Light Duty vs. Heavy Duty Overhead Cranes: Choosing Right Crane
Light duty & heavy duty overhead cranes for sale. Compare light duty & heavy duty bridge cranes, gantry cranes & jib cranes to select right crane for you.
Category: Bridge Crane
Your Trusted Overhead Bridge Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Light Duty vs. Heavy Duty Overhead Cranes: Choosing Right Crane
Light Duty & Heavy Duty Bridge Cranes, Gantry Cranes & Jib Cranes Comparison
Light duty & heavy duty overhead cranes for sale. Compare light duty & heavy duty bridge cranes, gantry cranes & jib cranes to select right crane for you. As for material handling and industrial operations, the choice of the right overhead crane can make all the difference. The decision to opt for a light duty or heavy duty overhead crane can significantly impact the efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness of your lifting and moving processes. In this article, we will delve into the key distinctions between these two categories of cranes and provide essential insights to help you make an informed decision.
To begin, it's crucial to understand the concept of "crane duty" and how it plays a pivotal role in crane selection. Crane duty is not merely a technical term; it holds the key to optimizing your material handling processes. Let's explore what crane duty entails and why it matters.
Understanding Crane Duty
When it comes to choosing the right overhead crane, the concept of "crane duty" is a fundamental consideration. Crane duty is a classification that defines the specific operating conditions for which a crane is designed. This classification takes into account a range of factors, including load capacity, usage patterns, and the frequency and duration of crane operation. Understanding crane duty is crucial as it directly impacts the crane's performance, safety, and overall suitability for your material handling needs.
What Does Crane Duty Mean?
Crane duty serves as a blueprint for engineers and manufacturers, outlining the crane's intended use and the conditions it should be able to withstand. The classification encompasses the following key aspects:
- Load Capacity: Crane duty classifies cranes based on their load-carrying capacity. Light duty cranes are engineered for relatively lighter loads, while heavy duty cranes are designed to handle much heavier and bulkier loads.
- Duty Cycle: Duty cycle refers to the frequency and duration of crane operation. It determines how often and for how long the crane will be in use. This is a crucial factor as it directly affects the crane's performance and longevity.
- Operational Conditions: Crane duty takes into account the environment in which the crane will operate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances can influence the crane's design and materials.
- Safety and Reliability: Safety features and reliability requirements are specified within the crane duty classification. Heavy duty cranes are engineered to ensure safety during prolonged and heavy usage, both for the operators and the loads they handle.
- Maintenance and Service Needs: The crane duty classification also provides insights into the crane's maintenance and service requirements. Heavy duty cranes, due to their higher capacity and frequent use, may demand more robust maintenance schedules and practices.
Differentiating Between Light Duty and Heavy Duty Cranes
Now that we have a basic understanding of crane duty, let's differentiate between two primary categories: light duty and heavy duty cranes.
Light Duty Cranes:
- Characteristics and Applications: Light duty cranes are typically designed for operations where lighter loads need to be lifted and moved. These cranes are suitable for tasks like assembly work, maintenance, and smaller-scale manufacturing.
- Benefits: Light duty cranes are cost-effective for lighter load applications, offer increased flexibility and maneuverability, and have minimal structural impact on the facility. They also require less maintenance.
- Capacity Range: Light duty bridge cranes often have capacities ranging from 250 pounds to 5 tons, while light duty gantry cranes can handle loads from 500 pounds to 5 tons. Light duty jib cranes have capacities ranging from 100 pounds to 2 tons, making them ideal for precision lifting. Light duty wall-mounted jib cranes are suitable for compact spaces and typically have capacities ranging from 100 pounds to 2 tons.
- Pricing Considerations: The affordability of light duty cranes makes them an attractive choice for businesses with budget constraints. However, specific pricing can vary depending on crane type and capacity.
Heavy Duty Cranes:
- Characteristics and Applications: Heavy duty cranes are designed for industrial settings where massive loads and challenging conditions are the norm. They find application in industries such as steel mills, shipyards, and heavy manufacturing.
- Advantages: Heavy duty cranes offer high load-carrying capacity, durability for continuous and heavy usage, enhanced safety features, and a longer operational life.
- Capacity Range: Heavy duty bridge cranes have capacities ranging from 5 tons to 100 tons or more, heavy duty gantry cranes can handle loads from 10 tons to 200 tons or more, heavy duty jib cranes can lift loads from 2 tons to 10 tons, heavy duty shop cranes have capacities ranging from 2 tons to 10 tons or more, and heavy duty mobile cranes offer on-site versatility with capacities that can range from 10 tons to 1,000 tons or more.
Understanding crane duty and the distinctions between light duty and heavy duty cranes is essential to making an informed decision when selecting the right crane for your material handling needs. In the following sections, we will explore duty cycles and other factors to consider in crane selection to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Here's a table summarizing the key similarities and differences between light duty and heavy duty overhead cranes:
Aspect | Light Duty Overhead Crane | Heavy Duty Overhead Crane |
Load Capacity | Typically for lighter loads, e.g., up to 5 tons | Designed for heavy loads, e.g., 5 tons to 100+ tons |
Duty Cycle | Intermittent or occasional use | Continuous or frequent use |
Applications | Suitable for tasks like assembly, maintenance, and small-scale manufacturing | Used in demanding environments like steel mills, shipyards, and heavy manufacturing |
Benefits | Cost-effective, flexible, and minimal structural impact | High load capacity, durability, enhanced safety features, and longer operational life |
Operational Conditions | Typically used in less demanding or controlled environments | Engineered to withstand challenging conditions |
Safety and Reliability | Designed for reliability in less demanding tasks | Engineered for safety and reliability in demanding operations |
Maintenance Requirements | Generally lower maintenance needs | May require more robust maintenance schedules and practices |
Price Range | Affordable, cost-effective for lighter load applications | Higher initial investment due to enhanced capacity and durability |
This table provides a concise overview of the similarities and differences between light duty and heavy duty overhead cranes, helping you to choose the right crane for your specific material handling needs.
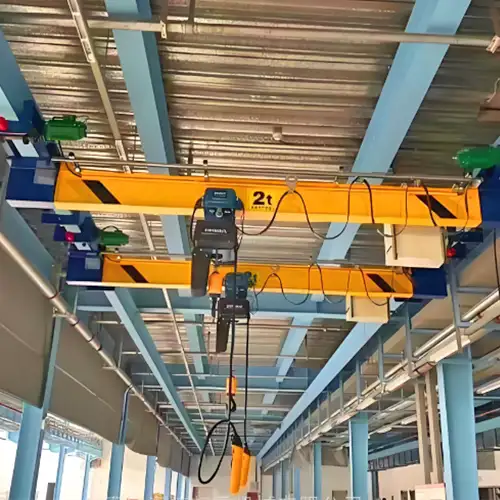
Light Duty Overhead Cranes: Efficiency and Versatility in Material Handling
Light duty overhead cranes are the unsung heroes of countless industries, quietly ensuring the efficient lifting and movement of lighter loads. These versatile cranes are tailored for applications where precision, flexibility, and cost-efficiency are paramount. In this section, we will provide an overview of light duty overhead cranes, explore their characteristics and applications, and delve into the benefits of using these versatile lifting solutions.
Characteristics and Applications:
- Characteristics: Light duty overhead cranes are designed with a focus on efficiency, maneuverability, and ease of use. They are typically engineered for tasks where loads fall on the lighter end of the spectrum.
- Applications: These cranes are found in a wide range of industries and tasks, including assembly work, maintenance operations, small-scale manufacturing, and warehousing. They excel in environments where precision and flexibility are key.
Benefits of Using Light Duty Overhead Cranes
Employing light duty overhead cranes offers several distinct advantages:
- Cost-Efficiency: Light duty cranes are a cost-effective solution for applications with lighter load requirements, making them accessible for businesses with budget constraints.
- Increased Flexibility: Their design prioritizes maneuverability and ease of use, offering increased flexibility in material handling tasks, particularly in tight spaces.
- Minimal Structural Impact: Light duty cranes typically have a smaller structural footprint, which minimizes their impact on the facility's layout and construction.
- Reduced Maintenance Requirements: These cranes often have simpler designs, which results in lower maintenance requirements and, consequently, cost savings over time.
Types of Light Duty Overhead Cranes
Let's explore the various types of light duty overhead cranes, each designed to address specific lifting requirements and facility constraints.
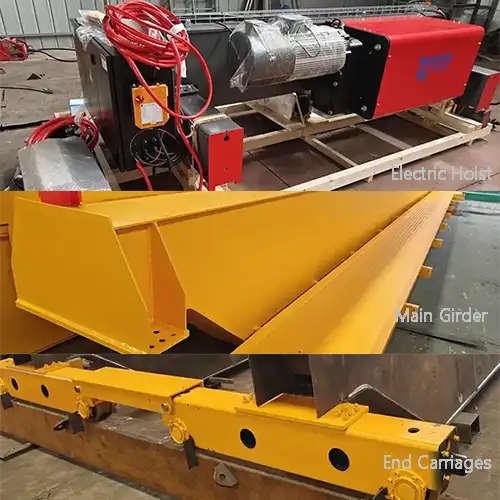
Light Duty Bridge Crane:
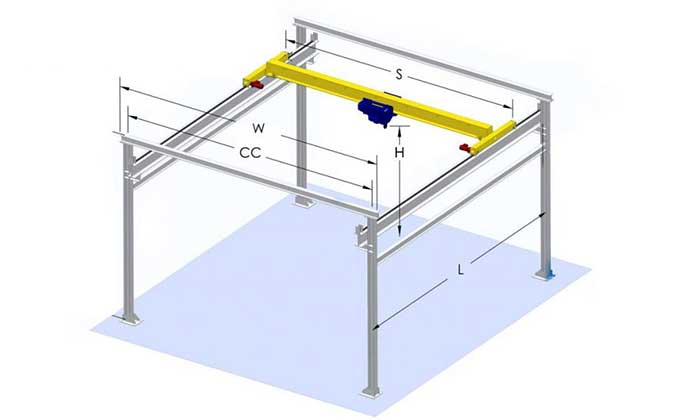
Light duty bridge cranes, also known as light duty overhead cranes, are material handling systems designed for lighter loads and less demanding applications. They typically feature a single girder (horizontal beam) and are cost-effective and easy to install. These cranes are ideal for tasks such as maintenance, assembly, and light manufacturing, where the need for precision lifting and efficient load movement is essential. Light duty bridge cranes are characterized by their versatility and suitability for smaller facilities and spaces where cost-effective material handling solutions are required.
- Characteristics: A light duty bridge crane operates on a runway system with two parallel runways. It is a versatile lifting solution for applications with lighter loads.
- Advantages:- Cost-Effective Lifting: Light duty bridge cranes provide a cost-effective means of lifting and moving lighter loads with precision and efficiency, making them an ideal choice for tasks that require precise positioning.

Description: A single girder bridge crane features a single horizontal beam (girder) as the main support structure for the hoist and trolley. It is known for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Key Features:
- Lightweight design.
- Cost-effective for light to medium-duty applications.
- Easy to install and maintain.
Typical Applications:
- Used in facilities where lighter loads need to be lifted and transported.
- Common in assembly lines, maintenance tasks, and small to medium-sized manufacturing.

Description: An under-running bridge crane has wheels that run on the bottom flange of the runway beam. It is designed for applications with limited vertical clearance.
Key Features:
- Compact design.
- Efficient for facilities with limited vertical clearance.
- Suitable for low-ceiling spaces.
Typical Applications:
- Found in low-ceiling workshops.
- Utilized in warehouses with restricted overhead space.
- Ideal for machine shops with limited headroom.

Light Duty Free-Standing Bridge Cranes:
Description: Light duty free-standing bridge cranes are overhead crane systems that are self-supporting and do not rely on the support of building structures or columns. They are designed for light-duty applications.
Key Features:
- Self-supporting structure.
- Suitable for light-duty tasks.
- Can be positioned in various locations within a facility.
Typical Applications:
- Used in assembly lines.
- Found in maintenance tasks.
- Ideal for smaller manufacturing operations.
The features of light duty bridge cranes include:
- Single Girder Design: Light duty bridge cranes typically have a single horizontal beam (girder) as the main support structure for the hoist and trolley. This design keeps the crane lightweight and cost-effective.
- Cost-Effective: These cranes are budget-friendly, making them an economical choice for businesses with light to medium-duty material handling needs.
- Easy Installation: Light duty bridge cranes are relatively easy to install, which reduces downtime during setup and minimizes installation costs.
- Versatility: They are versatile and can be used in a variety of applications, such as assembly lines, maintenance tasks, and small to medium-sized manufacturing operations.
- Efficient for Light Loads: Light duty bridge cranes are designed to handle lighter loads efficiently, making them well-suited for tasks that don't require high load capacities.
- Precision Lifting: They offer precision in load positioning, making them suitable for applications where accuracy is critical.
- Compact Design: The compact design of these cranes allows them to fit well in smaller workspaces and facilities.
- 8. Adaptability: Light duty bridge cranes are adaptable to different environments and can be customized to match specific material handling requirements.
- 9. Cost-Effective Maintenance: Their maintenance requirements are typically straightforward, resulting in cost-effective ongoing operation.
- 10. Durability: While not designed for heavy-duty use, they are durable and reliable for their intended applications.
Overall, light duty bridge cranes are known for their efficiency and cost-effectiveness in handling lighter loads in various industrial and commercial settings.
These bridge crane types offer different advantages and are chosen based on the specific load requirements and operational conditions of the facility in which they are used. Single girder bridge cranes are cost-effective and versatile, under-running bridge cranes maximize available headroom, and light duty free-standing bridge cranes are self-supporting and adaptable for light-duty tasks.
Light duty kbk cranes
KBK (Kettenfließkrane) cranes are versatile material handling systems known for their efficiency, flexibility, and precision in moving loads. These cranes consist of a modular design that includes enclosed tracks, trolleys, and hoists, allowing for easy customization to meet specific material handling needs.
Here is a detailed description of KBK cranes:
- Modular Design:- KBK cranes are defined by their modular design, which is their standout feature. They comprise a network of enclosed tracks that form the infrastructure for the crane system. Trolleys and hoists are designed to smoothly travel along these tracks, enabling the movement of loads.
- Light to Medium-Duty:- KBK cranes are well-suited for light to medium-duty material handling tasks. They excel in applications where loads typically range from a few hundred pounds to a few tons. This range of capacity makes them ideal for a wide variety of industries.
- Precise Load Positioning and Control:- One of the key strengths of KBK cranes is their ability to provide precise load positioning and control. This precision makes them valuable for applications that require accurate placement of materials or products.
- Limited Span:- KBK cranes usually have a limited span, which means they are designed for specific work areas, workstations, or assembly lines. Their compact design and limited span make them suitable for tasks within defined zones.
- Quiet Operation:- KBK cranes are known for their quiet and smooth operation. This feature is particularly beneficial in work environments where noise reduction is important, and operator comfort is a priority.
- Easy Installation and Integration:- KBK cranes are relatively easy to install and can be integrated into existing facilities without significant modifications. This ease of integration contributes to their versatility and appeal.
- Customization:- The modular nature of KBK cranes allows for a high degree of customization. They can be tailored to meet specific material handling requirements, making them adaptable to various industrial settings and applications.
KBK cranes come in several main types, including monorail KBK cranes, double girder KBK cranes, stacker KBK cranes, curved track KBK cranes, wall-mounted KBK cranes, and pillar-mounted KBK cranes. Each type serves different purposes and offers specific advantages, making them valuable tools in industries that require efficient and precise material handling.
Light Duty Gantry Crane for Versatile Operations
Light Duty Gantry Crane:
A Light Duty Gantry Crane is a versatile material handling system designed for relatively lighter loads and less demanding applications. It is characterized by its gantry structure, which consists of two vertical legs or columns and an overhead horizontal beam (bridge) that supports the hoist and trolley. Here is a detailed description of a Light Duty Gantry Crane:
- Characteristics: A light duty gantry crane is a mobile crane supported by two vertical legs with wheels that run along the ground. This design offers portability and flexibility.
- Advantages:- Versatile Operations: Light duty gantry cranes are highly versatile and can be used in various settings, including workshops, warehouses, and outdoor applications. Their mobility allows for adaptability in changing environments.
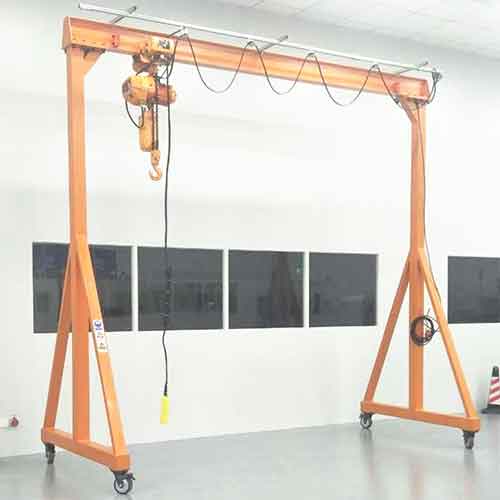

Fixed Height Portable Gantry Crane:
- Designed for easy transport and setup in various locations.
- Lightweight and compact, making it suitable for temporary or mobile applications.
- Commonly used in construction sites and for maintenance tasks.
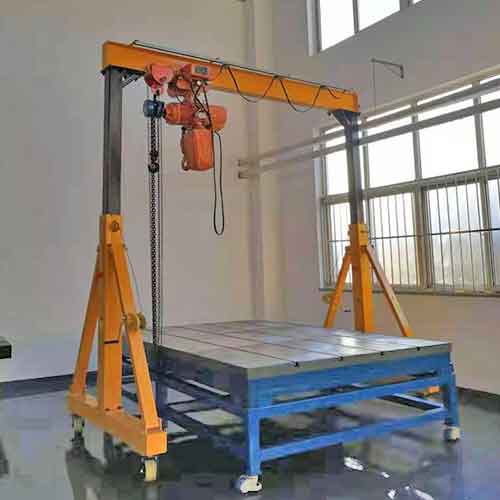

Adjustable Height Gantry Crane:
- Allows for the adjustment of the crane's height to accommodate varying load sizes and working environments.
- Versatile and adaptable to different tasks.
- Often used in workshops and warehouses.
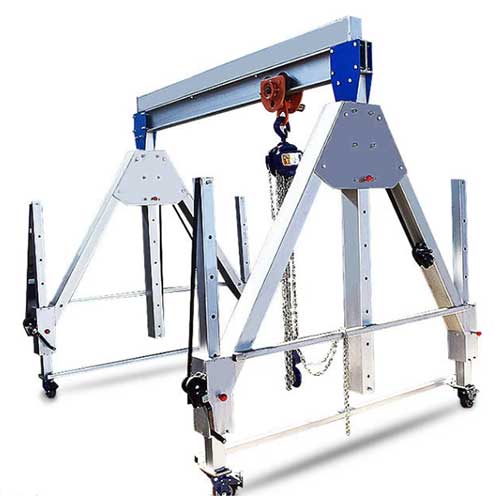

- Constructed from lightweight aluminum, reducing the crane's weight and enhancing its portability.
- Ideal for applications that require corrosion resistance and easy mobility.
- Commonly used in industries where a lightweight and portable solution is essential.
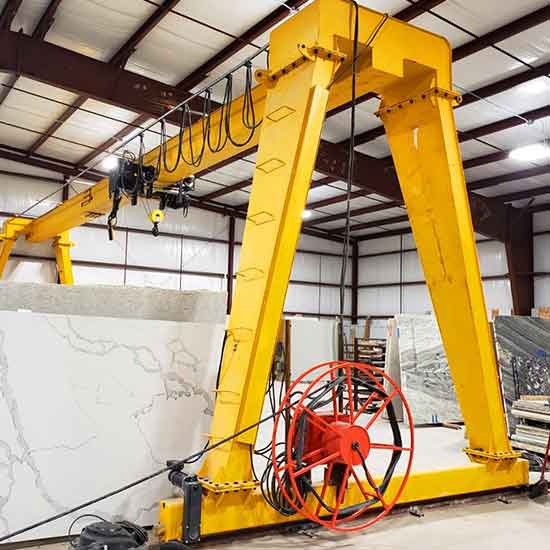

- Features a single horizontal girder and is designed for lighter loads.
- Ideal for applications where high load capacity is not required.
- Cost-effective and efficient for small to medium-sized facilities.

- Features a truss-style bridge structure for added strength.
- Ideal for lifting heavy and bulky loads in construction sites and shipping terminals.

- A crane with one supporting leg on one side while the other side runs along a fixed structure.
- Cost-effective and suitable for moderate to heavy loads.
- Ideal for applications in warehouses, manufacturing, assembly lines, workshops, and material yards.
These types of light duty gantry cranes are suitable for applications with lighter loads and less intensive use. They offer cost-effective and efficient solutions for various industries and working environments where high load capacity is not a primary requirement.
Key Features:
- Gantry Structure: The distinguishing feature of a gantry crane is its gantry structure, which allows for mobility and flexibility. The crane moves along the ground on wheels or casters attached to the legs, eliminating the need for permanent installation.
- Light to Medium-Duty: Light duty gantry cranes are engineered to handle loads ranging from a few hundred pounds to several tons. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications where high load capacities are not required.
- Versatile Movements: The horizontal bridge beam of the crane provides lateral movement, while the crane's mobility along the ground allows for load transportation in various directions.
- Precise Load Positioning: Light duty gantry cranes offer precise control, making them suitable for tasks that demand accurate load placement.
- Easy Installation: These cranes are relatively easy to set up, and they do not require a permanent installation, which can save on installation costs and downtime.
- Adaptability: Light duty gantry cranes are adaptable to different work environments and can be customized to match specific material handling needs.
- Compact Design: Their compact design and mobility make them suitable for smaller facilities or work areas with space constraints.
- 8. Cost-Effective: Light duty gantry cranes are cost-effective solutions for businesses with lighter load requirements, offering efficiency without overburdening costs.
Light Duty Jib Crane for Precision Lifting
Light Duty Jib Crane:
- Characteristics: A light duty jib crane features a horizontal arm that can be rotated to lift and position loads with precision.
- Advantages: - Precision Lifting: Light duty jib cranes are ideal for tasks that require precise positioning and lifting. Their ability to rotate the arm provides flexibility and accuracy.
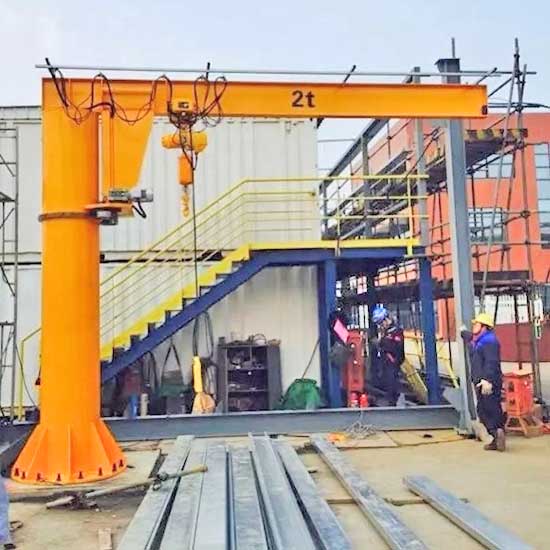

- This type of jib crane is not attached to a building structure and is self-supporting.
- It offers 360-degree rotation and can be placed in various locations within a facility.
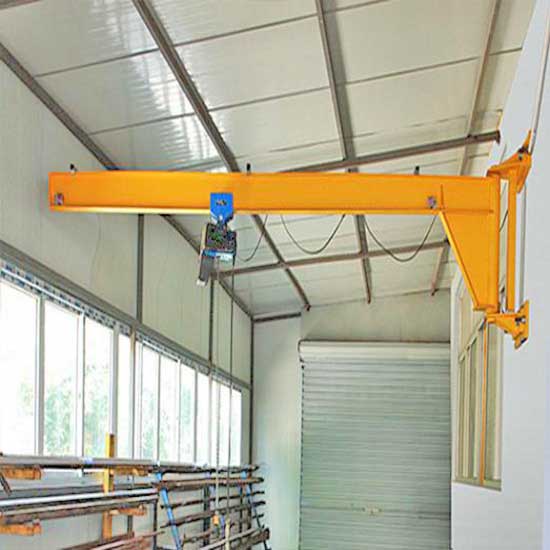

- Mounted on a wall or vertical surface, saving floor space and offering 180-degree rotation.
- Ideal for workstations and areas with limited floor space.
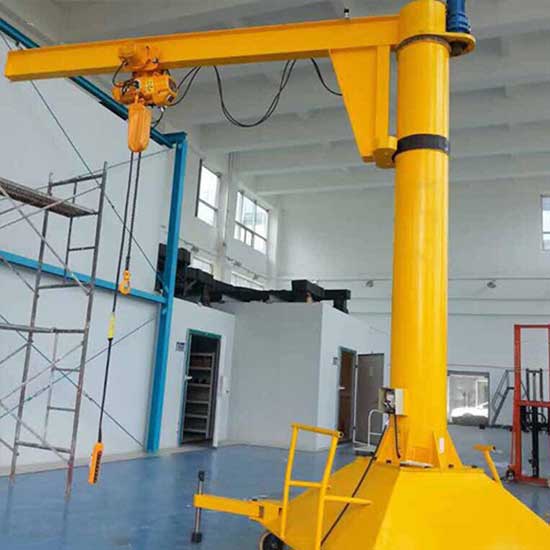

- Designed for easy transport and setup in different locations.
- Often used for temporary or mobile material handling needs, such as construction sites.
These types of light duty jib cranes provide efficient solutions for applications with lighter loads and less intensive material handling requirements. They offer versatility and adaptability to various work environments and are a cost-effective option for many industries.
Pricing Considerations for Light Duty Cranes
When considering the purchase of light duty overhead cranes, it's essential to factor in pricing considerations. The cost of light duty cranes can vary based on several factors, including:
- Load Capacity: The crane's load capacity directly influences its price, with higher capacity cranes generally being more expensive.
- Customizations: Optional features and customizations, such as advanced control systems, specialized hooks or attachments, and safety features, can add to the overall cost.
- Manufacturer and Brand: Different manufacturers offer light duty cranes at varying price points. Choosing reputable brands often ensures high-quality equipment but may come at a premium.
- Installation and Maintenance: Installation costs and long-term maintenance requirements should also be considered as part of the overall cost of owning a light duty crane.
In summary, light duty overhead cranes are essential tools for industries that require efficient, flexible, and cost-effective material handling solutions for lighter loads. Understanding their characteristics, advantages, and the specific types available, including bridge cranes, gantry cranes, and jib cranes, can help you make an informed decision for your material handling needs. Additionally, considering pricing factors is essential to budget effectively for your crane investment.
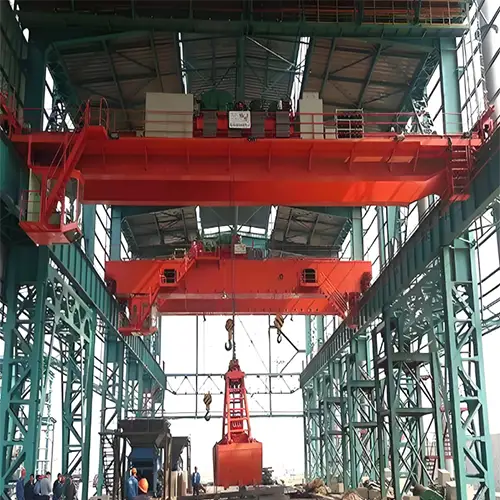
Heavy Duty Overhead Cranes: Raising the Bar in Industrial Lifting
When the need arises to handle colossal loads in demanding industrial environments, the heavy duty overhead crane steps into the spotlight. These robust giants of the material handling world are engineered to tackle the heaviest and bulkiest of loads with precision and reliability. In this section, we'll provide an overview of heavy duty overhead cranes, explore their characteristics and applications, and delve into the advantages of investing in these industrial powerhouses.
Characteristics and Applications:
- Characteristics: Heavy duty overhead cranes are designed to operate in some of the most challenging industrial conditions. They boast high load-carrying capacities, durability, and a robust construction that can withstand prolonged, heavy usage.
- Applications: These cranes are the go-to choice for industries such as steel production, shipbuilding, large-scale manufacturing, and heavy machinery production. They are essential in environments where loads can range from several tons to well over a hundred tons.
Advantages of Investing in Heavy Duty Overhead Cranes
Choosing heavy duty overhead cranes for your industrial operations provides a multitude of advantages:
- High Load Capacity: The primary advantage of heavy duty cranes is their ability to lift and transport massive loads, making them indispensable in industries that handle heavy materials.
- Durability: These cranes are built to withstand continuous and heavy usage, offering a longer operational life and high return on investment.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Safety is paramount in demanding industrial settings. Heavy duty cranes are equipped with advanced safety features to protect both operators and valuable cargo.
- Longevity: Heavy duty cranes have a reputation for longevity, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run. Their robust construction ensures they stand the test of time.
Types of Heavy Duty Overhead Cranes
Heavy Duty Bridge Crane for Robust Industrial Operations
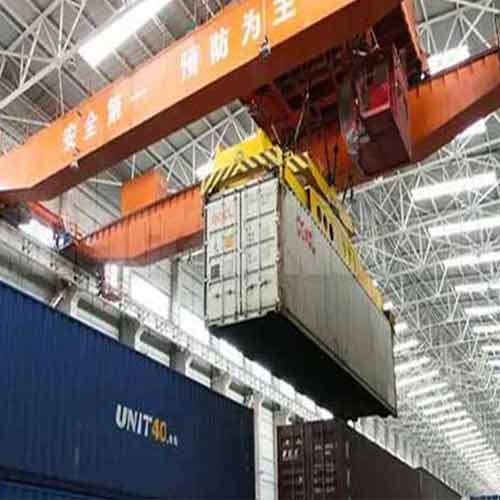
A Heavy Duty Bridge Crane is a powerful material handling system designed for lifting, moving, and positioning heavy and bulky loads in industrial settings. It typically features a bridge with horizontal girders that span a defined area, supporting a hoist or trolley for vertical and horizontal load movement.
- Characteristics: A heavy duty bridge crane operates on a runway system with two parallel runways. It is the workhorse of large industrial operations.
- Applications:- Heavy duty bridge cranes are commonly used in industries like steel manufacturing, automotive production, and large-scale metal fabrication. They are essential for moving and positioning heavy materials and components.
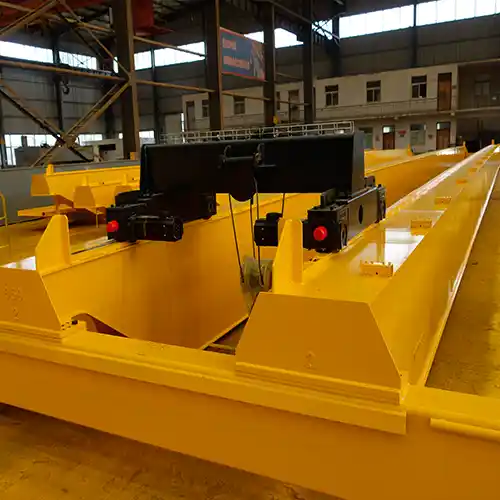

- Equipped with a wire rope hoist system and a crab trolley for heavy load movement.
- Ideal for precision and high-capacity applications, such as manufacturing and steel processing.
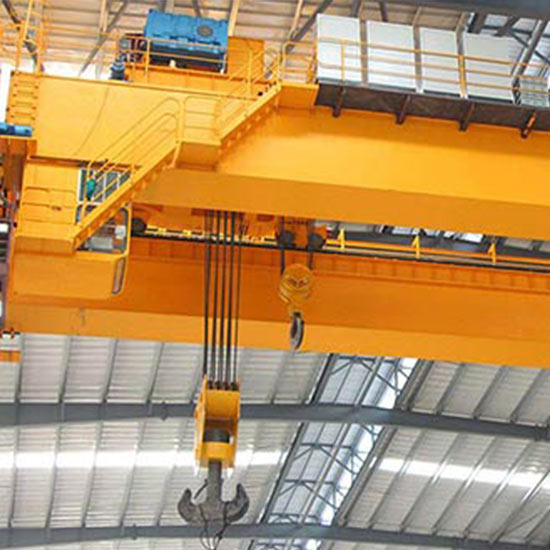

- Features an open winch hoist system for high lifting capacities and precise control.
- Commonly used in industries like heavy manufacturing and shipyards for efficient material handling.
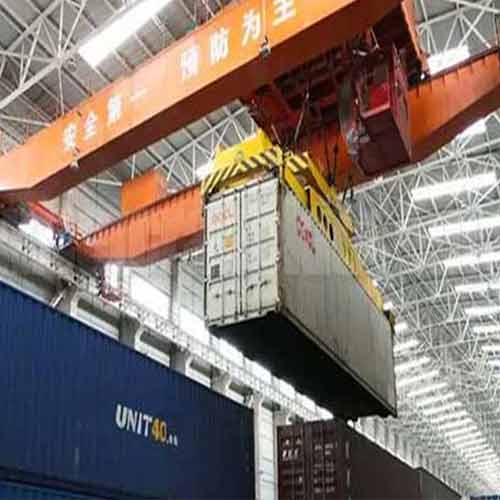

Custom Top Running Overhead Crane
Utilize two parallel horizontal beams for added load capacity and stability. Check More on top running double girder overhead cranes.
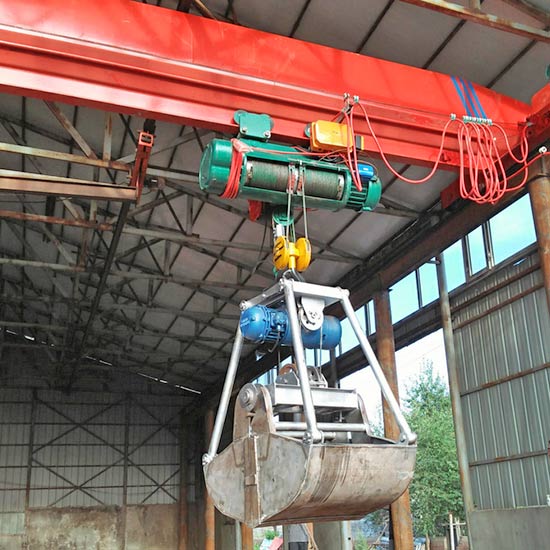

Feature a grab bucket or clamshell attachment for handling bulk materials.
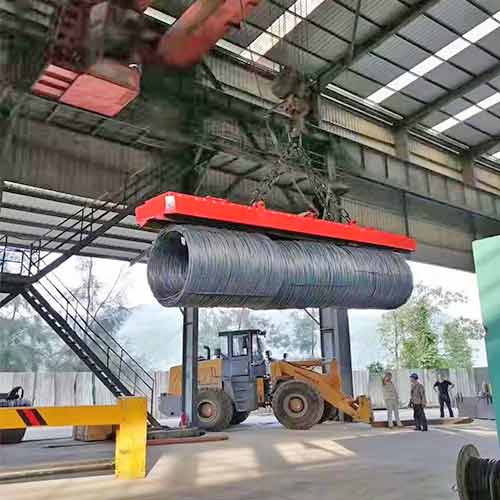

Equipped with a magnetic hoist for lifting and moving ferrous materials.
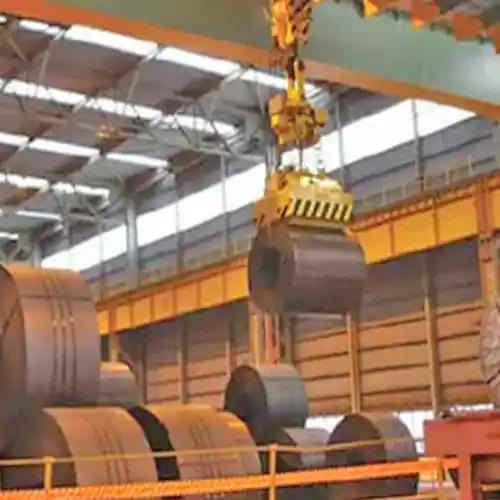

Designed specifically for handling steel coils, with equipment tailored for coil-related tasks.
Key characteristics of heavy duty bridge cranes include:
- High Load Capacity: Heavy duty bridge cranes are built to handle substantial loads, making them suitable for industries with demanding material handling requirements.
- Precision and Control: These cranes offer precise load positioning and control, ensuring safe and accurate movement of heavy items.
- Durability: Constructed with robust materials and components, heavy duty bridge cranes are engineered to withstand rigorous use and challenging operating conditions.
- Versatility: They can be customized to suit various applications, from manufacturing and construction to steel processing and shipyards.
- Reliability: Known for their dependable performance, these cranes are vital tools in industries where efficiency and safety are essential.
Heavy duty bridge cranes come in different configurations, including single and double girder designs, and they can be equipped with various hoisting mechanisms, such as wire rope hoists or open winch systems. These cranes play a crucial role in enhancing productivity, reducing manual labor, and ensuring the safe movement of heavy materials in industrial environments.
These groupings provide a classification of heavy duty bridge cranes based on girder configuration, running mechanism, and specialized features to help businesses select the most suitable crane for their specific material handling needs.
Heavy Duty Gantry Crane for Heavy and Bulky Loads
Heavy Duty Gantry Crane:
- Characteristics: A heavy duty gantry crane is a mobile crane supported by two vertical legs with wheels that run along the ground. This design offers portability and flexibility.
- Applications: - These cranes are ideal for shipyards, construction sites, and outdoor industrial applications. They are used to transport and position heavy and bulky loads, including large machinery and containers.

Double Girder Double Leg Gantry Crane:
- Features two vertical legs on both sides of the crane.
- Offers robust support and high lifting capacity, making it ideal for demanding industrial tasks.

Rubber Tired Gantry Crane (RTG):
- Equipped with rubber tires for mobility, typically used in shipping ports and container handling yards.
- Provides flexibility in moving and stacking containers.

Rail-Mounted Gantry Crane (RMG):
- Runs on rails and is commonly used in container terminals for efficient stacking and retrieval of containers.
- Offers high precision and load capacity.
Heavy Duty Jib Crane for Extreme Lifting Capacity
Heavy Duty Jib Crane:
- Characteristics: A heavy duty jib crane features a horizontal arm that can be rotated to lift and position loads with precision.
- Applications: - Heavy duty jib cranes are employed in challenging industrial environments where extreme lifting capacity and precision are required. They are found in sectors like aerospace, heavy machinery manufacturing, and large-scale energy production.
Heavy Duty Shop Crane for In-House Handling
Heavy Duty Shop Crane:
- Characteristics: These cranes are designed for in-house material handling and are often used in large manufacturing facilities.
- Applications: - Heavy duty shop cranes are crucial in the production of heavy machinery, where components need to be moved and assembled efficiently. They are also found in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Pricing Factors for Heavy Duty Cranes
The investment in heavy duty overhead cranes is substantial, and pricing can vary based on several factors, including:
- Load Capacity: The crane's load capacity is a primary determinant of its price. Larger capacity cranes, capable of lifting heavier loads, generally come at a higher cost.
- Customizations: Optional features and customizations, such as advanced control systems, load monitoring, and specialized lifting equipment, can add to the overall cost.
- Manufacturer and Brand: Different manufacturers offer heavy duty cranes at varying price points. Choosing reputable brands often ensures high-quality equipment but may come at a premium.
- Installation and Maintenance: Installation costs and long-term maintenance requirements should also be considered as part of the overall cost of owning and operating a heavy duty crane.
In conclusion, heavy duty overhead cranes are the backbone of industries that deal with enormous loads. Their characteristics, applications, and advantages make them indispensable in environments where precision, safety, and durability are paramount. Understanding the types of heavy duty cranes and pricing factors is essential for making a well-informed decision when choosing the right crane for your heavy lifting needs.
Crane Duty Cycles: Optimizing Performance and Safety
In the realm of material handling, the concept of "crane duty cycle" plays a pivotal role in ensuring the efficient and safe operation of overhead cranes. Understanding duty cycles is essential for making informed decisions when selecting the right crane for your specific needs. In this section, we'll explore the importance of comprehending duty cycles, delve into the duty cycles for both light and heavy duty cranes, and shed light on the role of hoist duty cycles in crane performance.
Exploring the Importance of Understanding Duty Cycles
Crane duty cycles are not mere technical jargon; they are a critical factor in the selection and operation of overhead cranes. A duty cycle classifies the expected operational conditions a crane is designed to withstand. It takes into account the following key factors:
- Load Capacity: Crane duty classifies cranes based on their load-carrying capacity. This classification helps match the crane's capacity to the specific requirements of the tasks it will perform.
- Duty Cycle: Duty cycle refers to the frequency and duration of crane operation. It determines how often and for how long the crane will be in use. Understanding the duty cycle is essential as it directly affects the crane's performance, safety, and longevity.
- Operational Conditions: Crane duty considers the environment in which the crane will operate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances can influence the crane's design and materials.
- Safety and Reliability: Safety features and reliability requirements are specified within the crane duty classification. Heavy duty cranes, for example, are engineered to ensure safety during prolonged and heavy usage, both for the operators and the loads they handle.
- Maintenance and Service Needs: The crane duty classification also provides insights into the crane's maintenance and service requirements. Heavy duty cranes, due to their higher capacity and frequent use, may demand more robust maintenance schedules and practices.
Understanding these aspects is crucial because it helps in selecting the right crane for a particular application, ensuring that it operates efficiently, safely, and reliably.
Light Duty Crane Duty Cycle
Light duty cranes, designed for less demanding operations, have specific duty cycle characteristics:
- Frequency: Light duty cranes are typically designed for intermittent or occasional use. They are not intended for continuous, heavy-duty operation.
- Duration: The duty cycle for light duty cranes allows for shorter operation periods. These cranes are suited for tasks with lighter loads and more infrequent lifting requirements.
- Applications: Light duty cranes are commonly found in assembly lines, maintenance workshops, and smaller manufacturing facilities. Their duty cycle matches the needs of these applications, ensuring efficient operation without the need for constant, heavy lifting.
Heavy Duty Crane Duty Cycle
- Heavy duty cranes, engineered for industrial settings with demanding conditions, exhibit the following duty cycle characteristics:
- Frequency: Heavy duty cranes are designed for continuous or frequent use. They can operate for extended periods without compromising safety or performance.
- Duration: The duty cycle for heavy duty cranes allows for prolonged operation, making them suitable for tasks that involve heavy loads, such as steel production or shipbuilding.
- Applications: Heavy duty cranes are essential in industries where precision and durability are paramount, such as in steel mills, shipyards, and large-scale manufacturing plants. Their duty cycle aligns with the rigorous demands of these applications.
Hoist Duty Cycle and Its Role in Crane Performance
The hoist, a critical component of overhead cranes, plays a central role in crane performance. The hoist duty cycle, which is a subset of the overall crane duty cycle, outlines the frequency and duration of hoist operation. Understanding the hoist duty cycle is essential for optimizing performance and safety:
- Frequent Starts and Stops: The hoist duty cycle often involves frequent starts and stops. This aspect is critical for applications that require precise positioning of loads, such as in manufacturing or assembly processes.
- Continuous Operation: In some heavy-duty applications, the hoist may need to operate continuously for extended periods. This continuous operation is a feature of certain hoist duty cycles, designed for reliability and efficiency.
- Safety and Maintenance: The hoist duty cycle also takes into account safety and maintenance requirements. Hoists used in heavy-duty applications may require more frequent maintenance to ensure their continued reliability and safety.
In conclusion, understanding crane duty cycles, whether for light duty or heavy duty cranes, and the specific duty cycles for hoists, is essential for optimizing crane performance and safety. Matching the crane's duty cycle to the specific requirements of the application ensures efficient operation and minimizes the risk of operational issues. Careful consideration of duty cycles is a fundamental step in selecting the right crane for your material handling needs.
Typical tonnages & capacity of light duty and heavy duty overhead cranes
The typical tonnages or capacity of light duty overhead cranes and heavy duty overhead cranes can vary depending on the specific design and application. Here are some general guidelines for the typical capacity ranges of these two crane categories:
Light Duty Overhead Cranes:
- Light Duty Bridge Cranes: These are often designed for relatively lighter loads and may have capacities ranging from 250 pounds (113 kilograms) to 5 tons (4,536 kilograms).
- Light Duty Gantry Cranes: Light duty gantry cranes can handle loads in the range of 500 pounds (227 kilograms) to 5 tons (4,536 kilograms). They are commonly used for light manufacturing and maintenance tasks.
- Light Duty Jib Cranes: Light duty jib cranes typically have capacities from 100 pounds (45 kilograms) to 2 tons (1,814 kilograms). They are suitable for small workshops and workstations.
Heavy Duty Overhead Cranes:
- Heavy Duty Bridge Cranes: Heavy duty bridge cranes are designed for more substantial industrial applications. They often have capacities ranging from 5 tons (4,536 kilograms) to 100 tons (90,718 kilograms) or more, depending on the specific needs of the facility.
- Heavy Duty Gantry Cranes: Heavy duty gantry cranes can handle significantly heavier loads, with capacities typically ranging from 10 tons (9,072 kilograms) to 200 tons (181,436 kilograms) or even more. These cranes are commonly used in shipyards and large-scale manufacturing.
- Heavy Duty Jib Cranes: Heavy duty jib cranes are designed for heavy-duty lifting in industrial settings. Their capacities can range from 2 tons (1,814 kilograms) to 10 tons (9,072 kilograms) or more.
- Heavy Duty Mobile Cranes: These cranes are highly versatile and can have capacities ranging from 10 tons (9,072 kilograms) to 1,000 tons (907,185 kilograms) or more, making them suitable for a wide range of heavy lifting applications.
It's important to note that the capacity of an overhead crane is determined by several factors, including the design, structural strength, and hoisting equipment. When selecting a crane, it's crucial to match the crane's capacity to the specific requirements of your operations to ensure efficient and safe material handling. Additionally, local regulations and safety standards should be considered when determining the appropriate capacity for your facility.
Factors to Consider in Crane Selection
Selecting the right overhead crane is a critical decision that can significantly impact the efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness of your material handling operations. To make an informed choice, it's essential to consider several key factors. Here are the primary elements to keep in mind when selecting an overhead crane:
Load Capacity Requirements
Load capacity is one of the most fundamental considerations in crane selection. You need to determine the maximum weight that the crane will need to lift and move. Ensure that the crane's capacity aligns with your heaviest load requirements. Keep in mind that the crane should have a sufficient load capacity with a safety margin to accommodate any unexpected weight variations.
Working Environment and Space Constraints
The working environment in which the crane will operate plays a crucial role in selecting the right crane type. Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances. Additionally, assess the space constraints in your facility, as this will influence the type of crane, its size, and its maneuverability. For facilities with limited space, a compact crane design or specialized mounting options like wall-mounted jib cranes may be necessary.
Safety Features for Operator and Load Protection
Safety should be a top priority in crane selection. Look for cranes with advanced safety features that protect both operators and the loads they handle. Features to consider include overload protection, anti-sway technology, emergency stop buttons, collision avoidance systems, and precision controls. The crane should also be equipped with adequate lighting and signaling devices to enhance visibility and awareness.
Maintenance and Service Considerations
Maintenance is a crucial aspect of crane ownership. Different types of cranes may have varying maintenance needs. It's essential to assess your facility's capabilities and available resources for maintenance and service. Heavy duty cranes may require more robust maintenance schedules, and you should have a maintenance plan in place to ensure the crane's continued reliability. Additionally, consider factors such as ease of access for maintenance personnel and the availability of spare parts.
Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Ensure that the chosen crane complies with all industry standards and regulations. Different regions and industries may have specific requirements for crane design, operation, and safety. Complying with these standards not only ensures the crane's safety but also helps prevent potential legal and regulatory issues.
To facilitate your selection process, it's advisable to consult with crane manufacturers and suppliers who can provide expert guidance based on your specific needs and constraints. They can help you determine the most suitable crane type, capacity, and features to optimize your material handling operations while ensuring safety and compliance with industry standards.
By considering these factors in crane selection, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your operational requirements and long-term goals, ultimately enhancing productivity and safety in your facility.
Choosing the Right Crane for Your Needs: A Strategic Approach
Selecting the right overhead crane is a strategic decision that directly impacts the efficiency, safety, and productivity of your material handling operations. To make a well-informed choice, consider the following key aspects:
Evaluating Specific Applications
Start by thoroughly evaluating your specific applications and material handling requirements. Take into account the types of loads you'll be handling, the frequency and precision of the movements, and any unique challenges presented by your working environment. This assessment will help you determine the type of crane and its load capacity that best suits your needs. For example, if you're dealing with smaller loads in a workshop, a light duty crane may be suitable, while heavy manufacturing operations may require a heavy duty crane.
Balancing Initial Costs with Long-Term Benefits
While the initial cost of purchasing and installing an overhead crane is an important consideration, it's crucial to balance these costs with long-term benefits. Look beyond the upfront investment and consider the crane's total cost of ownership. Heavy duty cranes, for example, might have higher initial costs, but their durability and longevity can result in cost savings over time. Evaluate factors such as maintenance requirements, energy efficiency, and the potential impact on operational productivity.
Consulting with Crane Experts for Tailored Solutions
Engaging with crane experts and manufacturers is an invaluable step in selecting the right crane for your needs. These professionals can offer tailored solutions based on your specific requirements and constraints. They have the expertise to help you choose the appropriate crane type, load capacity, and features that align with your operational objectives. Additionally, they can provide insights into industry standards, safety regulations, and maintenance considerations to ensure that your crane operates efficiently and safely.
Working with experts also allows for customizations that meet your unique needs. They can recommend safety features, control systems, and hoisting equipment that enhance the crane's performance and address any specific challenges you may face.
By following this strategic approach, you can make an informed decision that optimizes your material handling operations while ensuring safety and long-term cost-effectiveness. It's essential to consider not only the immediate requirements of your facility but also its future growth and evolving operational needs. Choosing the right crane is an investment in efficiency and safety that can yield substantial returns for your business over time.
Conclusion: Elevating Efficiency and Safety in Material Handling
In the realm of material handling, the choice of the right overhead crane is a decision that carries significant weight. This article has provided a comprehensive exploration of light duty and heavy duty overhead cranes, the importance of understanding crane duty cycles, and the critical factors to consider in crane selection. Let's summarize the key takeaways and emphasize the significance of selecting the right crane for your material handling operations.
- Crane Duty Cycles: Understanding the concept of crane duty cycles is essential. It helps match the crane's capabilities to the specific requirements of your tasks, ensuring efficient and safe operation.
- Light Duty and Heavy Duty Cranes: Light duty overhead cranes are versatile, cost-effective solutions for tasks with lighter loads, while heavy duty cranes excel in demanding industrial environments, offering high load capacity, durability, and advanced safety features.
- Crane Selection Factors: When choosing an overhead crane, consider load capacity requirements, the working environment, safety features, maintenance needs, and compliance with industry standards to optimize efficiency and safety.
- Choosing the Right Crane: Evaluate your specific applications, balance initial costs with long-term benefits, and consult with crane experts for tailored solutions. This strategic approach ensures that the crane you select aligns with your operational objectives and constraints.
In conclusion, selecting the right overhead crane is more than just a logistical decision; it's a strategic investment in the efficiency and safety of your material handling operations. The choice you make will impact your business's productivity and bottom line, as well as the well-being of your employees. By understanding the unique demands of your operations, considering all relevant factors, and seeking expert guidance when needed, you can elevate efficiency and safety in your facility. Make this investment wisely, and it will pay dividends for years to come, helping you meet and exceed your material handling goals.
Main Projects
Related Products

Latest project
32/5 Ton Overhead Crane Sale in India: Case Study
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch