How Underhung Bridge Cranes Handle Loads Near Workshop Walls
Discover how underhung bridge cranes optimize space and efficiently handle loads close to walls, enhancing workshop productivity and accessibility.
Category: Low Built Cranes & Hoists
Your Trusted Overhead Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
How Underhung Bridge Cranes Handle Loads Near Workshop Walls
Discover how underhung bridge cranes optimize space and efficiently handle loads close to walls, enhancing workshop productivity and accessibility.
How Underhung Bridge Cranes Efficiently Handle Loads Near Workshop Walls
In modern industrial environments, efficiency and space optimization are crucial for maintaining competitive operations. Among the various lifting solutions available, underhung bridge cranes stand out for their versatility and ability to operate in confined spaces. These cranes are suspended from the ceiling rather than being supported by floor-mounted columns, which makes them particularly advantageous in workshops with limited floor space.
Brief Overview of Underhung Bridge Cranes
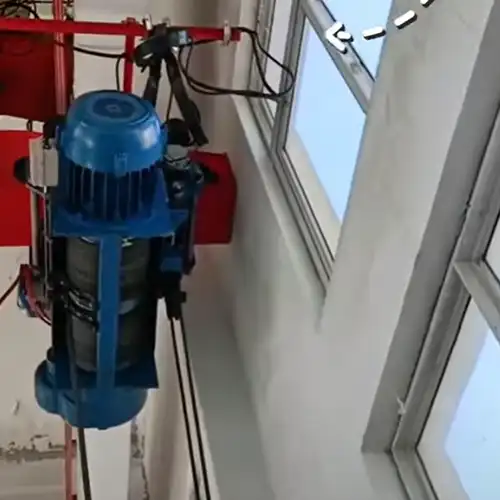
Underhung bridge cranes, also known as under-running cranes, feature a bridge that is suspended from the ceiling structure. This design allows the crane to maximize the use of the vertical space in a facility. Unlike traditional overhead cranes that require substantial floor support, underhung cranes are supported from the roof structure, freeing up valuable floor space for other operations. They are typically used for lighter loads, ranging from a few hundred pounds to several tons, and are ideal for applications where headroom is limited.
Key components of underhung bridge cranes include:
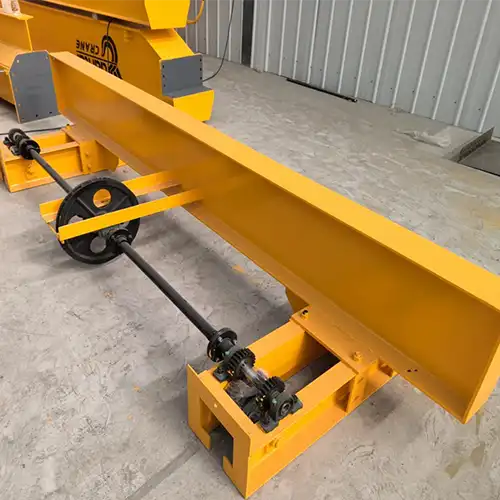
- Runway System: The tracks or rails attached to the ceiling from which the crane is suspended.
- Bridge: The horizontal beam that spans the runway system and supports the hoist.
- Hoist and Trolley: The hoist lifts and lowers the load, while the trolley moves the hoist along the bridge.
- Control System: Can be manual, semi-automated, or fully automated, allowing precise control of the crane's movements.
Importance of Maximizing Reach in Limited Space Workshops
In workshops where space is at a premium, maximizing reach and lifting capacity without compromising safety and efficiency is essential. Underhung bridge cranes excel in these environments for several reasons:
- Space Optimization: Underhung cranes eliminate the need for floor-mounted supports, allowing for unobstructed movement of personnel and equipment on the ground. This is particularly beneficial in crowded workshops where every square foot counts.
- Flexibility: These cranes can be adapted to various building configurations, including those with complex layouts or low ceilings. The ability to navigate around obstacles and reach tight areas enhances operational flexibility.
- Improved Workflow: By utilizing the overhead space, underhung cranes help streamline workflow and reduce bottlenecks. This is especially important in industries where quick and efficient material handling is critical to productivity.
- Enhanced Safety: With the crane operating above the work area, there is less risk of collisions with ground-level equipment and personnel. This contributes to a safer working environment and reduces the likelihood of accidents.
- Cost-Effective: The installation of underhung bridge cranes is often more cost-effective compared to other types of cranes, especially in existing buildings where floor space is limited. The reduced need for structural modifications translates to lower overall costs.
In conclusion, underhung bridge cranes offer a practical and efficient solution for maximizing reach and lifting capabilities in workshops with limited space. Their ability to operate in confined areas, combined with the benefits of space optimization, flexibility, improved workflow, enhanced safety, and cost-effectiveness, make them an invaluable asset in various industrial settings.
Design Features of Underhung Bridge Cranes
Underhung bridge cranes are specifically designed to optimize space and efficiency in industrial environments. Their unique ceiling-mounted design and other key features make them suitable for workshops with limited floor space. Here, we explore the crucial design features that set underhung bridge cranes apart from other types of cranes.
Ceiling-Mounted Design
One of the most distinctive features of underhung bridge cranes is their ceiling-mounted design. This configuration involves suspending the crane's runway system from the ceiling or roof structure of a building. This offers several advantages:
- Maximized Floor Space: By suspending the crane from the ceiling, underhung bridge cranes free up valuable floor space that would otherwise be occupied by support columns or tracks. This allows for more efficient use of the workspace, accommodating other machinery and facilitating the movement of personnel.
- Enhanced Mobility: The ceiling-mounted design enables the crane to cover a larger area without obstruction, making it easier to transport materials across the entire workshop. The absence of floor-mounted supports also reduces the risk of tripping hazards and collisions.
- Adaptability: These cranes can be installed in buildings with low ceilings or other structural constraints, offering flexibility in various industrial settings. The runway can be tailored to follow the contours of the building, including curves and corners, to suit specific operational needs.
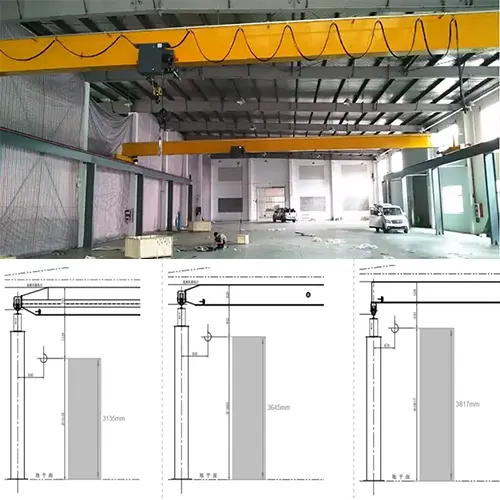
Ability to Reach Extreme Ends Close to Walls
Underhung bridge cranes are designed to maximize reach, particularly in confined spaces. They excel in their ability to access extreme ends and areas close to walls, which is crucial in maximizing the utility of a workshop:
- Proximity to Walls: The crane's runway system can be extended close to the walls of the building, allowing the hoist and trolley to reach areas that might be inaccessible with floor-mounted cranes. This is particularly beneficial in maximizing the use of the available space for storage or workstations.
- Extended Coverage: The design allows the bridge to travel the full length of the runway and the trolley to traverse the entire span of the bridge, providing comprehensive coverage of the work area. This ensures that materials can be moved efficiently to and from any point within the workshop.
- Precision Handling: The precise control systems used in underhung bridge cranes facilitate accurate positioning of loads, even in tight spaces. This is essential for delicate or complex operations where exact placement of materials is required.
Comparison with Floor-Mounted Cranes
While both underhung and floor-mounted cranes have their respective advantages, understanding their differences helps in choosing the right type of crane for specific applications:
Space Utilization
Underhung Bridge Cranes:
Underhung bridge cranes are designed to be mounted from the ceiling or overhead beams, which effectively utilizes the vertical space in a workshop. This design provides several benefits:
Maximized Floor Space:
- No Floor Obstructions: Since the crane's support structure is mounted above, there are no columns or legs occupying valuable floor area. This allows for unobstructed movement of personnel and equipment on the ground level.
- Enhanced Workflow: With more available floor space, workshops can better organize workstations, storage, and machinery, leading to improved workflow and efficiency.
Flexibility in Layout Planning:
- Adaptability: Underhung bridge cranes can be integrated into various workshop layouts without needing to rearrange existing floor-based machinery and equipment.
- Expansion Capabilities: As businesses grow, additional equipment or workstations can be added without needing to reconfigure the entire floor plan, thanks to the overhead crane system.
High-Traffic Areas:
- Uninterrupted Movement: In busy workshops, the absence of floor-based crane structures allows for seamless movement of workers, vehicles, and materials, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall productivity.
- Efficient Material Handling: The crane can move loads over obstacles and reach areas that might be difficult to access with a floor-mounted crane, optimizing material handling processes.
Floor-Mounted Cranes:
Floor-mounted cranes, on the other hand, come with their own set of challenges related to space utilization:
Dedicated Floor Space:
- Support Structures: Floor-mounted cranes require significant floor space for their support columns and tracks, which can take up valuable working area and limit the space available for other operations.
- Reduced Flexibility: The fixed position of the support structures means that the workshop layout is less adaptable, making it difficult to modify or expand without major reconfigurations.
Restricted Movement:
- Obstacle Creation: The presence of crane support columns can create obstacles on the workshop floor, hindering the movement of workers, equipment, and materials. This can lead to inefficiencies and increased time to complete tasks.
- Limited Access: Certain areas of the workshop may become less accessible due to the fixed positions of the support structures, restricting the effective use of the entire workspace.
Planning and Installation Challenges:
- Complex Installation: Installing a floor-mounted crane requires careful planning to ensure that the support structures do not interfere with existing machinery or workflows. This can be time-consuming and may require significant adjustments to the workshop layout.
- Space Allocation: Allocating space for the crane's support structure often means sacrificing other potential uses for that area, potentially limiting the workshop's overall functionality.
In summary, underhung bridge cranes offer significant advantages in terms of space utilization by freeing up floor area and allowing for more flexible and efficient layout planning. In contrast, floor-mounted cranes require dedicated floor space for their support structures, which can restrict movement and reduce the available working area in the workshop.
Structural Requirements
Underhung Bridge Cranes:
Ceiling or Roof Structure:
- Load-Bearing Capacity: Underhung bridge cranes are mounted from the ceiling or roof beams, which must be strong enough to support the weight of the crane and the maximum loads it will handle. The ceiling structure should be assessed to ensure it can safely bear these loads.
- Reinforcements: In some buildings, especially older or less robust structures, additional reinforcement may be necessary. This could involve strengthening beams, adding support columns, or installing additional load-bearing elements to accommodate the crane system.
- Alignment and Stability: The mounting infrastructure needs to be precisely aligned to ensure the crane operates smoothly and safely. Any misalignment could affect the crane's performance and safety.
Installation Considerations:
- Clearance Requirements: Adequate clearance must be maintained between the crane components and the ceiling to allow for smooth operation and avoid obstructions. This includes ensuring that the crane's trolleys and hoists have enough vertical space to function properly.
- Access for Maintenance: The ceiling-mounted design should allow for easy access to the crane for maintenance and repairs. Sufficient space must be provided around the crane's mounting points for inspection and servicing.
Floor-Mounted Cranes:
Flooring Requirements:
- Solid and Level Surface: Floor-mounted cranes depend on a solid and level flooring surface to support their columns and tracks. The floor must be capable of bearing the weight of the crane and the loads it will handle without settling or deformation.
- Load Distribution: The weight of the crane is distributed across its support columns, so the flooring must be engineered to handle these concentrated loads. This often involves ensuring that the floor is reinforced or constructed to handle heavy loads.
Installation Considerations:
- Foundation and Anchoring: The crane's columns must be securely anchored to the floor, which may require installing concrete foundations or other anchoring methods. Proper anchoring ensures stability and prevents shifting or tipping.
- Space Allocation: The installation of floor-mounted cranes requires dedicated space for the support columns and tracks, which can limit the available floor area. This must be planned carefully to avoid interfering with other workshop operations and equipment.
Advantages in Certain Buildings:
- Suitability for Existing Structures: Floor-mounted cranes can be advantageous in buildings where the ceiling or roof cannot support additional loads. They provide a viable lifting solution without altering the structural integrity of the existing ceiling or roof.
In summary, underhung bridge cranes necessitate a robust ceiling or roof structure capable of supporting the crane and its loads, which may require structural reinforcements. In contrast, floor-mounted cranes rely on solid and level flooring to support their columns and tracks, which can be advantageous in buildings where the ceiling cannot handle additional loads. Each type of crane has specific structural requirements that must be addressed to ensure safe and effective operation.
Installation and Maintenance
Underhung Bridge Cranes:
Installation:
- Ease of Integration: Underhung bridge cranes are generally easier to install in existing buildings as they do not require extensive modifications to the floor. The primary requirement is a suitable ceiling or roof structure to support the crane.
- Mounting: Installation involves securing the crane's support beams or tracks to the ceiling or overhead beams. This process typically requires precise alignment but does not interfere with the floor space, making it less disruptive to existing operations.
Maintenance:
- Access Challenges: Maintenance of underhung bridge cranes often requires working at heights, which can present additional safety considerations. Specialized equipment such as ladders or elevated platforms may be needed to access the crane's components for inspection and repairs.
- Safety Measures: Proper safety protocols must be in place to ensure safe access during maintenance activities. This includes using appropriate fall protection equipment and ensuring that maintenance personnel are trained to work safely at elevated heights.
Floor-Mounted Cranes:
Installation:
- Complexity: The installation of floor-mounted cranes can be more complex due to the need for precise alignment of tracks and support columns. This often involves significant planning and may require modifications to the floor or foundation to ensure stability.
- Floor Modifications: Installing floor-mounted cranes may necessitate alterations to the existing floor, such as reinforcing or leveling, to accommodate the crane's support structures. This can be more disruptive and time-consuming compared to installing underhung cranes.
Maintenance:
- Ground-Level Access: Maintenance of floor-mounted cranes is generally more straightforward as it occurs at ground level. Accessing the crane's components is typically easier, and safety concerns are reduced compared to working at heights.
- Routine Checks: Maintenance tasks include inspecting tracks, supports, and lifting mechanisms. Regular checks can be performed without the need for specialized access equipment, making the maintenance process more efficient and less hazardous.
In summary, underhung bridge cranes offer easier installation in existing buildings by utilizing overhead space and avoiding floor modifications, although maintenance can pose challenges due to the need for working at heights. Floor-mounted cranes, while more complex to install due to precise alignment and potential floor modifications, generally have simpler maintenance requirements as they occur at ground level.
Load Capacity and Applications
Underhung Bridge Cranes:
Load Capacity:
- Lighter Loads: Underhung bridge cranes are typically designed to handle lighter loads compared to their floor-mounted counterparts. They are well-suited for applications where the load requirements fall within moderate weight ranges, generally up to several tons.
- Precision Handling: These cranes are ideal for tasks that require precise positioning and careful handling of components. They provide smooth and controlled lifting, which is essential for delicate or high-value items.
Applications:
- Precision Manufacturing: In settings like electronics or precision machinery manufacturing, where components need to be moved carefully and accurately.
- Assembly Lines: Perfect for assembly lines in industries such as automotive or aerospace, where space is limited and loads are relatively light.
- Storage Solutions: Useful for warehouses or storage facilities where items need to be moved efficiently within confined spaces without occupying floor area.
Floor-Mounted Cranes:
Load Capacity:
- Heavier Loads: Floor-mounted cranes are designed to handle heavier loads, often capable of lifting several tons or more. They are built with robust support structures and are suitable for applications involving substantial weight.
- High Capacity: These cranes are ideal for environments where heavy and large components need to be moved, offering higher lifting capacities and stability.
Applications:
- Heavy Manufacturing: Commonly used in industries such as steel production, heavy machinery manufacturing, and shipbuilding, where moving large and heavy materials is essential.
- Construction: Ideal for construction sites where the lifting and movement of large building materials, equipment, and structural components are required.
- Industrial Facilities: Suitable for facilities with demanding industrial processes that involve heavy-duty lifting and handling of significant loads.
Underhung bridge cranes are best suited for lighter loads and applications requiring precise handling in space-constrained environments. Floor-mounted cranes, with their higher load capacities, are designed for heavy-duty applications in manufacturing, construction, and other industries requiring substantial lifting power.
In summary, underhung bridge cranes offer distinct advantages in terms of space utilization, reach, and flexibility, making them an excellent choice for workshops with limited floor space and complex layouts. Their ability to operate close to walls and cover extensive areas enhances operational efficiency, while the comparison with floor-mounted cranes highlights their suitability for specific applications.
Benefits of Efficient Load Handling Near Walls
Efficient load handling near walls is a critical aspect of optimizing workshop operations. Underhung bridge cranes, with their ability to maximize reach and cover areas close to walls, provide significant advantages in terms of space utilization, accessibility, maneuverability, and safety. Here are the key benefits:
Optimized Use of Workshop Space
One of the most prominent benefits of efficient load handling near walls is the optimized use of workshop space. In many industrial settings, space is at a premium, and the ability to utilize every square foot effectively can greatly enhance productivity.
- Maximizing Usable Area: By reaching areas close to walls, underhung bridge cranes enable the full utilization of the workshop's footprint. This means that storage racks, workstations, and machinery can be placed closer to the walls, freeing up central areas for other critical operations.
- Flexible Layouts: The enhanced reach allows for more flexible and dynamic workshop layouts. Equipment and materials can be organized in a way that maximizes efficiency, with easy access to all areas of the workshop. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in adapting to changing operational needs.
- Efficient Storage Solutions: Efficient load handling near walls allows for the installation of vertical storage solutions along the periphery of the workshop. This can significantly increase the storage capacity without encroaching on valuable floor space, improving overall organization and material management.
Improved Accessibility and Maneuverability
Efficient load handling near walls greatly improves accessibility and maneuverability within the workshop. This is essential for maintaining smooth and uninterrupted operations.
- Ease of Access: The ability to handle loads close to walls means that materials and equipment can be placed and retrieved easily, even in tight spaces. This improves the overall flow of materials, reducing delays and increasing throughput.
- Enhanced Maneuverability: Underhung bridge cranes provide excellent maneuverability, allowing for precise positioning of loads. This is particularly important in workshops with complex layouts or where space is limited. The crane can navigate around obstacles and reach difficult areas with ease.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: By efficiently utilizing the space near walls, the central working area remains free from congestion. This facilitates the movement of personnel and equipment, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall workflow.
Enhanced Safety by Reducing Manual Load Handling
Safety is a paramount concern in any industrial setting, and efficient load handling near walls significantly contributes to a safer working environment by reducing the need for manual load handling.
- Minimized Manual Lifting: Underhung bridge cranes reduce the reliance on manual lifting and transporting of heavy loads. This minimizes the risk of injuries associated with manual material handling, such as strains, sprains, and other musculoskeletal disorders.
- Improved Load Stability: The precise control offered by underhung bridge cranes ensures stable and secure handling of loads, even when operating close to walls. This reduces the likelihood of load shifting or dropping, enhancing overall safety.
- Decreased Workplace Accidents: With the crane handling loads near walls, the need for workers to navigate tight and potentially hazardous spaces is reduced. This lowers the risk of accidents caused by tripping, slipping, or colliding with objects.
- Enhanced Ergonomics: By automating the movement and placement of heavy loads, underhung bridge cranes improve ergonomics for workers. This leads to a more comfortable and safer working environment, reducing fatigue and improving productivity.
In conclusion, efficient load handling near walls provides substantial benefits in terms of optimizing workshop space, improving accessibility and maneuverability, and enhancing safety by reducing manual load handling. Underhung bridge cranes are particularly effective in achieving these benefits, making them a valuable asset in modern industrial operations.
Applications in Limited Space Workshops
Underhung bridge cranes are highly effective in workshops with limited space, where their unique design and capabilities can be fully utilized to enhance efficiency and productivity. Here are some common scenarios where underhung bridge cranes excel, along with examples of industries and tasks that benefit from this feature.
Common Scenarios Where Underhung Bridge Cranes Excel
- Crowded Workshop Floors: In workshops where floor space is crowded with machinery, workstations, and storage units, underhung bridge cranes provide an overhead lifting solution that doesn't interfere with ground operations. This allows for seamless material handling without the need for additional floor space.
- Low Ceiling Heights: Workshops with low ceiling heights benefit from the compact design of underhung bridge cranes, which can operate efficiently within confined vertical spaces. This makes them ideal for older buildings or facilities with structural limitations.
- Complex Layouts: Facilities with irregular or complex layouts can leverage the flexibility of underhung bridge cranes to navigate around obstacles and reach difficult areas. The crane's ability to operate close to walls and tight corners is particularly advantageous in such environments.
- Precision Handling Requirements: In scenarios where precise positioning of materials is crucial, underhung bridge cranes offer the necessary control and accuracy. This is essential for tasks that require careful handling of delicate or valuable components.
How Underhung Bridge Cranes Handle Loads Near Workshop Walls 1 T, 2 T, 3 T, 5 T, 7.5 T, 10 Ton
Industries and Tasks Benefiting from This Feature
Automotive Manufacturing:
Tasks: Assembly line operations, component handling, and storage.
Benefits: In automotive plants, space is often at a premium. Underhung bridge cranes facilitate the efficient movement of parts and assemblies, improving workflow and reducing downtime. Their ability to operate in tight spaces and around other equipment enhances productivity and safety.
Electronics and Precision Manufacturing:
Tasks: Handling delicate components, assembly processes, and inventory management.
Benefits: The electronics industry requires precise and careful handling of small, delicate components. Underhung bridge cranes provide the necessary accuracy and stability, reducing the risk of damage and improving assembly efficiency.
Fabrication and Metalworking:
Tasks: Moving heavy materials, positioning workpieces, and managing inventory.
Benefits: In metalworking shops, floor space is often occupied by large machinery and raw materials. Underhung bridge cranes free up floor space and enable efficient handling of heavy materials, improving operational efficiency and safety.
Aerospace Industry:
Tasks: Assembly of aircraft components, maintenance, and material handling.
Benefits: The aerospace industry requires precise handling of large and valuable components. Underhung bridge cranes provide the necessary reach and maneuverability in confined spaces, enhancing the efficiency of assembly and maintenance operations.
Pharmaceutical and Chemical Processing:
Tasks: Handling raw materials, equipment maintenance, and storage.
Benefits: In pharmaceutical and chemical plants, cleanliness and space optimization are critical. Underhung bridge cranes help maintain a clutter-free environment by utilizing overhead space, facilitating efficient and safe handling of materials.
Warehousing and Distribution:
Tasks: Loading and unloading goods, inventory management, and order fulfillment.
Benefits: Warehouses with limited floor space benefit from the vertical lifting capability of underhung bridge cranes. These cranes enhance the efficiency of loading and unloading operations and improve inventory management by enabling better access to stored goods.
Textile and Garment Manufacturing:
Tasks: Moving rolls of fabric, positioning materials for cutting and assembly, and managing inventory.
Benefits: The textile industry often involves large rolls of fabric and complex production lines. Underhung bridge cranes facilitate the efficient handling of materials, improving workflow and reducing manual labor.
In summary, underhung bridge cranes excel in limited space workshops across various industries by optimizing floor space, improving maneuverability, and ensuring precise and safe handling of materials. Their versatility and adaptability make them an invaluable tool for enhancing productivity and efficiency in environments with spatial constraints.
Technical Considerations
When implementing underhung bridge cranes in workshops with limited space, it's crucial to consider various technical aspects to ensure safe and efficient operation. These considerations include the structural requirements for ceiling mounting, load capacity and limits, as well as maintenance and operational guidelines.
Structural Requirements for Ceiling Mounting
Ceiling Strength and Integrity:
Load-Bearing Capacity: The ceiling or roof structure must be able to support the weight of the crane, its components, and the maximum anticipated load. This typically requires an engineering assessment to ensure structural integrity.
Reinforcement Needs: In some cases, existing structures may need reinforcement to safely accommodate the crane system. This can involve adding beams or strengthening current supports.
Mounting Infrastructure:
Runway Installation: The runway tracks must be securely mounted to the ceiling structure. This involves precise alignment to ensure smooth and safe crane operation.
Anchoring Points: Proper anchoring points must be established to distribute the load evenly and prevent undue stress on any single point of the ceiling structure.
Building Considerations:
Clearances: Adequate clearance is necessary between the crane components and the ceiling, as well as between the crane and any other overhead obstructions (e.g., ductwork, lighting).
Accessibility: Ensure there is sufficient space for installation and future maintenance activities, including access for personnel and equipment.
Load Capacity and Limits
Rated Load Capacity:
Manufacturer Specifications: Always adhere to the load capacity specified by the crane manufacturer. Exceeding this limit can lead to equipment failure and safety hazards.
Safety Margins: Implement safety margins in your load calculations to account for dynamic loading and potential variations in the weight of materials handled.
Load Distribution:
Even Distribution: Ensure that loads are evenly distributed along the crane's bridge and trolley. Uneven loading can cause undue stress on the crane components and structure.
Center of Gravity: Be mindful of the load's center of gravity, ensuring it is properly aligned with the hoist to prevent tipping or swinging.
Dynamic Loads:
Movement Considerations: Take into account the forces generated by the movement of the crane and load, including acceleration, deceleration, and any potential impact forces.
Load Stability: Use appropriate rigging and securing methods to maintain load stability during transport.
Maintenance and Operational Guidelines
Regular Inspections:
Routine Checks: Perform regular inspections of the crane components, including the runway, bridge, hoist, and control systems. Look for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment.
Preventive Maintenance: Follow a preventive maintenance schedule as recommended by the manufacturer. This includes lubrication, tightening of fasteners, and replacement of worn parts.
Operational Training:
Operator Certification: Ensure that all crane operators are properly trained and certified. Training should cover safe operating procedures, load handling techniques, and emergency protocols.
Safety Procedures: Implement and enforce safety procedures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and adherence to load capacity limits.
Emergency Protocols:
Emergency Stops: Ensure that emergency stop controls are easily accessible and functional. Train operators on how to use them in case of an emergency.
Fault Handling: Establish procedures for handling faults and malfunctions, including immediate shutdown of the crane and notification of maintenance personnel.
Load Handling Practices:
Proper Rigging: Use appropriate rigging methods and equipment for securing loads. Inspect rigging gear regularly for wear and damage.
Controlled Movements: Operate the crane with smooth, controlled movements to minimize dynamic forces and ensure load stability.
Documentation and Record-Keeping:
Maintenance Logs: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, inspections, and repairs. This helps in tracking the crane's condition and scheduling future maintenance.
Operational Records: Keep records of crane usage, including load weights and operating hours. This information can be useful for identifying patterns and planning maintenance.
In conclusion, implementing underhung bridge cranes in limited space workshops requires careful consideration of structural requirements, load capacities, and maintenance practices. Adhering to these technical guidelines ensures safe, efficient, and reliable crane operations, maximizing the benefits of this versatile lifting solution.
Case Studies and Examples
Underhung bridge cranes have been successfully implemented in a variety of industries, demonstrating their versatility and efficiency in real-world scenarios. Below are several case studies and examples highlighting workshops that utilize underhung bridge cranes, showcasing success stories and productivity improvements.
Case Study 1: Automotive Manufacturing Plant
Overview: An automotive manufacturing plant faced challenges with space constraints on its assembly line floor. The plant required a lifting solution that could handle various components efficiently without interfering with other operations.
Implementation: The plant installed several underhung bridge cranes along the assembly line. These cranes were mounted from the ceiling, allowing for unobstructed floor space. The cranes were used to transport engine blocks, transmissions, and other heavy components between workstations.
Results:
- Increased Efficiency: The installation of underhung bridge cranes reduced the time required to move components between workstations, significantly speeding up the assembly process.
- Improved Workflow: The unobstructed floor space allowed for better organization of workstations and tools, improving overall workflow and reducing bottlenecks.
- Enhanced Safety: By minimizing manual lifting and handling of heavy components, the plant saw a reduction in workplace injuries.
Case Study 2: Electronics Manufacturing Facility
Overview: An electronics manufacturing facility needed a solution for handling delicate components and assemblies in a confined space with low ceilings. The facility required precise and controlled lifting to prevent damage to sensitive equipment.
Implementation: The facility installed underhung bridge cranes with advanced control systems for precise positioning. The cranes were used to handle and transport circuit boards, semiconductor equipment, and other sensitive components.
Results:
- Precision Handling: The cranes provided precise and stable movement of delicate components, reducing the risk of damage and improving product quality.
- Space Optimization: The ceiling-mounted design freed up valuable floor space, allowing for more efficient layout of assembly lines and storage areas.
- Productivity Gains: The facility experienced increased productivity due to the streamlined handling process and reduced need for manual intervention.
Case Study 3: Metal Fabrication Workshop
Overview: A metal fabrication workshop required a flexible lifting solution to handle heavy raw materials and finished products in a space-constrained environment. The workshop needed to maximize the use of available space while ensuring safe and efficient operations.
Implementation: The workshop installed underhung bridge cranes capable of handling heavy loads. The cranes were used to transport metal sheets, beams, and finished products to various workstations and storage areas.
Results:
- Enhanced Load Handling: The cranes facilitated the efficient movement of heavy materials, reducing manual labor and improving workflow.
- Safety Improvements: The reduction in manual handling of heavy materials led to a decrease in workplace injuries and enhanced overall safety.
- Operational Flexibility: The ability to move materials efficiently in a confined space allowed the workshop to take on more projects and increase production capacity.
Case Study 4: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Plant
Overview: A pharmaceutical manufacturing plant required a clean and organized environment for handling raw materials and finished products. The plant needed a lifting solution that could operate in a space with stringent cleanliness requirements.
Implementation: The plant installed underhung bridge cranes with stainless steel components to meet cleanliness standards. The cranes were used to handle raw materials, transport them to processing areas, and move finished products to packaging lines.
Results:
- Clean Environment: The use of stainless steel cranes helped maintain a clean and contamination-free environment, essential for pharmaceutical production.
- Efficient Material Handling: The cranes optimized material handling processes, reducing the time and effort required to move materials within the plant.
- Increased Productivity: The streamlined handling process allowed the plant to increase production rates and meet higher demand.
Case Study 5: Aerospace Manufacturing Facility
Overview: An aerospace manufacturing facility required a precise and reliable lifting solution to handle large and valuable components such as aircraft parts. The facility needed a system that could operate efficiently in a space with complex layouts and tight clearances.
Implementation: The facility installed underhung bridge cranes with advanced control systems for precise and safe lifting. The cranes were used to transport large aircraft components, such as wings and fuselage sections, between different workstations.
Results:
- Precision and Reliability: The advanced control systems provided precise movement and positioning of large components, ensuring safe handling and reducing the risk of damage.
- Operational Efficiency: The cranes improved the efficiency of material handling processes, allowing for faster assembly and production times.
- Enhanced Safety: The reduction in manual handling of large components minimized the risk of workplace accidents and injuries.
Success Stories and Productivity Improvements
- Increased Production Rates: Many workshops that implemented underhung bridge cranes reported significant increases in production rates due to the streamlined handling processes and reduced downtime.
- Cost Savings: The optimized use of space and improved workflow led to cost savings in terms of reduced labor costs and increased operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Employee Morale: The reduction in manual labor and improved safety conditions contributed to higher employee morale and job satisfaction.
- Scalability: The flexibility and adaptability of underhung bridge cranes allowed workshops to scale their operations and take on more projects without the need for extensive modifications.
In conclusion, the implementation of underhung bridge cranes in various industries has led to significant productivity improvements, enhanced safety, and optimized use of space. These real-world examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of underhung bridge cranes in addressing the challenges of limited space workshops
Conclusion
Underhung bridge cranes offer a versatile and efficient solution for workshops with limited space. Key benefits include:
Design Features:
- Ceiling-Mounted Design: Maximizes floor space and enhances mobility.
- Reach and Accessibility: Efficiently handles loads near walls and tight spaces.
- Comparison with Floor-Mounted Cranes: Highlights advantages in space utilization and installation ease.
Benefits of Efficient Load Handling Near Walls:
- Optimized Workshop Space: Maximizes usable area and allows for flexible layouts.
- Improved Maneuverability: Enhances accessibility and workflow.
- Enhanced Safety: Minimizes manual lifting and improves load stability.
Technical Considerations:
- Structural Requirements: Ensures ceiling strength and proper mounting.
- Load Capacity and Limits: Adheres to specifications and considers dynamic loads.
- Maintenance and Operational Guidelines: Emphasizes regular inspections and operator training.
In conclusion, underhung bridge cranes are essential for optimizing space, enhancing productivity, and ensuring safety in various industrial settings. Their future potential is vast, with technological advancements promising even greater efficiency and effectiveness.
Related Products

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch