Comprehensive Guide on Overhead Bridge Crane Pricing
Detailed guide explaining key factors, pricing breakdown, and strategies to optimize overhead bridge crane cost while ensuring quality.
Category: Featured
Your Trusted Overhead Bridge Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Comprehensive Guide: Unlocking the Secrets of Overhead Bridge Crane Pricing
Overview of Overhead Bridge Cranes and Their Significance in Industrial Applications
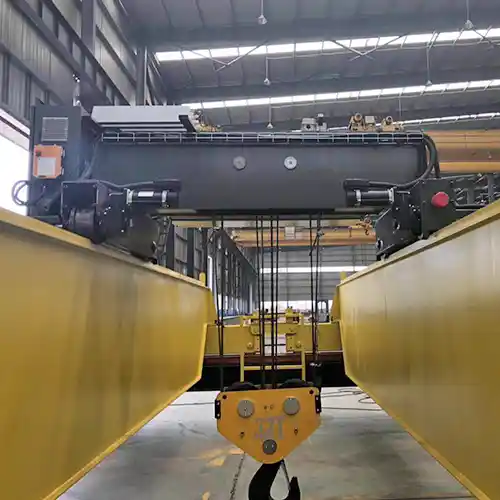
Overhead bridge cranes are essential lifting devices used across a wide range of industries to move heavy materials and products efficiently within a defined workspace. These cranes consist of a bridge that spans the width of the facility, with a hoist running along the bridge, allowing for precise lifting and positioning of loads.
The significance of overhead bridge cranes lies in their ability to handle heavy loads with precision, increase operational efficiency, and improve workplace safety. Industries such as manufacturing, steel production, automotive assembly, aerospace, and shipping heavily rely on these cranes for tasks like lifting machinery, moving raw materials, assembling components, and transporting goods across production areas. With their versatile applications, overhead bridge cranes are a backbone for heavy-duty operations, enabling businesses to maximize productivity while minimizing downtime and manual labor.
The Complexity of Pricing and Factors That Influence the Cost of These Cranes
Pricing an overhead bridge crane is not a simple process. Several factors influence the cost, which can vary widely depending on the crane's specifications and the complexity of the project. These factors include:
- Capacity: The weight that the crane is designed to lift plays a significant role in the overall price. Cranes with higher lifting capacities will generally be more expensive due to the need for stronger materials and more robust engineering.
- Span and Lifting Height: The length of the crane's span (the distance it can cover) and the height it can lift are critical factors in pricing. Larger spans and greater lifting heights often require custom designs, which add to the cost.
- Control Systems: Overhead cranes can come with different control systems, such as pendant controls, remote controls, or even a driver's cabin. Each option varies in cost based on its complexity, ease of use, and safety features.
- Customization: Many companies require specific crane features based on their unique needs, such as specialized hoists, hazardous environment certifications, or custom materials for corrosive or extreme conditions. These customizations increase the crane's price.
- Industry Requirements: Certain industries, like the automotive or steel industries, may demand higher-grade materials or specific safety features, which further complicates the pricing structure.
Given these variables, it's important to recognize that the price for an overhead bridge crane isn't just a flat rate but a combination of these many factors. Understanding these variables can help in assessing the true cost of the crane for a specific application.
Why Understanding Overhead Bridge Crane Pricing is Crucial for Making an Informed Purchase Decision
Understanding overhead bridge crane pricing is critical for businesses to ensure they make the best investment for their needs. Here's why:
- Budget Planning: Knowing the factors that contribute to pricing allows businesses to set a realistic budget for their crane purchase. This is particularly important for companies with limited capital or strict financial constraints.
- Cost-Effectiveness: With a clear understanding of what drives crane prices, businesses can avoid overpaying for unnecessary features or expensive customizations they don't need. Additionally, they can identify opportunities for cost savings by choosing more standard options or negotiating with suppliers for better pricing.
- Long-Term Investment: Overhead cranes are a significant investment, and their purchase cost often represents only part of the overall expenditure. Maintenance, installation, training, and operational costs should also be considered. Knowing the full cost breakdown ensures that businesses make a purchase that aligns with their long-term financial planning.
- Custom Needs: Different industries require cranes with varying specifications. By understanding pricing, companies can ensure that their specific needs—whether it's increased capacity, special controls, or custom designs—are factored into the cost estimate, helping to avoid overpaying for features that are unnecessary for their operations.
- Negotiation Power: When businesses understand crane pricing and the factors that influence it, they are better positioned to negotiate better deals. This includes getting quotes from multiple suppliers, understanding where flexibility exists in the price, and ensuring that the terms of sale align with their operational needs.
In conclusion, knowing how overhead bridge cranes are priced—and the key factors that contribute to these prices—helps businesses make informed decisions that align with both their immediate and long-term operational needs. This knowledge empowers buyers to select the right crane at the right price, optimizing their investment and ensuring the crane's suitability for the tasks at hand.
Key Factors Influencing Overhead Bridge Crane Pricing
Overhead bridge cranes are a significant investment, and their pricing is influenced by various factors, from the crane's design and capacity to customization options. Understanding these key factors helps businesses make an informed decision while managing their budget effectively.
Design and Construction: Crane Type, Materials, and Design Complexity
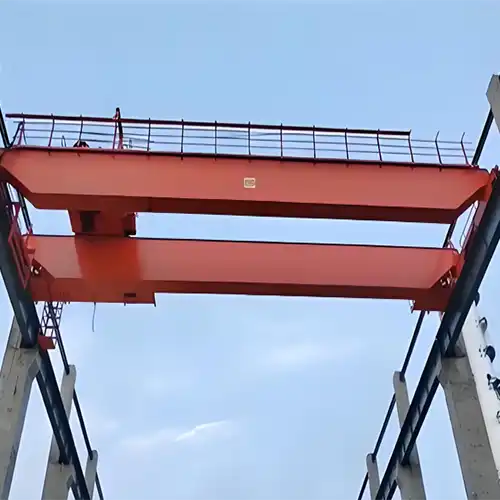
The design and construction of the crane are primary factors that determine its price. The most significant design decisions are whether the crane is a single girder or double girder crane.
- Single Girder vs. Double Girder Cranes: A single girder crane is typically more affordable because it uses a single beam to support the hoist, making it simpler and lighter in design. These cranes are ideal for lighter load capacities (typically under 20 tons) and smaller spans. On the other hand, a double girder crane offers increased stability and can handle heavier loads (25 tons and above). The added complexity and engineering required for double girder cranes increase the overall price, as they are designed to support larger capacities, wider spans, and higher lifting heights.
- Materials Used: The materials selected for crane construction—such as steel alloys for strength and durability—also contribute to the cost. Heavy-duty industrial cranes often require materials that can withstand higher stresses, environmental factors, and corrosion. Cranes built for harsh environments (e.g., high temperatures or corrosive substances) may need specialized coatings, which will increase the overall price.
- Design Complexity: A crane's design complexity can also raise costs. For instance, a customized design to fit specific space limitations or complex lifting requirements (e.g., rotating hoists, heavy-duty motors, etc.) will add to the overall price. Cranes with advanced features such as high-tech control systems, integrated sensors, or built-in safety features also require more detailed engineering.
Capacity and Load Requirements: Impact on Pricing
The lifting capacity of an overhead bridge crane plays a key role in determining its price. Generally, the higher the capacity, the more expensive the crane. Cranes are available in a wide range of capacities, from 1 ton to 100 tons or more, and their pricing typically reflects the increased load-bearing requirements and structural engineering necessary to support these loads.
- Crane Capacity: For example, a 25-ton crane is more expensive than a 1-ton crane because the larger crane requires stronger materials, larger hoists, and motors capable of handling heavier loads. The design also needs to incorporate additional safety features to ensure the stability and performance of the crane under heavy loads.
- Load Specifications: In addition to the general capacity, the specific load requirements of the crane, such as the nature of the materials being lifted (e.g., bulk material vs. precise, sensitive equipment), can influence the crane's design and, consequently, its cost. Cranes designed for precision and delicate handling will often have specialized features, including advanced hoists, that raise the price.
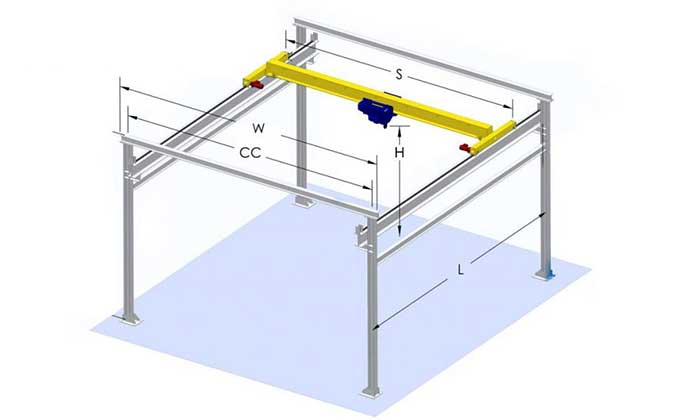
Span and Lifting Height: The Role in Pricing
Span length and lifting height directly influence the price of an overhead bridge crane.
- Span Length: The span refers to the distance the crane can cover from one end to the other. Larger spans require longer bridge beams, heavier components, and a more robust structure, all of which contribute to higher costs. A crane with a wider span will require additional engineering and larger supports, which significantly impacts the overall pricing.
- Lifting Height: The lifting height indicates the maximum vertical distance a crane can lift a load. Cranes designed for taller buildings or specific tasks requiring greater lifting heights will need longer vertical support structures and additional hoist capacity, which increases the cost. Higher lifting heights are particularly important for operations that need to stack materials at different elevations or reach elevated storage areas, requiring an additional engineering effort to ensure proper safety and functionality.
Control Systems: Influence on Pricing
The control system is another critical factor that affects the price of overhead bridge cranes. The type of control system chosen will depend on the crane's application, operating environment, and desired level of user interaction.
- Pendant Control: This basic control option allows the operator to move the crane using a wired controller. While affordable, it limits the operator's ability to perform operations from a distance. The lower cost makes this option suitable for straightforward, less complex tasks.
- Remote Control: A remote control system enables operators to control the crane from a distance without being physically tethered to the machine. While more expensive than pendant control, it enhances the safety and flexibility of crane operation, especially in hazardous or confined environments.
- Driver's Cabin: For heavy-duty operations, a driver's cabin offers the most control, as the operator can manage the crane from within a protected, enclosed space. This setup is commonly found in cranes that handle large capacities and are used in challenging conditions, such as steel mills or large construction sites. The cabin's complexity and the associated costs raise the price significantly.
Each control system type increases in complexity and cost, with the more advanced options—such as remote control and driver's cabins—providing more flexibility and operator safety at a higher price point.
Work Duty Classification: Impact on Pricing and Performance Expectations
Crane work duty classification defines the intensity and frequency of operation the crane can handle over its lifetime. The classification is essential for determining how well the crane will perform under various operational conditions.
Duty Ratings (A5, A6, A7): The most common duty classifications are A5, A6, and A7, which describe how often the crane will be used and the level of wear it will experience.
- A5: Light-duty use with low to moderate operation cycles.
- A6: Moderate-duty use with frequent lifting cycles.
- A7: Heavy-duty use for high-frequency operations with continuous loading.
The higher the duty rating, the more robust the components need to be. Cranes with higher duty ratings, such as A7, often come with reinforced structures, stronger motors, and longer-lasting parts, which contribute to a higher price. It's essential for businesses to select the correct duty rating for their operational needs to ensure the crane's longevity and performance.
Customization Options: Impact of Custom Features on Cost
Customization plays a significant role in determining the overall price of an overhead bridge crane. Depending on the unique requirements of the facility or industry, cranes can be equipped with a variety of custom features, which can significantly raise the price.
- Hoists: Custom hoists for specific lifting needs, such as high-speed hoists or hoists designed for specialized materials (e.g., temperature-sensitive loads), can increase costs.
- Materials: Cranes that need to operate in specific environments, such as extreme temperatures, corrosive atmospheres, or hazardous locations, may require special coatings, corrosion-resistant materials, or explosion-proof components. These specialized materials increase the price due to their rarity and the manufacturing processes involved.
- Safety Features: Advanced safety features such as anti-collision systems, overload protection, automatic load monitoring, and emergency stop buttons are critical in high-risk environments. These features can also add to the total cost, but they help prevent accidents and downtime, making them a worthwhile investment in safety.
Customization allows a crane to be tailored precisely to a business's operational needs, but it often involves a premium price. However, these investments may be essential for ensuring the crane can handle specific tasks effectively and safely.
Understanding these key factors influencing the price of overhead bridge cranes enables businesses to make informed decisions. From design and construction to control systems, work duty classifications, and customization options, each element plays a significant role in determining the final cost. By carefully considering the specific needs of your operation, you can choose the right crane with the optimal features and performance characteristics, ensuring the best possible return on investment.
Pricing Breakdown
When purchasing an overhead bridge crane, the price you initially see is not the final amount you'll pay. The total cost involves several additional factors beyond the base price of the crane itself. Understanding the breakdown of these costs will help you budget accurately and avoid unexpected expenses.
Base Price vs. Total Price: What's Included in the Base Price?
The base price of an overhead bridge crane typically covers the following essential components:
- Crane Structure: This includes the main structural components of the crane, such as the bridge, hoist, and runway beams.
- Standard Features: The base price also includes standard features such as the basic hoisting system, basic control options (pendant or remote), and typical lifting capacities (e.g., 5-ton, 10-ton, 25-ton).
- Material: The base price is based on the materials required for a typical crane, such as steel, hoist components, and wiring.
However, total pricing will often exceed the base price due to additional elements such as shipping, installation, and customization, which are not typically included in the initial quote.
Freight and Shipping: How Shipping Costs Affect Pricing
Shipping costs can be a significant portion of the overall price, especially for international orders. Several factors influence these costs:
- International Freight: If you're ordering a crane from a foreign manufacturer, international freight charges are inevitable. These charges depend on the distance, the weight and size of the crane, and the method of transportation (e.g., sea freight or air freight). Since cranes are large and heavy, these costs can be substantial, especially when shipping large double girder or custom cranes.
- Destination-Specific Fees: Shipping fees can vary greatly depending on the destination country. Import duties, taxes, and other regulatory costs may be added, depending on the region's customs laws. It's essential to understand these additional fees early on so they don't come as an unexpected expense.
- Local Transportation: Once the crane arrives at the port or warehouse, there will be local shipping costs to deliver the crane to your facility. These costs will depend on the distance from the port to your location and any logistical challenges, such as navigating narrow roads or requiring special handling for oversized loads.
Installation and Setup: The Costs Involved
Installing an overhead bridge crane is a complex process, and its cost is another key part of the pricing breakdown. Installation involves:
- Labor Costs: The cost of labor for installation can vary based on location, the complexity of the installation, and the specific crane model. For instance, installing a double girder crane with complex electrical and mechanical systems will require skilled labor, which may increase costs.
- Equipment Costs: Specialized equipment (e.g., cranes, forklifts, or rigging tools) may be necessary for positioning and installing the crane. These are often included as part of the installation service, but in some cases, they may be billed separately.
- Site-Specific Modifications: Depending on your facility, additional modifications may be needed to accommodate the crane. This could involve adjusting the height of the building to accommodate higher lifting heights, reinforcing structural supports, or modifying the runway beams. These changes can increase the installation cost significantly.
- Testing and Commissioning: After the crane is installed, it needs to undergo testing to ensure everything is functioning correctly. This step typically includes load testing, calibration of control systems, and safety checks. Testing ensures the crane meets all performance standards and safety regulations before it goes into full operation.
Maintenance and After-Sales Services: Long-Term Costs
Once the crane is installed, it's important to consider the long-term costs of owning and operating the crane, including:
- Routine Maintenance: Overhead cranes require periodic inspections and maintenance to ensure they remain in good working order. This includes checking the hoist mechanism, inspecting the structure for wear and tear, lubricating moving parts, and ensuring the electrical systems are functioning correctly. Maintenance contracts can be a valuable investment to ensure the crane's longevity and minimize downtime.
- Warranties: Most manufacturers offer warranties on their cranes, typically covering parts and defects for a specific period. It's essential to review the warranty details, as the coverage may vary based on the crane's design, usage, and manufacturer.
- Replacement Parts: Over time, certain components, such as hoist motors, control systems, or cables, may need to be replaced. Having access to replacement parts is crucial for maintaining crane functionality and minimizing downtime.
- Support Services: In addition to maintenance, support services may be required for troubleshooting and operational support. This could include remote monitoring, operator training, and consultation for any technical issues that arise during the crane's operation.
- Upgrades: In some cases, the crane may need upgrades, such as new control systems, safety features, or customized hoists, to meet changing operational demands or to comply with updated safety regulations. These upgrades add to the ongoing costs of crane ownership.
The total cost of an overhead bridge crane extends far beyond the base price listed in the initial quote. By understanding the breakdown of additional costs—such as freight, installation, and ongoing maintenance—you can better manage your budget and ensure that you're fully prepared for all the expenses involved in purchasing, installing, and operating a crane. Understanding these factors helps you make more informed decisions and prevents unexpected financial surprises.
Examples of Overhead Bridge Crane Pricing
To better understand how the pricing for overhead bridge cranes works in practice, let's look at three different case studies. Each example highlights a different crane type, showcasing various features, capacities, and customizations that influence the overall cost.
Case Study 1: Example of a 10-Ton Single Girder Crane with Basic Features
- Crane Type: Single Girder Overhead Crane
- Capacity: 10 tons
- Span Length: 12 meters
- Lifting Height: 6 meters
- Work Duty: A5
- Control Mode: Pendant control
- Features: Basic hoist system, standard steel construction, and no additional customization.
Price Breakdown:
Base Price: $15,000 USD
Additional Costs:
- Shipping: $1,500 USD (within the same region)
- Installation: $2,000 USD (including labor and testing)
- Total Estimated Cost: $18,500 USD
This example represents a standard, entry-level crane used for light-duty applications in general manufacturing. The low base price is reflective of the single girder design, which is simpler and less expensive than double girder models. The basic control system (pendant control) and non-customized hoist system keep the price relatively low. The work duty classification of A5 suggests the crane is designed for moderate usage, making it suitable for tasks that don't require frequent operation or heavy loads.
Case Study 2: Example of a 50-Ton Double Girder Crane with Advanced Features and Customizations
- Crane Type: Double Girder Overhead Crane
- Capacity: 50 tons
- Span Length: 24 meters
- Lifting Height: 20 meters
- Work Duty: A7
- Control Mode: Driver's cab control + Remote control
- Features: Advanced hoist system, custom steel materials, enhanced safety features (e.g., overload protection), and remote monitoring.
Price Breakdown:
Base Price: $95,000 USD
Customization and Features:
- Custom Steel Materials: $10,000 USD
- Safety Features: $5,000 USD
- Advanced Control System (Cab + Remote): $7,000 USD
Shipping: $3,000 USD (international)
Installation: $5,500 USD (includes setup, testing, and commissioning)
Total Estimated Cost: $125,500 USD
This crane is designed for heavy-duty operations in industries like steel mills, where high-capacity lifting and durability are critical. The double girder design ensures better load distribution and higher stability, especially when handling large and heavy materials. The custom materials enhance strength, while the addition of safety features like overload protection and remote monitoring ensures optimal performance. With a high work duty classification (A7), this crane is built for continuous operation in demanding environments. The total cost includes international shipping and installation, which contribute to the higher final price. Learn more What Affect Your Overhead Crane Price & Crane Rate? and Check Crane Price Range for your reference. And Contact us to get specific crane price for your needs. WhatsApp: + 86 151 3871 1597.
Case Study 3: Example of a Specialized Crane for a High-Duty Operation (Explosion-Proof Crane for Chemical Plant)
- Crane Type: Explosion-Proof Double Girder Overhead Crane
- Capacity: 20 tons
- Span Length: 18 meters
- Lifting Height: 12 meters
- Work Duty: A6
- Control Mode: Remote control (with explosion-proof systems)
- Features: Explosion-proof motor and components, high-grade corrosion-resistant materials, anti-spark safety features.
Price Breakdown:
Base Price: $60,000 USD
Explosion-Proof Customization:
- Explosion-Proof Components: $20,000 USD
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials: $7,000 USD
- Advanced Control Systems: $4,000 USD
Shipping: $2,500 USD (special handling for hazardous materials)
Installation: $4,500 USD (including safety testing and compliance certification)
Total Estimated Cost: $98,000 USD
This crane is designed for highly specialized operations in a chemical plant or oil refinery, where hazardous materials and explosive gases are present. The explosion-proof components ensure that the crane operates safely in volatile environments, protecting both equipment and personnel. The corrosion-resistant materials help prevent degradation due to exposure to chemicals and moisture. With a work duty classification of A6, the crane is built for frequent operation in moderate-duty environments. The customizations, such as explosion-proof systems and anti-spark safety features, add significantly to the total cost, making this a highly specialized and expensive crane.
These case studies illustrate the wide range of factors that influence the pricing of overhead bridge cranes. Whether you're considering a basic 10-ton single girder crane for light-duty tasks, a heavy-duty 50-ton double girder crane with advanced features, or a specialized explosion-proof crane for hazardous environments, each crane comes with unique requirements that affect its overall cost. By understanding the specific needs of your industry and application, you can better evaluate crane pricing and make an informed purchasing decision.
Factors That Can Affect Overhead Bridge Crane Pricing
Several factors influence the pricing of overhead bridge cranes, beyond just the specifications and features of the cranes themselves. Understanding these factors can help businesses make more informed decisions when purchasing a crane. Let's explore how geographical location, industry-specific requirements, and economic trends can impact the cost of your overhead bridge crane.
Geographical Location
The geographical location of both the crane manufacturer and the end user can significantly impact the price of an overhead bridge crane. This influence is driven by several factors:
- Shipping and Freight Costs: Shipping overhead cranes internationally or over long distances can add substantial costs to the overall price. The further the crane has to travel, the higher the freight cost, particularly for large, heavy equipment that requires special handling or permits.
- Local Regulations and Standards: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements related to safety, environmental impact, and construction codes. Cranes designed to meet these local standards often require additional certifications or specialized components, which can drive up the cost. For example, a crane built to meet European Union safety standards may cost more than one designed for a less-regulated region due to the higher compliance and certification costs.
- Labor and Installation Costs: Labor costs for installation can vary widely depending on the region. For example, crane installation in a remote area or a location with high labor costs could add significant expenses to the total price.
- Infrastructure and Accessibility: The location's infrastructure can also play a role in pricing. If a crane is being installed in a facility that is difficult to access (e.g., remote mining locations or sites with restricted entry), there may be additional costs for transport and setup.
Industry-Specific Requirements
Each industry may have specific needs that affect the design, features, and ultimately the pricing of overhead bridge cranes. Let's break down how these requirements vary by industry:
- Automotive Industry: In the automotive industry, cranes are often required to handle large, heavy components like engines, transmissions, or body parts. They need to be precise, durable, and capable of handling very specific loads. Additionally, the cranes may need to integrate with automated systems or be capable of operating in a just-in-time manufacturing environment. These special requirements, such as advanced hoists, automation capabilities, and specific lifting mechanisms, can increase the price.
- Manufacturing and Warehousing: Cranes used in manufacturing or warehousing environments might be needed to lift raw materials, pallets, or finished goods. These cranes often don't need specialized features but may require longer spans or higher lifting capacities depending on the type of materials being handled. The need for durable construction, ease of maintenance, and ergonomic controls may add to the cost.
- Oil and Gas Industry: The oil and gas sector requires overhead cranes that can operate in extreme environments, often with hazardous conditions like high temperatures, corrosive substances, or explosive atmospheres. Explosion-proof cranes, cranes designed with corrosion-resistant materials, and those with additional safety features can cost significantly more. Cranes used in these industries may also need to meet strict compliance standards, further increasing costs.
- Steel Mills and Heavy Industries: Cranes in steel mills or heavy manufacturing plants often have specialized features, such as high heat resistance, heavy lifting capacities, and rugged construction. These cranes may need additional safety mechanisms, high-duty motors, and highly customized control systems to handle the extreme loads and conditions. These features can add significantly to the price compared to standard models.
- Construction Industry: Cranes in construction often need to be adaptable to different environments and loads, with varying lifting heights and spans depending on the project. Custom cranes with features like adjustable spans, variable lifting heights, or the ability to handle exceptionally heavy loads may cost more.
Economic Trends
Economic trends can have a significant influence on the pricing of overhead bridge cranes due to factors such as raw material prices, labor costs, and global trade conditions.
- Raw Material Prices: The price of raw materials such as steel, aluminum, and other metals directly affects crane manufacturing costs. A rise in metal prices, driven by factors such as supply chain disruptions, tariffs, or global demand, can lead to higher production costs, which are then passed on to the customer.
- Labor Costs: Labor is another critical factor in crane pricing. High labor costs in the manufacturing and installation process can result in higher crane prices. For instance, labor costs in North America or Western Europe tend to be higher compared to other regions, meaning cranes produced and installed in these regions may have a higher overall price.
- Global Trade Conditions: Tariffs, import/export taxes, and trade restrictions can impact the cost of importing cranes or their components. For instance, if a manufacturer is importing components from overseas, tariffs on those parts could increase the overall cost. Trade wars or disruptions in the global supply chain (such as those caused by pandemics or political conflicts) can create price volatility in raw materials and finished goods, further affecting crane prices.
- Inflation and Economic Growth: In times of economic growth and high demand for construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure projects, crane prices may increase due to the higher demand for heavy machinery. Conversely, during economic slowdowns or recessions, crane prices may drop as manufacturers look to stimulate sales, although this can also be influenced by reduced demand.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in crane technology, such as automation, digital control systems, or improved energy efficiency, can also influence pricing. As new technologies emerge, they can either lower the cost of cranes (by increasing efficiency in production) or raise the price (by incorporating more advanced, costly components).
Geographical location, industry-specific requirements, and economic trends play significant roles in determining the pricing of overhead bridge cranes. The cost of a crane is influenced not just by its design and features, but also by factors such as local regulations, shipping costs, raw material prices, and labor expenses. By understanding these variables, you can better anticipate the costs involved and make more informed decisions when purchasing a crane that fits your specific needs and budget.
How to Get the Best Price for Your Overhead Bridge Crane
When purchasing an overhead bridge crane, securing the best price while ensuring quality and reliability is a crucial step. Several strategies can help you achieve a fair deal, from selecting the right supplier to negotiating better terms and exploring cost-saving options. Below are some tips to guide you through this process:
Selecting the Right Supplier
The first step to getting the best price for your overhead bridge crane is choosing the right manufacturer or supplier. The supplier plays a key role in both the pricing and the quality of your crane. Here's what to consider when selecting a supplier:
- Reputation and Experience: Look for suppliers with a strong reputation in the industry. A reliable supplier will have a proven track record of delivering high-quality cranes and meeting deadlines. Reading reviews, checking testimonials, and asking for references can give you insights into the supplier's reputation.
- Certifications and Compliance: Ensure the supplier adheres to industry standards and complies with local safety regulations. A crane that meets or exceeds safety and quality standards is an investment in the longevity and safety of your operations. Certified suppliers also tend to provide more reliable warranties and after-sales support.
- Manufacturing Capabilities: Evaluate the supplier's manufacturing capabilities. Can they meet your specific needs, including customizations like special lifting capacities, spans, or control systems? A supplier with advanced manufacturing capabilities can often offer more flexibility and competitive pricing.
- Customer Support and After-Sales Services: Quality customer service doesn't end with the sale. A good supplier will offer robust after-sales support, including maintenance, training, and troubleshooting services. Ensure that they are willing to assist with installation, regular maintenance, and any other needs that may arise after the crane is delivered.
- Pricing Transparency: Choose a supplier that provides clear and detailed pricing. The supplier should be transparent about what is included in the price and any additional costs, such as shipping, installation, or customization. This will help you avoid surprises and budget more effectively.
Negotiation Strategies
Once you've selected a supplier, the next step is to negotiate the best price and terms. Good negotiation can help you secure a better deal, whether it's through price reduction, better payment terms, or added value. Here are some tips for effective negotiation:
- Know Your Budget: Before entering negotiations, have a clear idea of your budget and your maximum price range. Knowing what you are willing to spend will help you stay focused during the negotiation process.
- Request Multiple Quotes: Don't settle for the first quote you receive. Reach out to several suppliers and request detailed quotations. This will not only give you a better idea of market pricing but also provide leverage during negotiations. Suppliers may be willing to match or beat a competitor's offer.
- Negotiate Payment Terms: The payment structure can significantly impact your overall costs. For example, asking for extended payment terms or a lower upfront deposit can improve your cash flow. Some suppliers may also offer discounts for early payment or flexible financing options.
- Leverage Bulk or Repeat Purchases: If you are purchasing multiple cranes or expect to make repeat orders, use this as a bargaining chip. Suppliers often provide discounts for bulk orders or long-term commitments.
- Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Instead of only focusing on the initial price, consider the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and energy consumption. If a crane costs more upfront but offers lower long-term operational costs (such as energy savings or lower maintenance needs), it may be worth negotiating for a higher initial price.
- Include Additional Services: Negotiate for value-added services, such as extended warranties, free installation, or free inspections. These services can often be bundled into the price, saving you money down the road.
Cost-Saving Tips
While securing a good deal on the crane itself is essential, there are other ways to reduce the total project cost. Here are some practical cost-saving tips:
- Bundle Services: Many crane suppliers offer bundled services that can help you save money. For example, you may be able to bundle installation, training, and maintenance into a single package, which often results in a lower combined price compared to paying for each service individually.
- Standardize Features: Custom features such as specialized hoists, control systems, or advanced materials can significantly increase the cost of your crane. If your operations don't require specialized features, opt for standardized designs. This will save you money without sacrificing essential performance.
- Consider Pre-Owned Cranes: If your budget is tight, consider purchasing a pre-owned or refurbished crane. Many suppliers offer used equipment that has been thoroughly inspected and reconditioned. These cranes often come at a fraction of the price of new ones but can still offer reliable performance. However, ensure that you understand the condition of the crane and any warranties that apply.
- Evaluate Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient cranes may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to significant long-term savings. Look for cranes that offer lower energy consumption, as this can reduce operational costs over time.
- Negotiate Shipping Costs: Shipping can be a significant additional cost, especially if you are purchasing from an international supplier. Consider negotiating with the supplier to include free or discounted shipping as part of the deal. If shipping is unavoidable, compare different freight providers to find the most cost-effective option.
- Plan for Long-Term Maintenance: Rather than opting for the cheapest initial price, consider the long-term maintenance and operational costs. Cranes with higher-quality components and more durable designs may cost more initially, but their reliability and longevity can save you money in repairs, downtime, and replacements.
Getting the best price for your overhead bridge crane is a combination of selecting the right supplier, negotiating effectively, and taking advantage of cost-saving opportunities. By understanding what to look for in a supplier, using negotiation strategies, and considering long-term operational costs, you can ensure that you are getting the best value for your investment. Additionally, exploring cost-saving measures such as bundled services, standardized features, and pre-owned equipment can further reduce your total costs without compromising on quality or performance.
Crane Quotes and Contracts
When purchasing an overhead bridge crane, it's essential to fully understand the details of the quote and contract you are presented with. This ensures that you know what you're paying for, what's included, and what potential additional costs or obligations may arise. Below, we break down the key components of crane quotes and highlight the most important elements in the contract.
Breaking Down the Quote
A well-structured crane quote will provide a detailed breakdown of the costs involved in purchasing, shipping, installing, and maintaining your crane. Here's how to interpret each component:
- Base Price: This is the primary cost of the crane itself, including its design and manufacturing. It typically covers standard features such as the crane's basic lifting capacity, span length, and control system. However, it may not include extra services, custom features, or shipping.
- Customization Costs: If you've requested customizations (e.g., special lifting heights, custom hoists, or a specific control system), these will be listed separately in the quote. It's important to review these costs carefully to ensure they are accurate and align with your needs.
- Additional Components: Some quotes may include optional components that are not part of the base crane, such as additional safety features (e.g., anti-collision devices, overload protection), specialized controls (e.g., pendant or remote controls), or energy-saving components. Ensure these are clearly listed so you can see exactly what is included.
- Shipping and Freight: This section covers the cost of transporting the crane from the supplier's location to your site. International shipments may incur additional costs like customs duties, taxes, or delivery charges based on the destination. Verify that the quote clearly specifies the shipping method and estimated delivery time.
- Installation Costs: This item outlines the labor and equipment needed to install the crane at your site. If installation is not included in the base price, it should be clearly itemized in the quote. Make sure the quote specifies whether the installation is included or if it will be an additional charge.
- Inspection and Testing: Often, cranes are subject to pre-delivery inspections and testing to ensure they meet quality standards and operational specifications. Make sure the quote includes a clear explanation of inspection procedures and any associated costs.
- Warranty and After-Sales Support: Look for a warranty section that specifies the coverage, including what is covered under the warranty (e.g., parts, labor), the duration of the warranty period, and any exclusions. It's also useful to note the availability of after-sales support, including technical assistance or service plans.
- Maintenance Services: Some quotes may include optional maintenance agreements or service contracts that provide regular inspections, maintenance, and emergency repairs. These services can be valuable in ensuring your crane remains operational over the long term.
Terms and Conditions
Before finalizing your purchase, it's crucial to review the terms and conditions in the contract. These documents lay out the legal framework for the sale and protect both parties in the transaction. Pay close attention to the following key contractual elements:
- Delivery Timeframes: The contract should specify when the crane will be delivered and when you can expect installation to be completed. Delays in manufacturing or shipping can have significant impacts on your project timeline, so ensure that the delivery times are reasonable and clearly outlined. If penalties or compensation are applicable for missed deadlines, these should be mentioned.
- Warranty Terms: The warranty terms are essential to understand, as they determine how long the crane is covered for repairs or replacement of defective parts. The warranty should clearly explain the duration (typically 1-3 years), the scope of coverage, and the procedures for making warranty claims. Additionally, check for any exclusions (e.g., damage caused by improper use or lack of maintenance).
- Payment Terms: The contract should outline the payment schedule, including the deposit amount, due dates, and any financing options available. Make sure to understand whether the full payment is due before or after delivery and installation. Be cautious about any hidden fees or charges that could arise during the payment process.
- Penalties for Delays: The contract should specify any penalties for delays, whether by the crane supplier or the customer. If the supplier fails to meet delivery deadlines, they might be required to provide compensation, such as a partial refund or additional services at no charge. Conversely, if you delay payments or approvals, the supplier may impose late fees or suspension of services.
- Liability and Insurance: The contract will typically outline the liability of both parties, including who is responsible for damages during shipping, installation, or use of the crane. It's important to ensure that both parties have adequate insurance coverage for potential risks like damage, theft, or accidents that may occur during the crane's operation or transport.
- Force Majeure Clause: This clause outlines what happens if unforeseeable events, such as natural disasters, political unrest, or pandemics, cause delays or prevent the completion of the contract. While this is generally not something you can control, understanding the provisions around force majeure events can help you prepare for any potential disruptions.
- Termination Clause: If the purchase is canceled or delayed, the contract should specify the terms for terminating the agreement, such as penalties or the process for returning deposits. This clause protects both the buyer and seller if the deal needs to be called off due to unforeseen circumstances.
- Dispute Resolution: This section specifies how any disagreements between the buyer and seller will be resolved, whether through arbitration, mediation, or legal action. Having a clear process for dispute resolution can help prevent costly and time-consuming legal battles if issues arise during the contract period.
Crane quotes and contracts is essential to making an informed purchase. A well-structured quote will clearly itemize all costs involved, from the base price to additional services such as shipping and installation. Meanwhile, the contract outlines the terms and conditions that govern the sale, including delivery timeframes, warranties, penalties, and liability. By carefully reviewing both the quote and contract, you can ensure that you're making a sound investment and avoid unexpected costs or legal issues down the line.
Conclusion
When purchasing an overhead bridge crane, understanding the key factors that influence pricing is crucial for making a smart investment. These include:
- Design and Construction: The crane type (single girder vs. double girder) and the materials used significantly impact the overall cost.
- Capacity and Load Requirements: The crane's lifting capacity and load specifications will determine the price, especially for heavy-duty models.
- Span and Lifting Height: Larger spans and greater lifting heights often increase the crane's price due to the added complexity and engineering required.
- Control Systems: Advanced control systems (e.g., remote control, driver's cabin) can raise the cost but offer improved safety and operational efficiency.
- Customization Options: Tailored solutions, whether for industry-specific needs or custom features, will add to the cost but ensure the crane meets your precise requirements.
- Work Duty Classification: Higher work duty ratings (A6, A7) correspond to cranes designed for more demanding operations, impacting both the price and long-term durability.
Final Recommendations for Optimizing Cost Without Compromising on Safety, Quality, and Performance
While the cost of purchasing an overhead bridge crane is an important factor, it's vital not to sacrifice safety, quality, or performance in the name of savings. Here are some strategies to balance cost-effectiveness with these core priorities:
- Invest in quality: While it might seem tempting to go for the cheapest option, a higher-quality crane will often deliver better performance, lower maintenance costs, and longer operational life.
- Prioritize key features: Consider the most essential features for your operations and avoid unnecessary customizations or upgrades that won't add significant value.
- Work with experienced suppliers: Select a reputable supplier with a proven track record of offering reliable, well-designed cranes. An experienced supplier can also advise on the best crane specifications for your particular needs.
- Negotiate bundled services: When purchasing, consider bundling installation, maintenance, and warranty services. Suppliers may offer discounts for bundled packages, which can help you save on long-term ownership costs.
Encouragement for Thorough Research, Expert Consultation, and Long-Term Planning
The purchase of an overhead bridge crane is a significant investment, and it's important to approach it with careful consideration:
- Conduct thorough research: Take the time to evaluate different suppliers, crane types, and specifications. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and performance data to help guide your decision.
- Consult with experts: If you're unsure about which crane is best suited to your needs, consult with industry experts or crane engineers who can help assess your requirements and recommend the best options.
- Plan for long-term costs: Beyond the initial purchase price, factor in long-term costs such as maintenance, energy consumption, and potential repairs. Budgeting for these ongoing costs ensures your crane remains a cost-effective solution throughout its operational life.Click to learn more on what you needs to know when asking for crane price.
Related Products

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch