Overhead Rail Cranes | Overhead Cranes & Bridge Cranes on Rails
Single Girder & Double Girder Overhead Rail cranes for sale. Custom overhead cranes on rail & track for sale, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3 ton, 5 ton, 10 ton, 15 ton 20 ton up to 80 ton.
Category: Crane on Rail
Your Trusted Overhead Rail Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Overhead Rail Cranes,Overhead Cranes & Bridge Cranes on Rails
Custom Overhead Cranes on Rail & Track for Sale 1 Ton to 80 Ton Good Price
Single Girder & Double Girder Overhead Rail cranes for sale. Custom overhead cranes on rail & track for sale, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3 ton, 5 ton, 10 ton, 15 ton 20 ton up to 80 ton.
A Comprehensive Handbook for Leveraging Cranes on Rails in Diverse Industries
In the dynamic landscape of industrial operations, the utilization of cranes on rails stands as a testament to efficiency, precision, and adaptability. This comprehensive handbook aims to delve deep into the realm of these rail-based crane systems, shedding light on their significance, diverse types, practical applications, and much more.
At the heart of industrial evolution lie the innovative systems of cranes meticulously designed to glide along rail tracks. These cranes, known as cranes on rails, operate on specifically laid tracks or rails, offering enhanced mobility, stability, and maneuverability within industrial settings. Whether it's the seamless movement of overhead cranes, the adaptability of gantry cranes, or the precision of jib cranes, these systems owe their operational prowess to the rail tracks that guide their path.
Industrial Significance:
Rail-based cranes are the backbone of numerous industrial operations worldwide. Their significance lies in their ability to facilitate efficient material handling, streamline production processes, and optimize logistical workflows. These cranes play an integral role across a myriad of industries, ranging from manufacturing and construction to warehousing and heavy industries. Their adaptability and precision make them indispensable in achieving operational excellence and meeting diverse industrial needs.
Rail-based crane systems have revolutionized the way industries approach material handling, elevating efficiency, and productivity to new heights. In the forthcoming sections of this handbook, we will delve deeper into the various types of cranes operating on rails, exploring their features, benefits, applications across industries, user concerns, and more.

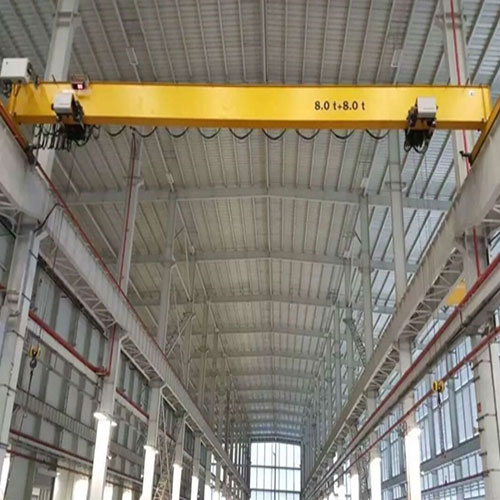
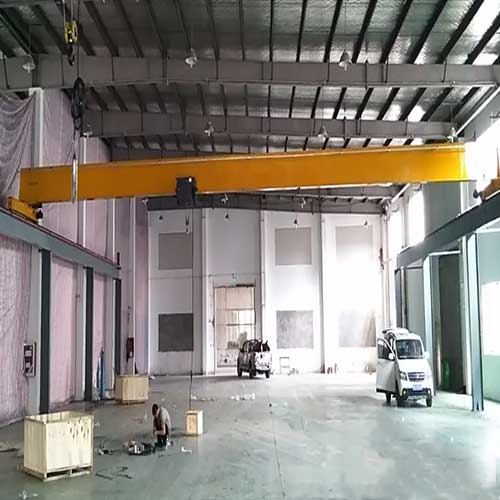
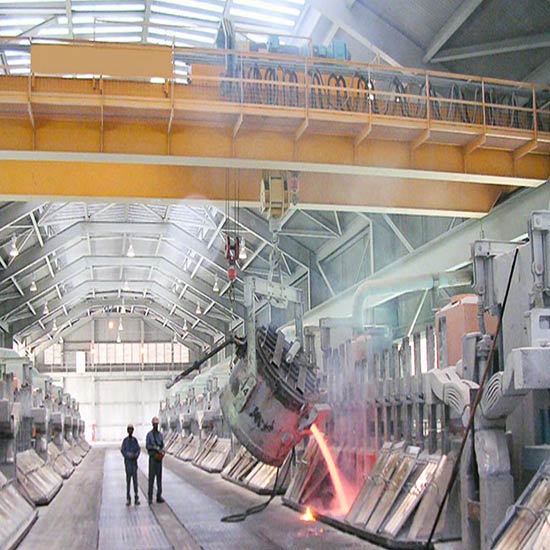
Bridge Crane on Rails(or Overhead Traveling Crane):
Rail System: Bridge cranes typically run on elevated tracks or rails attached to the ceiling structure of the building. These tracks facilitate the horizontal movement of the crane along the length of the workspace.

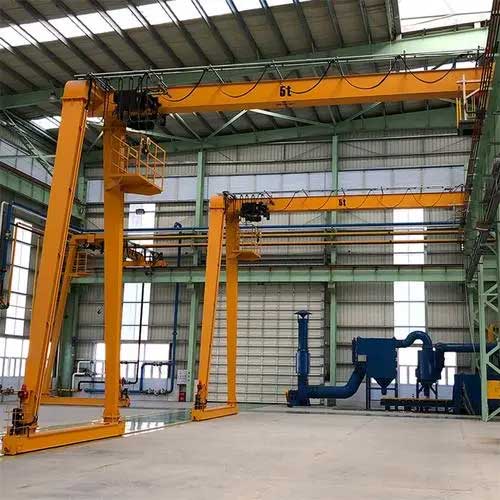
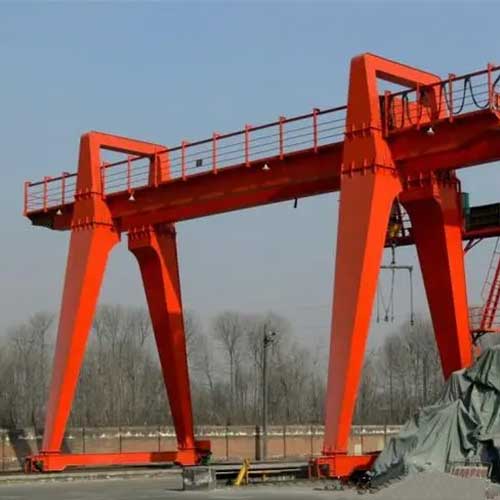
Gantry Crane on Rail(Gantry or Portal Bridge Crane):
Rail System: Gantry cranes utilize rails placed on the ground or floor level to guide their movement. They are similar to bridge cranes but are supported by freestanding legs or columns, allowing them to move materials both indoors and outdoors.

Jib Crane on Rail(Wall Travelling Jib Cranes ):
Rail System: Jib cranes can be wall-mounted or freestanding and are often used for localized lifting tasks. Wall-mounted jib cranes move along rails attached to the wall, whereas freestanding jib cranes may have their rail systems installed on the floor or foundation.
Mastering Overhead Rail Cranes: A Complete Handbook
Overhead rail cranes stand as pivotal elements within industrial settings, facilitating efficient material handling and seamless operations. They are robust, elevated systems equipped with a track and a lifting mechanism designed to transport heavy loads horizontally along a defined path within a facility.
The versatility of overhead rail cranes transcends industries, finding indispensable applications in manufacturing, warehousing, construction, and more. In manufacturing plants, they aid in assembling heavy machinery, while in warehouses, they streamline the movement of goods. Their adaptability extends to supporting construction projects by handling massive loads in confined spaces.
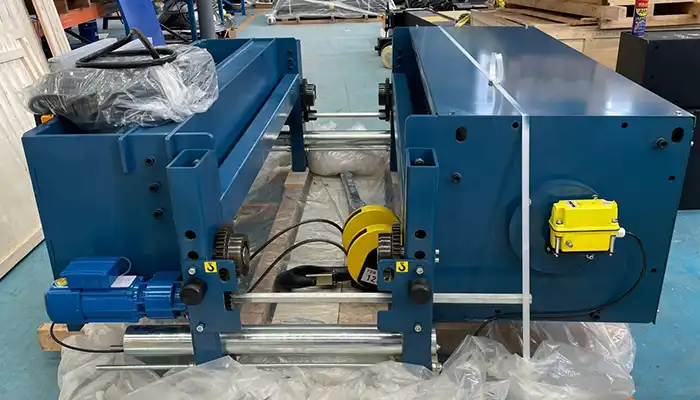
Key components, including the rails, power tracks, and lifting mechanisms, work in tandem to ensure seamless functionality. The overhead crane track system provides the guiding path for the crane's movement. Power tracks supply the necessary electricity for the crane's operations. The lifting mechanism, often a hoist or winch, attaches to the load and facilitates movement along the track.
Your Trusted Overhead Rail Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Types of Overhead Crane on Rails
Overhead cranes on rails come in various configurations based on their mounting structures and rail placements. Here are the types of overhead cranes based on their rail configurations:

Overhead Crane on Wall Mounted Rails:
This type of overhead crane is installed on rails attached to the walls of the building or structure. Wall-mounted rails provide support and guidance for the crane's movement along the predetermined path, making efficient use of available space while ensuring effective material handling.

Overhead Crane on Ceiling Mounted Rails:
Overhead cranes on ceiling-mounted rails are fixed to the ceiling structure using mounting systems. These cranes move along tracks installed on the ceiling, allowing maximum floor space utilization for material handling operations in industries such as manufacturing, warehouses, and workshops.

Overhead Crane on Freestanding Column Rails:
Overhead cranes on freestanding column rails use columns or support structures erected independently from the building structure. These columns support the rails on which the crane travels, providing flexibility in installation locations and offering efficient material handling solutions within the workspace.
Each type of overhead crane on rails offers unique advantages concerning space utilization, maneuverability, and load handling capacities. The selection of the appropriate overhead crane type often depends on the layout of the facility, the specific requirements of the application, and the available structural support.
Overhead cranes are essential industrial tools used for lifting and transporting heavy loads within various settings. Here's an overview of different types of overhead cranes along with their rail systems mounted on wall, ceiling, and freestanding column rails:
Features and Advantages of Overhead Cranes on Rails
Overhead cranes, equipped with their distinctive features, stand as stalwarts of efficiency and precision within industrial settings.
High Lifting Capacity: One of the primary features of overhead cranes is their ability to handle heavy loads efficiently. With varying lifting capacities, these cranes are designed to hoist and transport substantial weights, facilitating seamless material handling.
- Versatile Configurations: Overhead cranes offer versatile configurations such as single girder or double girder designs, providing flexibility in accommodating different operational requirements.
- Precise Movement Control: Equipped with precise control mechanisms, these cranes ensure accurate load positioning and movement, minimizing handling errors and enhancing operational precision.
- Space Optimization: By operating on elevated tracks or rails, overhead cranes optimize floor space, allowing unobstructed movement of goods within the workspace.
Advantages in Industrial Settings:
- Enhanced Productivity: The efficiency and lifting capabilities of overhead cranes expedite material handling processes, boosting overall productivity.
- Safety and Ergonomics: These cranes offer a safer working environment by reducing manual handling, minimizing the risk of accidents, and enhancing ergonomics for operators.
- Cost-Efficiency: Through streamlined operations and optimized material movement, overhead cranes contribute to cost-efficiency by reducing labor hours and material damage.
Varied Applications:
The versatility of overhead cranes translates into diverse applications across various industries, each leveraging their unique functionalities.
- Manufacturing: Overhead cranes play a pivotal role in manufacturing units, facilitating the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products across assembly lines. Overhead cranes are instrumental in manufacturing units for lifting heavy machinery parts, raw materials, or finished products along assembly lines. They aid in the precise movement of materials, contributing to efficient production processes and reducing manual labor.
- Warehousing and Logistics: In warehousing facilities, these cranes aid in the efficient stacking, retrieval, and movement of goods, optimizing storage space and order fulfillment processes. Warehousing and Logistics: In warehouses, overhead cranes assist in stacking and retrieving goods from shelves or storage areas, optimizing space and facilitating efficient inventory management. These cranes streamline material handling operations, expediting order fulfillment processes in logistics centers.
- Heavy Industries: Industries dealing with large-scale materials like steel, automotive, and construction benefit from overhead cranes' robustness and lifting capacities for handling heavy loads.
Comparisons of Single Girder vs Double Girder Overhead Rails Cranes
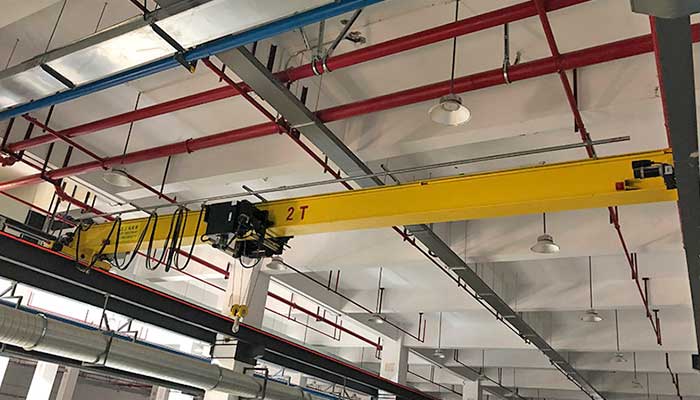

Single Girder Overhead Rail Cranes:
Optimal for Lighter Loads and Cost Efficiency
Single girder overhead rail cranes feature a single bridge beam, making them lighter and more cost-effective compared to other models. They are suitable for facilities handling lighter loads with spans covering moderate distances. Their design allows for easier installation and maintenance, making them a popular choice for various industrial applications where precision handling and moderate lifting requirements are prevalent.
Features:
- Lightweight Construction: Single girder cranes feature a single bridge beam, making them lighter and easier to install.
- Cost-Effective: Due to their simpler design, they are more cost-efficient compared to other types.
- Moderate Load Capacity: Suitable for handling lighter loads within moderate spans.
Benefits:
- Versatility: Ideal for various industries with moderate lifting requirements.
- Easy Maintenance: Simplified design leads to easier maintenance and repair procedures.
- Space Efficiency: Their compact design makes them suitable for facilities with space constraints.
Applications:
- Manufacturing: Used for assembly lines with moderate loads.
- Warehousing: Handling goods in storage facilities.
- Workshops: Suitable for machine shops or maintenance areas.
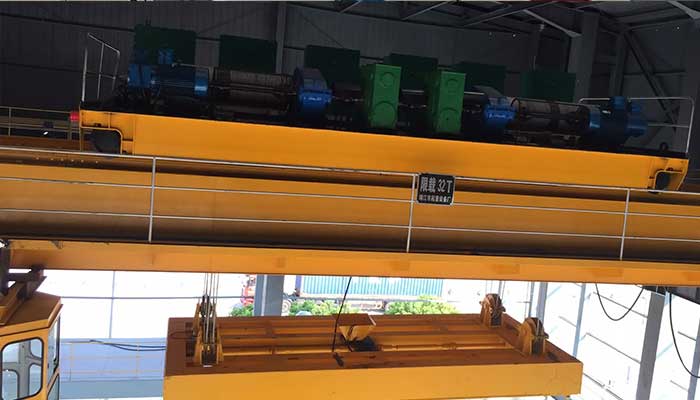

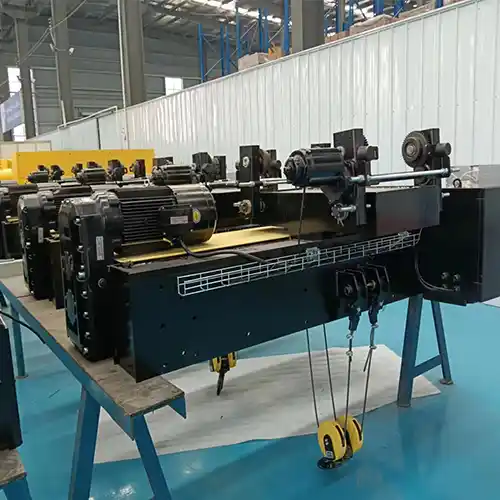
Double Girder Overhead Rail Cranes:
Ideal for Heavier Loads and Extended Spans
Contrarily, double girder overhead rail cranes boast two bridge beams, offering higher load-bearing capacities and increased stability. Designed to handle heavier loads and extended spans, these cranes are prevalent in industries requiring robust lifting solutions. They offer superior height and hook approaches, making them ideal for handling larger machinery or materials across substantial distances.
Features:
- Enhanced Load Capacity: Can handle heavier loads compared to single girder cranes.
- Increased Stability: Two bridge beams offer improved stability and rigidity.
- Height and Hook Approach: Superior height and hook approaches allow for handling larger equipment or materials.
Benefits:
- Heavy Load Handling: Ideal for heavy-duty lifting operations.
- Extended Spans: Suitable for covering larger areas within a facility.
- Versatility in Application: Adaptable to diverse industrial requirements.
Applications:
- Steel Industry: Handling heavy steel components.
- Shipbuilding: Lifting large ship parts during construction.
- Heavy Machinery Manufacturing: Moving substantial machinery components.
Your Trusted Overhead Rail Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Gantry Cranes on Rails
Gantry cranes come in various types based on their structural design and rail configuration, each serving specific industrial purposes. Here's an overview of the different types of gantry cranes on rails:

Single Girder Gantry Crane on Rails: Single girder gantry cranes have one main horizontal beam (girder) for hoist movement. They are suitable for lighter to moderate lifting capacities and are commonly used in workshops, warehouses, and small manufacturing units.

Double Girder Gantry Crane on Rails: Double girder gantry cranes feature two parallel horizontal beams (girders) providing increased stability and higher lifting capacities compared to single girder cranes. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications in industries like shipyards, steel mills, and ports.

A-Frame Gantry Crane on Rails: A-frame gantry cranes have a distinctive A-shaped structure, providing stability and support to the crane's horizontal beam (girder). These cranes run on rails and are suitable for various material handling tasks in industries like construction, warehouses, and manufacturing.

Truss Girder Gantry Crane on Rails: Truss girder gantry cranes use a truss-type structure for their horizontal beams, providing strength and rigidity while minimizing weight. These cranes are beneficial for handling materials in outdoor settings like construction sites.

Gantry Crane on Wall Rails: Gantry cranes mounted on wall rails are designed to run along fixed tracks or rails installed on walls. They are suitable for specific applications where floor space is limited or where overhead clearance is essential.

Gantry Crane on Floor Rails: Gantry cranes on floor rails run on tracks or rails installed on the floor surface. They are versatile and widely used in various industries for their ability to efficiently handle materials within the workspace.
Each type of gantry crane on rails offers specific advantages and is tailored to meet different industrial requirements based on load capacities, maneuverability, space constraints, and operational needs. The selection of the appropriate gantry crane type depends on the specific application and operational environment.
Features and Benefits of Gantry Cranes on Rails
Gantry cranes, with their distinctive features, are renowned for their versatility and efficiency in industrial environments.
- Robust Structural Design: Gantry cranes boast a sturdy and durable structure, comprising either single or double legs, providing stability and support for heavy lifting operations.
- Mobility and Flexibility: These cranes operate on tracks or wheels, facilitating their movement across expansive workspaces, allowing for precise positioning of loads.
- High Lifting Capacity: Gantry cranes offer substantial lifting capabilities, enabling the handling of massive loads with ease and precision.
- Customizable Configurations: With customizable spans and capacities, gantry cranes can be tailored to suit specific operational requirements, ensuring versatility in various industrial settings.
Advantages in Industrial Environments:
- Adaptability: Gantry cranes excel in diverse industrial environments, adapting seamlessly to tasks requiring heavy lifting and precise material handling.
- Efficiency and Speed: Their ability to swiftly transport and position heavy loads enhances operational efficiency, reducing downtime and optimizing workflow.
- Space Utilization: Gantry cranes optimize floor space, providing efficient material movement and freeing up ground-level areas for other operations.
Industrial Applications:
Gantry cranes find applications across a spectrum of industries, each benefiting from their versatility and robust capabilities.
- Construction Sites: Gantry cranes are instrumental in construction projects, lifting heavy materials like steel beams, precast concrete, and construction components. Gantry cranes are a common sight at construction sites, lifting and moving heavy construction materials such as steel beams, concrete panels, and machinery. These cranes contribute to timely project completion by facilitating the efficient movement of materials.
- Shipping and Ports: These cranes are pivotal in port operations, efficiently handling cargo containers for loading and unloading from ships. Gantry cranes play a crucial role in port operations, loading and unloading cargo containers from ships with precision and speed. Their ability to handle heavy containers enhances port efficiency and throughput.
- Manufacturing Facilities: In heavy industries like steel manufacturing or automotive plants, gantry cranes aid in handling large components or equipment, streamlining production processes and ensuring safe material handling. In manufacturing units, gantry cranes aid in the movement of large machinery, raw materials, and finished products along assembly lines.
Your Trusted Overhead Rail Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Jib Cranes on Rails
Jib Cranes on Rails -Wall Rail Travelling Jib Cranes : Exploring Characteristics and Functionality
Jib Cranes on rails stand out as versatile and highly maneuverable industrial tools known for their specialized functionalities and adaptability in various work environments. When integrated with rail systems, these cranes exhibit unique characteristics that enhance their utility across different industries.

Cantilever wall travelling jib crane on rails

Electric wall travelling jib cranes on rails

Wall mounted rail travelling jib cranes
Characteristics of Jib Cranes on Rails:
- Versatility in Movement: Jib Cranes, operating on rails, showcase remarkable flexibility in movement along designated tracks. Their pivotal feature lies in the rotational ability of the jib arm, which, when coupled with the rail system, allows for a wide range of motion, enabling precise and targeted material handling.
- Optimal Space Utilization: These cranes are adept at maximizing workspace efficiency. By operating along rails, jib cranes optimize floor space utilization, offering enhanced maneuverability within confined areas where traditional cranes might face spatial constraints.
- Diverse Configurations: Rail-mounted jib cranes come in various configurations, including wall-mounted and floor-mounted variants, each catering to specific operational requirements. The adaptability of these cranes allows for customized installations to suit distinct industrial setups.
Functionality of Jib Cranes on Rails:
- Precise Material Handling: Jib Cranes, with their rail-mounted design, enable precise and controlled movement, ideal for intricate material handling tasks. This precision is particularly beneficial in assembly lines, workshops, and other settings requiring accurate load positioning.
- Increased Reach and Accessibility: The rail-mounted feature extends the reach of jib cranes, allowing them to cover larger areas and access otherwise hard-to-reach locations within the workspace. This accessibility enhances their utility in diverse operational scenarios.
- Enhanced Safety Measures: Rail-mounted jib cranes offer enhanced safety features through controlled movements and specialized rail systems. The rail infrastructure ensures stability, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing overall workplace safety.
Typical Applications:
Jib cranes find common use in specific working environments where their specialized features cater to precise material handling needs.
Common Uses in Specific Environments:
- Assembly Lines: Jib cranes prove invaluable in assembly processes, aiding in the lifting and positioning of components or equipment during manufacturing operations. Jib cranes find their niche in assembly line operations by assisting in lifting and positioning components during manufacturing processes. Their ability to precisely place materials enhances assembly line efficiency.
- Maintenance and Repair:In maintenance workshops or garages, jib cranes support mechanics by lifting heavy machinery or vehicle parts for servicing, repair, or installation tasks. These cranes streamline maintenance operations and ensure safer handling of heavy equipment. These cranes excel in maintenance tasks, allowing mechanics to hoist heavy machinery or components for servicing or repair work.
- Workshops and Warehouses: Jib cranes facilitate efficient material handling in workshops and warehouses, enabling swift and precise movement of goods within limited spaces.
Your Trusted Overhead Rail Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Specialized Types of Overhead Rail Cranes for Varied Environments
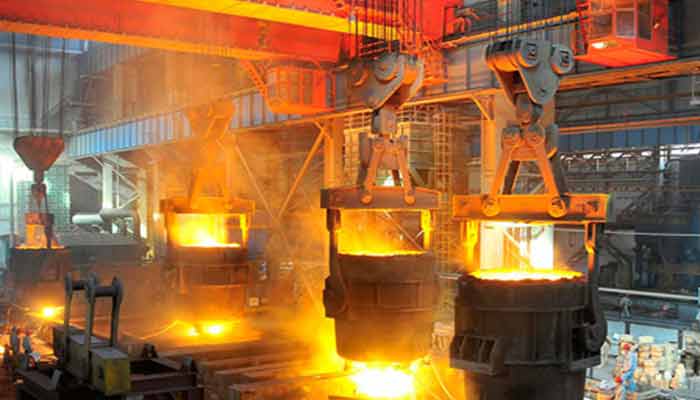

Overhead Rail Cranes for Harsh Environments (e.g., Corrosion-Resistant)
Features:
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials: Constructed using materials such as stainless steel or corrosion-resistant coatings.
- Sealed Components: Sealed motors, wiring, and other sensitive parts to protect against harsh elements.
- Robust Structure: Designed to withstand exposure to corrosive chemicals or harsh weather conditions.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Durability: Resistant to corrosion, extending the crane's lifespan.
- Maintains Performance: Operational efficiency despite challenging environmental factors.
- Safety Assurance: Reduced risk of mechanical failures due to environmental stressors.
Applications:
- Chemical Plants: Handling materials in corrosive environments like chemical processing plants.
- Offshore Operations: Lifting equipment in marine environments prone to saltwater exposure.
- Mining Industry: Dealing with corrosive materials in mining and mineral processing.
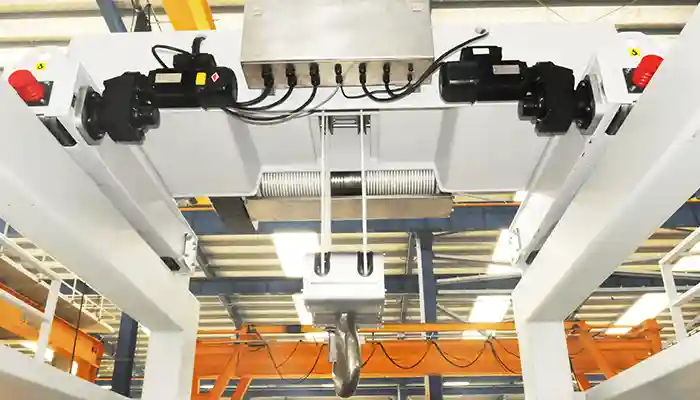
Overhead Rail Cranes for Clean Environments (e.g., Sterile Conditions)
Features:
- Enclosed Design: Fully enclosed to prevent dust, debris, or contaminants from entering.
- Stainless Steel Construction: Often made with stainless steel for cleanliness and resistance to corrosion.
- High-Grade Seals: Sealed mechanisms to prevent the entry of particles into the crane's components.
Benefits:
- Maintains Sterility: Prevents contamination in cleanroom environments.
- Compliance with Regulations: Meets stringent cleanliness standards.
- Longevity: Resistant to rust or degradation from cleaning agents used in clean environments.
Applications:
- Pharmaceutical Facilities: Handling sensitive materials in sterile environments.
- Biotech Laboratories: Lifting delicate equipment in controlled cleanrooms.
- Food Processing Plants: Operating in areas requiring high cleanliness standards.

Overhead Rail Cranes for Hazardous Environments (e.g., Explosion-Proof)
Features:
- Explosion-Proof Components: Motors, electrical systems, and wiring designed to prevent sparks.
- Enclosed Controls: Intrinsically safe control systems to avoid electrical hazards.
- Specialized Protection: Sealed and reinforced components to prevent ignition sources.
Benefits:
- Mitigates Risks: Reduces the risk of igniting flammable materials or gases in hazardous areas.
- Compliance: Meets safety standards for operating in explosive or volatile atmospheres.
- Safety Assurance: Provides a safe lifting solution in high-risk environments.
Applications:
- Chemical Processing: Operating in areas with potentially explosive gases or vapors.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Lifting equipment in environments with flammable substances.
- Refineries: Handling materials in areas with combustible atmospheres.
These specialized types of overhead rail cranes cater to specific environmental demands, ensuring safe and efficient material handling in challenging conditions while complying with industry standards and regulations.
Addressing Environmental and Operational Concerns
Adaptability to Harsh Environments:
Examining Crane Performance in Extreme Conditions:
- Extreme Temperature Handling: - Discussing how cranes on rails adapt to extreme temperatures, ensuring operational efficiency in both high and low-temperature environments.
- Resilience in Harsh Conditions: - Highlighting the resilience of crane systems against corrosive atmospheres, high humidity, or environments with high dust or debris levels.
Ensuring Operational Efficiency and Safety:
Prioritizing Safety Measures and Optimizing Efficiency in Operations:
- Safety Protocols and Training: - Emphasizing the importance of comprehensive safety protocols, operator training, and regular equipment inspections to ensure safe crane operations.
- Efficiency Optimization: - Detailing strategies to optimize crane operations for enhanced efficiency, such as workload management, streamlined workflows, and technological integrations.
- Safeguarding Operations: Addressing environmental challenges and operational concerns ensures the resilience and safety of crane operations. Emphasizing adaptability to harsh environments and prioritizing safety measures contributes to the efficiency and reliability of crane systems across varying working conditions.
Overhead Rail Cranes Categorized by Load Capacity

Light Duty Overhead Rail Cranes: Optimal for Small-Scale Material Handling
Characteristics:
- Lower Load Capacity: Designed for handling lighter loads within specific weight limits.
- Simplified Construction: Lighter components to accommodate smaller loads.
- Basic Lifting Mechanisms: Hoists or winches suitable for light material handling tasks.
Benefits:
- Cost-Effective: Lower initial investment due to simplified construction.
- Flexible Use: Suitable for small-scale operations in various industries.
- Space Efficiency: Ideal for facilities with limited space or confined areas.
Applications:
- Small Workshops: Handling tools and components in small-scale production.
- Retail Warehouses: Managing lightweight inventory items.
- Assembly Lines: Moving smaller parts during manufacturing processes.

Medium Duty Overhead Rail Cranes: Balancing Versatility and Load Capacity
Characteristics:
- Moderate Load Capacity: Capable of handling heavier loads compared to light-duty cranes.
- Sturdier Components: Stronger materials and mechanisms for increased load-bearing capacity.
- Enhanced Lifting Mechanisms: Hoists or winches with more power and durability.
Benefits:
- Versatility: Balances between load capacity and flexibility in various operations.
- Adaptability: Suitable for multiple industries requiring moderate lifting capabilities.
- Efficient Material Handling: Optimized for handling medium-sized loads efficiently.
Applications:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Moving car parts during assembly processes.
- Warehousing: Managing moderate-weight goods in storage facilities.
- Construction Sites: Lifting materials for medium-scale construction projects.

Heavy Duty Overhead Rail Cranes: Designed for Maximum Load Capacities
Characteristics:
- High Load Capacity: Engineered for handling the heaviest loads among overhead cranes.
- Robust Construction: Heavy-duty materials and reinforced structures.
- Powerful Lifting Mechanisms: High-powered hoists or winches for substantial loads.
Benefits:
- Maximum Load Handling: Suited for industries requiring heavy load lifting capabilities.
- Reliability: Designed for consistent and reliable performance under extreme loads.
- Durability: Sturdy construction for prolonged use in demanding environments.
Applications:
- Steel Mills: Handling heavy steel components and materials.
- Shipbuilding Yards: Lifting large ship sections during construction.
- Mining Operations: Moving massive loads in mining and extraction processes.
These categorized overhead rail cranes cater to a spectrum of load capacities, ensuring efficient and safe material handling across various industries with specific load requirements.
The most frequently used overhead rail crane capacities can vary significantly based on the specific industries, applications, and operational needs. However, some common load capacities are more frequently utilized due to their prevalence in various industrial settings:
- 5-10 Tons: Cranes with a capacity ranging from 5 to 10 tons are quite common in many manufacturing, assembly, and smaller-scale industrial settings. They cater to a wide range of applications, handling moderate loads efficiently.
- 10-20 Tons: Overhead rail cranes with capacities between 10 to 20 tons are also popular choices, especially in larger manufacturing plants, warehouses, and construction sites. They offer versatility and are suitable for handling heavier loads without being excessively large or expensive.
- 20-50 Tons: Cranes within this range are commonly used in heavier industrial applications such as steel mills, heavy machinery manufacturing, and larger-scale construction projects. They have the capability to handle substantial loads without being overly specialize
- 50+ Tons: For heavy-duty industries like shipbuilding, aerospace, large-scale infrastructure projects, and some specialized manufacturing processes, cranes with capacities exceeding 50 tons are employe These cranes are designed for handling extremely heavy loads and typically require substantial space and structural support.
The choice of overhead rail crane capacity primarily depends on the specific operational requirements, including the weight and size of materials or equipment being handled, the frequency of lifting, available space, and the nature of the industry.
It's essential to conduct a thorough assessment of the intended use and load requirements before selecting an overhead rail crane to ensure optimal performance and safety. Many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor crane capacities to specific operational needs.
Overhead Rail Cranes Based on Power Systems

Overhead Cranes with Cabled Power Supply
Features:
- Cabled Power Delivery: Utilizes cables or festoon systems for power supply.
- Constant Power Source: Continuous and direct electrical connection.
- Flexible Cable Arrangement: Cables suspended from the crane's structure for movement.
Benefits:
- Reliable Power: Consistent and uninterrupted power supply during operations.
- Ease of Maintenance: Accessible cables for inspection and maintenance.
- Suitability for Heavy Loads: Suitable for cranes handling substantial loads requiring consistent power.
Applications:
- Heavy Manufacturing Plants: Moving heavy machinery parts during production.
- Steel and Metal Industries: Handling large and heavy metal components.
- Automotive Assembly Lines: Transporting car body frames and large components.

Overhead Cranes with Conductor Bar Power Supply
Features:
- Conductor Bar System: Utilizes an electrified conductor bar for power supply.
- Segregated Power Segments: Sections of the conductor bar can be isolated for maintenance.
- Contact-Based Power Transfer: Crane's collectors make contact with the conductor bar for power.
Benefits:
- Flexibility and Safety: Allows for selective power isolation for maintenance.
- Reduced Maintenance Downtime: Segmented design facilitates targeted repairs.
- Adaptability: Suitable for various load capacities and applications.
Applications:
- Warehousing Operations: Handling goods in storage facilities.
- Assembly Lines: Transporting moderate-sized parts during assembly processes.
- General Material Handling: Handling loads in diverse industrial environments.

Overhead Cranes with Manual Power Supply
Features:
- Human-Powered Operation: Utilizes manual labor for crane movement and load handling.
- No Electrical Power Required: Operates without electricity or batteries.
- Hand Chain or Lever Mechanism: Manual cranes use chains or levers for lifting and movement.
Benefits:
- Cost-Effective Solution: Minimal initial investment and reduced operational costs.
- Simplicity in Design: Less complexity in operation and maintenance.
- Suitability for Light Loads: Ideal for handling lighter loads or occasional use.
Applications:
- Small Workshops: Handling light materials or equipment.
- Garages and Maintenance Shops: Lifting components during repairs.
- Low-Traffic Warehouses: Moving occasional or lightweight inventory.
Comparison with Other Power Systems:
- Versus Cabled or Conductor Bar Systems: Manual cranes do not rely on electrical power, making them suitable for environments without electricity or where power systems are impractical.
- Versus Battery-Powered Systems: Manual cranes do not require batteries or charging infrastructure, offering a simpler solution for light-duty operations but with limited mobility.
- Versus Conductor Bar Systems: While conductor bar systems are often used for moderate loads, manual cranes are suitable for even lighter loads and environments where electricity is not accessible or desirable.
Manual power supply overhead cranes offer a basic and economical solution for handling light loads in settings where electricity or battery-powered systems may not be practical or cost-effective. Their simplicity in design and operation makes them suitable for specific applications where the use of manual labor is viable and efficient.
Diverse Types of Overhead Rail Cranes Based on Rail Systems

- Configuration: Rails attached to the walls of a building or structure.
- Usage: These rails guide the movement of overhead cranes, allowing them to traverse along a specific path parallel to the wall.

- Configuration: Rails fixed to the ceiling structure of the facility.
- Usage: Overhead cranes move along these rails, utilizing the space above the working area and ensuring efficient material handling without occupying floor space.

Floor Mounted Freestanding Column Rails:
- Configuration: Rails supported by independent columns or support structures.
- Usage: These rails provide support and guidance for overhead cranes, offering flexibility in installation locations and enabling efficient material handling within the workspace.
Overhead Rail Cranes Based on Crane Rails and Crane Tracks
Based on crane rail tracks, the main types of overhead rail cranes can be categorized into several configurations, each designed for specific operational requirements and load capacities:

Single Girder Crane with Under-Running Rail Track:
- Description: Utilizes a single girder that runs beneath the crane between parallel rails fixed to the ceiling or support structure.
- Features: Economical, ideal for light to moderate loads, suitable for facilities with limited headroom.
- Typical Capacity: Ranges from 1 ton to 20 tons.
- Applications: Ideal for light to moderate loads in settings such as small workshops, maintenance areas, or assembly lines where headroom is limite

Single Girder Crane with Top-Running Rail Track:
- Description: Features a single girder supported by wheels that run on rails attached to the overhead structure.
- Features: Versatile, suitable for moderate loads, offers increased hook height and effective use of available space.
- Typical Capacity: Typically handles loads between 1 ton to 15 tons.
- Applications: Versatile for moderate loads in manufacturing, warehouses, or production facilities requiring increased hook height and efficient utilization of available space.

Double Girder Crane with Under-Running Rail Track:
- Description: Employs two girders running beneath the crane on parallel rails fixed to the support structure.
- Features: Offers higher load capacities compared to single girder cranes, increased stability, suitable for heavier loads and longer spans.
- Typical Capacity: Offers higher load capacities, commonly ranging from 5 tons to 250 tons.
- Applications: Suited for heavier loads and longer spans in industries like steel manufacturing, heavy machinery, or large-scale construction projects.

Double Girder Beam Crane with Top-Running Rail Track:
- Description: Features two girders supported by wheels running on rails attached to the overhead structure.
- Features: High load capacities, increased hook height, suitable for heavy-duty operations, and larger spans.
- Typical Capacity: Capable of handling loads from 5 tons up to 600 tons.
- Applications: Designed for heavy-duty operations requiring high load capacities and larger spans, often found in shipbuilding, aerospace, or industries handling massive equipment or structures.

Box Girder Crane with Custom Rail Tracks:
- Description: Utilizes a specialized box-shaped girder design with customized rail tracks that provide enhanced rigidity and stability.
- Features: Precision handling, reduced deflection, suitable for applications requiring high accuracy and delicate material handling.
- Typical Capacity: Varies widely based on customization, usually from 1 ton to 150 tons.
- Applications: Specifically tailored for applications requiring high precision, reduced deflection, and delicate material handling, often seen in specialized manufacturing, precision engineering, or industries with stringent accuracy requirements.

Specialized Configurations for Unique Applications:
- Description: Customized overhead rail crane configurations tailored for specific industries or unique operational needs.
- Features: Adapted designs, specialized rail tracks, and functionalities catering to niche industries like aerospace, automotive, or manufacturing processes requiring specific handling capabilities.
- Typical Capacity: Customized based on industry-specific requirements.
- Applications: Tailored for niche industries like aerospace, automotive, or manufacturing processes needing unique handling capabilities. These configurations cater to specialized requirements such as handling aerospace components, automotive assembly lines, or intricate manufacturing processes.
Each type of overhead rail crane based on crane rail tracks offers distinct advantages in terms of load capacities, stability, precision, and adaptability to various operational environments. The choice of crane configuration often depends on factors such as load requirements, available space, operational efficiency, and specific industry demands.
Understanding the nuances of various overhead cranes and their rail systems mounted on different structures helps in selecting the most suitable type of crane for specific industrial applications. The choice of overhead crane and its rail system configuration often depends on factors such as space availability, lifting capacities, operational requirements, and structural considerations within the workspace.
Rail Types, Installation, and Maintenance
Specifications and Configurations:
Discussing Different Rail Profiles and Material Considerations:
- Rail Profiles: - Detailing various rail profiles such as I-beams, box girders, and their suitability for specific crane applications based on load-bearing capacities and structural integrity.
- Rail Material Considerations: - Comparing materials like steel and aluminum for crane rails, highlighting their strengths, durability, and conductivity properties to meet operational requirements.
Installation Challenges and Solutions:
Overcoming Installation Obstacles in Various Industrial Settings:
- Environmental Adaptability: - Addressing challenges related to rail installation in diverse environments, including extreme temperatures, corrosive atmospheres, or high-dust areas, and proposing solutions for each scenario.
- Custom Configurations: - Exploring customized rail configurations to suit specific industrial layouts and space constraints, offering tailored solutions for efficient crane operations.
Maintenance Best Practices:
Providing Guidelines for Optimal Rail Maintenance and Inspection:
- Regular Inspection Protocols: - Outlining best practices for routine rail inspections, emphasizing the importance of identifying wear and tear, ensuring safety, and preventing operational disruptions.
- Maintenance Guidelines: - Detailing maintenance routines such as lubrication, alignment checks, and corrective measures, ensuring prolonged rail system lifespan and optimal crane performance.
Overhead Crane Rail Tracks: Variety and Configurations
Overhead crane rail tracks are fundamental components that provide guidance and support for crane movement within industrial settings. They exhibit a range of features designed to ensure precise, efficient, and safe operations.
One notable feature of these tracks is their diverse range of profiles, accommodating various crane types and load capacities. Different rail shapes and sizes are tailored to suit specific types of overhead cranes, offering versatility in handling different loads and accommodating diverse operational requirements. This adaptability allows industries to select the most suitable rail profile that aligns with their crane's design and the nature of the materials being handle
Moreover, these rail tracks offer configurations that guide the path of the crane. They encompass straight tracks, curves, switches, and intersections, allowing for intricate layouts within facilities. Straight tracks provide the main pathway for linear movements, while curved sections facilitate smooth transitions around corners. Switches and intersections allow cranes to maneuver between different tracks, enabling efficient material transportation across designated areas.
Material variations in these rail tracks also play a crucial role. The choice of materials, such as steel, aluminum, or specialty alloys, is determined by factors like load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and durability requirements. Steel rails, known for their strength and durability, are commonly used for heavy-duty applications, while aluminum tracks are preferred for their lightweight properties in certain settings. Specialty alloys may be employed for specific industrial needs, providing enhanced resistance to corrosion or other environmental factors.
In summary, the diversity in overhead crane rail tracks, characterized by their various profiles, configurations for guidance, and material variations, underscores their critical role in facilitating smooth and efficient crane movements within industrial environments. These tracks offer adaptability, precision, and structural support necessary for safe and effective material handling operations. Industries benefit from the flexibility to select rail configurations and materials that best suit their specific operational needs, ensuring optimal crane performance and safety standards.
Components and Features of Overhead Crane Track Systems
Overhead Crane Rail Tracks: Materials and Profiles
Materials:
- Steel Rails: Commonly used for their durability, strength, and resistance to wear.
- Aluminum Rails: Lightweight option suitable for specific applications with lower load requirements.
- Specialty Alloys: Utilized for their resistance to corrosion, extreme temperatures, or specific environmental conditions.
Profiles:
- I-Beam Rails: Commonly used due to their structural strength and load-bearing capabilities.
- Square Bar Rails: Used in specialized applications where specific load distribution or track configuration is necessary.
- Custom Profiles: Tailored designs to meet specific industry or operational requirements.
Power Tracks for Overhead Cranes: Design and Capacity Considerations
Design:
- Conductor Bar Systems: Electrified bars for power transmission to the crane.
- Cable Festoon Systems: Suspended cables providing power to moving cranes.
- Segmented Power Rails: Power tracks divided into sections for selective isolation during maintenance.
Capacity Considerations:
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Matching power track specifications with crane requirements.
- Amperage Load Capacity: Ensuring tracks can handle the electrical load demands of the crane system.
- Overload Protection: Incorporating safety measures to prevent power track overload situations.
Ensuring Durability and Efficiency in Rail Systems
Durability Factors:
- Material Selection: Choosing rails based on load requirements, environmental conditions, and longevity needs.
- Surface Coatings: Adding protective coatings to rails for corrosion resistance and reduced wear.
- Regular Maintenance: Implementing scheduled inspections and upkeep to ensure optimal functionality.
Efficiency Measures:
- Smoothness and Alignment: Ensuring tracks are straight, aligned correctly, and free from obstacles for smooth crane movement.
- Proper Lubrication: Applying lubricants to reduce friction and wear between wheels and tracks.
- Load Distribution: Ensuring tracks distribute loads evenly across the rail system to prevent strain and damage.
Understanding the materials, profiles, and design considerations of overhead crane rail tracks, as well as power track systems, is essential for ensuring the durability, efficiency, and safe operation of crane systems within industrial settings. Selecting appropriate materials, maintaining tracks, and ensuring efficient power transmission contribute significantly to the overall performance and longevity of overhead crane track systems.
Maintenance and Safety Protocols for Overhead Rail Cranes
Operator Training and Adherence to Safety Protocols
Comprehensive Training:
- Provide thorough training programs for crane operators emphasizing safe operating practices and emergency protocols.
- Ensure operators understand load capacities, operational limits, and safety features of the equipment.
Safety Adherence:
- Encourage adherence to safety protocols and guidelines during crane operation, emphasizing the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Promote a safety-conscious culture among all personnel involved in crane operations.
Significance of Load Monitoring and Safety Devices
Load Monitoring:
- Utilize load monitoring systems to prevent overloading, ensuring safe lifting practices.
- Implement warning systems that alert operators if loads exceed safe limits.
Safety Devices:
- Install safety devices such as limit switches, emergency stop buttons, and collision avoidance systems to prevent accidents.
- Regularly test and maintain safety devices to ensure their functionality.
Preventive Measures for Prolonged Lifespan and Optimal Performance
Proactive Approach:
- Address potential issues before they escalate, replacing worn parts and conducting preemptive repairs.
- Implement a proactive approach to prevent equipment breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the crane.
Documentation and Records:
- Maintain comprehensive records of maintenance activities, inspections, and repairs performe
- Use records for analysis and future planning, ensuring adherence to maintenance schedules.
Implementing these maintenance and safety protocols is crucial for ensuring the prolonged lifespan, optimal performance, and, most importantly, the safety of overhead rail cranes. Regular inspections, adherence to safety guidelines, operator training, and proactive maintenance play pivotal roles in sustaining the efficiency and reliability of these essential industrial assets.
Applications and Industries Utilizing Overhead Rail Cranes
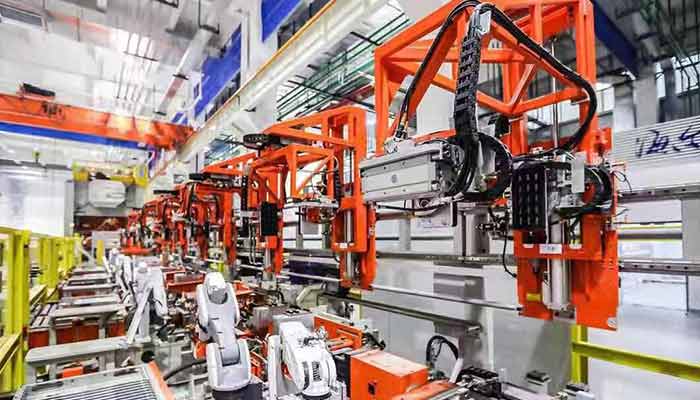

Manufacturing and Assembly Lines: Enhancing Productivity and Precision
Precision Handling:
- Overhead rail cranes efficiently transport components along assembly lines, enhancing production efficiency.
- Aid in precise positioning of materials during manufacturing processes, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
Increased Productivity:
- Facilitate swift material movement, reducing production downtime and optimizing workflow.
- Allow for continuous operations by streamlining the supply of materials to various workstations.
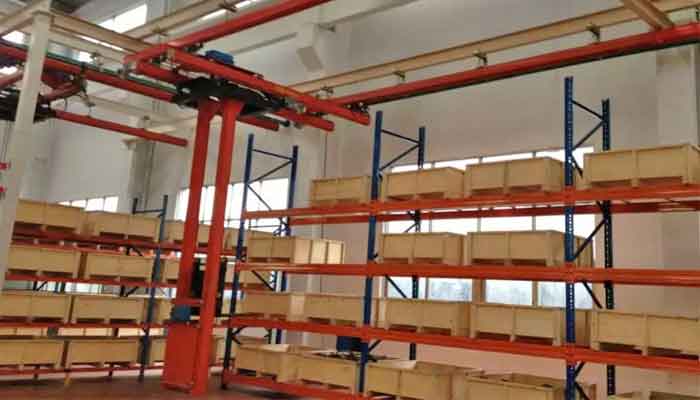

Warehousing and Logistics: Streamlining Material Movement and Storage
Showcasing the Efficiency in Material Handling and Logistics:
- Inventory Management: - Illustrating how cranes on rails streamline warehouse operations by efficiently stacking, retrieving, and transporting goods within warehouse premises.
- Logistics Optimization: - Emphasizing how rail-mounted cranes enhance logistics by enabling faster order processing and distribution, contributing to efficient supply chain management.
Efficient Material Handling:
- Enable rapid movement of goods within warehouses, optimizing storage and retrieval processes.
- Maximize space utilization by allowing vertical stacking of materials in storage facilities.
Inventory Management:
- Simplify inventory handling by facilitating the organized storage and retrieval of goods.
- Enhance logistics operations by expediting loading/unloading processes for transportation.

Construction and Infrastructure Projects: Facilitating Heavy Lifting Needs
Detailing the Role of Cranes on Rails in Construction Projects:
- Structural Development: - Highlighting how cranes on rails play a pivotal role in construction by facilitating the lifting and placement of heavy materials like steel beams, concrete panels, and machinery at construction sites.
- Precision and Efficiency: - Detailing how rail-mounted cranes ensure precision in material handling, expediting construction timelines and optimizing resource utilization.
Heavy Lifting Capabilities:
- Overhead rail cranes aid in lifting and transporting heavy construction materials, equipment, or prefabricated components.
- Contribute to the efficient and safe handling of bulky items required in construction projects.
Site Mobility:
- Offer flexibility in material movement across construction sites, improving operational efficiency.
- Facilitate precise placement of materials in different areas of construction projects.
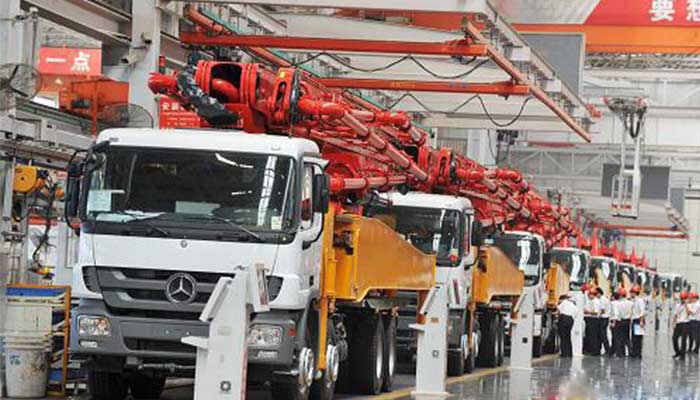

Aerospace, Automotive, and Heavy Machinery Industries: Critical Handling Demands
Heavy Industries and Manufacturing:
Highlighting Specific Applications in Heavy Industrial Settings:
- Material Handling: - Showcasing how cranes on rails assist heavy industries like steel manufacturing or automotive plants in handling large components, raw materials, and finished products.
- Process Streamlining: - Detailing how rail-mounted cranes optimize heavy industrial processes, ensuring safe and efficient material movement within manufacturing facilities.
- Transformative Utility: The applications of cranes on rails span across diverse industrial sectors, showcasing their transformative utility in construction, warehousing, logistics, and heavy manufacturing. Their role in streamlining operations, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring precision underscores their significance in driving industrial progress.
Specialized Handling:
- Overhead rail cranes cater to the specific handling requirements of large and delicate components in aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
- Ensure the safe transport and positioning of heavy machinery parts or specialized equipment.
Precision and Safety:
- Provide precise movement for delicate components while ensuring safety compliance in critical handling operations.
- Aid in the assembly, maintenance, or repair of complex machinery in these industries.
Overhead rail cranes play a pivotal role across diverse industries by optimizing material handling, facilitating heavy lifting, enhancing productivity, and ensuring precision in various applications. Their adaptability and efficiency make them indispensable tools in enhancing operational processes and meeting specific handling demands across different sectors.
Benefits of Overhead Rail Cranes for Industry Applications
Improved Efficiency in Material Handling Processes
Streamlined Operations:
- Overhead rail cranes facilitate quicker and more precise movement of materials within industrial facilities.
- Efficiently transport heavy or cumbersome loads, optimizing production timelines and reducing downtime.
Space Utilization:
- Utilize vertical space efficiently, allowing for the effective organization of storage or manufacturing areas.
- Free up floor space by eliminating the need for ground-based material handling equipment.
Enhanced Safety Measures and Increased Load Capacity
Safety Advantages:
- Reduce risks associated with manual handling by providing controlled and secure lifting mechanisms.
- Minimize accidents through advanced safety features such as overload protection and anti-sway technology.
Increased Load Capacity:
- Handle heavier loads compared to traditional material handling methods, improving overall productivity.
- Enable safe and controlled lifting of substantial weights, enhancing operational capabilities.
Adaptability to Various Work Environments and Configurations
Versatility:
- Suitable for diverse industrial environments, including manufacturing, warehousing, and assembly lines.
- Adapt to various layouts and configurations within facilities, including limited-space or complex layouts.
Customization:
- Tailorable to specific industry requirements, offering various crane configurations to suit unique needs.
- Fitment with specialized attachments for specific tasks or materials handling requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Reliability
Cost Savings:
- Reduce labor costs associated with manual material handling by streamlining operations.
- Longevity and durability of overhead rail cranes minimize frequent replacements or repairs.
Long-Term Reliability:
- Demonstrated durability and consistent performance contribute to their long-term reliability.
- Low maintenance requirements and high-quality components ensure prolonged operational reliability.
Overhead rail cranes provide a multitude of advantages across different industries, significantly impacting operational efficiency, safety standards, adaptability, and long-term cost-effectiveness. Their ability to enhance material handling processes while ensuring safety measures and reliability makes them indispensable assets in modern industrial settings.
Expert Guidance: How to Select Overhead Rail Cranes for Your Applications
Understanding Specific Industry Requirements and Challenges
Industry Analysis:
- Identify the unique material handling challenges within your industry, considering load types, sizes, and movement patterns.
- Analyze operational constraints, safety standards, and regulatory requirements impacting crane selection.
Application-Specific Needs:
Understand the precise requirements for material movement, precision, and load capacities specific to your industry or operation.
Collaborating with Experts for Tailored Crane Solutions
Expert Consultation:
- Engage with crane manufacturers or industry specialists to assess your unique operational needs.
- Seek advice on crane configurations, customization options, and features that align with your specific requirements.
Customized Solutions:
- Collaborate with experts to tailor crane solutions that address your industry-specific challenges.
- Explore customization possibilities to optimize crane functionalities for your application.
Assessing ROI and Long-Term Efficiency Gains
Return on Investment (ROI):
- Evaluate the cost-benefit analysis considering initial investment, operational efficiencies, and long-term savings.
- Assess potential returns in terms of increased productivity, reduced downtime, and improved safety.
Long-Term Efficiency:
- Analyze the expected lifecycle of the overhead rail crane, considering maintenance costs, lifespan, and durability.
- Assess the overall impact on operational efficiency and productivity over an extended perio
Making an informed decision in selecting overhead rail cranes involves a comprehensive understanding of your industry's unique demands, seeking expert guidance for tailored solutions, and conducting a thorough assessment of the anticipated ROI and long-term efficiency gains. Collaboration with industry experts ensures the procurement of overhead rail cranes optimized to meet your specific operational needs and deliver long-term value to your business.
Factors Influencing Selection of Overhead Rail Cranes

Consideration of Weight Capacity and Specific Load Requirements
- Evaluate the maximum weight the crane will handle and ensure it aligns with operational needs.
- Consider potential future requirements to ensure scalability and versatility.
Load Characteristics:
- Assess the type of materials or items to be lifted, considering their shape, size, and weight distribution.
- Ensure the crane's lifting mechanism suits the nature of the loads to be handle
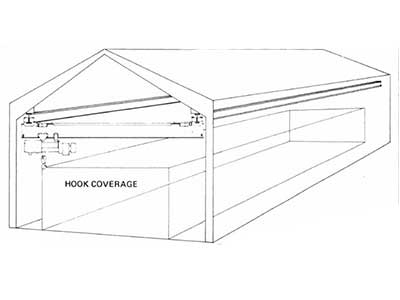
Span, Height & Hook Coverage Considerations for Site and Application Suitability
Span:
- Determine the distance the crane needs to cover horizontally to efficiently reach all necessary work areas.
- Optimize the span based on facility layout and material handling requirements.
- Assess the required lift height to ensure the crane accommodates stacking or vertical lifting needs.
- Consider the facility's ceiling height or obstructions that might restrict vertical movement.
Customization Options and Essential Additional Features
Customization:
- Evaluate customization options available to tailor the crane to specific operational needs.
- Consider additional features such as specialized hooks, attachments, or control mechanisms for enhanced functionality.
Essential Features:
- Assess safety features such as emergency stop buttons, overload protection, and anti-sway systems.
- Evaluate automation options or smart technologies for improved efficiency and safety.
Balancing Budgetary Constraints with Long-Term Maintenance Costs
Budget Considerations:
- Consider the initial investment cost for purchasing and installing the overhead rail crane.
- Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of different crane options concerning their capabilities and features.
Long-Term Maintenance:
- Assess maintenance requirements, predicted upkeep costs, and availability of spare parts.
- Balance initial costs with long-term maintenance expenses to ensure cost-effectiveness over the crane's lifespan.
Understanding these factors and their implications is crucial in selecting the most suitable overhead rail crane for specific industrial applications. Balancing technical specifications, customization options, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance considerations ensures the procurement of an overhead rail crane that aligns with operational needs while optimizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Tailoring Solutions for Industrial Needs
Summarizing the Versatile Solutions Provided by Cranes on Rails:
- Versatility in Operations: - Recapitulating how cranes on rails offer versatile solutions across diverse industrial sectors, enhancing efficiency, safety, and productivity in material handling.
- Adaptability and Precision: - Highlighting the adaptability of rail-mounted cranes in various working environments while ensuring precise and controlled material movement.
Recommendations for Crane Selection and Customization:
Offering Practical Suggestions for Optimal Crane Utilization and Customization:
- Understanding Operational Requirements: - Advising potential purchasers to assess their specific operational needs, considering factors like load capacities, working environments, and industry standards while selecting cranes.
- Consulting Expertise: - Recommending seeking advice from crane specialists or manufacturers to customize crane solutions that align with unique industrial requirements for enhanced efficiency.
In conclusion, the comprehensive guide on cranes on rails has provided insights into their versatile solutions across diverse industrial sectors. By emphasizing adaptability, precision, and efficiency, these solutions cater to the dynamic needs of industrial operations.
This handbook serves as a resourceful guide for users, potential purchasers, and industrial stakeholders, offering recommendations to tailor crane selections and configurations according to specific operational needs and industrial standards.
Concerns of Crane Users
Safety Standards and Regulations:
Prioritizing Compliance and Safety Measures:
- Compliance with Standards: - Crane users must adhere to stringent safety standards and regulations established by governing bodies. Ensuring compliance with these standards is crucial to mitigate workplace hazards and prevent accidents.
- Safety Protocols: - Implementing rigorous safety protocols, including operator training, regular inspections, and safety procedures, is imperative to guarantee the safe operation of cranes within industrial settings.
Maintenance and Durability:
Best Practices for Longevity and Reliability:
- Scheduled Maintenance: - Regular and comprehensive maintenance schedules are vital to uphold the durability and performance of cranes. This includes routine inspections, lubrication, and component replacements as needed.
- Proactive Repairs: - Prompt identification and resolution of potential issues through proactive repairs can prevent costly breakdowns and ensure the longevity of crane systems.
Operational Efficiency:
Strategies for Enhancing Productivity and Efficiency:
- Optimized Workflows: - Evaluating and optimizing workflows involving cranes can significantly enhance operational efficiency. Streamlining processes and reducing downtime leads to improved productivity.
- Technological Integration: - Incorporating advanced technologies such as automation or IoT-based monitoring systems can optimize crane operations, enabling data-driven decision-making and process improvement.
Cost and Investment Considerations:
Exploring Cost-Efficient Options and Long-Term Benefits:
- Lifecycle Cost Analysis: - Conducting a comprehensive lifecycle cost analysis helps users assess the overall expenses associated with crane operations, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
- Long-Term Benefits: - While initial investment considerations are crucial, users should weigh the long-term benefits of high-quality and efficient crane systems that offer reliability, durability, and enhanced productivity over time.
Addressing the concerns of crane users encompasses various aspects, from safety adherence to operational efficiency and cost considerations. In the upcoming sections, we will delve into frequently asked questions, providing detailed insights and solutions to common queries concerning crane operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Queries about Overhead Cranes:
What is the difference between single girder and double girder overhead cranes?
Single girder cranes have one girder beam supporting the hoist, while double girder cranes utilize two parallel beams, offering higher lifting capacities.
How often should overhead cranes undergo maintenance?
Regular inspections and maintenance should occur per manufacturer recommendations or as mandated by regulatory standards to ensure safety and optimal performance.
FAQs on Gantry Cranes:
What are the advantages of using rail-mounted gantry (RMG) cranes in ports?
RMG cranes facilitate efficient container handling, offer precise positioning, and optimize port space utilization compared to other handling equipment.
Can gantry cranes be customized for specific lifting capacities?
Yes, gantry cranes can be tailored to accommodate various lifting capacities based on the operational requirements of different industries.
Common Questions about Jib Cranes:
What is the typical radius coverage of a jib crane?
The radius coverage of jib cranes varies based on the design, but it generally ranges from a few meters to several meters, depending on the crane's configuration.
Are wall-mounted jib cranes suitable for limited space environments?
Yes, wall-mounted jib cranes are specifically designed for limited spaces, offering effective material handling solutions while minimizing floor space usage.
Providing clear and comprehensive answers to these common inquiries offers valuable insights into the functionalities and applications of overhead, gantry, and jib cranes. Understanding these fundamental aspects can guide users and potential purchasers toward informed decisions regarding crane selection and operational considerations.
What factors should be considered while selecting the appropriate crane design for an industrial setting?
Explaining the considerations like load capacity, working environment, and available space that influence crane design selection.
How do different rail configurations impact crane stability and performance?
Detailing how various rail profiles and configurations influence stability, maneuverability, and operational efficiency of cranes.
Industry-Specific Queries on Crane Application and Standards:
Addressing Industry-Specific Concerns and Standards:
Are there specific standards or regulations for cranes used in the petrochemical industry?
Exploring specialized standards or adaptations required for crane operations in hazardous environments like the petrochemical sector.
How do crane specifications differ for the pharmaceutical industry compared to other manufacturing sectors?
Discussing unique crane specifications ensuring compliance with strict hygiene standards in pharmaceutical settings.
Maintenance and Safety FAQs:
Offering Precise and In-Depth Answers to Maintenance and Safety Queries:
What are the recommended intervals for conducting crane inspections and maintenance checks?
Outlining optimal inspection frequencies and maintenance schedules for ensuring crane safety and longevity.
How can crane operators ensure safe operations in high-risk environments?
Providing guidelines and safety measures for crane operators working in high-risk or specialized environments.
Addressing these common questions and concerns related to crane design, rail configurations, industry-specific applications, standards, maintenance, and safety offers detailed insights and solutions. These precise and in-depth answers guide users and potential purchasers toward informed decisions and safe crane operations.
Wrap it Up: Get Your Custom Overhead Cranes on Rails
Recapitulation of Overhead Rail Crane Advantages Across Industries
Versatile Applications:
- Overhead rail cranes have proven invaluable across industries, enhancing productivity, efficiency, and precision in material handling processes.
- From manufacturing and warehousing to construction and specialized industries, their adaptability addresses diverse operational needs.
Safety and Efficiency: - They contribute significantly to improved safety standards by offering controlled and secure material handling while maximizing operational efficiencies.
Emphasizing Safety, Maintenance, and the Criticality of System Selection
Safety and Maintenance Prioritization:
- Highlighting the criticality of adhering to strict safety protocols, regular maintenance checks, and operator training to ensure accident-free operations.
- Underlining the importance of selecting the right system aligned with industry-specific requirements for optimal performance and safety.
Encouragement for Further Exploration and Adoption in Varied Industries to Enhance Productivity and Safety Standards
Continuous Improvement:
- Encouraging industries to explore and adopt overhead rail crane solutions further to elevate productivity, streamline operations, and advance safety benchmarks.
- Emphasizing the role of innovative technologies and industry collaboration in driving continuous improvement.
In conclusion, overhead rail cranes stand as indispensable assets, providing multifaceted advantages across industries, from enhancing operational efficiency and safety standards to ensuring precise and controlled material handling processes. Emphasizing safety, maintenance, and the criticality of selecting the right system tailored to specific industry needs encourages further exploration and adoption, propelling industries towards heightened productivity and elevated safety standards.
Main Projects
Related Products

Latest project
32/5 Ton Overhead Crane Sale in India: Case Study
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch











