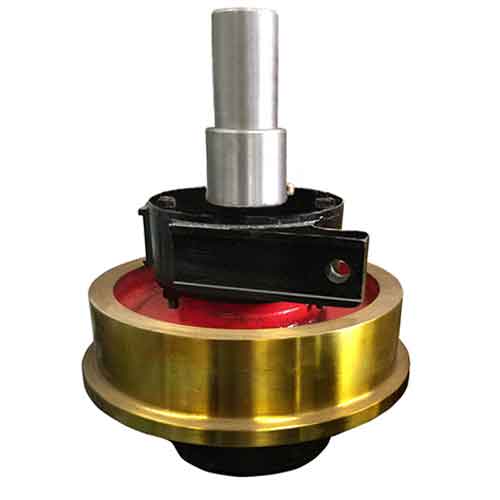
Overhead Crane Wheels, Gantry Crane Wheels & Crane Trolley Wheels
All on crane wheel - types of crane wheels, specification, wheel hardness & heat treatment. Get your overhead crane wheel & gantry crane wheel design now.
Category: Crane Kit Parts
Overhead Crane Wheels, Gantry Crane Wheels & Crane Trolley Wheels
Crane wheels are used in overhead cranes, gantry cranes, metallurgical casting cranes, slab handling cranes, magnet cranes, and steel coil clamp cranes, among other applications.Types of crane wheels are for sale, such as, overhead crane wheels, gantry crane wheels, and crane trolley wheels, etc. All of our crane wheels are with the features of high precision assembly, stable operation, and easy for replacement. If you have any need of crane wheel design, please feel free to contact us.

Technical description of crane wheels:
- Application: Overhead crane, gantry crane, crane trolley, transfer car, heavy-duty industry, Port crane, Steel factory, etc.
- Material of crane wheels : 4140/SCM440/42CrMo,SSW-QIR/65#steel,65Mn,50SiMn,QT800,ZG35SiMn,SSW-Q1
- Dimension of crane wheels: φ250, φ350, φ400, φ500, φ600, φ700, φ800, φ 1000, φ 1200 or Customized overhead crane wheels and gantry crane wheels are supplied with the specificaitons
- Quality control of crane wheels : All the required crane wheel tests are applied including UT, MT, RT, PT, chemical composition test, mechanical property test, etc.
- Heat treatment of crane wheels : Quenching and Tempering
- Quenching depth of crane wheels : ≥20mm
- Coating of crane wheels : Black Oxide + Rust-proof oil
- Inspection of crane wheels : A third-party inspection is possible if required.
- Standard of crane wheels : ASTM, ASME, DIN, JIS, ISO, BS, API, EN, GOST, etc
- Certificate of crane wheels : All the testing certifications are provided if required including Raw material certificate(material chemical composition), Heat treatment sheet report, Dimension inspection report,and UT/MT test report, etc.
- Packing of crane wheels : Seaworthy plywood packaged on steel pallets or customized.
- Delivery date of crane wheels : 15~30 working days
- Competitive advantage of crane wheels : Quality control and management of the entire manufacturing process, including ingot smelting, forging, heat treatment, machining, and final inspection prior to delivery.
- Certification of crane wheels: All our crane wheels have obtained CCC, ISO9001, and CE certification.
Crane wheels are the most important parts in overhead crane and gantry crane crane traveling system which are also the most vulnerable crane parts and components due to the friction between crane wheels and rail. As a result, when flange wear, flange breaking, or fatigue pitting occurs, the crane wheels should be replaced.
(a)Double wheel rim wheel (b) Single wheel rim wheel (c)None wheel rim wheel
Types of crane wheels
Crane wheels are classified into numerous categories based on different standards, such as single edge and double edge crane wheels, casting and forging crane wheels, overhead crane wheels, gantry crane wheels or crane trolley wheels, and so on.
Bases on the crane wheel designs, the crane wheels are often divided into three categories: double flange crane wheels, single flange crane wheels, and non-flange crane wheels, among others. The lengths of single edge and double edge crane wheels will be introduced in the following sections.
Double flange crane wheels

Double rim crane wheel

Double rim crane wheel
Features of double flange crane wheel
- Crane wheels Application: Trolley traveling of the bridge and gantry crane
- Flange height of crane wheels: 25mm-30mm
- Materials of crane wheels: ZG340-640 cast steel , ZG-50SiMn low alley steel,
- Hardening depth of the crane wheels tread part: ≥20mm
- Hardness of the rolling surface: ZG340-640 cast steel with the hardness of 300-350HB, ZG-50SiMn with the hardness of420-480HB
Single flange crane wheels
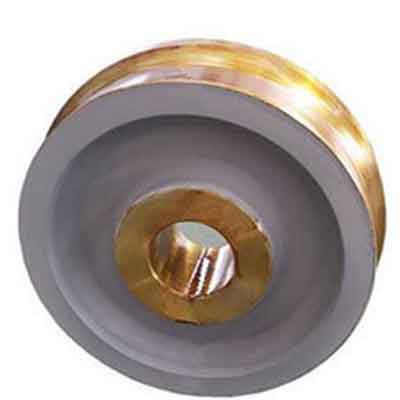

single flange crane wheel
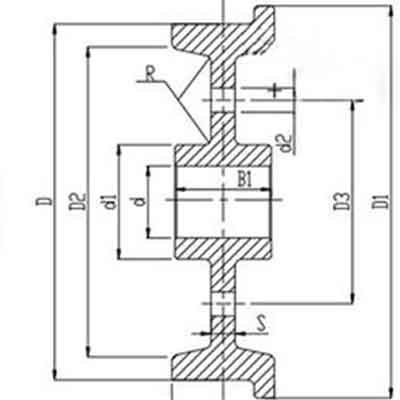
single flange crane wheel
Features of single flange crane wheels
- Crane wheels Application: Travelling of bridge crane, gantry crane
- Flange height of crane wheels: 20mm-25mm
- Materials of crane wheels: ZG340-640 cast steel, ZG-50SiMn low alley steel
- Hardening depth of crane wheels tread part: ≥20mm
- Hardness of the rolling surface: ZG340-640 cast steel with the hardness of 300-350HB, ZG-50SiMn with the hardness of420-480HB
Non-flange crane wheels
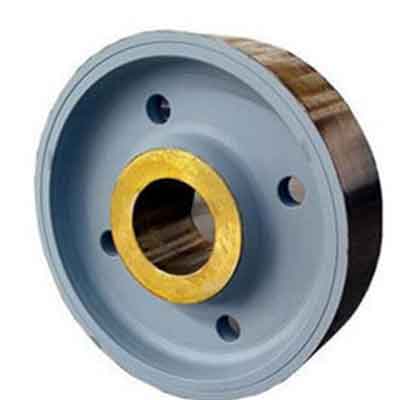

Non-flange crane wheel
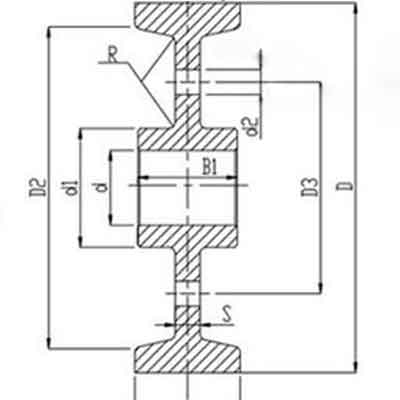
Non-flange crane wheel drawing
Features of crane wheels:
- Diameter and material of crane wheel consider the most adverse conditions that bears the largest force, which will be designed based on the loading capacity and overload is not allowed.
- Crane wheels are made of 65Mn/ ZG430-640(CL60)cast steel, and the surface of crane wheel is frequency undergo the heat treatment and the, hardness of crane wheels usually comply with the following:
- The hardness of tread and inner of wheel flange(HB)≥300~380
- Min depth of quenching is more than 20mm
- Min. hardness of hardening zone shall be no less than HB 260
- Tread and wheel inner flange of wheel shall not impair the performance and shall not be fixed by welding.
Regulations on crane wheels
The crane wheels must be discarded after the rim thickness has worn down to 50% of its original thickness, according to rule GB6067 –1985. The crane wheel rim bears the lateral pressure of the crane, with 70 percent to 80 percent of the crane wheels rubbing against the side of the track, which can cause the flange to wear out and the wheel to be discarded, according to the "Crane design manual."
As a result, the heat treatment of the crane wheel should incorporate the rim profile, i.e., if the heat induction coil is too narrow during power frequency quenching, the rim inside surface hardness will not satisfy requirements.
When the wheel tread thickness wears down to 15% of the original thickness, it must be discarded, according to rule GB6067 –1985. Maintaining a moderate tread hardness (too high would cause severe rail wear) and a 20mm wheel tread depth (too low will cause severe wheel wear) during the production process is unquestionably tough. Years of experience have shown that when the carbon content of cast steel or conventional carbon steel material is less than 0.5 percent, the hardened layer depth on the surface of the wheel tread will not meet requirements.
Some manufacturers used table flame quenching heat treatment method due to capacity constraints or cost considerations. This method has only 2-5mm of hardened depth and the surface is brittle. During the running process, the wheel tread cracks and hardens off, causing wheel scrap. This approach should not be used.
Materials of overhead crane wheels
Generally, crane wheels are made of 60 steel ZG340-640 cast steel 42Crmo65Mn.
Overhead crane wheels are often made of ZG310-570 cast steel or higher-quality steel. The small size overhead crane wheels can be manufactured of forged steel but not below the 45th stainless steel. Alloy steel wheels, such as ZG55CrMn, ZG50MnMo, and others, are used to support heavy loads on bear crane wheels. When it's necessary to minimize the diameter of overhead crane wheels and, finally, the height of overhead cranes, alloy material is used.
Processing of crane wheels
In order to ensure the high quality of crane wheels assembly, the quality inspections should be applied through the whole crane wheel production procedure from design, material selection, heat treatment and others, etc.
The main production of crane wheels are as follow:
Crane wheel drawing, 3d modeling, Fem Analysis, Blank wheel, rough machining, Heat treatment, Finish machining, Hardness testing, Assembling,etc.
Crane wheel drawing
Crane wheel 3d modeling

Crane wheel fem Analysis

Crane wheel blank wheel

Crane wheel rough machining

Crane wheel heat treatment

Crane wheel finish machining

Crane wheel hardness Testing

Crane wheel assembling
Heat treatment of overhead crane wheels
The wheel tread must be heat treated to increase the load capacity and service life of crane wheels. The medial surface of the wheel hardness must be 300-380HB, with a 20mm hardened depth of not less than 260HB, which can be achieved utilizing a variety of heat treatments under current technical conditions.
The hardness of crane wheels raw material
Crane wheels are typically built of raw materials such alloys, low-carbon steel, or medium-carbon steel. Because of its wide availability and low cost, medium-carbon steel is the most often utilized raw material in crane wheel production.
Heat treatment procedures are used to increase the hardness of metals.
The hardness of crane wheels constructed of medium-carbon steel has been rising as a result of developments in heat treating technology, which is particularly noticeable at the tread and where the tread meets the rail.
Forging crane wheels or casting crane wheels?
Crane wheels that have been forged are substantially more durable. Crane wheels forging ensures constant strength, grain flow, and directional strength, all of which are plainly visible metallurgical faults throughout the forging process.
Forging crane is more reliable. Forging crane wheels has improved reliability for the following reasons:
- During the production, the grain pattern is refined.
- The strength of the crane wheels is maximized by generating grain flow orientation.
- According to third-party study, the forging crane wheel has a 26 percent higher tensile strength and a 37 percent higher fatigue strength.
Forging crane wheel

Casting crane wheel
Note: Higher the hardness, the better the crane wheel?
A hardened crane wheel tread does, in fact, reduce wear and extend the life of crane wheels. However, the following dilemma arises:
- Is it true that the harder the crane wheels are, the better they are?
- No.
When a crane wheel's hardness surpasses 65 Rockwell "C," it becomes brittle and susceptible to cracking if it comes into touch with a section of the rail that is missing parts or other sharp things. Furthermore, the top of the wheel flange and the outer section of the flange should not be hardened since ductility is required for them to flex without breaking when subjected to lateral forces, such as a misaligned rail. To extend the life of a crane wheel, the inner side of the flange must be the same depth and hardness as the tread.
The depth of hardness of the crane wheel must be measured. Spalling occurs when hardening does not penetrate deep into the wheel tread, resulting in metal particles falling off the surface and decreasing the crane wheel's life.
A wheel's lifespan depends on more than hardness alone.
The crane wheels, which come into direct touch with the crane runway, are the crane's weakest link. Crane wheels are usually the first crane parts to reveal signs of difficulties with the crane, such as misaligned rails or an unsquared crane.
Inspection of overhead cranes and gantry cranes, particularly the crane wheels, on a regular basis will detect early wheel wear and provide indications to repair problems before they become serious.
The thickness of crane wheel flanges should be measured and documented so that the rate of wear may be tracked between inspections.
Advantages of crane wheels
- Designed with high-quality materials that can be modified.
- Supervised and advanced manufacture assures a uniform contour hardness in the tread and inner flange wear surfaces, as well as a ductile core to withstand shock loads.
- High wear resistance, flange fracture resistance, pitting and spalling resistance, and a long operating life.
- Improve your rail's lift.
- Quick delivery within the specified time frame.
Crane wheels repair and maintenance
- The wheel group's shaft hole must be checked on a regular basis, and flaws and shaft hole depth must be rigorously specified. If the specified amount is surpassed, the new parts must be replaced.
- If the radial wear of the wheel group's pulley groove exceeds 32% of the thickness, it needs to be replaced. It can be kept if the thickness does not exceed 32 percent and the distance does not exceed 0.5 mm. Overhead When the new pieces do not surpass this value, the crane wheel tread wear, which is more than 15% of the original thickness, should be replaced. If the new pieces do not exceed this value, the system can be re-carried and heat treatment repaired. The diameter of the overhead crane wheel should be within the tolerance range, with a surface hardening hardness of HB300 to 500. If the crane wheel diameter is greater than 400mm, the quenching layer thickness should be greater than 20mm if the crane wheel diameter is less than 400mm, the quenching layer thickness should not be less than 15mm if the crane wheel diameter is less than 400mm, the quenching layer thickness should not be less than 15mm.
- The wheel pulley group must be checked for cracks during maintenance. Shaft neck parts must have a wear rate of less than 40% or the components must be replaced.
- After inspection and maintenance, the removable wheel crane accessories should be assembled in a timely manner. It must be tested after it has been assembled.
- The diameter deviation of the two mutually matching crane wheels must be less than 0.1 percent of the nominal diameter, and the diameter deviation of the driven wheel must be less than 0.2 percent. The diameter of the electric hoist wheel must be within 1% of the nominal diameter. The departure of the moving wheel should not exceed 0.2 percent, and the diameter deviation of the electric hoist wheel should not exceed 1% of the nominal diameter.
- Rim wear and tear, deformation: the edge of the wear and tear should be scrapped if it is 50 percent of the original thickness or if it breaks the area of more than 30mm2, and the thickness of the flange distortion should be scrapped if it is 20 percent of the original thickness.
- Wheel cracks in overhead cranes: the wheels should be discarded if detected in the cracks.
- Overhead crane wheel tread ovals of less than 1mm should be destroyed.
- Overhead crane wheel assembly: The overhead crane wheel assembly installation should be able to hand flexible rotation, installed in the same balance frame on a few wheels in the same vertical plane, with a 1mm permissible variation.
Crane Wheel blocks
The wheel block's bearing support is a corner box construction that is bolted to the trolley frame or the bending plate of the crane end beam. The framework may adjust the wheel during usage and maintenance, ensuring that the wheel is deflected horizontally and vertically and preventing the wheel from nibbling the rail. In China nowadays, the corner box structure is the most extensively utilized mature technology.
Crane wheels service for you
- Crane wheels with superior design and quality control are available.
- A wide range of crane wheels with diameters ranging from 150mm to 900mm (6" to 36") are available.
- Crane wheels come in a variety of shapes and sizes, including single and double flange wheels, forging and casting wheels, and so on.
- For various crane manufacturers throughout the world, customized crane wheels are available to give the most suitable crane for overhead crane and gantry crane.
Crane wheels are made to fit your specific needs. How can you find the best crane wheels for your overhead or gantry crane? We've been chosen by Demag Crane. Why don't you take advantage of our Crane Wheels? Please use the form below to send us a message.
Related Products

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch



