge Cranes: These cranes feature a single horizontal beam, or girder, supported by upright columns at both ends. They are well-suited for light to moderate lifting applications and offer a cost-effective solution for facilities with limited headroom.
- Double Girder Free-Standing Bridge Cranes: Double girder cranes have two horizontal girders and provide greater load capacity and stability compared to single girder cranes. They are ideal for heavy-duty lifting tasks and applications where precision and control are essential.
- Top-Running Free-Standing Bridge Cranes: Top-running cranes have wheels that run on a track attached to the top of the support columns. This design maximizes the hook height and is suitable for lifting and moving heavy loads. Top-running cranes are commonly used in manufacturing and industrial settings.
- Underhung Free-Standing Bridge Cranes: Underhung cranes, on the other hand, have wheels running on the bottom flange of the support columns. They are typically used for lighter loads and applications where headroom is limited. Underhung cranes are common in workstations, assembly lines, and warehouses.
The choice of free-standing bridge crane system depends on factors such as the load capacity requirements, available space, and the specific material handling tasks in your facility. Each type offers its own advantages, so selecting the right one is essential for efficient and safe material handling operations.
Unveiling the Advantages
Free-standing bridge crane systems offer a host of advantages that make them a compelling choice for various material handling tasks. These advantages include:
- Independence from Building Structure: Unlike ceiling-mounted or underhung cranes, free-standing cranes are not reliant on the building's structural support. This independence allows for more flexible placement within your facility.
- Easy Installation: Installing a free-standing crane typically requires less modification to the building structure. It can be a more straightforward and cost-effective solution.
- Increased Mobility: Free-standing cranes can be relocated if needed, offering versatility for changing material handling requirements.
- Enhanced Load Capacity: The design of free-standing cranes often allows for higher load capacities, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Applications
Free-standing bridge crane systems find their place in various industries and scenarios, including:
- Manufacturing: They are frequently used in manufacturing facilities for tasks such as assembly, maintenance, and material handling.
- Warehousing: Free-standing cranes are well-suited for optimizing warehouse operations, helping with the efficient storage and retrieval of goods.
- Construction: In construction projects, these cranes provide the lifting capacity required for tasks like placing heavy materials or equipment.
- Agriculture: Farms and agricultural facilities benefit from free-standing cranes for tasks such as handling produce, machinery, and equipment.
Comparing Benefits
When evaluating free-standing cranes against other mounting options, consider factors such as space utilization, installation complexity, and load capacity. While ceiling-mounted cranes save floor space, free-standing cranes offer more flexibility in placement and are often more cost-effective than underhung cranes. Ultimately, the choice between mounting options depends on your specific material handling needs and facility layout.
In the following sections, we'll explore more aspects of bridge crane systems, including ceiling-mounted and free-standing options, empowering you to make the right choice for your material handling operations.
Key Components of Bridge Crane Systems
Bridge crane systems are complex machines that rely on several key components working together seamlessly to lift and move heavy loads. Understanding these components is essential for the safe and efficient operation of bridge cranes. In this section, we'll delve into the critical components that make bridge crane systems function, including trolleys, hoists, runways, and controls.
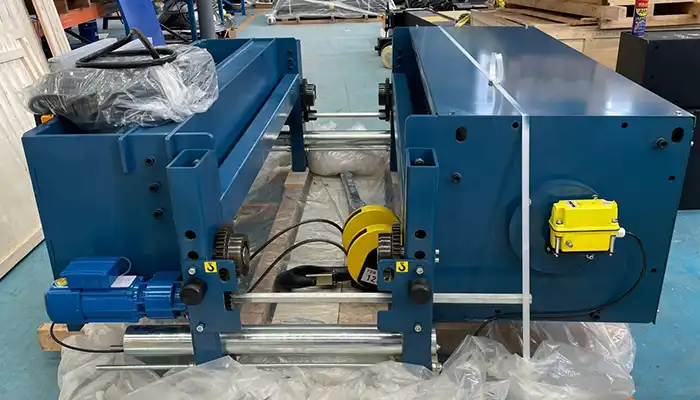
- Trolley System: - The trolley is a vital part of the bridge crane that carries the hoist and load horizontally along the bridge beam. It allows for precise positioning and movement of the load within the facility. Trolleys can be manual or powered, with powered trolleys providing greater efficiency and control.
- Hoist System: - The hoist is responsible for lifting and lowering the load. It is attached to the trolley and is equipped with a hook, rope, or chain for securing the load. Bridge cranes may use various types of hoists, such as wire rope hoists, chain hoists, or electric hoists, depending on the load capacity and application.
- Runway System: - The runway consists of rails or tracks on which the bridge crane travels. It provides support and guidance for the crane's movement. Runways can be either top-running or underhung, depending on the design and load capacity of the crane. Proper installation and maintenance of runways are crucial for the crane's safe and smooth operation.
- Controls and Electrification: - Bridge crane systems rely on a control system to manage the crane's movements. Modern cranes often use radio remote control systems, allowing operators to control the crane from a safe distance. Additionally, electrification systems, such as power tracks and festoon systems, provide power to the crane for various functions, including hoisting, trolley travel, and bridge movement.
Understanding how these components work together is essential for crane operators and maintenance personnel. Regular inspections and maintenance of these components ensure the continued safe and efficient operation of bridge crane systems. Additionally, advancements in control technology and electrification systems have improved the precision and safety of bridge cranes, making them even more valuable in today's industrial and manufacturing environments.
Safety Features and Accessories in Bridge Crane Systems
When it comes to operating bridge crane systems, safety is of paramount importance. These heavy-duty machines are designed to lift and transport substantial loads, and ensuring the well-being of workers and the protection of materials is a top priority. In this section, we'll explore the various safety features and accessories that enhance the security of bridge crane operations.
- Collision Avoidance Systems: - Collision avoidance systems are designed to prevent accidents and collisions. They utilize sensors and technology to detect obstacles or other cranes in the crane's path. When a potential collision is detected, the system can trigger automatic actions, such as slowing down the crane's movement or even stopping it altogether. This feature is invaluable in busy industrial environments where multiple cranes may be operating simultaneously.
- Audible Alarms: - Audible alarms are a fundamental safety feature in bridge crane systems. They provide audio warnings to alert workers and others in the vicinity of the crane's movements. Audible alarms are especially crucial in busy workplaces with high noise levels, ensuring that people are aware of the crane's actions and can take appropriate precautions.
- Safety Standards and Regulations: - Compliance with safety standards and regulations is non-negotiable in crane operations. Different regions and industries may have specific safety requirements that must be adhered to. These standards cover aspects such as load capacities, maintenance schedules, operator training, and safety protocols. Staying up to date with these regulations and ensuring compliance is a shared responsibility among crane operators, manufacturers, and facility managers.
- Additional Safety Accessories: - Bridge crane systems may incorporate additional safety accessories, such as emergency stop buttons, warning lights, load limit indicators, and anti-sway systems. These accessories contribute to the overall safety of crane operations, providing multiple layers of protection against potential hazards.
Safety is not an option but a necessity in the world of bridge crane systems. The integration of collision avoidance systems, audible alarms, and other safety enhancements not only reduces the risk of accidents but also promotes a safer and more productive work environment. By complying with safety standards and regulations, bridge crane operators and facility managers demonstrate their commitment to the well-being of their workforce and the efficiency of their material handling operations.
Bridge Crane Runway Systems: The Backbone of Efficient Operations
In the bustling world of material handling and heavy lifting, precision, safety, and efficiency are paramount. Whether in manufacturing, warehouses, or construction sites, overhead cranes stand as the workhorses that make it all possible. But have you ever wondered what keeps these mechanical marvels gliding smoothly and securely above our heads? Enter the unsung heroes of the overhead crane world – the runway systems.
In this comprehensive guide, we're diving deep into the world of "bridge crane runway Systems: The Backbone of Efficient Operations." Let's embark on a journey to unravel the crucial role of runway systems in ensuring the seamless operation of overhead cranes. From the fundamentals of design to materials, construction, configuration, maintenance, and safety considerations, we'll explore every aspect you need to know. So fasten your seatbelts, and let's soar through the skies of crane efficiency and reliability.
The Fundamentals of Runway Systems
In the realm of material handling and heavy lifting, the efficiency and safety of operations often rely on a fundamental but frequently underestimated component – the bridge crane runway system. These systems serve as the backbone of efficient crane operations, providing a defined path for crane movement and a robust foundation on which the crane can operate seamlessly.
An bridge crane runway system is a structural framework designed to support and guide the movement of overhead cranes within an industrial or commercial space. It includes various components working in harmony to ensure the crane's smooth and controlled traversal across the designated area. These components typically consist of:
- Runway Beams: These horizontal beams act as tracks for the crane to move along. They are typically made of durable materials like steel or aluminum and are precisely engineered to handle the weight and stress of the crane and its loads.
- Runway Columns: Vertical structures that provide support for the runway beams. Runway columns are securely anchored to the floor or building structure and play a critical role in bearing the crane's weight.
- Support Brackets: These connect the runway beams to the runway columns, adding stability and load-bearing capacity to the entire system. They ensure that the beams are firmly in place, preventing any lateral movement during crane operations.
The Foundation for Overhead Crane Operations
Runway systems are integral to overhead crane functionality, serving as a stable and predefined path for crane movement. They play several pivotal roles in crane operations:
- Guided Movement: The runway beams create a designated path for the crane, ensuring that it moves precisely where it's needed. This guided movement is essential for tasks that require accuracy and efficiency.
- Load Capacity: The materials used in the construction of runway beams and columns are carefully chosen to provide the necessary load-bearing capacity. This ensures that the crane can safely handle the weight of the loads it's intended to lift.
- Stability: The combination of runway beams, columns, and support brackets creates a structurally sound foundation. This stability is vital for preventing any sway, wobble, or unintended movement of the crane, especially when carrying heavy loads.
- Safety: A well-designed and maintained runway system enhances safety during crane operations. It minimizes the risk of accidents, collisions, and load drops by keeping the crane on a predictable and secure path.
- Efficiency: Runway systems enable overhead cranes to work with precision and efficiency. They facilitate the swift and accurate transport of materials, improving overall productivity in industries that rely on crane operations.
In essence, the bridge crane runway system is the structural framework that supports the crane's operations, much like the tracks guiding a train. Without a solid and well-designed runway system, the crane's performance and safety would be compromised, making it a crucial component for any organization that relies on overhead cranes for material handling.
In the upcoming sections of this guide, we will delve deeper into the intricate details of runway systems, exploring their various configurations, design principles, materials, installation considerations, and maintenance requirements. We will also emphasize the importance of adhering to safety standards and provide practical insights for optimizing runway system efficiency. So, let's continue our journey through the backbone of efficient crane operations: the bridge crane runway systems.
Design Principles for Runway Systems
When it comes to the design of bridge crane runway systems, there are several critical principles that must be considered to ensure efficient and safe crane operations. These design considerations play a pivotal role in determining the performance, longevity, and overall functionality of the runway system. Let's explore the key principles that guide the design process:
- Load Capacity -The load capacity of a runway system is one of its most fundamental design parameters. It refers to the maximum weight that the system can safely support, including the weight of the crane itself, the load it is carrying, and any additional equipment. Design engineers must calculate the anticipated loads based on the intended use of the crane and ensure that the runway system can handle these loads without compromising safety or structural integrity.
- Runway Span -The runway span is the distance between the columns that support the runway beams. It's a critical design parameter because it influences the crane's coverage area and the system's load-carrying capacity. The span should be carefully determined based on the crane's requirements, the workspace layout, and the desired coverage area. A well-chosen runway span ensures that the crane can access all necessary work areas without overloading the system.
- Structural Integrity -The structural integrity of the runway system is paramount. It involves the selection of materials and the engineering of the components to ensure that the system can withstand the forces and stresses imposed by the crane during operation. The materials used for the beams, columns, and support brackets must meet specific strength and durability standards. Additionally, the design should account for factors such as wind loads, seismic activity, and any dynamic loads that may be present.
- Runway Configuration -The configuration of the runway system is another crucial consideration. The system can be designed in various configurations, including single girder or double girder systems. Single girder systems are lighter and often used for lighter loads and smaller spans, while double girder systems provide increased load capacity and are suitable for larger spans and heavier loads.
- Runway Alignment -Proper alignment of the runway system is essential for the crane's smooth and precise movement. Misalignment can lead to premature wear and tear on the crane components, reduced efficiency, and safety hazards. Design engineers must ensure that the runway beams are installed parallel to each other and at the correct elevation.
- Safety Measures -Safety is a non-negotiable aspect of runway system design. Design engineers must incorporate safety features into the design, such as runway end stops, safety buffers, and anti-derailment devices. These measures are critical for preventing accidents and protecting personnel and equipment.
- Future Expansion -Forward-thinking runway system design should also consider the potential for future expansion or modifications. The design should accommodate the possibility of adding additional cranes or extending the runway system as the needs of the facility evolve.
By carefully adhering to these design principles, engineers can create runway systems that not only meet current material handling requirements but also have the flexibility and capacity to adapt to changing operational needs. The result is a runway system that serves as a reliable and efficient backbone for overhead crane operations. In the subsequent sections of this guide, we'll explore the materials commonly used in runway system construction, the installation process, and the critical role of maintenance in ensuring the continued performance and safety of these essential systems.
Runway System Configuration
Runway system configuration is a critical aspect of overhead crane design, impacting the crane's performance, load capacity, and versatility. Understanding the various configurations and their suitability for specific applications is essential to ensure efficient material handling. Let's explore different runway system configurations, including top-running and underhung systems, and the scenarios where each configuration excels:

Top-Running Runway Systems
In top-running runway systems, the crane wheels or end trucks run on the top flange of the runway beam.
These systems are designed to support the weight of the crane, its load, and the structural forces.
Top-running systems are commonly used in industrial and manufacturing settings where heavy loads and high load capacity are required.
Benefits:
High Load Capacity: Top-running systems are known for their ability to handle significant loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Versatility: They can accommodate various types of overhead cranes, including single and double girder cranes.
Durability: The robust design of top-running systems ensures long-term durability and reliability.
Suitable Applications:
Manufacturing facilities with heavy material handling needs.
Warehouses and distribution centers with large and bulky items.
Construction sites requiring the movement of heavy construction materials.

Underhung Runway Systems
Underhung runway systems feature a crane that hangs or is suspended from the bottom flange of the runway beam.
The load is mainly supported by the building's structure, while the crane provides lateral movement.
Underhung systems are suitable for light to moderate load applications.
Benefits:
Lightweight Design: Underhung systems are lightweight and cost-effective, making them ideal for smaller, budget-conscious projects.
Efficient Use of Space: They require minimal space, making them suitable for facilities with space constraints.
Precision: Underhung systems offer precise load movement and positioning.
Suitable Applications:
Workstations and assembly lines where precision is crucial.
Warehouses with limited space for material handling.
Light to moderate load lifting needs in various industries.
The choice between top-running and underhung runway systems depends on the specific requirements of the application. Heavy-duty operations that involve substantial loads typically benefit from top-running systems due to their high load capacity and durability. On the other hand, underhung systems are an excellent choice for smaller-scale projects where space and budget constraints are factors, and precise load movement is essential.
By selecting the most suitable bridge crane runway system for your overhead crane system, you can optimize efficiency, safety, and overall performance in your material handling operations. Whether you need to lift heavy machinery or transport lighter materials with precision, the right runway system configuration is a key consideration in achieving your goals. Check How to Measure Your Runway Sizes and Runway Length.
Installation and Alignment
Proper installation and alignment of runway rail systems are pivotal steps in ensuring the smooth operation and load-bearing efficiency of overhead cranes. In this section, we'll delve into the essential aspects of installing runway systems and the critical importance of precise alignment:
Installation Process
- Professional Expertise: The installation of runway systems should always be performed by experienced professionals with expertise in crane system installation. It's a complex task that involves structural considerations and safety measures.
- Foundation Preparation: The foundation where the runway beams are anchored must be appropriately prepared. This includes ensuring the foundation's structural integrity, load-bearing capacity, and adequate anchor points.
- Runway Beam Assembly: The assembly of runway beams is a meticulous process. Beams need to be correctly aligned, leveled, and securely fastened to the support structure.
- Trolley and Crane Assembly: Installing the trolley and crane components must be done with precision, ensuring that they run smoothly along the runway beams. This includes aligning wheels, ensuring proper clearances, and attaching the hoist.
- Electrification and Controls: Electrification systems, including power tracks and control panels, must be integrated into the runway system. Proper electrical connections and testing are essential to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Alignment Matters
- Smooth Crane Movement: Precise alignment of the runway beams is crucial for smooth crane movement. Misalignment can result in jerky motion, increased wear and tear, and reduced operational efficiency.
- Safety: Misalignment poses safety risks as it can lead to accidents, such as load shifting or derailment. Proper alignment is essential to maintain a safe working environment.
- Load Distribution: A well-aligned runway system ensures even load distribution across the crane wheels and runway beams. This prevents overloading on specific sections and extends the system's lifespan.
- Efficiency and Productivity: In an industrial setting, efficient crane operation is essential for productivity. Properly aligned runway systems minimize downtime and contribute to efficient material handling.
- Longevity: Misalignment can lead to premature wear of crane components and runway beams. Ensuring alignment prolongs the lifespan of the entire crane system.
- Alignment Check: Regular alignment checks and maintenance are essential. If misalignment is detected, prompt corrective action is necessary to prevent further issues.
In summary, the installation and alignment of runway systems demand meticulous attention to detail and a focus on safety and operational efficiency. Professional installation is paramount, and alignment checks should be part of regular maintenance to ensure that your overhead crane system operates seamlessly and safely. Properly installed and aligned runway systems are the backbone of efficient material handling operations, and they contribute to the longevity of your equipment and the safety of your workspace.
Runway System Maintenance
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of runway systems for overhead cranes relies heavily on regular maintenance. Neglecting maintenance can lead to issues that compromise safety and operational efficiency. In this section, we'll delve into the importance of runway system maintenance, common maintenance tasks, and their impact:
Importance of Regular Maintenance
- Safety: Regular maintenance is a crucial component of ensuring the safety of overhead crane operations. It helps detect potential issues and prevents accidents resulting from equipment failure.
- Operational Efficiency: A well-maintained runway system contributes to the operational efficiency of an overhead crane. It helps prevent unexpected downtime and maintains smooth load movement.
- Cost-Efficiency: Addressing maintenance needs promptly is often more cost-effective than dealing with major repairs or replacements. It prolongs the lifespan of the runway system.
- Compliance: Regular maintenance ensures that the runway system complies with safety standards and regulations. This is essential for legal and safety reasons.
Common Maintenance Tasks
- Lubrication: Regularly lubricating moving parts, such as trolley wheels and crane tracks, reduces friction and wear. Proper lubrication prevents excessive strain on components and prolongs their lifespan.
- Inspections: Scheduled inspections identify issues before they escalate. Inspectors check for misalignment, signs of wear, corrosion, and other potential problems.
- Load Testing: Periodic load testing helps ensure that the system can bear the designated loads safely. It's especially important if there have been significant structural changes or repairs.
- Electrification Maintenance: Maintaining electrification components, such as power tracks, ensures consistent power supply to the crane. It prevents electrical issues that can disrupt operation.
- Alignment Checks: Regular alignment checks confirm that the runway system's beams are correctly aligned. Misalignment can lead to operational inefficiencies and safety risks.
- Corrosion Control: Corrosion can weaken the structure. Applying corrosion-resistant coatings or performing anti-corrosion treatments is essential, especially in environments with high humidity or corrosive substances.
- Bolt and Fastener Inspection: Bolts and fasteners must be checked regularly to ensure they remain securely fastened. Loose bolts can lead to structural instability.
Impact on Longevity
- Prolonged Lifespan: Regular maintenance significantly extends the lifespan of the runway system and overhead crane components. It reduces the risk of premature wear and tear.
- Minimized Downtime: Proper maintenance reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and downtime. This is especially critical in industrial settings where downtime can be costly.
- Optimal Performance: Well-maintained runway systems ensure optimal performance, contributing to the efficiency of material handling operations.
- Safety Assurance: Maintenance helps identify and address safety concerns promptly, providing a safe working environment for crane operators and other personnel.
In conclusion, runway system maintenance is a critical aspect of ensuring the safety, longevity, and efficiency of overhead crane operations. Regular maintenance tasks, including lubrication, inspections, load testing, and corrosion control, play a pivotal role in preventing operational issues and costly breakdowns. Prioritizing maintenance not only extends the lifespan of your equipment but also minimizes downtime and ensures a safe workplace.
Safety Considerations of Runway Systems
Safety is paramount in any industrial setting, and when it comes to overhead crane operations, ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment is of utmost importance. In this section, we'll discuss various safety considerations related to runway systems and how proper design and maintenance contribute to a secure working environment.
Runway Guardrails
- Importance: Guardrails along the runway system serve as a protective barrier to prevent unintended falls of personnel or materials. They are especially crucial if the runway is positioned at an elevated level, such as in mezzanines or platforms.
- Design Standards: Guardrails should be designed and installed in accordance with relevant safety standards, ensuring that they can withstand potential impacts and forces.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of guardrails is necessary to ensure they remain structurally sound and capable of fulfilling their protective role. This includes inspections for any signs of damage or corrosion.
Warning Signs
- Visibility: Clearly visible warning signs should be placed in areas where the runway system is in operation. These signs alert personnel to potential hazards and remind them to exercise caution.
- Safety Messages: Warning signs can convey various safety messages, such as "Danger: Overhead Crane in Operation" or "No Unauthorized Personnel Allowed." The language and content of the signs should be tailored to the specific site's needs.
- Inspections: Periodic inspections of warning signs are essential to confirm their visibility and readability. Fading or damaged signs should be replaced promptly.
Proper Design and Maintenance
- Structural Integrity: Runway systems should be designed and constructed with a focus on structural integrity. This involves selecting appropriate materials, adherence to load-bearing capacity requirements, and considerations for factors like wind loads and seismic forces.
- Alignment and Smooth Operation: Proper alignment of the runway system's beams and rails is essential for smooth crane operation and safety. Misalignment can cause uneven load distribution, posing safety risks.
- Maintenance's Role in Safety: Maintenance tasks directly contribute to the safety of the runway system. Regular inspections can identify structural issues, wear and tear, and corrosion that may compromise safety.
- Load Capacity Testing: Regular load capacity testing ensures that the runway system can safely handle the designated loads. It helps prevent overloading, which can be a significant safety hazard.
In conclusion, safety considerations are a fundamental aspect of bridge crane runway systems. Runway guardrails and warning signs contribute to the prevention of accidents and the promotion of safety awareness. Proper design, alignment, and regular maintenance are pivotal in creating a safe working environment and ensuring the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of the runway system. By prioritizing safety, companies can create a workplace where both personnel and equipment are protected from harm.
Applications of Bridge Crane Systems
Bridge crane systems are versatile material handling solutions that find applications across various industries and settings. Their ability to efficiently lift and move heavy loads makes them indispensable in a wide range of scenarios. In this section, we will explore some of the key applications of bridge crane systems, showcasing how they play a pivotal role in enhancing productivity and efficiency.
- Manufacturing Excellence: - Bridge crane systems are the workhorses of manufacturing facilities. They facilitate the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products on assembly lines. By providing precise load positioning and efficient material transport, bridge cranes contribute to increased productivity and streamlined manufacturing processes.
- Construction Versatility: - Construction sites often require the handling of bulky and heavy materials, from steel beams to concrete blocks. Bridge crane systems are deployed in construction projects to lift and position these materials with precision. Their adaptability and load-bearing capacity make them indispensable for large-scale construction tasks.
- Warehousing Solutions: - Warehouses rely on bridge crane systems for efficient storage and retrieval of goods. These cranes enable high-density storage and quick access to inventory, improving warehouse logistics. They are particularly beneficial in facilities with limited floor space.
- Agricultural Advantage: - In the agricultural sector, bridge crane systems are used for tasks like lifting heavy bags of grain, loading and unloading equipment, and handling produce. They reduce the need for manual labor and minimize the risk of injury, contributing to improved farm efficiency.
- Case Studies: - To illustrate the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of bridge crane solutions, we'll delve into real-world case studies. These examples will demonstrate how bridge cranes have transformed material handling operations in specific industries, resulting in increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
Bridge crane systems are not just equipment; they are drivers of efficiency, safety, and productivity in various industries. Their versatility and adaptability make them valuable assets in settings where lifting and transporting heavy loads are essential. Whether it's streamlining manufacturing processes, supporting construction projects, optimizing warehouse operations, or enhancing agricultural tasks, bridge crane systems are at the heart of modern material handling.
Environmental Considerations, Installation, and Maintenance of Bridge Crane Systems
Bridge crane systems are reliable workhorses in material handling, but like any machinery, they are subject to the influence of environmental factors and require proper installation and maintenance for peak performance. In this section, we'll explore the environmental considerations that can affect bridge crane systems, delve into the installation and setup process, and discuss the critical aspects of maintenance and troubleshooting.
Environmental Considerations:
Bridge crane systems are often exposed to various environmental conditions that can impact their performance. These include:
- Temperature Variations: Extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, can affect the structural integrity of crane components. Heat can lead to expansion and wear on equipment, while cold temperatures can make metals more brittle.
- Humidity: High humidity levels can accelerate the corrosion of metal parts, affecting both safety and functionality.
- Corrosive Conditions: Cranes in facilities with corrosive substances, such as chemical plants or saltwater environments, are susceptible to accelerated wear and tear.
Mitigating these environmental effects involves:
- Protective Coatings: The use of protective coatings on metal components can safeguard them from corrosion and extend their lifespan.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensuring proper ventilation in the crane area can help regulate temperature and humidity levels.
Installation and Setup:
The installation and setup of bridge crane systems are intricate processes that directly impact their performance and safety. Key considerations include:
- Professional Installation: It is essential to engage experienced professionals for the installation of bridge crane systems. They are familiar with safety standards and can ensure that the crane is properly secured and aligned.
- Foundation Requirements: The crane's foundation must be stable and capable of supporting the crane's weight and the loads it will handle. Inadequate foundations can lead to safety hazards and crane malfunctions.
- Safety Standards: Adherence to safety standards during installation is critical. It is essential to comply with regional and industry-specific safety regulations to ensure the crane's safe operation.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting:
Regular maintenance is the key to prolonging the life of a bridge crane system and preventing unexpected breakdowns. Maintenance includes:
- Routine Inspections: Periodic inspections are vital for identifying wear and tear, loose components, or other issues that may compromise the crane's safety and efficiency.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of moving parts is necessary to reduce friction and extend the life of components.
- Troubleshooting: When issues do arise, quick identification and resolution are essential. Common problems include electrical malfunctions, hoist hiccups, and trolley alignment challenges.
By considering environmental factors, following proper installation procedures, and adhering to a rigorous maintenance schedule, bridge crane systems can operate safely and efficiently for many years. Addressing these aspects proactively not only safeguards the crane's performance but also enhances workplace safety and minimizes operational downtime.
Wrap it Up,
In our comprehensive guide to bridge crane systems, we've journeyed through the world of material handling and explored the pivotal role that bridge cranes play in various industries. From manufacturing to construction, warehouses to agriculture, these robust systems have proven to be essential tools for enhancing productivity and efficiency.
As we conclude this guide, let's recap the key takeaways and reinforce the importance of making informed decisions when it comes to bridge crane systems.
- Selecting the Right Bridge Crane System: Choosing the right bridge crane system is crucial. Each type, whether overhead bridge crane, free-standing bridge crane, or ceiling-mounted crane, offers distinct advantages. Consider the specific needs of your application, including load capacity, available space, and industry requirements, to make the most suitable choice.
- Prioritizing Safety and Compliance: Safety is paramount when working with bridge crane systems. Be sure to implement safety features, including collision avoidance systems and audible alarms. Additionally, ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations to protect both your workers and your equipment.
- Environmental Considerations: Understand the impact of environmental factors on bridge crane systems. Whether it's extreme temperatures, humidity, or corrosive conditions, taking measures such as protective coatings and proper ventilation can safeguard your equipment.
- Professional Installation and Setup: Engage experienced professionals for the installation and setup of your bridge crane system. Proper foundation requirements and safety standards adherence are vital for ensuring long-term performance and safety.
- Routine Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Regular maintenance is the key to extending the life of your bridge crane system. Conduct routine inspections, lubricate moving parts, and troubleshoot common issues promptly to prevent unexpected breakdowns.
By following these guidelines and making well-informed decisions, you can ensure the efficient and safe operation of your bridge crane system. Bridge cranes are more than just equipment; they are partners in enhancing productivity, streamlining operations, and supporting your industry's success. So, prioritize safety, stay informed, and continue to explore the ever-advancing world of bridge crane technology. Your journey into the world of efficient material handling has only just begun.
Main Projects
Related Products
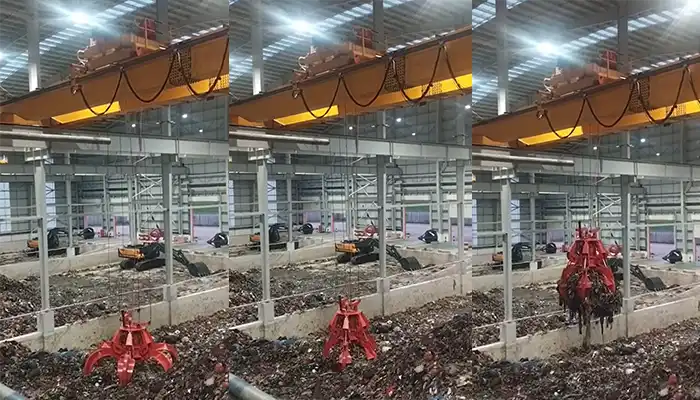

Supplied three grab bucket crane kits to Indonesia, enhancing garbage handling efficiency with high load capacity and reliable performance.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch