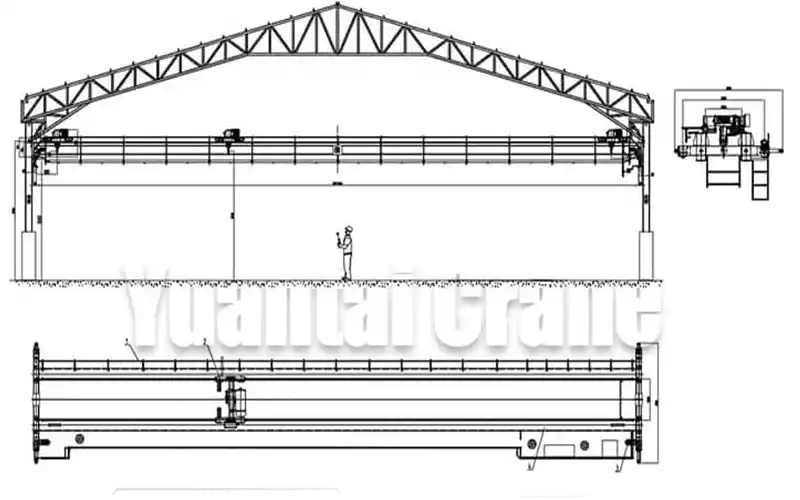
Arched vs. Flat Beam 5-Ton Overhead Cranes
Compare arched and flat beam cranes to optimize headroom and lifting height for low-ceiling gable roof facilities.
Category: Featured
Your Trusted Overhead Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Arched vs. Flat Beam 5-Ton Overhead Cranes
Choosing the Best Design for Low-Ceiling Gable Roof Spaces
Overview of Crane Selection for Low-Ceiling Facilities
Selecting the right overhead crane for a low-ceiling facility is a critical decision that can impact the efficiency and safety of daily operations. In spaces with limited vertical clearance, the crane must be carefully chosen to make the most of the available room without sacrificing performance. This is especially important for businesses that need to lift and maneuver loads in confined environments.
In low-ceiling settings, two main factors play a significant role in crane selection: clearance and lifting height. Clearance refers to the vertical distance between the crane's beam and the facility's floor, while lifting height defines how high the crane can raise loads. Both are essential for determining whether the crane can handle specific tasks, such as stacking materials, moving parts, or transporting heavy loads between different levels.
Choosing a crane that optimizes these factors ensures smooth, efficient operations and reduces the risk of accidents or damage to the facility. A well-chosen crane can help businesses maximize their space and meet operational needs while staying within the constraints of a low-ceiling environment.
Key Challenges in Low-Ceiling Spaces
The main challenge for businesses operating in low-ceiling facilities is balancing the need for sufficient clearance and lifting height.
- Clearance: With limited space between the crane's beam and the floor, achieving enough clearance to lift and move loads safely is critical. If the clearance is too low, the crane will not be able to function effectively, limiting its ability to lift heavier or larger loads. This can cause operational delays, inefficiencies, or even safety risks.
- Lifting Height: Lifting height is another key concern. In many industries, it’s important to be able to lift materials or equipment to significant heights. In a low-ceiling facility, this means the crane must be designed to maximize vertical lift while avoiding interference with the roof structure or other obstacles. Without proper lifting height, operations may be restricted, and businesses could face increased costs or delays.
Finding the right balance between clearance and lifting height is crucial. The design of the crane will either enable optimal space usage or become a limiting factor in the facility’s productivity.
Purpose of the Guide
The purpose of this guide is to compare two popular crane designs—arched beam and flat beam—specifically for 5-ton overhead cranes used in low-ceiling facilities. By understanding the differences between these two designs, businesses can make informed decisions about which crane type will best suit their needs.
This guide will focus on how each design affects key factors such as:
- Headroom and Clearance: Arched beam cranes typically provide more clearance beneath the crane, while flat beam designs may offer less clearance but can be suitable for tighter spaces.
- Lifting Height: How each crane design influences the maximum lifting height and how that can impact day-to-day operations.
- Space Utilization: How each design works with the available vertical space, ensuring maximum operational efficiency.
By the end of this guide, businesses will have a clearer understanding of the advantages and limitations of both arched and flat beam cranes, helping them select the most appropriate option based on their facility's specific ceiling height, space constraints, and lifting requirements.
Overhead Crane Designs
Flat Beam Cranes: Description and Design Characteristics
A flat beam crane features a horizontal, flat main beam supported by two end trucks that run along crane rails. The beam is typically a single, continuous piece of steel, designed for simplicity and compactness. Compared to arched beam cranes, this design has fewer complex elements, which makes it easier to manufacture and maintain.
- Structure: The beam is generally rectangular or I-shaped, spanning the width of the facility. This design supports the lifting mechanism, ensuring smooth operations.
- Main Components: Key components of a flat beam crane include the main beam, hoist, trolley, end trucks, and crane rails. The hoist travels along the beam, lifting and lowering loads as needed.
- Installation: The simple, flat design makes flat beam cranes particularly suitable for facilities with limited headroom, as it reduces the overall height of the crane system.
Advantages of Flat Beam Cranes
- Simplicity and Lower Cost:Simple Design: Fewer components are needed for construction, making flat beam cranes a cost-effective option for businesses with tighter budgets.Lower Manufacturing Costs: The simple design also means lower manufacturing and installation costs compared to more complex crane systems.
- Ease of Maintenance:The fewer moving parts in a flat beam crane translate into easier maintenance. There are fewer specialized components that could need repair or replacement over time.
- Compact and Efficient for Low-Ceiling Facilities:Ideal for facilities with very low ceiling heights, the minimal vertical profile ensures the crane doesn't obstruct other overhead systems or reduce headroom unnecessarily.This design maximizes available space while minimizing the footprint.
- Effective for Light to Medium Duty Loads:Flat beam cranes are commonly used for lighter loads (up to 5 tons), offering smooth operation for these types of applications.
- Reliability and Durability:The simple design is typically reliable over time, and with regular maintenance, these cranes have a long operational lifespan.
Arched Beam Cranes: Description and Design Characteristics
An arched beam crane features a curved main beam, providing greater clearance beneath the beam compared to flat beam cranes. This curvature allows for a higher lift and more space between the beam and the floor, which is beneficial for facilities where maximizing headroom is a priority.
- Structure: The arched beam has a gentle curve, enabling the hoist to travel under the arch, providing increased vertical clearance for lifting taller materials or larger loads.
- Main Components: An arched beam crane includes the arched main beam, hoist and trolley system, end trucks, and crane rails. Similar to the flat beam crane, it operates along the rails, but the key difference is the additional vertical space.
- Installation: Arched beam cranes are best suited for facilities that require higher clearance, such as those with sloped or gable roofs. The design allows for more flexibility in terms of architectural design, making it adaptable to various facility layouts.
Advantages of Arched Beam Cranes
- Increased Headroom:The arched design provides extra clearance beneath the beam, which is highly beneficial in facilities with low ceilings. This additional height enables operators to perform tasks that require vertical lift, such as stacking or moving larger components.
- Enhanced Lifting Height:The curvature of the beam increases the lifting height compared to flat beam cranes. This feature allows operators to lift taller materials without sacrificing space or modifying the building’s structure.
- Improved Space Utilization:The increased clearance allows arched beam cranes to help facilities utilize vertical space more efficiently. This is particularly valuable in heavy-duty manufacturing environments where the ability to lift larger loads without obstruction is crucial.
- Higher lifting capacity and better clearance improve the overall efficiency of operations, reducing the need for costly facility alterations.
- Suitable for Heavier Loads:The arched design provides better structural support, making these cranes ideal for heavier loads. They can accommodate medium to heavy-duty operations, where lifting capacities beyond 5 tons are required.
Choosing the Best Crane for Your Needs
Both flat beam and arched beam cranes offer unique advantages based on the specific needs of a facility. The choice between the two designs will largely depend on factors such as ceiling height, load requirements, and space constraints:
- Flat Beam Cranes are more suitable for low-ceiling facilities, offering a compact design with lower costs and easier maintenance. They are most effective for light to medium-duty applications where vertical lift is less critical.
- Arched Beam Cranes, on the other hand, provide greater vertical clearance, making them ideal for facilities that require higher lifting heights and the ability to handle heavier loads. The increased headroom can significantly improve space utilization and operational flexibility in higher-clearance environments.
Key Differences: Arched vs. Flat Beam Cranes
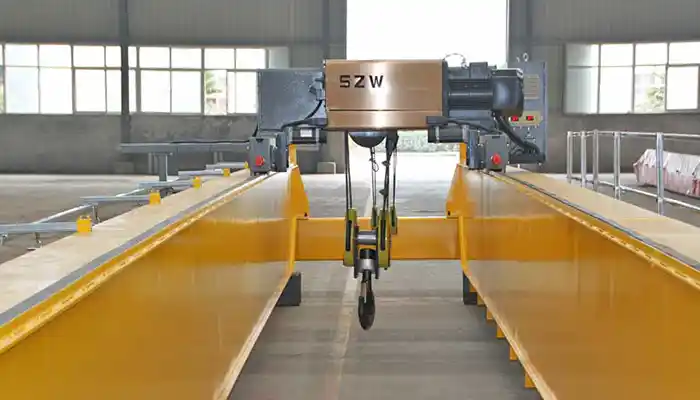

box girder with flat beam design, European style double girder overhead crane with electric hoist trolley
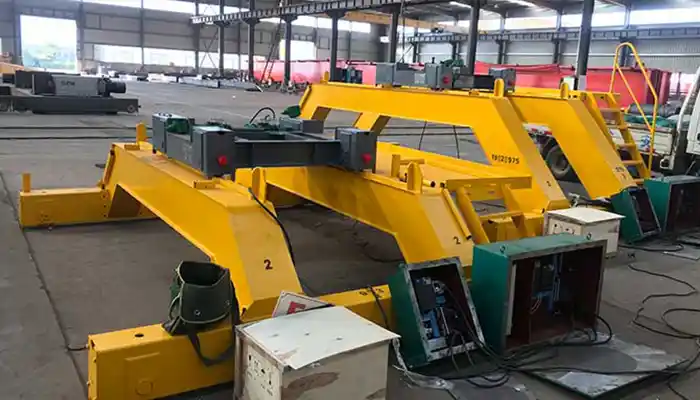

box girder explosion proof crane 5 ton with arched girder design project for sale Yeman
Clearance and Headroom
Arched Beam Cranes:
The arched beam design is specifically engineered to provide greater clearance beneath the crane’s main beam. The curve in the beam creates extra vertical space, allowing for more headroom for operators and equipment underneath. This is particularly valuable in low-ceiling facilities, as it enables the crane to be used in areas where there may not be enough vertical space for flat beam cranes. The increased clearance allows for easier handling of taller loads and helps prevent obstacles from interfering with the crane's operation.
- Key Benefit: The main advantage of the arched design is its ability to maximize vertical space without sacrificing the crane's ability to lift heavy loads. This is crucial in environments like manufacturing plants or warehouses where clearance beneath the beam can be a limiting factor.
Flat Beam Cranes:
On the other hand, flat beam cranes have a much lower headroom, as the main beam lies flat. The beam's design does not allow for significant vertical clearance beneath it, making flat beam cranes suitable for facilities where ceiling height is extremely limited. In these spaces, flat beam cranes can still be used efficiently, but the clearance will always be limited by the height of the beam itself.
- Key Limitation: Flat beam cranes are not ideal for environments that require lifting objects or handling materials that are taller than the limited space beneath the beam. For operations that need more clearance, flat beam cranes may not be the best choice.
| Factor | Arched Beam Cranes | Flat Beam Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Clearance and Headroom | Higher clearance beneath the beam due to the curved design. Ideal for maximizing vertical space in low-ceiling facilities. | Limited headroom, with the beam sitting flat against the ceiling. Best for very low-ceiling spaces. |
| Key Benefit | Provides more usable vertical space for taller loads. | Suitable for spaces with minimal vertical clearance. |
| Key Limitation | Requires more height for installation, may not be ideal for very low ceilings. | Less clearance beneath the beam, limiting taller operations. |
Lifting Height
Arched Beam Cranes:
An arched beam design provides increased lifting height, as the curvature of the beam creates additional vertical space for the hoist and load. This design allows the crane to lift objects higher without interfering with the ceiling or other overhead obstacles. The extra height provided by the arched beam makes it easier to handle larger or bulkier loads, or to operate in facilities with elevated stacking requirements.
- Impact on Lifting Operations: The higher clearance and lifting height of arched beam cranes can improve operational efficiency, as operators can stack and lift materials to greater heights without the concern of running out of headroom.
Flat Beam Cranes:
In contrast, flat beam cranes provide limited lifting height. Since the beam sits directly across the crane’s travel path without any curvature, the hoist has less space to lift objects. This can be a disadvantage when increased vertical lift is needed. Facilities that need to lift tall objects or materials to higher levels will find flat beam cranes less effective in comparison to arched beam designs.
- Impact on Lifting Operations: While flat beam cranes are still functional for lifting loads within the limited height range, they may not be suitable for operations where lifting height is critical. If more lifting height is needed in low-ceiling facilities, an arched beam crane might be the better option.
| Factor | Arched Beam Cranes | Flat Beam Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Lifting Height | Higher lifting height due to the beam’s curvature, allowing the hoist to travel higher without interference from overhead structures. | Lower lifting height, as the beam is flat and restricts the vertical lift of the hoist. |
| Impact on Operations | Allows for taller loads and greater vertical stacking without obstruction. | Best for operations where the load height requirement is minimal. |
| Key Advantage | Increases the range of vertical lift and better for operations requiring high lifting capabilities. | Suitable for light-duty operations where vertical lift isn’t a priority. |
Space Utilization
Arched Beam Cranes:
Arched beam cranes are particularly beneficial when it comes to maximizing the vertical space in a low-ceiling facility. By providing extra headroom, the crane allows operators to use the space above the beam for other functions, such as storing equipment, maintaining clearances for ventilation systems, or maximizing available working space beneath the beam. This extra space can enhance overall facility layout and increase productivity.
Pros:
- Better space efficiency: Increased vertical clearance allows for greater operational flexibility in crowded environments.
- More flexibility in use: Can be used for taller loads or multiple-layer storage without sacrificing vertical space.
Cons:
- More complex installation: The curved beam can make installation more challenging in certain environments, especially where the ceiling is irregular or sloped.
- Higher cost: Arched beam designs are typically more expensive to manufacture and install due to their complexity and the materials required for the arched structure.
Flat Beam Cranes:
Flat beam cranes make the most efficient use of horizontal floor space but are more restricted when it comes to maximizing vertical clearance. Because the beam sits flat against the ceiling, it can make use of almost all the ceiling height available, but this comes at the cost of reduced space beneath the crane. Flat beam designs are ideal for facilities where horizontal space is a premium, but vertical clearance is not as critical.
Pros:
- Compact design: Ideal for facilities with minimal vertical space and can be easily installed without significant structural changes.
- Cost-effective: Typically, flat beam cranes are less expensive to design and install compared to arched beam cranes.
Cons:
- Limited vertical space: Because of the flat beam, there is less flexibility in terms of the clearance and lifting height for operations involving larger or taller loads. This could result in less overall space utilization in environments that require more height for operations.
- Restricted operational flexibility: In facilities where height is a major factor, flat beam cranes may not fully capitalize on available space, limiting their potential.
| Factor | Arched Beam Cranes | Flat Beam Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Space Utilization | Maximizes vertical space, allowing for taller stacks, better workflow, and more flexibility for material handling. | Optimizes horizontal space for lighter loads and smaller operations in confined spaces. |
| Key Benefit | Better for complex operations requiring more headroom, such as stacking or working with larger loads. | Compact design, ideal for spaces where horizontal space is the main concern. |
| Key Limitation | May require more complex installation due to the beam’s curvature and higher cost. | Limited operational flexibility in facilities requiring vertical lift and taller loads. |
| Space Efficiency | Efficient use of vertical height but could reduce horizontal space usage. | More efficient for facilities that need to maximize horizontal space while minimizing vertical clearance. |
Summary of Key Differences
- Clearance and Headroom: Arched beam cranes provide more headroom and clearance beneath the crane’s beam, making them ideal for taller loads or maximizing the usable vertical space. Flat beam cranes, on the other hand, are better suited for facilities with limited ceiling height, offering less clearance beneath the beam.
- Lifting Height: Arched beam cranes offer greater lifting height, enabling operators to lift materials higher and more effectively utilize vertical space. Flat beam cranes are more restricted in their lifting height, which can be a significant drawback in certain applications.
- Space Utilization: Arched beam cranes enhance vertical space utilization, allowing for better flexibility in how the facility can be arranged and used. Flat beam cranes, while more compact and cost-effective, are better suited for maximizing horizontal space, but may not fully optimize the vertical space available.
Choosing between an arched beam and flat beam crane ultimately depends on the specific needs of the facility—whether clearance, lifting height, or space efficiency is the primary concern.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Arched and Flat Beam Designs
Ceiling Height and Roof Shape
When selecting between arched and flat beam cranes, the ceiling height and roof shape are crucial factors to consider, as they directly impact the crane's performance and installation feasibility.
Ceiling Height:
- Arched Beam Cranes: Ideal for facilities with low or limited ceiling height. The arched design provides extra headroom beneath the crane, making it a better choice for low-ceiling environments where maximizing vertical space is critical.
- Flat Beam Cranes: Best suited for facilities with very low ceilings where vertical space is already minimal. However, flat beam cranes provide less clearance underneath, so they are not ideal for spaces where lifting taller loads is required.
Roof Shape:
- Arched Beam Cranes: Perform well in facilities with a gable roof or sloping roof design. The curved beam design accommodates the slope, ensuring that the crane can be positioned without interference from the roof structure.
- Flat Beam Cranes: Perform well in facilities with flat roof structures. These cranes do not require adjustments based on roof shape and are simpler to install in straightforward environments with flat ceilings.
Importance of Understanding Clearance Limitations: Each crane type has unique clearance requirements that must be carefully assessed based on the facility’s ceiling height. Ensuring that the crane design fits within the available space without compromising lifting capabilities is essential for efficient operations.
Operational Requirements
Load Capacity:
For both arched and flat beam cranes, meeting the operational load capacity is essential. The 5-ton load requirement should be well within the capabilities of both designs, but other factors come into play for long-term performance.
- Arched Beam Cranes: These cranes are typically well-suited for heavier loads and environments requiring high lifting heights. The increased headroom can allow for the handling of larger, bulkier materials, which may be required in industries like manufacturing or construction.
- Flat Beam Cranes: These are ideal for handling light to medium loads, such as materials up to 5 tons, in lower-ceiling environments. They are typically used in facilities where lifting height is not as important.
Frequency and Nature of Crane Operations:
The frequency and nature of crane operations can also influence the choice of crane type.
- Arched Beam Cranes: These cranes are more suited for environments where operations are repetitive and involve heavy or frequent lifting. The additional headroom provided by the arched design ensures that these cranes can operate efficiently over long periods without clearance issues.
- Flat Beam Cranes: These cranes are better suited for lighter, less frequent lifts. They are often used in smaller spaces where low to moderate lifting needs exist but may struggle in environments with heavy-duty, repetitive lifting tasks.
Space Constraints
In facilities where space is limited, the beam design plays an important role in determining maneuverability and how efficiently the crane utilizes the available area.
- Arched Beam Cranes: The arched design requires more vertical space, but this can often be an advantage in narrow or crowded spaces, where the crane needs to lift taller loads or stack materials higher. However, the installation might be more complex in areas with limited ceiling space due to the height required for the arch.
- Flat Beam Cranes: Flat beam cranes are more compact and suitable for narrow or crowded spaces where horizontal space is more critical than vertical clearance. The flat beam design allows the crane to fit into areas with limited vertical space but doesn’t offer the flexibility to handle taller loads or materials that need higher lifting heights.
Impact on Maneuverability:
- Arched Beam Cranes: The increased height from the arched design might make the crane harder to maneuver in very tight areas, though the trade-off is greater headroom for lifting.
- Flat Beam Cranes: More maneuverable in very tight or confined areas due to the lower profile. However, this comes at the cost of limited lifting height and vertical clearance, which could hinder performance in operations requiring high lifts or larger equipment.
Budget and Cost-Effectiveness
When choosing between arched and flat beam cranes, the initial cost, installation, and maintenance are important factors to consider.
- Arched Beam Cranes: Typically, arched beam cranes are more expensive due to their complex design, the materials required to support the arch, and the greater headroom they provide. Installation is also more challenging, as the crane's structural requirements may demand more labor and time for assembly. Additionally, maintenance may be slightly higher due to the added components involved in the curved design.
- Flat Beam Cranes: Flat beam cranes are generally more affordable and simpler to install. The design requires fewer materials and components, resulting in lower manufacturing costs. Installation is faster and requires fewer modifications to the facility, making it a cost-effective option for businesses with a tight budget. Maintenance is also easier and less expensive due to the simple structure.
Cost Comparison:
Arched Beam Cranes:
- Higher initial cost for manufacturing and installation.
- Higher long-term maintenance costs due to more complex structural design.
- Suitable for environments where headroom and lifting height are essential, justifying the extra investment.
Flat Beam Cranes:
- Lower initial cost, offering significant cost savings upfront.
- Lower maintenance costs and simpler repairs.
- Ideal for operations that do not require significant vertical clearance or high lifting heights, making it a cost-effective solution for lighter-duty tasks.
Summary of Factors to Consider
| Factor | Arched Beam Cranes | Flat Beam Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Ceiling Height & Roof Shape | Better for low-ceiling spaces with gable or sloping roofs; offers more headroom and clearance. | Best for facilities with flat roofs and very low ceilings, where minimal vertical clearance is needed. |
| Load Capacity | Suited for handling heavy loads and taller materials, offering more flexibility in lifting height. | Suitable for lighter loads up to 5 tons, with more limited lifting height. |
| Frequency & Nature of Operations | Ideal for repetitive, heavy, and frequent lifting tasks. | Best for lighter, less frequent lifting tasks. |
| Space Constraints | Provides more headroom, but may be less maneuverable in extremely tight spaces. | More maneuverable in narrow spaces but with limited lifting height and headroom. |
| Budget & Cost-Effectiveness | Higher upfront cost, more complex installation and maintenance, but suitable for taller loads. | More affordable, quicker installation, and lower maintenance costs, suitable for simpler tasks. |
When selecting between arched and flat beam cranes, businesses must carefully evaluate their specific needs in terms of space, operational requirements, and budget to choose the design that best aligns with their facility's constraints and lifting needs.
Benefits of Arched Beam Cranes for Low-Ceiling Gable Roof Spaces
Increased Clearance
The arched beam design provides significant advantages in terms of clearance, particularly in low-ceiling environments. The curvature of the beam allows for more vertical space beneath the crane, offering the following benefits:
- More headroom for lifting operations, allowing workers to move taller materials or handle larger loads.
- The higher clearance can also reduce the risk of damage to materials or equipment due to restricted vertical space.
- The additional clearance allows for greater flexibility in choosing lifting heights without interference from overhead structures such as beams or ductwork.
For businesses operating in tight spaces where maximizing headroom is crucial, arched beam cranes provide a distinct advantage in enabling efficient and safe lifting.
Enhanced Lifting Capacity
With the increased headroom afforded by the arched beam design, these cranes are better equipped to handle larger loads and higher lifting heights. The impact on lifting efficiency includes:
- Improved lifting range: The greater clearance beneath the beam allows for a higher hoist travel, enabling more efficient lifting of taller or bulkier materials.
- Better load handling: With the ability to lift higher, arched beam cranes can handle heavier or larger loads without interference from the beam.
- Higher stacking capability: The extra vertical space allows for stacking operations or handling taller equipment, which is essential for industries like manufacturing or warehouse storage.
For operations that require moving heavy materials or taller objects, the arched beam crane maximizes lifting capacity and enhances operational efficiency.
Improved Space Flexibility
In addition to providing better headroom, the arched beam design improves space utilization within the facility. This can have multiple benefits for operations and workflow:
- Better integration with other equipment: The increased headroom can make it easier to position other machinery or equipment under the crane without interference.
- More usable floor space: The crane’s structure takes up less horizontal space while maximizing vertical clearance, allowing businesses to fit more operations into a given area.
- Increased flexibility for future expansion: With extra space available for equipment or inventory, businesses have more room to grow without worrying about crane interference.
The flexibility in space usage allows for more efficient workflows and can optimize facility operations by accommodating other machinery or storage systems alongside the crane.
Benefits of Flat Beam Cranes for Low-Ceiling Gable Roof Spaces
Lower Initial Costs
Flat beam cranes are typically more cost-effective than their arched counterparts, making them ideal for businesses on a budget or with limited lifting needs:
- Lower manufacturing costs due to the simpler design with fewer components.
- Reduced installation costs because the crane can be installed quickly without the need for special adjustments or structural reinforcements.
- Ideal for facilities with basic or low-intensity lifting requirements, where the additional cost of an arched beam crane would not provide a proportional return on investment.
For businesses looking to keep initial costs down while still achieving efficient lifting, a flat beam crane offers a budget-friendly solution.
Simplicity and Reliability
Flat beam cranes are simpler in design, which translates to several operational benefits:
- Fewer complex components: The lack of an arched beam reduces the number of parts involved, which can make the crane easier to maintain and operate.
- Lower maintenance costs: With fewer moving parts and a straightforward structure, flat beam cranes typically experience less wear and tear, resulting in reduced downtime and maintenance expenses.
- Reliability: The simpler design increases the reliability of the crane in operations, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns or technical issues.
For businesses with straightforward operational requirements or those looking for a low-maintenance solution, flat beam cranes offer a reliable and cost-efficient choice.
Best for Extremely Low Ceilings
In environments where ceiling height is extremely limited, flat beam cranes are the ideal choice for the following reasons:
- Minimal vertical clearance: Flat beam cranes are designed to sit close to the ceiling, offering maximized use of limited vertical space.
- Optimal fit for low-ceiling spaces: These cranes can be installed in areas where other crane types, including arched beam designs, would not fit due to their height requirements.
- Effective for light-duty lifting: With a focus on lower lifting heights, flat beam cranes are well-suited for operations requiring light-to-moderate lifting with minimal need for vertical clearance.
For facilities with extremely low ceilings, flat beam cranes provide the perfect solution, delivering functional lifting capabilities without compromising available vertical space.
Summary of Benefits:
| Benefit | Arched Beam Cranes | Flat Beam Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Clearance | Provides higher clearance, allowing for taller loads and greater vertical space for operations. | Limited clearance, better suited for extremely low-ceiling spaces where no extra headroom is needed. |
| Enhanced Lifting Capacity | Enables higher lifting heights, improving efficiency in handling larger or bulkier loads. | Lower lifting height, best for lighter loads or operations with no need for significant vertical travel. |
| Improved Space Flexibility | Maximizes available vertical space, allowing more room for other operations or machinery. | Better for horizontal space utilization, but limited by the low ceiling. |
| Lower Initial Costs | Typically more expensive due to design complexity and installation requirements. | More affordable with a simple design, quick installation, and reduced operational costs. |
| Simplicity and Reliability | More complex design may increase maintenance costs and operational issues. | Simpler design, with lower maintenance costs and greater operational reliability. |
| Best for Low Ceilings | Ideal for low-ceiling facilities where maximizing vertical space is essential. | Best for facilities with extremely low ceilings, where headroom is minimal and space is tight. |
Both arched beam and flat beam cranes offer distinct advantages for low-ceiling gable roof spaces, with arched beams excelling in terms of vertical clearance and lifting capacity, while flat beams offer cost-effectiveness and reliability in constrained spaces.
How to Choose the Right Crane for Your Facility
Selecting the right overhead crane for your facility, especially when dealing with low-ceiling or confined spaces, requires a thoughtful and methodical approach. The crane design you choose can impact efficiency, space utilization, and long-term operational costs. Below is a step-by-step guide and key considerations to help you choose the best crane design—whether it’s arched beam or flat beam—for your facility.
Step-by-Step Guide to Selecting the Best Crane Design
Assess Your Ceiling Height and Facility Layout
- Measure ceiling height: Before making any decisions, accurately measure the available ceiling height in various areas of your facility. Consider whether the ceiling is flat or has a gable roof, as this can influence the crane's design choice.
- Identify operational zones: Divide your facility into operational areas based on their space constraints and the types of loads you’ll be lifting. Certain areas might have more vertical space, while others are more cramped.
Why it matters: A flat beam crane is ideal for areas with minimal headroom, while an arched beam crane can provide extra clearance in taller areas, allowing for better lifting capabilities.
Consult with Crane Manufacturers and Engineers
- Work with experts: Consult with crane manufacturers or engineering consultants who specialize in overhead cranes. They can analyze your facility's layout and recommend the best crane design for your specific needs.
- Crane configuration options: Discuss whether an arched beam crane or a flat beam crane would better suit your facility’s unique structure. An expert can also provide insight into factors like beam materials, load capacity, and lifting mechanisms.
- Custom solutions: If your ceiling height is unusually low or your operational needs are complex, manufacturers can provide custom crane solutions tailored to your space.
Why it matters: Consultation with professionals ensures that you make an informed decision based on real-time data, avoiding costly mistakes and ensuring the crane fits well into your facility's design.
Evaluate the Lifting Needs
- Determine load requirements: Assess the weight and size of the loads you need to lift. For instance, a 5-ton crane may be sufficient for some operations, while others might require a crane with higher lifting capacity.
- Frequency of lifting: Consider how often the crane will be used. If it will be operating continuously or performing heavy lifts, you may need a more robust design.
- Lifting height requirements: Identify the maximum lifting height needed for the crane, factoring in any clearance obstacles like overhead pipes or ducts.
Why it matters: Knowing your lifting requirements will help you determine whether a flat beam crane (which is more suitable for limited vertical space) or an arched beam crane (providing higher lifting heights) is the best fit.
Final Decision-Making: Key Considerations
Once you’ve consulted with experts and assessed your space and lifting needs, several critical factors must guide your final decision:
Key Considerations for Final Decision
Weight Distribution
- Even weight distribution is essential for safe and efficient crane operation. Ensure that the crane’s structure and beam design are appropriate for the loads it will handle.
- Flat beam cranes may be better for evenly distributed, lighter loads, while arched beam cranes are more suited for lifting uneven, heavier loads due to their increased headroom and enhanced structural integrity.
Ease of Operation
- User-friendly operation is crucial for productivity. Choose a crane that can be operated smoothly and safely by your team.
- Consider features like remote control systems, variable speed drives, and easy access for maintenance. Both flat and arched beam cranes can offer these features, but the ease of installation and integration may differ depending on the crane design.
Why it matters: A crane that is difficult to operate or maintain can lead to downtime and operational inefficiency. Ensure that your crane design supports easy handling and minimal maintenance.
Safety Features
- Ensure the crane meets safety standards required for your facility. Safety features may include emergency stop buttons, anti-collision systems, overload protection, and safety sensors.
- Arched beam cranes may offer better clearance for safe load handling, reducing the risk of accidents in tight spaces.
Why it matters: A crane with inadequate safety features can result in workplace accidents and injuries. It’s crucial to prioritize safety in your crane selection process to protect workers and assets.
Future Scalability
- Consider future growth: Choose a crane design that can accommodate potential changes in your business needs. If you anticipate increasing load requirements, higher ceilings, or different operational needs, it’s better to choose a crane design that offers flexibility for upgrades.
- Modular design: Some crane systems are modular, meaning they can be upgraded or expanded as needed. This is an advantage for businesses planning for future expansion.
Why it matters: Planning for scalability ensures that your crane system will continue to meet your needs as your business grows, avoiding the need for frequent replacements or costly upgrades.
Summary of Key Steps to Choosing the Right Crane:
| Step | Action | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Assess Ceiling Height & Facility Layout | Measure ceiling height, evaluate operational zones, and ceiling shape. | Ensure that crane design fits within vertical space and operational needs. |
| Consult with Manufacturers & Engineers | Get expert advice on crane configuration and custom solutions. | Obtain recommendations based on facility layout and operational needs. |
| Evaluate Lifting Needs | Determine load requirements, frequency, and lifting height. | Choose a crane that meets the load capacity and lifting height needed. |
| Consider Weight Distribution, Ease of Operation, Safety, & Scalability | Evaluate weight handling, operational ease, safety features, and future growth. | Ensure the crane supports safe, efficient, and scalable operations. |
By following these steps and considering the key factors, you can confidently select the right arched or flat beam crane for your facility, ensuring optimal performance, safety, and space utilization for years to come.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Differences Between Arched and Flat Beam Designs for 5-Ton Cranes
When deciding between arched beam and flat beam designs for a 5-ton overhead crane, the primary distinction lies in the clearance and lifting height each design offers.
- Arched Beam Cranes provide increased headroom, making them the ideal choice for facilities with higher lifting needs or those operating in areas with higher ceilings or more complex operational requirements. The arched design allows for better utilization of vertical space, accommodating taller loads and offering more flexibility in operations.
- Flat Beam Cranes, on the other hand, are best suited for low-ceiling environments where maximizing headroom is less of a concern. These cranes are more compact and cost-effective, offering an efficient solution for facilities with limited vertical space but needing reliable lifting for lighter to moderate loads. Their simple design also makes them a practical choice for operations with straightforward lifting needs.
Both designs offer unique advantages depending on the specific challenges faced by your facility, whether that be space constraints, load types, or budget considerations.
Final Advice on How to Select the Best Design Based on Headroom, Operational Requirements, and Facility Constraints
Choosing the right crane design requires an in-depth evaluation of your facility’s unique constraints and operational needs:
- Headroom: If your facility has low ceilings, a flat beam crane may be the best option. If you have a gable roof or slightly higher ceilings, an arched beam crane will likely provide more headroom, which can increase efficiency and accommodate taller loads.
- Operational Requirements: Assess the type of materials you’re lifting and the frequency of crane use. If your operations require frequent or heavy lifting, an arched beam crane may offer better long-term efficiency due to its higher lifting height and stronger structure. However, if your lifting requirements are less frequent or lighter, the flat beam crane can handle the task with less investment.
- Facility Constraints: For confined spaces or narrow aisles, flat beam cranes are often more suitable due to their compact design. If your layout allows for more flexibility and you need the additional headroom to maximize operational capacity, arched beam cranes are worth considering.
Encouragement to Consider Both Short-Term and Long-Term Needs Before Making a Final Decision
Selecting the right crane design isn’t just about meeting immediate needs—it’s important to consider how your operational requirements might evolve over time.
- Short-term needs may lead you to prioritize factors like budget or space constraints. However, thinking ahead to long-term growth is crucial. Consider how your lifting capacity or facility layout might change in the next 5 to 10 years. An arched beam crane could offer more flexibility as your operations scale up, while a flat beam crane might be better for your current, simpler needs.
By factoring in both your immediate requirements and future scalability, you’ll be able to make a decision that supports your business’s growth and maximizes your investment in the long term.
Ultimately, whether you choose an arched beam crane or a flat beam crane, the goal is to optimize efficiency, maximize space utilization, and meet your lifting needs safely and cost-effectively. With careful consideration of your facility's layout, operational demands, and future needs, you'll make the right choice for your crane system, ensuring smooth operations and long-term success.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between arched and flat beam cranes?
The main difference between arched and flat beam cranes is the shape of the main beam, which directly affects headroom and lifting height:
- Arched Beam Cranes have a curved beam design, providing more vertical clearance under the crane. This makes them ideal for operations needing higher lifting capacities or additional headroom.
- Flat Beam Cranes have a horizontal, straight beam that offers limited headroom. They are suitable for low-ceiling environments where vertical space is at a premium but headroom is less of a concern.
2. Which crane design is better for a low-ceiling facility?
For low-ceiling environments, a flat beam crane is often the better choice. Its simple, straight design is compact and efficient for facilities with minimal vertical space.
However, if your facility has a slightly higher ceiling or if you anticipate needing more lifting height in the future, an arched beam crane could still be a viable option, offering better flexibility in the long term.
3. Can a flat beam crane handle the same lifting capacity as an arched beam crane?
Yes, both arched and flat beam cranes can handle 5-ton capacities or more, but the key difference lies in the crane's lifting height and clearance. While both designs can handle the same weight, the arched beam crane offers better clearance beneath the beam, allowing for more flexibility when lifting taller loads.
4. How do operational factors affect the choice between arched and flat beam cranes?
Several operational factors influence the crane choice:
- Frequency of Use: If you require frequent lifting, an arched beam crane may provide better efficiency due to its ability to handle higher loads and reach greater lifting heights.
- Load Types: For larger or taller loads, an arched beam crane allows better clearance, while flat beam cranes are suitable for smaller, more routine loads.
- Operational Space: A flat beam crane is a good option when space is tight, especially in low-ceiling areas, as it maximizes floor space with its lower profile.
5. What maintenance considerations should I be aware of for arched vs. flat beam cranes?
- Flat Beam Cranes: Generally, flat beam cranes have fewer components and a simpler design, which can lead to lower maintenance costs. They are less complex mechanically, reducing the chance of breakdowns. However, regular inspections are still essential to ensure they continue to function safely.
- Arched Beam Cranes: Arched beam cranes may require more maintenance due to their more intricate design. The additional headroom and complex mechanisms (such as increased structural supports) can add to maintenance costs. However, the long-term durability and greater lifting capacity can make it a worthwhile investment for facilities with more intensive crane operations.
6. How does crane design affect the overall space utilization in a facility?
- Flat Beam Cranes: These cranes are designed for maximum use of floor space in tight or confined areas. Their lower profile allows you to make better use of the available horizontal space, making them ideal for smaller workshops or warehouses with limited headroom.
- Arched Beam Cranes: Although these cranes take up more vertical space due to their arched design, they offer greater flexibility in utilizing vertical space efficiently. The added clearance beneath the beam allows operators to lift taller loads, which can lead to better space utilization for more diverse types of operations.
7. Can both crane types be used in the same facility?
Yes, it's possible to use both arched and flat beam cranes in the same facility, especially if your operation involves different types of tasks or requires flexibility.
For instance, areas with higher ceiling heights and heavier lifting requirements may benefit from arched beam cranes, while areas with lower ceilings or less frequent lifting may be better suited for flat beam cranes. This hybrid approach allows you to maximize efficiency and tailor crane usage to the specific needs of each area.
8. What are the long-term benefits of choosing an arched beam crane over a flat beam crane?
Choosing an arched beam crane offers several long-term advantages:
- Increased Lifting Height: The extra headroom provided by an arched design means that it can accommodate taller loads, increasing its flexibility and lifting capacity.
- Enhanced Efficiency: The additional clearance can improve overall workflow by enabling the crane to operate without hitting overhead obstacles, reducing the risk of accidents and improving lifting speeds.
- Future Scalability: As your facility grows or your operations become more complex, the arched beam crane provides better scalability for handling heavier or larger loads.
While an arched beam crane may come with higher upfront costs, its ability to adapt to future needs and handle more diverse operations can lead to greater long-term returns on investment.
9. Are there any special safety considerations for these crane types?
- Flat Beam Cranes: Due to their limited headroom, there is less risk of overhead collision with objects, making them a safer option in low-ceiling areas. However, regular maintenance and inspections are essential to ensure safe operation.
- Arched Beam Cranes: With their increased clearance and higher lifting capacity, these cranes may require additional safety measures to prevent accidents, particularly when lifting heavy or unstable loads. Features like load limiters, emergency stop systems, and collision avoidance sensors are essential for improving safety in operations involving arched beam cranes.
10. How can I determine which crane design is best for my facility?
To make the right decision:
- Evaluate ceiling height and the specific headroom available.
- Consider load types and lifting frequency. Determine if the arched beam crane's extra headroom is needed.
- Consult with experts to understand the space limitations and operational needs specific to your facility.
- Account for long-term scalability and potential changes in operational requirements.
By addressing these factors, you can select a crane design that meets both current and future operational needs, ensuring efficient use of space, safety, and productivity.
Related Products

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch