Overhead Gantry Cranes v.s. Overhead Bridge Cranes 5 Ton- 50 Ton
Overhead gantry cranes & overhead bridge crane for sale 5 Ton, 10 Ton, 20 Ton, 30 Ton, 40 Ton & 50 ton. How to select from overhead gantry crane & bridge crane?
Category: Bridge Crane
Your Trusted Overhead Travelling Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Overhead Gantry Cranes v.s. Overhead Bridge Cranes
5 ton, 10 ton, 20 ton, 30 ton, 40 ton, 50 ton +
Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes
Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes
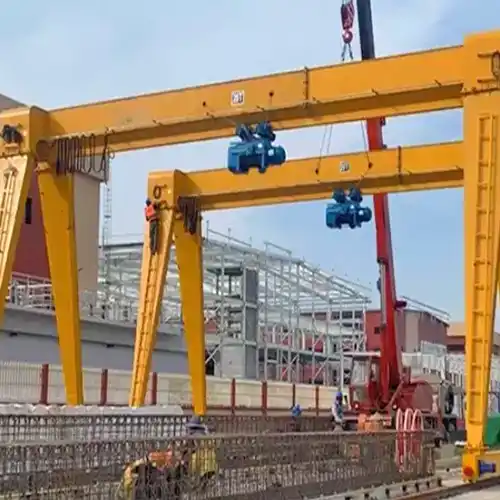
Overhead Gantry Cranes, characterized by their supportive legs, provide exceptional mobility and flexibility. These cranes often find their place in outdoor settings and excel in scenarios demanding higher load capacities, delivering cost-effective solutions in specialized contexts.
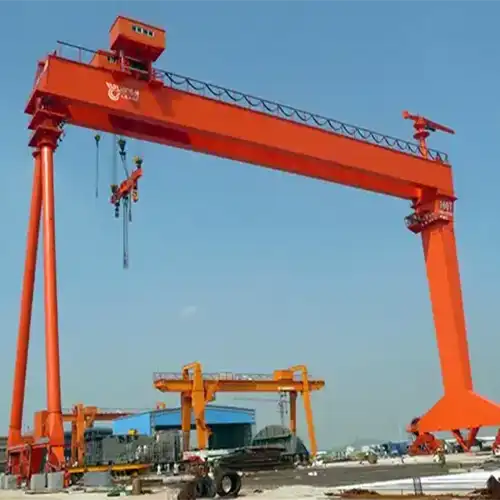
On the other hand, Overhead Bridge Cranes, securely mounted on fixed runways, are distinguished by their stable structure. They provide precise and controlled movements, making them a preferred choice for indoor applications with varied load capacities catering to different operational setups.
Importance of Choosing the Right Crane for Specific Industrial Applications
The choice between these two stalwarts—Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes—extends beyond the realm of mere functionality. It's a decision intricately woven into the fabric of industrial efficiency. Selecting the suitable crane is not just about lifting weights; it's about navigating the unique demands of industries, optimizing workflows, ensuring safety, and maximizing productivity.
From shipping yards and construction sites to warehousing, logistics, manufacturing, automotive, steel mills, and aerospace facilities, each industry requires a specific set of functionalities from its material handling equipment. The precision, adaptability, and load-bearing capacities of these cranes significantly influence operational success.
Choosing the right crane means aligning the nuances of crane design, load capacities, operational environments, and specific industry demands. It's about identifying the perfect match that ensures seamless integration into existing workflows, enhances productivity, and ultimately contributes to the bottom line of an industrial venture.
Crane Basics: Understanding Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes
In the intricate landscape of material handling, the fundamental understanding of Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes is pivotal. Each type of crane possesses distinct components, designs, and structural variations, crucial for making informed decisions in industrial operations.
Overhead Bridge Cranes and Overhead Gantry Cranes stand as two prominent types of industrial lifting equipment, each tailored for distinct operational environments and applications. These cranes play pivotal roles in material handling, offering unique features and capabilities suited to diverse industrial settings.
Overhead Bridge Cranes, characterized by their fixed structure mounted on elevated runways within indoor facilities, excel in precision, stability, and controlled movements. They find their niche in manufacturing plants, automotive facilities, steel mills, and aerospace industries, where confined spaces and specific load capacities demand precise handling of heavy materials and equipment. These cranes operate with accuracy along fixed paths, aiding in assembly line operations, heavy machinery lifting, and precise positioning of materials within confined spaces.
Definition and Components of Overhead Gantry Cranes
Overhead Gantry Cranes, characterized by their supportive legs or stands, operate on a track or rail system. These cranes consist of several essential components:
- Girders: These form the primary framework and provide structural support to the crane.
- Hoist: The hoisting mechanism attaches to the load and enables lifting and lowering.
- Trolley: A movable component along the crane's girders, facilitating lateral movement of the loa
- Legs or Stands: Supporting pillars that allow mobility and stability.
- End Trucks: Mounted at each end of the girder, these house the wheels to move along the track.
On the other hand, Overhead Gantry Cranes, supported by legs or stands and adaptable for outdoor usage, provide mobility, higher load capacities, and adaptability to varied terrains and weather conditions. They thrive in outdoor settings such as shipping yards, construction sites, warehousing, and railway maintenance. Offering versatility and robustness, these cranes are designed for mobility across different terrains, making them indispensable in scenarios requiring heavy load lifting and material handling in open environments.
Definition and Components of Overhead Bridge Cranes
Contrastingly, Overhead Bridge Cranes are fixed structures that operate on a runway system installed on elevated beams or tracks. Their components include:
- Bridge Girder or Beam: The primary horizontal beam supporting the hoist and trolley.
- Hoist: Similar to Gantry Cranes, this component performs the lifting and lowering tasks.
- Trolley: Mounted on the bridge, it enables lateral movement of the loa
- Runway or Track: The fixed structure on which the crane moves horizontally.
- End Trucks: Supporting wheels that move along the runway, facilitating horizontal mobility.
While both crane types share the primary goal of facilitating efficient material handling, their design, structure, and operational focus differ significantly. The choice between an Overhead Bridge Crane and an Overhead Gantry Crane hinges on the specific needs of the industry or operational environment, emphasizing precision and stability in controlled indoor spaces or mobility and adaptability in outdoor settings. Understanding the unique strengths and applications of each crane type is fundamental in selecting the optimal solution for streamlined and safe material handling operations within distinct industrial landscapes.
Differentiation in Design and Structure
The core differentiation between Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes lies in their structural design:
Gantry Crane: Supported by legs or stands, Gantry Cranes provide exceptional mobility, allowing them to be used in outdoor settings and granting higher load capacities. The legs or stands contribute to their stability and adaptability across various terrains.
Bridge Crane: Bridge Cranes, fixed on elevated runways, offer stability and precision. Their fixed structure ensures controlled movements, making them ideal for indoor applications. They cater to varied load capacities and are well-suited for specific operational setups within industrial environments.
Understanding these structural differences helps industries tailor their choices to suit the specific demands of their operations. This foundational knowledge forms the bedrock upon which the selection of the right crane for precise industrial applications rests.
Differences between Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes:

Structural Designof Overhead Gantry Crane:
Supported by legs or stands.
Offers exceptional mobility and flexibility.
Suited for outdoor applications.
Higher load capacities due to its supportive structure.
Components of Gantry Crane:
Girders, hoist, trolley, legs or stands, end trucks.
Suitable for diverse terrains due to mobility.
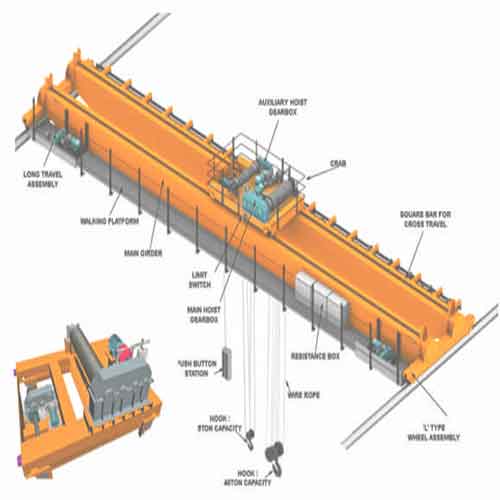
Structural Design of Overhead Brige Crane
Fixed on elevated runways.
Provides stability and precise movements.
Primarily designed for indoor applications.
Varied load capacities suitable for different setups.
Components of Bridge Crane:
Bridge girder or beam, hoist, trolley, runway or track, end trucks.
Offers controlled movements in fixed spaces.
Similarities between Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes:
- Core Components:Both use similar core components such as hoists, trolleys, and end trucks for lifting and lateral movement.
- Material Handling Functionality:Both types are used for material handling and lifting operations in industrial settings.
Now, let's represent these differences and similarities in a comparative table:
| Aspect | Overhead Gantry Crane | Overhead Bridge Crane |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Design | Supported by legs or stands | Fixed on elevated runways |
| Offers exceptional mobility and flexibility | Provides stability and precise movements | |
| Suited for outdoor applications | Primarily designed for indoor applications | |
| Higher load capacities due to support | Varied load capacities for different setups | |
| Core Components | Girders, hoist, trolley, legs or stands, end trucks | Bridge girder, hoist, trolley, runway or track, end trucks |
| Suitable for diverse terrains due to mobility | Offers controlled movements in fixed spaces | |
| Material Handling Function | Used for material handling and lifting operations | Used for material handling and lifting operations |
This table succinctly outlines the differences and similarities between Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes, showcasing their structural designs, core components, and functional similarities.
Types of Cranes: Variants and Classifications
Variants and Classifications of Overhead Gantry Cranes
Overhead Gantry Cranes come in various configurations, each tailored to specific industrial needs. These variants include:

Single Girder Overhead Gantry Crane:
- Utilizes a single girder for support.
- Suited for lighter lifting applications.
- Offers cost-effective solutions for various industries.

Double Girder Overhead Gantry Crane:
- Incorporates two girders for increased stability.
- Suitable for heavier loads and more demanding operations.
- Provides higher lifting capacities compared to single girder cranes.
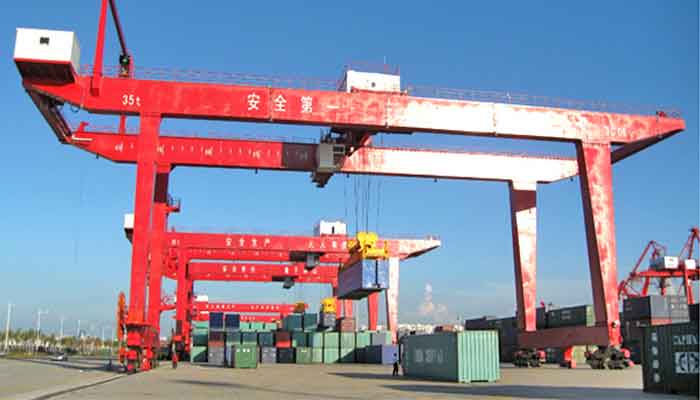

Rail-Mounted Overhead Gantry Crane (RMG):
- Runs on rails, enabling horizontal movement.
- Commonly used in container handling at ports or shipping yards.
- Offers efficient load movement in confined spaces.
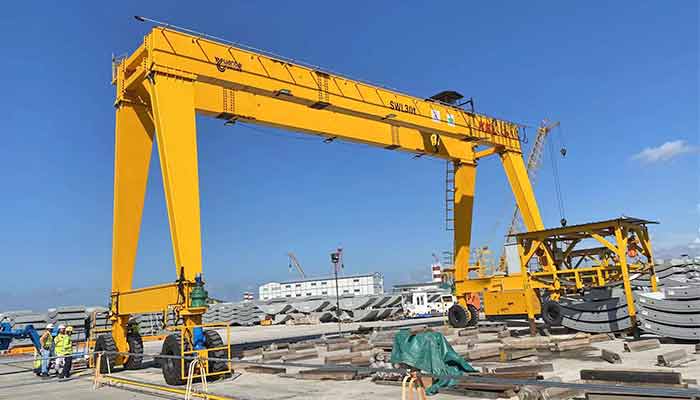

Rubber-Tired Overhead Gantry Crane (RTG):
- Equipped with rubber tires for mobility.
- Ideal for flexible and versatile material handling tasks.
- Frequently used in construction sites and warehouses.
Variants and Classifications of Overhead Bridge Cranes
Overhead Bridge Cranes also feature various classifications to suit different industrial requirements:

Single Girder Overhead Bridge Crane:
- Incorporates a single girder for support.
- Provides cost-effective solutions for light to medium lifting.
- Suited for low headroom applications.

Double Girder Overhead Bridge Crane:
- Utilizes two girders for increased stability.
- Handles heavier loads and offers higher lifting capacities.
- Commonly used in heavy manufacturing and steel mills.

Top Running Overhead Bridge Crane:
- The crane runs on top of the runway beams.
- Offers higher hook heights and capacities.
- Suitable for heavy-duty lifting in manufacturing environments.

Underhung Overhead Bridge Crane:
- Operates below the runway beams.
- Occupies less space and works well in confined areas.
- Often utilized in workshops and assembly lines.
These variants and classifications cater to a wide spectrum of industrial needs, offering versatility, specialization, and optimized solutions for specific material handling tasks within different operational environments. Understanding these types aids in selecting the most suitable crane variant for particular industrial applications.
Single Girder Cranes:

Single Girder Overhead Bridge Crane:
Differences:
- Design: Mounted on a fixed elevated runway.
- Usage: Suitable for lighter to moderate lifting applications.
- Space Requirement: Offers greater clearance due to its top-running design.
- Common Applications: Ideal for workshops, warehouses, and assembly lines.
- Cost: Generally more cost-effective than double girder variants.

Single Girder Overhead Gantry Crane:
Differences:
- Design: Supported by legs or stands with a single girder.
- Usage: Suited for outdoor and indoor tasks requiring lighter loads.
- Mobility: Offers mobility across various terrains.
- Common Applications: Used in shipping yards, construction sites, and smaller warehouses.
- Adaptability: Provides flexibility in handling materials outdoors and indoors.
Similarities:
- Both configurations are suitable for lighter lifting tasks.
- Offer cost-effective solutions for specific applications.
- Utilize a single girder for support.
Double Girder Cranes:

Double Girder Overhead Bridge Crane:
Differences:
- Design: Operates on a fixed runway with two girders for added stability.
- Capacity: Capable of handling heavier loads than single girder variants.
- Height: Provides increased hook height for lifting taller objects.
- Common Applications: Often used in heavy manufacturing and steel mills.
- Cost: Generally more expensive due to the heavier construction.

Double Girder Overhead Gantry Crane:
Differences:
- Design: Utilizes two girders supported by legs or stands.
- Capacity: Offers higher lifting capacities compared to single girder gantry cranes.
- Stability: Enhanced stability due to the double girder structure.
- Common Applications: Suited for heavy-duty outdoor and indoor tasks.
- Versatility: Provides flexibility in handling heavier loads in various environments.
Similarities:
- Both configurations offer enhanced stability compared to their single girder counterparts.
- Designed to handle heavier loads and provide higher lifting capacities.
- Utilize two girders for increased support and stability.
Let's represent this information in a comparative table for easier reference:
| Aspect | Single Girder Overhead Bridge Crane | Single Girder Overhead Gantry Crane | Double Girder Overhead Bridge Crane | Double Girder Overhead Gantry Crane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Design | Fixed on elevated runway | Supported by legs/stands | Fixed on elevated runway | Supported by legs/stands |
| Usage | Lighter to moderate lifting applications | Lighter loads, outdoor and indoor tasks | Heavier lifting applications | Heavier loads, outdoor and indoor tasks |
| Mobility | Less mobility, fixed in one location | Mobility across various terrains | Less mobility, fixed in one location | Mobility across various terrains |
| Common Applications | Workshops, warehouses, assembly lines | Shipping yards, construction sites | Heavy manufacturing, steel mills | Heavy-duty outdoor and indoor tasks |
| Capacity/Cost | Lighter loads, cost-effective solution | Lighter loads, cost-effective solution | Heavier loads, higher cost | Heavier loads, higher cost |
This table highlights the differences and similarities between single and double girder configurations for both Overhead Bridge Cranes and Overhead Gantry Cranes, outlining their structural designs, uses, applications, and comparative aspects.
Features and Benefits: Overhead Gantry Cranes
Unique Features of Overhead Gantry Cranes:
Mobility and Flexibility:
- Distinctive Trait: Equipped with supportive legs/stands allowing movement.
- Advantage: Offers mobility across various terrains and operational areas.
- Benefit: Facilitates versatile material handling tasks in different environments.
Outdoor Applications:
- Characteristic: Designed for outdoor usage due to supportive structure.
- Advantage: Withstands varying weather conditions and outdoor elements.
- Benefit: Ideal for industries like shipping, construction, and outdoor logistics.
Higher Load Capacities:
- Trait: Built to handle heavier loads efficiently.
- Advantage: Offers increased lifting capacities compared to some other crane types.
- Benefit: Suited for heavy-duty tasks in industries requiring robust material handling.
Cost-Effective Solutions for Specific Scenarios:
- Trait: Tailored to provide efficient solutions for certain specialized tasks.
- Advantage: Offers economical handling for specific applications.
- Benefit: Provides cost-effective material handling solutions tailored to unique industrial needs.
Benefits and Strengths of Overhead Gantry Cranes:
- Versatility in Applications: Suited for a wide range of industries due to their adaptable design.
- Enhanced Mobility: Offers flexibility in moving materials across different areas.
- Stability and Strength: Provides stability for lifting heavier loads efficiently.
Benefits and Strengths of Overhead Gantry Cranes:
- Outdoor Durability: Withstands harsh environmental conditions for prolonged use.
- Cost Efficiency: Provides cost-effective material handling solutions for specific industrial scenarios.
These distinctive features and benefits of Overhead Gantry Cranes underscore their suitability for various industries, highlighting their adaptability, strength, and cost-effectiveness in handling materials across diverse operational landscapes.
Key Features of Overhead Bridge Cranes:
Overhead Bridge Cranes are distinguished by several key features that make them indispensable for various industries. Let's delve into these fundamental characteristics:
Fixed Structure and Stability:
- Rigid Configuration: Mounted on fixed elevated runways or beams, ensuring stability during material handling operations.
- Enhanced Stability: Offers a sturdy, fixed structure, providing a secure platform for lifting and moving loads with minimal swaying or movement.
Precise and Controlled Movements:
- Controlled Operation: Equipped with precise controls for accurate movements in vertical and horizontal directions.
- High Precision: Allows for controlled and fine-tuned handling, crucial in applications demanding precise positioning of loads.
Indoor Applications:
- Tailored for Indoor Environments: Specifically designed for indoor use, making them suitable for manufacturing plants, warehouses, and other indoor facilities.
- Space Efficiency: Their fixed structure maximizes vertical space utilization within indoor settings.
Varied Load Capacities for Different Setups:
- Scalability: Available in a range of load capacities, offering flexibility to handle various load sizes and weights.
- Customization: Can be customized for different setups, accommodating diverse operational requirements within industrial settings.
These core features collectively define the essence of Overhead Bridge Cranes, positioning them as pivotal assets for indoor material handling operations across industries. Their stable structure, precise movements, adaptability, and varied load capacities make them essential tools for ensuring efficient and controlled material handling within confined operational spaces.
Here's a table comparing the unique features of Overhead Gantry Cranes and highlighting their differences and similarities:
| Features | Overhead Gantry Cranes | Overhead Bridge Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility and Flexibility | Equipped with supportive legs/stands for movement | Fixed on elevated runways |
| Offers mobility across various terrains | Limited mobility, designed for fixed locations | |
| Outdoor Applications | Specifically designed for outdoor usage | Primarily intended for indoor applications |
| Withstands varying weather conditions | Not as weather-resistant as gantry cranes | |
| Higher Load Capacities | Built for handling heavier loads efficiently | Capable of handling moderate to heavy loads |
| Offers increased lifting capacities | Lifting capacities may vary based on setup | |
| Cost-Effective Solutions | Tailored for cost-effective specialized tasks | Provides economical solutions for certain applications |
| Economical handling for specific scenarios | Offers cost-efficiency for various applications |
Similarities:
- Both types of cranes offer lifting and material handling capabilities.
- Serve as vital equipment in industrial settings for varied applications.
- Utilize hoists, trolleys, and other similar core components for material handling.
Differences:
- Mobility and Application: Gantry cranes offer mobility and are well-suited for outdoor usage, while bridge cranes are primarily designed for fixed indoor applications.
- Load Capacities: Gantry cranes generally handle heavier loads compared to bridge cranes.
- Specificity in Design: Gantry cranes are tailored for outdoor and versatile applications, whereas bridge cranes are more specialized for indoor setups.
This table highlights the distinctions and similarities between Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes, emphasizing their unique features in terms of mobility, application versatility, load capacities, and cost-effective solutions tailored to specific industrial needs.
Comparison of crane price and cost-affecting factors
Comparing the prices of Overhead Bridge Cranes and Overhead Gantry Cranes of the same capacity used in similar applications involves various factors that impact the overall cost. Typically, several elements influence the pricing of these crane types:
- Structure and Design: Overhead Bridge Cranes are installed on elevated runways, requiring sturdy structural support within indoor settings. This setup may involve additional expenses related to structural modifications, runway construction, and installation, impacting the overall cost.
- Installation Requirements: Overhead Gantry Cranes, designed for outdoor usage, may require less groundwork and structural modifications compared to the fixed runways needed for Overhead Bridge Cranes. The ease of installation in outdoor settings might affect the total installation cost.
- Customization and Features: Both crane types offer various customization options such as different span lengths, hoist configurations, control systems, and additional features. The level of customization desired can significantly influence the overall price.
- Operational Environment: The specific operational environment where the cranes will be utilized also impacts pricing. Overhead Gantry Cranes adapted for outdoor applications may need weather-resistant features, which could affect the price compared to indoor-oriented Overhead Bridge Cranes.
- Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs: Consideration of maintenance requirements and associated costs over the crane's lifespan is crucial. Outdoor cranes might incur different maintenance costs due to exposure to weather elements compared to indoor cranes.
- Brand, Supplier, and Market Variations: Different manufacturers, suppliers, geographic locations, and market fluctuations can cause price variations for similar capacity cranes.
In a general sense, Overhead Bridge Cranes may sometimes have a higher upfront cost due to installation complexities and indoor infrastructure requirements. On the other hand, Overhead Gantry Cranes might involve lower initial setup costs but could have higher maintenance expenses in certain scenarios, especially if specialized features for outdoor durability are require
The actual price comparison would depend on the specific requirements of the application, the customization needed, and other factors mentioned above. Evaluating these factors comprehensively is crucial in determining the most cost-effective solution that meets both operational needs and budget constraints. Consulting crane suppliers or manufacturers to get precise quotes based on specific requirements would provide a clearer picture of the price differences between the two crane types for similar capacities and applications.
Here's a comparison table showcasing potential cost factors between Overhead Bridge Cranes and Overhead Gantry Cranes of the same capacity used in similar applications:
| Cost Factors | Overhead Bridge Cranes | Overhead Gantry Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Structure and Design | Fixed structure on elevated runways within indoor settings might require structural modifications, impacting costs | Supported by legs/stands, potentially requiring less groundwork for installation, reducing structural modification expenses |
| Installation Requirements | Installation might involve complexities related to runway construction and indoor structural support | May require less groundwork and structural changes, potentially easing installation and reducing associated costs |
| Customization and Features | Customization options available for spans, hoist configurations, and control systems, influencing overall costs | Similar customization options, but potential differences in weather-resistant features could impact prices |
| Operational Environment | Primarily designed for indoor settings, impacting potential weather resistance and specialized features | Designed for outdoor usage, might require additional weather-resistant features, affecting costs |
| Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs | Maintenance costs within indoor settings may vary compared to potential weather-related maintenance for outdoor use | Maintenance expenses could differ due to weather exposure, affecting long-term costs |
| Brand and Supplier Variations | Different manufacturers, suppliers, and market variations could impact prices for similar capacities | Market variations and brand choices could affect pricing for similar capacity cranes |
| Total Cost Evaluation | Higher upfront costs due to installation complexities and indoor infrastructure requirements | Potentially lower initial setup costs but may have varying maintenance expenses depending on outdoor-specific features |
Please note that the costs mentioned above are subject to various factors such as customization, specific application needs, supplier quotes, geographic location, and market dynamics. The table serves as a general comparison guide highlighting potential cost variances between Overhead Bridge Cranes and Overhead Gantry Cranes based on their distinct features, installation requirements, and operational environments.
Typical Applications: Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes
Industries where Overhead Gantry Cranes Excel:
Shipping Yards:
- Container Handling: Overhead Gantry Cranes efficiently load and unload containers from ships and move them around storage yards.
- Port Operations: They facilitate the smooth flow of cargo in maritime logistics, handling goods of varying sizes.
Construction Sites:
- Material Handling: Ideal for lifting and moving heavy construction materials and equipment across construction sites.
- Flexibility: Their mobility allows for easy repositioning, aiding in diverse construction activities.
Warehousing and Logistics:
- Inventory Management: Overhead Gantry Cranes assist in managing inventory by lifting and relocating goods within warehouses.
- Efficient Storage: They enable stacking and organizing goods in high-rise storage facilities.
Railroad Maintenance:
- Railway Operations: Overhead Gantry Cranes support railway maintenance by lifting heavy components for repairs and installations.
- Efficient Maintenance: They aid in the upkeep of rail infrastructure, ensuring smooth railway operations.
Industries Benefitting from Overhead Bridge Cranes:
Manufacturing Plants:
- Assembly Line Operations: Overhead Bridge Cranes facilitate the movement of materials and components across manufacturing assembly lines.
- Equipment Handling: Efficiently handles heavy machinery in manufacturing processes.
Automotive Industry:
- Vehicle Production: Overhead Bridge Cranes aid in vehicle assembly by transporting car parts within automotive plants.
- Heavy Component Handling: They handle heavy components like engines and chassis effectively.
Steel Mills:
- Steel Handling: Overhead Bridge Cranes are instrumental in lifting and moving raw materials and finished steel products within steel manufacturing plants.
- High Load Capacities: Their capability to handle heavy loads suits the demands of steel production.
Aerospace Facilities:
- Aircraft Manufacturing: Overhead Bridge Cranes assist in the assembly of aircraft by maneuvering large and heavy aerospace components.
- Precision Handling: Their precise movements are crucial for handling delicate aerospace parts.
These typical applications highlight the industries where Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes play pivotal roles, showcasing their significance in diverse sectors by facilitating efficient material handling, maintenance, and logistics operations within specific industrial environments.
Differences:
Overhead Gantry Cranes:
- Excel in open environments such as shipping yards, construction sites, and railroads.
- Emphasize mobility and adaptability in handling varied loads across diverse terrains.
Overhead Bridge Cranes:
- Predominantly thrive in indoor settings within manufacturing plants, automotive, steel mills, and aerospace facilities.
- Highlight precision movements and suitability for assembly line operations and heavy machinery handling.
Similarities:
- Both crane types offer efficiency in material handling and maintenance within their respective industries.
- Provide crucial support in lifting heavy loads, but their specialization lies in different operational environments and applications.
This table outlines the specific industries where Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes excel, showcasing their distinct applications and environments where their unique features and capabilities are most beneficial.
Comparison by Capacity: Overhead Gantry Cranes vs. Overhead Bridge Cranes
Design and Configuration of Different Capacities:

Overhead Gantry Cranes 40 ton project in Kenya for your reference:
5 to 50 tons: Designed with sturdy girders, supported by legs/stands.
- Configuration: Single or double girder setups depending on capacity.
- Mobility: Offered with rubber-tired or rail-mounted options.
- Controls: Can feature radio remote control or cabin operation for larger capacities.
- Structural Variants: Adaptability in span width and lift heights based on the application requirements.

Overhead Bridge Cranes 40 ton project in USA for your reference :
5 to 50 tons: Utilize robust girder structures fixed on elevated runways.
- Configuration: Single or double girder based on lifting capacities.
- Movement: Controlled movement along fixed runways.
- Controls: Equipped with pendant or cabin control systems for efficient operations.
- Customization: Tailored designs for specific spans and lifting heights, ensuring precision in material handling.
Typical Applications for Different Capacities:
5 ton Capacity:
- Gantry Crane: Used in small-scale manufacturing, workshops, and maintenance areas.
- Bridge Crane: Ideal for light-duty tasks in assembly lines and small warehouses.
10 ton Capacity:
- Gantry Crane: Commonly employed in automotive plants and medium-sized manufacturing units.
- Bridge Crane: Used in larger warehouses and distribution centers.
15 ton Capacity:
- Gantry Crane: Found in shipyards and medium-scale manufacturing.
- Bridge Crane: Applied in heavy fabrication and machining industries.
20 ton Capacity:
- Gantry Crane: Seen in steel mills and foundries for handling heavy components.
- Bridge Crane: Used in aerospace and heavy manufacturing sectors.
30 ton Capacity:
- Gantry Crane: Employed in container handling at ports and construction sites.
- Bridge Crane: Utilized in the paper industry for handling large rolls.
40 ton Capacity:
- Gantry Crane: Used in railway maintenance and large-scale infrastructure projects.
- Bridge Crane: Found in mining operations and heavy construction sites.
50 ton Capacity:
- Gantry Crane: Common in heavy industries such as steel processing and petrochemical plants.
- Bridge Crane: Applied in power generation plants for turbine handling and maintenance.
These comparisons highlight the design aspects, configurations, and typical applications across various capacities for both Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes. Understanding their capabilities aids in choosing the most suitable crane for diverse industrial applications based on lifting requirements and operational needs.
Providing exact cost comparisons for different tonnages of Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes can be challenging due to the variability in pricing influenced by multiple factors like brand, customization, geographic location, and market dynamics. However, I can offer a general comparison of potential cost considerations based on the tonnage and typical applications:
| tonnage | Typical Applications | Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 5 ton | Gantry: Small-scale manufacturing, workshops | Generally lower compared to higher tonnages due to smaller capacities |
| Bridge: Light-duty tasks in assembly lines, warehouses | Lower cost due to lighter capacity, suitable for smaller operations | |
| 10 ton | Gantry: Automotive plants, medium-sized manufacturing | Moderate cost, higher than 5 ton due to increased load capacity |
| Bridge: Larger warehouses, distribution centers | Moderate cost for increased capacity, suitable for medium-scale operations | |
| 15 ton | Gantry: Shipyards, medium-scale manufacturing | Moderate to higher cost due to increased capacity and application diversity |
| Bridge: Heavy fabrication, machining industries | Moderately higher cost, suitable for heavy-duty tasks | |
| 20 ton | Gantry: Steel mills, foundries | Higher cost due to increased load handling capabilities |
| Bridge: Aerospace, heavy manufacturing sectors | Higher cost for heavy industries and specialized applications | |
| 30 ton | Gantry: Ports, construction sites | Higher cost due to increased capacity and usage in heavy applications |
| Bridge: Paper industry for large roll handling | Higher cost due to heavy-duty usage in specific industries | |
| 40 ton | Gantry: Railway maintenance, large-scale infrastructure | Considerably higher cost due to heavy-duty usage and specialized applications |
| Bridge: Mining operations, heavy construction sites | Considerably higher cost for specialized heavy industries | |
| 50 ton | Gantry: Steel processing, petrochemical plants | Higher cost due to high load capacity and usage in heavy industries |
| Bridge: Power generation for turbine handling | Higher cost for specialized handling in power generation |
Please note, these estimations are general and indicative, subject to variations based on specific requirements, brand choices, geographical locations, and other influencing factors. Actual pricing details should be obtained by consulting crane suppliers or manufacturers, considering customization needs and specific industry applications.
Top Concerns of Users: Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes
Safety Considerations for Both Types of Cranes:
Overhead Gantry Cranes:
- Concerns: Potential risks during outdoor operations, especially in varying weather conditions.
- Safety Measures: Regular inspections of structural integrity, adherence to load capacities, and weather-related precautions.
Overhead Bridge Cranes:
- Concerns: Safety during indoor operations, ensuring precise movements in confined spaces to prevent accidents.
- Safety Measures: Regular checks of control systems, operator training for precise maneuvering, and adherence to safety protocols in enclosed spaces.
Maintenance Requirements and Downtime:
Overhead Gantry Cranes:
- Maintenance Needs: Regular checks for wear and tear due to outdoor usage, such as corrosion prevention for components exposed to the elements.
- Downtime Mitigation: Scheduled maintenance during non-peak hours to minimize operational disruptions.
Overhead Bridge Cranes:
- Maintenance Needs: Monitoring of control systems and runway beams to ensure smooth operations within indoor settings.
- Downtime Mitigation: Planned maintenance and timely repairs to prevent unforeseen breakdowns.
Initial Investment and Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness:
Overhead Gantry Cranes:
- Initial Investment: Consideration of initial setup costs, including outdoor-specific infrastructure requirements.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluation of long-term benefits in outdoor applications against initial investments.
Overhead Bridge Cranes:
- Initial Investment: Assessment of setup costs for indoor installations and control systems.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Focus on long-term efficiency and productivity gains within indoor operational environments.
Suitability for Specific Operational Environments:
Overhead Gantry Cranes:
- Considerations: Assessing adaptability across different terrains and varying weather conditions.
- Suitability Measures: Selection based on mobility requirements and load capacities specific to outdoor tasks.
Overhead Bridge Cranes:
- Considerations: Suitability within limited indoor spaces and varying manufacturing layouts.
- Suitability Measures: Customization based on height and span requirements for efficient operations within confined spaces.
Understanding and addressing these concerns are critical for users and potential purchasers to make informed decisions based on safety, maintenance, cost-effectiveness, and suitability within specific operational environments while selecting the appropriate crane type for their industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes
Comparison of Load Capacities and Lifting Heights:
Q: How do load capacities and lifting heights differ between Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes?
A: Overhead Gantry Cranes are well-suited for heavy loads in outdoor settings, with capacities reaching up to 50 tons or more. Meanwhile, Overhead Bridge Cranes, commonly used indoors, may have similar load capacities but are tailored for different lifting heights based on facility requirements.
Differences in Installation and Setup:
Q: What are the primary differences in the installation and setup processes for these crane types?
A: Overhead Gantry Cranes generally require more groundwork, such as creating stable foundations for their supportive legs/stands. In contrast, Overhead Bridge Cranes involve mounting on fixed runways or beams, requiring structural support within indoor settings.
Adaptability to Varying Weather Conditions:
Q: How adaptable are these cranes to different weather conditions?
A: Overhead Gantry Cranes are designed with weather-resistant features for outdoor usage, providing better adaptability to varying weather conditions compared to Overhead Bridge Cranes, which are primarily suitable for controlled indoor environments.
Customization Options Available for Different Industries:
Q: Are there customization options available for specific industries using these cranes?
A: Both types offer customization options. Overhead Gantry Cranes can be customized for various terrains and outdoor tasks, whereas Overhead Bridge Cranes can be tailored for different spans, lifting capacities, and height requirements within indoor industrial setups.
E. Maintenance Schedules and Expected Lifespan:
Q: What are the maintenance schedules and expected lifespans of these crane types?
A: Maintenance schedules vary based on usage and environmental factors. Typically, regular inspections, lubrication, and part replacements are scheduled to ensure optimal performance. The expected lifespan also varies but can range from 20 to 30 years with proper maintenance and care for both types of cranes.
Understanding these frequently asked questions regarding load capacities, installation, adaptability, customization options, maintenance, and expected lifespan is crucial for users and purchasers seeking clarity before selecting the appropriate crane type that best suits their industrial needs.
Conclusion
Overhead Gantry Cranes:
- Strengths: Excel in outdoor settings, offering mobility, higher load capacities, and adaptability to diverse terrains and weather conditions.
- Applications: Ideal for shipping yards, construction sites, warehousing, and railway maintenance due to their versatility and robustness.
Overhead Bridge Cranes:
- Strengths: Primarily designed for indoor use, providing precise movements, stability, and varied load capacities for manufacturing, automotive, steel, and aerospace industries.
- Applications: Suited for assembly lines, heavy machinery handling, and precise material positioning within confined spaces.
Selecting the right crane type is pivotal in ensuring efficient material handling operations within industrial environments. Understanding the specific operational requirements, such as load capacities, environment (indoor or outdoor), mobility needs, and precise movements, is essential for optimal crane selection. Whether it's the adaptability of Overhead Gantry Cranes in outdoor scenarios or the precision of Overhead Bridge Cranes in controlled indoor spaces, tailoring the choice to meet distinct needs significantly impacts productivity, safety, and cost-effectiveness in material handling processes.
In conclusion, both Overhead Gantry Cranes and Overhead Bridge Cranes offer unique strengths and applications. Choosing the most suitable crane type requires a comprehensive assessment of specific operational demands, emphasizing the significance of a tailored approach to ensure optimal efficiency and safety in material handling operations across diverse industrial landscapes.
Related Products

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch




