How to Plan Your Facility Layout When an Overhead Crane is Needed
Plan your facility layout by assessing space, selecting the right overhead crane, ensuring safe operations, and optimizing workflow for efficiency.
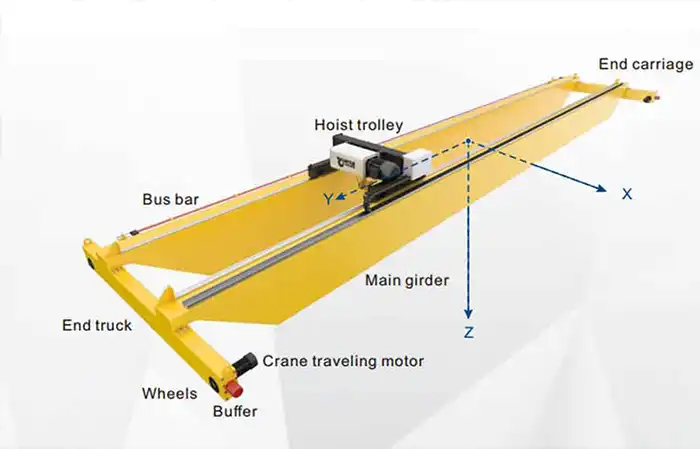
Overhead cranes are essential lifting devices widely used in various industrial settings. These cranes are designed to move heavy loads across large areas, making them invaluable for tasks such as assembly, manufacturing, and warehousing. They typically consist of a hoist, a trolley, and a bridge that runs along tracks mounted on the ceiling or overhead structure. The primary purpose of overhead cranes is to enhance material handling efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve safety by minimizing the need for manual lifting.
Integrating overhead cranes into facility layouts is crucial for optimizing workflow and productivity. Proper placement and planning of these cranes ensure that they can effectively reach all areas of the facility, allowing for seamless movement of materials and reducing bottlenecks in operations. Additionally, thoughtful integration enhances safety by providing adequate clearance and designated zones for crane operations, thereby minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries.
The purpose of this outline is to provide a step-by-step guide for planning an effective facility layout that accommodates an overhead crane. By following this guide, facility managers and engineers can create a layout that maximizes efficiency, ensures safety, and supports the specific needs of their operations. This approach not only improves day-to-day functionality but also contributes to long-term operational success and adaptability in an ever-evolving industrial landscape.
Assessing Operational Needs
The Workflow
To effectively integrate an overhead crane into a facility layout, it's essential first to analyze the workflow. This involves examining the various processes and tasks that occur within the facility. By understanding how materials move through the facility—from receiving to storage, production, and shipping—managers can identify critical points where crane assistance is most beneficial.
- Process Mapping: Start by mapping out the key processes in your operation. This includes detailing each step in production or material handling, such as assembly, machining, or quality control. Understanding the sequence of operations helps pinpoint where an overhead crane can streamline movement and improve efficiency.
- Material Handling: Identify the key materials and equipment that will require crane assistance. This may include raw materials, components, and finished goods. Consider the frequency and volume of these materials, as this will inform decisions about crane capacity and layout placement.
- Interaction Points: Look for areas where different processes intersect. For example, a workstation that receives heavy parts may benefit from an overhead crane to facilitate quick and safe loading. By understanding these interaction points, you can optimize crane placement to enhance workflow and minimize delays.
Determining Load Specifications
Once the workflow is understood, the next step is to determine the load specifications required for effective crane operation. This involves calculating the maximum load capacity and considering the characteristics of the loads to be handled.
- Maximum Load Capacity: Assess the maximum weight that the overhead crane will need to lift. This includes not only the weight of the materials but also any fixtures or attachments used during lifting. Consider peak loads that may occur during busy times to ensure the crane can handle fluctuations in demand.
- Types and Sizes of Loads: Evaluate the types and sizes of loads the crane will handle. Different materials may have unique handling requirements; for example, large and bulky items may need specialized lifting attachments, while smaller, heavier loads may require a different approach. Understanding the load characteristics helps in selecting the appropriate crane type and designing the facility layout to accommodate these needs.
- Load Dynamics: Consider the dynamics of lifting and moving loads. This includes understanding how loads may shift during transportation, the potential for swinging, and any special handling needs for fragile items. These factors can influence both the crane design and the safety measures that need to be implemented.
By thoroughly assessing operational needs and load specifications, facility managers can make informed decisions about crane selection and placement. This foundational step is crucial for creating an efficient and safe facility layout that maximizes the benefits of overhead crane operations.Click to check hook coverage of overhead crane in workshop facility.
Evaluating Facility Characteristics

Space Constraints
Evaluating space constraints is a critical step in planning an effective facility layout that accommodates an overhead crane. This involves a thorough assessment of both the available floor space and the ceiling height.
- Measuring Available Floor Space: Start by measuring the total area of the facility where the crane will be installed. This includes determining the dimensions of the work areas, aisles, and any adjacent spaces that will be impacted by crane operations. Adequate floor space is essential for maneuvering loads, ensuring safety, and allowing for efficient workflow.
- Ceiling Height: Measure the ceiling height in the areas designated for crane operations. The height will determine the crane’s lifting capabilities and may influence the type of crane that can be installed. Ensure that the ceiling is high enough to accommodate the crane's hoist and any vertical clearance required for the loads being lifted.
- Identifying Obstacles: Conduct a thorough inspection of the facility to identify any potential obstacles that could affect crane operations. This may include structural columns, existing machinery, storage racks, and other installations. Understanding these obstacles allows for strategic planning of crane placement to avoid interference and optimize the operational area.
Existing Infrastructure
The current infrastructure of the facility plays a significant role in determining the feasibility and configuration of an overhead crane installation. Assessing existing facilities and equipment is crucial for ensuring a seamless integration.
- Assess Current Facilities: Evaluate the existing layout and structure of the facility. This includes understanding the strength and condition of floors, ceilings, and walls, as these elements must support the weight and operational stresses of the crane. If the facility is not structurally sound, reinforcements or modifications may be necessary.
- Equipment Compatibility: Consider any existing equipment that may interact with the overhead crane. For example, if there are other lifting devices, automated systems, or conveyor belts in place, ensure that the crane's operation will not disrupt these systems. Understanding how different pieces of equipment will work together can enhance overall efficiency.
- Power Supply and Utilities: Review the current electrical and utility infrastructure to ensure it can support the overhead crane's requirements. This includes checking the availability of power supply, necessary electrical connections, and any other utilities that may be required for the crane's operation and maintenance.
By carefully evaluating facility characteristics, including space constraints and existing infrastructure, organizations can effectively plan for the installation of an overhead crane. This thorough assessment lays the groundwork for creating a safe and efficient layout that enhances operational capabilities and meets the specific needs of the facility.
Selecting the Right Type of Overhead Crane
Types of Cranes
When selecting an overhead crane, it's essential to understand the various types available and how they align with the specific operational needs of your facility. Here’s an overview of some common types of overhead cranes:
Types of Cranes
Bridge Cranes
- Description: Bridge cranes are composed of two horizontal beams (the bridge) that traverse elevated tracks. This design enables a trolley and hoist to move seamlessly across the entire span, facilitating efficient lifting operations.
- Best For: Ideal for expansive areas, bridge cranes can handle heavy loads with ease. They are commonly employed in manufacturing and assembly lines, providing maximum coverage and flexibility, making them essential for various lifting tasks.
Gantry Cranes
- Description: Similar to bridge cranes, gantry cranes utilize a structure supported by legs that move along the ground. This configuration allows for increased mobility within the workspace, as the crane can be repositioned as needed.
- Best For: Gantry cranes excel in outdoor applications or in environments where a permanent overhead structure cannot be established. They are frequently used for heavy lifting in construction sites and shipping yards, providing versatility and adaptability.
Jib Cranes
- Description: Jib cranes consist of a horizontal arm (jib) extending from a vertical post. The hoist is mounted at the end of the jib, allowing for a wide range of movement and flexibility in lifting operations.
- Best For: These cranes are particularly suited for localized lifting tasks, such as transferring materials between workstations or facilitating loading and unloading activities. Jib cranes are commonly found in warehouses and manufacturing facilities, where they enhance efficiency in material handling.
By understanding the distinct features and optimal applications of bridge cranes, gantry cranes, and jib cranes, businesses can make informed decisions on the best crane type for their specific operational needs.
Matching Crane Types to Specific Operational Needs: When selecting a crane type, consider the specific operational needs of your facility. For instance, if your operations require extensive lifting across a large area, a bridge crane may be the best choice. On the other hand, if you need mobility and flexibility, a gantry crane could be more suitable. Assessing the unique requirements of your workflow, the space available, and the types of loads being handled will guide you in making the right selection.
Selecting the appropriate crane for your operations necessitates a thorough evaluation of its capacity and specifications to ensure it aligns with your operational demands.
Weight Capacities
- Overview: Begin by determining the maximum weight the crane will need to lift. This assessment includes not only the weight of the materials but also any additional equipment that may be handled during operations.
- Significance: Choosing a crane with the right weight capacity is vital for maintaining safety and operational efficiency. An undersized crane may struggle with heavy loads, which can lead to delays, increased wear on equipment, or even catastrophic failure.
Span Lengths
- Overview: Span length refers to the distance between the crane's support structures, which directly impacts the area the crane can cover and the types of loads it can accommodate.
- Significance: It’s crucial to ensure that the span length is compatible with your facility layout and lifting requirements. A longer span provides greater coverage, while a shorter span is more suitable for compact spaces.
Lifting Heights
- Overview: Lifting height indicates the maximum vertical distance the crane can achieve to lift loads. This specification is influenced by the facility's ceiling height and the crane's design.
- Significance: Adequate lifting height is essential for operational efficiency, particularly in environments where vertical space is at a premium. Ensuring the crane can reach the necessary height is crucial for smooth and effective lifting operations.
By carefully considering these aspects of capacity and specifications, you can ensure that the overhead crane selected will effectively meet the operational demands of your facility.
Customization for Unique Applications: In some cases, standard cranes may not fully meet operational needs. Customization options can include specialized hoisting equipment, tailored controls, and specific materials to suit unique applications. For example, if you handle hazardous materials, you may require cranes with explosion-proof features or additional safety measures. Customization ensures that the crane effectively supports your specific workflow and enhances overall productivity.
By carefully considering the types of cranes available and evaluating their capacity and specifications, you can select the right overhead crane for your facility. This thoughtful approach will lead to enhanced operational efficiency and safety in your material handling processes.
Shared Considerations Across Industrial Sectors
Load Handling Requirements
Understanding the varying load characteristics is fundamental for selecting and operating overhead cranes effectively. Different types of loads can have significant implications for crane selection and operational processes.
- Weight: The weight of the load is the most critical factor in crane selection. Each crane type has a specific maximum load capacity, and understanding the weight of materials to be handled ensures safe lifting operations. Overloading a crane can lead to equipment failure and pose serious safety risks.
- Shape: The shape of the load affects how it can be lifted and maneuvered. Irregularly shaped loads may require special rigging equipment or lifting attachments to ensure stability during transport. For instance, a load with a large surface area may need a spreader beam, while cylindrical objects may require specific hoisting techniques to prevent rolling.
- Handling Requirements: Each type of load may have unique handling requirements. Fragile materials may need more delicate handling, while heavy machinery might require robust slings and attachments. Understanding these requirements is crucial for designing effective lifting and transportation strategies within the facility.
Safety Regulations and Compliance
Adhering to industry-specific safety standards and regulations is paramount for any facility utilizing overhead cranes. These regulations ensure the safety of operators, employees, and the integrity of the materials being handled.
- Regulatory Standards: Different industries are governed by specific safety standards, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States or the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in the UK. Understanding these regulations is essential for compliance and preventing legal issues.
- Inspection and Certification: Regular inspections of overhead cranes are often mandated to ensure they meet safety standards. Facilities must have procedures in place for routine checks, certifications, and maintenance records to comply with regulations.
- Emergency Protocols: Establishing emergency protocols is vital for ensuring employee safety. This includes training employees on evacuation procedures and proper responses to equipment malfunctions or accidents.
Maintenance and Reliability
Planning for regular maintenance and reliability is crucial to ensure overhead cranes operate efficiently and safely over their lifespan.
- Regular Maintenance Schedules: Developing a maintenance schedule that includes routine inspections, lubrication, and part replacements is vital for preventing breakdowns. Regular maintenance can identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring smooth operations.
- Minimizing Downtime: Facilities should have strategies in place to minimize downtime during maintenance. This could include having backup cranes or scheduling maintenance during off-peak hours. A well-maintained crane reduces the risk of unexpected outages that can disrupt operations.
- Reliability Assessment: Assessing the reliability of equipment and scheduling preventive maintenance helps extend the lifespan of overhead cranes. Understanding the wear and tear of various components allows for timely interventions and repairs.
Integration with Existing Systems
Compatibility with other equipment and systems in the facility is an essential consideration when planning for overhead cranes.
- Compatibility with Equipment: Overhead cranes must work in harmony with other equipment, such as conveyors and forklifts, to create a seamless workflow. This integration facilitates efficient material handling and reduces the risk of accidents or equipment damage.
- System Automation: If the facility utilizes automated systems, the crane must be compatible with these technologies. Integration can lead to improved efficiency, as automated cranes can streamline operations and reduce manual handling.
- Layout Considerations: When planning the facility layout, consider how the crane will interact with existing systems. This includes ensuring adequate space for movement and preventing obstructions in workflow.
Operator Training and Safety Protocols
Comprehensive training programs are essential for ensuring safe and efficient crane operation.
- Training Programs: Operators must undergo thorough training to understand the equipment's features, load handling techniques, and safety protocols. Proper training reduces the likelihood of accidents and improves overall operational efficiency.
- Safety Protocols: Establishing and enforcing safety protocols is vital for maintaining a safe working environment. This includes using personal protective equipment (PPE), following safe operating procedures, and conducting regular safety drills.
- Continuous Education: Ongoing education and training updates should be provided to keep operators informed about new technologies, regulations, and safety practices. This commitment to continuous learning enhances safety and efficiency in crane operations.
By considering these shared considerations across industrial sectors, facilities can enhance the safety, efficiency, and reliability of their overhead crane operations. Addressing these factors ensures that cranes are not only effective in handling loads but also compliant with industry regulations and best practices.
Specialized Considerations for Specific Industrial Sectors
Manufacturing Plants
Scale and Application: In manufacturing plants, overhead cranes and gantry cranes are essential for high-capacity assembly line operations. These cranes frequently transport components between different workstations, facilitating a smooth and efficient production flow.
Load Types: Manufacturing facilities handle a diverse range of materials, from small parts to heavy machinery. Overhead cranes are often used to lift and move heavy components, while jib cranes provide localized lifting for smaller, more manageable loads.
Practical Information:
- Versatility: Choose cranes that can accommodate various load types, incorporating adjustable lifting mechanisms for enhanced flexibility.
- Workflow Optimization: Position cranes strategically within the facility to minimize travel distances for materials, optimizing the assembly line process.
Construction Sites
Scale and Application: Construction sites require a flexible approach to crane use, with gantry cranes and overhead cranes adapted to varied projects. The adaptability in capacity and configuration is crucial for handling different types of construction materials and equipment.
Load Types: Cranes at construction sites often lift heavy and oversized materials, such as steel beams and concrete blocks. Overhead cranes can facilitate the movement of these loads over significant distances, while jib cranes can provide additional support for localized lifting.
Practical Information:
- Mobile Options: Consider mobile gantry cranes for projects where mobility is essential. They can be easily repositioned as project needs change.
- Operator Training: Ensure operators are well-versed in the specific capabilities and limitations of the cranes used, especially in dynamic environments.
Shipping and Ports
Scale and Application: In shipping and port facilities, overhead cranes are vital for large-scale operations with high-volume and turnaround requirements. These cranes help streamline the loading and unloading processes, ensuring timely handling of goods.
Load Types: Overhead cranes and gantry cranes handle a variety of loads, including shipping containers, bulk materials, and heavy machinery. The cranes must be robust enough to manage these heavy loads efficiently.
Practical Information:
- Container Handling Systems: Invest in specialized container handling cranes designed for rapid loading and unloading. Automated systems can enhance efficiency and reduce turnaround times.
- Safety Measures: Establish strict safety protocols around crane operations to protect workers and ensure efficient handling of heavy loads.
Aerospace Facilities
Scale and Application: Aerospace facilities involve specialized, high-precision operations where careful handling of sensitive components is critical. Overhead cranes are often used for moving large parts and assemblies within production areas.
Load Types: These facilities typically handle large aircraft components and engines that require precise placement to avoid damage. The use of overhead and jib cranes can facilitate accurate movements.
Practical Information:
- Precision Control Systems: Employ overhead cranes equipped with precision control systems to enhance accuracy in lifting and placing delicate components.
- Clean Room Requirements: Maintain clean environments where cranes operate to prevent contamination of sensitive parts.
Power Generation Plants
Scale and Application: Power generation plants are infrastructure-heavy facilities focused on efficient material handling. Overhead cranes are essential for moving heavy machinery and components throughout the facility.
Load Types: Common loads in power generation include turbines, generators, and large fuel containers. The cranes used must be capable of handling significant weights and bulky items.
Practical Information:
- Heavy-Duty Cranes: Select heavy-duty overhead cranes with high load capacities to ensure safe handling of critical components.
- Regular Maintenance: Implement comprehensive maintenance schedules to keep cranes operational, especially in facilities that operate continuously.
Steel Mills and Foundries
Scale and Application: Steel mills and foundries operate under high-capacity conditions and often in extreme environments. Overhead cranes are essential for managing the intense demands of material handling in these settings.
Load Types: The loads consist of heavy and often extremely hot metal materials, requiring specialized handling techniques. Overhead cranes must be designed to withstand high temperatures and hazardous conditions.
Practical Information:
- Heat-Resistant Materials: Utilize cranes made from heat-resistant materials and equipped with specialized lifting attachments for handling hot metals safely.
- Safety Protocols: Establish robust safety protocols and training programs for crane operators to navigate the unique challenges of these environments.
Recycling and Waste Management Facilities
Scale and Application: Recycling and waste management facilities focus on efficiently sorting and processing a wide variety of materials. Overhead and jib cranes are essential for moving and managing these diverse loads effectively.
Load Types: These facilities handle irregularly shaped waste and bulky recyclable materials, requiring cranes that can adapt to different handling challenges.
Practical Information:
- Adaptive Equipment: Equip cranes with versatile lifting attachments, such as grapples and clamshells, to efficiently manage a range of waste materials.
- Operational Efficiency: Create clearly defined pathways for crane movement and loading areas to enhance overall operational efficiency and reduce processing delays.
By understanding the specialized considerations for different industrial sectors regarding overhead cranes, gantry cranes, and jib cranes, facilities can ensure that they select the appropriate equipment for their unique operational needs. This tailored approach enhances efficiency, safety, and productivity across various applications.
Designing the Facility Layout

Define the Travel Path: When designing the facility layout, it is crucial to define the travel path for the overhead crane. This involves mapping out the routes that the crane will take to move materials efficiently throughout the facility. The path should be designed to minimize interference with personnel and other equipment, promoting a safe working environment.
Clearance Considerations: Ensure that there is sufficient clearance above and around the crane for lifting and maneuvering loads. This includes accounting for the height of the loads being lifted, as well as any overhead obstructions such as beams, lights, or HVAC systems. Proper clearance prevents accidents and ensures smooth operation.
Workstation Arrangement
Strategically Position Workstations: The arrangement of workstations and storage areas is critical for optimizing workflow. Position workstations close to the crane's travel path to reduce travel time when moving materials. This arrangement promotes efficient operations and minimizes the time spent transporting items.
Access to Materials and Equipment: Plan for easy access to materials and equipment at each workstation. Ensure that the layout allows workers to retrieve items quickly without obstructing crane movements. By designing a layout that prioritizes accessibility, productivity can be significantly enhanced.
Safety Considerations
Incorporate Safety Zones: Designate specific safety zones around the crane's operation area to keep personnel at a safe distance from moving equipment. These zones can be marked with signage, barriers, or floor markings to remind workers of safe distances.
Emergency Exits: Plan for clear and accessible emergency exits within the layout. Ensure that all personnel can quickly evacuate the area in case of an emergency, with designated pathways that remain unobstructed.
Compliance with Regulations: Ensure that the facility layout adheres to relevant safety regulations and standards. This includes conducting risk assessments and following guidelines provided by industry regulatory bodies. Regular safety audits can help identify potential hazards and ensure compliance.
Practical Tips for Effective Facility Layout Design
- Simulation Tools: Consider using simulation software to visualize crane movements and workflow before finalizing the layout. This allows for adjustments to be made based on potential challenges identified during the planning stage.
- Collaborative Planning: Involve operators and other staff in the layout planning process. Their insights can provide valuable information about practical needs and potential issues, leading to a more effective and user-friendly design.
- Flexibility for Future Needs: Design the layout with future expansion in mind. As operational needs evolve, flexibility in the layout allows for modifications without significant disruptions.
- Regular Review: Establish a schedule for reviewing the facility layout regularly. This can help identify areas for improvement based on changes in operational demands or technology.
By carefully designing the facility layout with these considerations in mind, businesses can create an efficient, safe, and effective working environment that maximizes the utility of overhead cranes and enhances overall productivity.
Incorporating Supporting Systems
Control Systems
Determine Control System Type: The first step in incorporating supporting systems for your overhead crane is to determine the type of control systems needed. Options include manual controls, electric controls, or remote-operated systems. The choice depends on the complexity of operations, the layout of the facility, and the specific tasks the crane will perform. For instance, remote controls can enhance safety and efficiency by allowing operators to control the crane from a safe distance.
Operator Visibility and Control: It’s essential to ensure that operators have optimal visibility during crane operation. Design the control system layout to allow operators to have a clear view of the load and surrounding area while controlling the crane. This may involve strategically placing control panels or using cameras and sensors that enhance visibility. Operator comfort should also be considered to facilitate extended periods of operation without fatigue.
Power Supply and Maintenance Access
Evaluate Electrical Requirements: Assess the electrical requirements for the overhead crane and its supporting systems. This includes determining the power supply needed for the crane's operation, as well as any additional systems, such as lights and controls. Ensure that the electrical infrastructure can support these requirements without overloading.
Plan for Maintenance Access: Easy access for maintenance and inspections is vital for ensuring the crane's longevity and operational reliability. Design the layout to allow maintenance personnel to reach all parts of the crane without obstacles. This may involve positioning the crane in a way that provides ample space for maintenance tools and equipment, or creating dedicated maintenance areas nearby. Regular inspections should be facilitated by clear access paths, making it easier to identify and address any potential issues before they become significant problems.
Practical Considerations for Supporting Systems
- Integration with Facility Systems: Ensure that the crane’s control systems are compatible with other facility systems, such as inventory management software or automated storage solutions. This integration can streamline operations and enhance overall efficiency.
- Emergency Protocols: Incorporate emergency shutdown systems within the control systems to quickly disable the crane in case of an emergency. Clearly communicate these protocols to all operators and provide training on how to respond in various scenarios.
- Regular Training: Conduct regular training sessions for operators on using the control systems and performing maintenance checks. Keeping operators informed about the latest technologies and safety protocols can significantly reduce accidents and improve operational efficiency.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation for all electrical systems and control mechanisms. This should include schematics, operation manuals, and maintenance logs. Having this information readily available can assist with troubleshooting and repairs.
By thoughtfully incorporating supporting systems, businesses can ensure that their overhead cranes operate efficiently and safely, ultimately enhancing productivity in their facility.
Simulating the Layout
3D Modeling and Visualization
Utilize CAD Software: To effectively simulate the layout of your facility, utilize Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to create a detailed visual representation. This tool allows you to design and visualize the overhead crane's path, workstation arrangements, and other critical elements within the facility. By creating a 3D model, you can gain insights into spatial relationships and workflows, making it easier to identify potential obstacles or inefficiencies.
Conduct Simulations: Once the initial layout is designed, run simulations to test the crane's operation within the modeled environment. This step helps identify potential issues such as conflicts with other equipment, insufficient clearance, or safety hazards before the layout is physically implemented. By addressing these concerns early, you can reduce the likelihood of costly modifications after installation.
Stakeholder Feedback
Gather Input from Stakeholders: Engaging with key stakeholders—such as operators, engineers, and safety personnel—during the design phase is crucial. Their firsthand experience and knowledge can provide valuable insights into operational needs and safety considerations. Conduct workshops or meetings to discuss the layout and gather feedback on the proposed design.
Make Necessary Adjustments: Based on the feedback received and results from simulations, make necessary adjustments to the layout. This iterative process ensures that the final design effectively meets the operational requirements and addresses any potential safety concerns. Iterating on the design before implementation will help foster a smoother transition during the installation process.
Implementation and Review
Installation Process
Outline Steps for Installation: Create a clear outline of the steps required for crane installation and any necessary modifications to the facility. This outline should include timelines, required materials, and the roles of team members involved in the installation. It’s important to detail how the crane will be integrated into the existing facility infrastructure and any adjustments that need to be made to accommodate it.
Minimize Disruption: Plan the installation process to ensure minimal disruption to ongoing operations. This may involve scheduling work during off-peak hours or in phases, so that other critical processes can continue without significant downtime. Communicating with all affected departments about the installation timeline and procedures can also help manage expectations and maintain workflow.
Post-Implementation Review
Assess Effectiveness: After the installation is complete, conduct a post-implementation review to assess the effectiveness of the new layout and crane integration. Gather quantitative data on productivity, safety incidents, and operational efficiency to evaluate the success of the changes made.
Gather Operator Feedback: Solicit feedback from operators who work directly with the crane and layout. Their insights can help identify any lingering issues or opportunities for improvement. Regular feedback sessions can be organized to ensure continuous improvement and optimization of operations.
Make Improvements as Necessary: Based on the assessment and feedback, be prepared to make further adjustments. Continuous improvement should be a key focus, with an ongoing commitment to enhancing the facility's efficiency and safety through informed modifications and updates.
By incorporating thorough simulations and careful planning during installation and review phases, businesses can effectively implement their overhead crane systems while optimizing facility layout and operations. This proactive approach will ultimately lead to increased productivity, enhanced safety, and improved overall performance in the workplace.
Conclusion
In summary, the thoughtful planning of facility layout when integrating overhead cranes is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring safety. By thoroughly assessing operational needs, evaluating facility characteristics, selecting the right type of crane, and incorporating supporting systems, organizations can create an effective workspace that enhances productivity. Specialized considerations for different industrial sectors further underscore the importance of tailoring crane integration to meet specific requirements, such as load types and safety standards. Finally, simulating the layout through 3D modeling and gathering stakeholder feedback are essential steps that contribute to a successful implementation.
To maintain an efficient and safe working environment, it is essential to encourage ongoing evaluation and adaptation of the facility layout to accommodate changing operational needs. Regular assessments of the crane's performance, operator feedback, and advancements in technology can help identify areas for improvement. By being proactive and responsive to changes in production demands, businesses can ensure that their facility layout remains optimized for the future.