Securing Crane Orders with Letters of Credit: Key Insights into Payment Risks and Mitigation
Overview of Crane Industry Transactions
The crane industry plays a pivotal role in construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure sectors. Cranes are essential for lifting and moving heavy loads, and their applications range from building high-rise structures to assembling large machinery. The production and purchase of cranes, especially for large projects, require a high level of coordination, investment, and expertise.
- Large-Scale Crane Orders: In industries like construction, mining, and shipbuilding, crane orders are often large in scale and high in value. These cranes can be custom-built to meet specific needs, such as overhead bridge cranes for factories, gantry cranes for shipyards, or tower cranes for construction sites. Such projects involve significant investment, with prices often running into hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars. The crane purchasing process typically includes design, manufacturing, delivery, and installation phases, which can span months or even years, depending on the complexity of the order.
- The Role of International Trade: International trade plays an important role in the crane industry. Due to the specialized nature of cranes, many buyers source their equipment from manufacturers in different countries, often where there is better access to materials or more advanced manufacturing capabilities. For example, companies in North America or Europe may order heavy-duty cranes from manufacturers in Asia or the Middle East. As cranes are large, complex machines, the logistics of shipping, customs clearance, and delivery must be carefully manage International trade allows companies to source the best quality equipment at competitive prices but also introduces risks, such as payment delays and complications in cross-border transactions.
Introduction to Letters of Credit (LC)
What is a Letter of Credit (LC)?
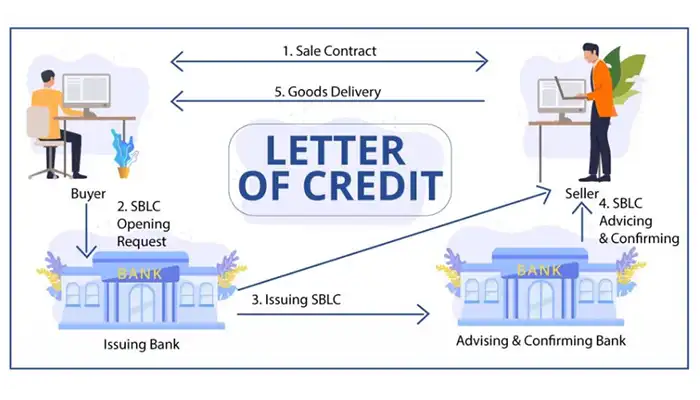
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a payment method widely used in international trade, where a bank guarantees payment on behalf of the buyer to the seller, as long as the seller meets the terms outlined in the agreement. Essentially, the LC ensures that the seller will be paid for their goods or services once the specific conditions are met, such as the delivery of the crane and submission of required documentation (e.g., shipping invoices, inspection certificates, et). The buyer’s bank issues the LC, and the seller’s bank confirms the conditions for payment.
Why LCs are Commonly Used in High-Value Transactions like Crane Orders:
Cranes and other heavy machinery are typically high-value items, with orders often reaching substantial amounts of money. For both the buyer and the seller, ensuring that payments are securely made is critical. A Letter of Credit protects both parties in the transaction:
- For the Buyer: It offers peace of mind that the payment will not be released until the crane meets the agreed specifications and delivery conditions. It also provides a structured and secure payment method when dealing with an overseas manufacturer or supplier.
- For the Seller: It ensures that once they fulfill the contractual conditions, they will receive payment, even if the buyer is in a different country or unfamiliar with the seller's reputation. The LC acts as a financial safety net, reducing the risk of non-payment or frau
Using LCs in crane transactions is common because of the high stakes involved in such deals. Buyers and sellers want to ensure that both parties fulfill their contractual obligations before money changes hands, especially in cases where the product is expensive or custom-made.
Purpose of the Article
The purpose of this article is to provide insights into the payment risks that can arise when using Letters of Credit (LC) in crane transactions and how these risks can be mitigated to ensure smooth and secure payments for both buyers and sellers. While LCs provide a layer of security, there are still potential challenges that can cause delays or complications in crane production and delivery.
Key Insights into Payment Risks:
- Delays in LC Issuance or Payment: One common risk is the delay in issuing the LC or the payment release, which can hold up the production or shipping of cranes. If the LC is not issued on time, the manufacturer may not have the cash flow needed to purchase raw materials or proceed with production. In turn, this causes delays in meeting deadlines for delivery.
- Non-Compliance with LC Terms: Another risk is that the documents presented by the seller may not exactly match the terms of the L This can result in the buyer's bank refusing to release payment, forcing the seller to make revisions and delaying the process.
- Currency Fluctuations and Cross-Border Challenges: In international transactions, currency exchange rate fluctuations can affect the final amount paid, which could impact profitability for either the buyer or the seller.
Strategies for Mitigating These Risks: To prevent delays and ensure timely payments, both buyers and sellers can adopt strategies such as:
- Clear Agreement on LC Terms: Both parties should agree on the terms and documentation needed before the LC is issued, including exact specifications of the crane, shipment details, and delivery deadlines.
- Timely Issuance and Confirmation of LC: Buyers should ensure that the LC is issued promptly to avoid delays in production. Both parties must also confirm that the LC meets the agreed-upon terms.
- Partial or Progress Payments: Negotiating partial payments or progress payments based on milestones can ensure that the seller has cash flow throughout the production process, reducing the risk of financial strain due to delayed payments.
Letters of Credit (LC)
What is a Letter of Credit?
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial instrument used in international trade to guarantee payment between the buyer and seller, providing security for both parties. Essentially, an LC is issued by a bank on behalf of the buyer to the seller, confirming that payment will be made upon the fulfillment of agreed-upon terms and conditions.
Key Features of a Letter of Credit:
- Conditional Guarantee of Payment: An LC guarantees that the seller will be paid as long as they meet the specific terms and conditions outlined in the L This often includes submitting the required documents, such as invoices, shipping documents, and inspection certificates.
- Documentary Transaction: Payment is made not based on a direct cash transaction but rather on the presentation of certain documents that prove the seller has fulfilled the conditions of the contract (such as delivering the crane or completing certain milestones in production).
- Time-Bound: LCs usually specify a set timeframe within which the required documents must be presente This ensures the seller receives payment after completing the necessary steps, while the buyer receives the goods as agree
- Risk Reduction: For the buyer, the LC reduces the risk of paying for goods that may not meet the agreed standards or that might not be delivered at all. For the seller, it ensures that payment will be made as long as they meet the terms, even when dealing with a foreign buyer or an unfamiliar market.
How an LC Acts as a Guarantee of Payment:
- Buyer’s Bank Role: When the buyer and seller agree to an LC, the buyer's bank guarantees payment to the seller upon the presentation of proper documents. This gives the seller confidence that, once the terms are fulfilled, they will receive the agreed payment.
- Seller’s Security: The seller has security because the LC removes the risk of not receiving payment, which is particularly important in international transactions where the buyer and seller may not have a longstanding relationship.
Types of LCs in Crane Transactions
Crane transactions, being high-value deals, often involve the use of different types of LCs depending on the specific needs of the buyer and seller. Below are the common types of LCs used in these transactions:
Sight LC (Immediate Payment upon Document Presentation):
- How It Works: Under a Sight LC, the buyer’s bank guarantees payment to the seller as soon as the required documents are presented to the bank. The payment is made without delay once the documents are checked and deemed in compliance with the terms of the L
- Crane Transaction Use: Sight LCs are typically used when the buyer and seller have a high level of trust or when the seller needs immediate payment after the shipment of a crane or equipment. This is often preferred when the crane is already built or ready for dispatch, and the payment needs to be finalized quickly.
Usance (Time) LC (Deferred Payment):
- How It Works: Unlike the Sight LC, a Usance LC allows for a deferred payment, meaning the payment is made at a future date, usually within 30, 60, or 90 days after the documents are presented and accepte
- Crane Transaction Use: Usance LCs are often used in crane transactions when the buyer needs extra time to arrange payment after delivery. This type of LC benefits the buyer by providing additional time to secure financing, while still guaranteeing payment to the seller once the documents are presente
Revolving LC (For Multiple Shipments or Ongoing Orders):
- How It Works: A Revolving LC is a renewable credit line that can be used for multiple shipments or ongoing orders, without the need to reissue a new LC for each transaction.
- Crane Transaction Use: This is useful for long-term contracts or continuous crane orders, where a manufacturer or supplier might be supplying cranes over a period of time. The Revolving LC saves administrative work and offers continuous payment security as long as the conditions of the LC are met.
Standby LC (Used as a Backup for Payment):
- How It Works: A Standby LC acts as a backup payment method, only becoming effective if the buyer fails to fulfill the terms of the agreement. If the buyer defaults or does not make a payment, the standby LC ensures the seller will still be compensate
- Crane Transaction Use: Standby LCs are often used for high-risk transactions or when the buyer is uncertain about meeting payment deadlines. In crane transactions, a Standby LC provides the seller with an additional layer of security, particularly when dealing with first-time customers or complex orders.
The Role of Banks in LC Transactions
Banks play a critical role in facilitating and ensuring the success of LC transactions. They act as intermediaries that manage the flow of documents and payments between the buyer and the seller. Here’s how banks help in the LC process:
Issuing the LC (Buyer’s Bank):
- The buyer approaches their bank to issue an LC, which acts as a guarantee for payment. The buyer’s bank checks the buyer’s creditworthiness before issuing the LC to ensure that funds are available.
- The bank ensures that the LC terms align with the purchase contract between the buyer and seller. The buyer's bank takes on the risk of payment once the terms are met, giving the seller confidence in the transaction.
Confirming the LC (Seller’s Bank):
- After the LC is issued by the buyer's bank, the seller's bank confirms the L This means the seller's bank checks that the terms of the LC are acceptable to the seller and guarantees that payment will be made once the seller complies with all requirements.
- If the seller’s bank is involved in confirming the LC, it adds a level of reassurance, especially in international transactions where both parties may not know each other well.
Document Review and Payment Processing:
- Banks ensure that the required documents—such as shipping invoices, inspection certificates, and insurance papers—match the conditions laid out in the L The bank carefully reviews the documents presented by the seller to ensure that all conditions are met before processing the payment.
- The buyer’s bank ensures the payment is made to the seller once the documents are verified, preventing fraud and errors in the transaction.
Ensuring Compliance with International Standards:
- Banks also play a key role in making sure that the LC complies with international trade regulations. The Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP 600) governs LCs globally, ensuring that transactions adhere to international trade standards and reducing the risk of discrepancies in cross-border trade.
In essence, banks provide a trusted intermediary role, ensuring that both parties fulfill their obligations under the LC terms, minimizing the risk of non-payment or frau This makes LCs a reliable method for facilitating international crane transactions and ensuring both buyers and sellers are protecte
Certainly! Below is the section discussing Payment Risks in Crane Orders Using Letters of Credit (LC), focusing on potential risks such as delayed issuance, non-compliance with LC terms, LC expiration, currency fluctuations, and bank errors or delays.
Payment Risks in Crane Orders Using Letters of Credit
Delayed Issuance or Confirmation of LC
Risk Overview: One of the primary risks in crane transactions using Letters of Credit is the delayed issuance or confirmation of the L In some cases, the buyer may fail to initiate the LC process promptly, or the bank may take longer than expected to issue or confirm the L This delay can halt production or disrupt critical timelines, especially when cranes are custom-built or require specific components that need timely procurement.
Consequences:
- Halted Production: Without the LC in place, manufacturers may lack the necessary financial security to proceed with production. This is particularly problematic for crane manufacturers, as these are often complex, long-lead-time products. For example, without a confirmed LC, a manufacturer may hesitate to order expensive materials or start assembly work.
- Delayed Delivery: If the crane production is delayed, the agreed delivery schedules are at risk. This can create a ripple effect, with production and installation timelines for customers becoming extended, leading to missed project deadlines.
- Strained Relationships: Persistent delays in issuing or confirming the LC can strain relationships between the buyer and seller. Trust is vital in large-scale transactions, and delays can lead to a loss of confidence in the ability to fulfill the order on time. In competitive markets, this can lead to lost business or contractual disputes.
Non-Compliance with LC Terms
Risk Overview: Non-compliance with the terms specified in the LC is another significant risk. This happens when the documents submitted by the seller—such as shipping invoices, inspection certificates, or other required paperwork—do not align precisely with the conditions outlined in the L Even minor discrepancies, such as mismatched dates or slight variations in product specifications, can result in rejection of payment.
Consequences:
- Rejection of Payment: If the documents do not meet the specified terms, the buyer’s bank may refuse to release the payment. This rejection can create significant financial strain on the seller, particularly if they have already delivered the crane or incurred costs for raw materials or manufacturing.
- Document Corrections: The seller may be required to correct the discrepancies in the documents, leading to delays in payment processing. These corrections can take time, during which the crane manufacturer may need to halt or delay subsequent production activities.
- Further Delays: The time it takes to address discrepancies could lead to a domino effect, causing more delays in the production and shipment of cranes. Additionally, the buyer may start losing patience, which could jeopardize future business dealings.
LC Expiration and Delays in Document Submission
Risk Overview: Letters of Credit are typically issued with an expiration date by which the seller must present the required documents to the buyer’s bank. If the seller fails to submit the necessary documents before the expiration date, the LC becomes voi In the crane industry, where production schedules are often complex and subject to delays, this can be a significant risk.
Consequences:
- Delays in Receiving Payment: If the seller is unable to submit the correct documents before the LC expires, they will face delays in receiving payment. Without the LC, the buyer is under no obligation to pay, and the manufacturer may face difficulties in securing the funds needed to complete the project.
- Difficulty in Extending the LC: If the LC expires before the seller has submitted the required documents, the buyer may need to request an extension or issue a new L This can introduce delays and extra administrative burden on both parties, and in some cases, the buyer may refuse to extend the LC, leading to a standoff.
- Disrupted Production Timelines: With delayed payment and the risk of further administrative complications, the production of cranes may stall. This can disrupt the overall project timeline, which is particularly damaging in industries where cranes are critical to construction or manufacturing processes.
Currency and Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Risk Overview: For crane transactions involving international buyers and sellers, currency exchange rates can present a significant risk. If the payment terms of the LC are based on a specific currency, fluctuations in exchange rates can cause a discrepancy between the agreed amount and the final value pai
Consequences:
- Loss of Value: If the currency exchange rate moves unfavorably between the time the LC is issued and when the payment is made, the value of the payment could be less than expecte For example, if the buyer’s currency weakens against the seller’s currency, the seller may end up receiving less than the agreed amount, which could impact their ability to cover production costs.
- Payment Discrepancies: Currency fluctuations may lead to discrepancies in the final payment amount, causing confusion or disputes between the buyer and seller. This could delay the payment process and cause frustration on both sides.
- Unexpected Costs: Currency risk can also result in unexpected costs. For example, if the buyer and seller have not agreed on a fixed exchange rate and one party has to absorb the loss due to currency fluctuations, it could impact their profitability. In the crane industry, where transactions are often high in value, even small currency fluctuations can lead to substantial financial impacts.
Bank Errors or Delays
Risk Overview: While banks are central to facilitating LC transactions, errors or delays in processing the documents or payments can cause significant issues for both the buyer and the seller. Bank errors can result from miscommunication between the buyer’s and seller’s banks, incorrect document handling, or delays in processing payments.
Consequences:
- Increased Lead Times: If there are mistakes in processing the LC, such as incorrect document review or delayed payment approval, this can extend the lead time for the crane transaction. For manufacturers, these delays can disrupt production schedules and cause cascading delays in other ongoing projects.
- Missed Deadlines: Any delays in the payment process due to bank errors may cause the seller to miss crucial deadlines, including crane delivery or installation. These delays can also harm the relationship with the buyer, especially if they are operating on tight project timelines.
- Disrupted Cash Flow: For sellers, any delay in receiving payment due to bank errors or issues with the LC can disrupt cash flow. This may hinder the manufacturer’s ability to purchase new materials or fund ongoing operations, potentially affecting their ability to fulfill other customer orders or commitments.
Strategies for Mitigating Payment Risks in Crane Orders
Successfully managing payment risks in crane transactions that involve Letters of Credit (LCs) requires careful planning, clear agreements, and proactive steps to ensure both the buyer and seller are protected from potential delays, errors, or financial discrepancies. Here are several strategies that can help mitigate these risks and maintain smooth and secure crane production and delivery.
Clear Agreement on LC Terms
Strategy Overview: Establishing clear and mutually agreed-upon LC terms is crucial in avoiding any confusion or disputes during the payment process. Both the buyer and the seller should engage in detailed discussions to ensure that all the terms are understood and documented properly. This step is especially important in the crane industry, where contracts often involve complex specifications and high-value transactions.
Key Terms to Specify:
- Required Documents: Clearly outline all documents required for payment release, such as invoices, inspection certificates, packing lists, and shipping documents. These should match the specifications set in the contract.
- Inspection Certificates: Specify who will conduct any inspections (such as third-party certification) and what criteria will be used to verify the product’s quality and compliance.
- Shipment Deadlines: Establish clear deadlines for shipment and delivery to ensure the LC is tied to realistic production schedules.
- Payment Schedules: Define when and how payments will be made (whether in full or in installments) and ensure they align with production milestones and shipment dates.
Actionable Tip: Before finalizing the contract and LC terms, take the time to discuss these points in detail with the buyer. Both parties should be aligned to avoid potential misunderstandings when it’s time to submit documents for payment.
Timely Issuance and Confirmation of the LC
Strategy Overview: To avoid production delays or stalled crane orders, it's essential that the LC is issued and confirmed in a timely manner. Since cranes are typically large, customized, or highly technical items, manufacturers require sufficient time to procure materials, organize production, and deliver the final product. Delays in the LC issuance can lead to halted production and strained project timelines.
Importance: Issuing the LC well in advance of production helps ensure that the payment process is guaranteed before major investments are made in materials or labor. This minimizes the risk of financial strain on the manufacturer during production.
Actionable Tip: Agree on a clear timeline for the LC issuance with the buyer. Set deadlines for the issuance of the LC that align with the manufacturing schedule, and follow up with the bank or the buyer to ensure the process is on track. Both parties should prioritize the timely confirmation of the LC to prevent any production disruptions.
Thorough Review of LC Terms
Strategy Overview: A careful review of the LC terms is vital to ensure that they align with the agreed contract. Both parties should work closely with legal advisors or trade experts to ensure that all the terms are correct and comply with international trade regulations. This step minimizes the risk of discrepancies between the documents and the conditions of the LC, which could otherwise result in payment rejection.
Importance: Misunderstandings or mistakes in the LC terms can delay payment, disrupt production, and cause financial losses. Therefore, careful scrutiny of the terms is essential to ensure the documents submitted meet the exact requirements for a smooth transaction.
Actionable Tip: Before submitting documents for payment, both parties should conduct a thorough review of the LC with the assistance of legal professionals or trade experts. This ensures that all the terms—especially the required documents and deadlines—are clearly understood and comply with international standards.
Partial Payments or Progress Payments
Strategy Overview: For large-scale crane orders, relying solely on a final payment after delivery can sometimes lead to cash flow issues. To mitigate this risk, consider negotiating for partial or progress payments throughout the production process. This strategy ensures that manufacturers have the necessary funds to continue production without relying on the final payment, which could be delayed due to issues with the LC or other complications.
Importance: Progress payments tied to production milestones help maintain cash flow, reduce financial strain, and ensure that production doesn’t stall while waiting for the final payment.
Actionable Tip: Negotiate with the buyer to include progress payments based on key milestones in the production process. For example, payments could be tied to the completion of the crane’s assembly, quality checks, or shipment preparations. This approach allows the seller to receive a steady cash flow throughout the project, reducing financial risks.
Working with Trusted Banks
Strategy Overview: Engaging with trusted banks that specialize in international trade and have a solid reputation for handling Letters of Credit is crucial. The role of the bank is to verify that both parties meet their obligations and to guarantee payment once the terms are met. However, not all banks offer the same level of reliability or experience in handling high-value transactions, so careful selection is important.
Importance: Banks with proven expertise in managing LCs and international trade transactions can help streamline the process and avoid unnecessary errors or delays. A reputable bank ensures that all documents are reviewed thoroughly and that payment is processed in a timely manner.
Actionable Tip: Before entering into a crane transaction involving an LC, ensure that both the buyer and seller are working with banks that have a strong track record in handling international LCs. Choose banks with experience in large-scale transactions and ensure they understand the specific needs of the crane industry.
Currency Exchange Management
Strategy Overview: In international crane transactions, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can present a significant risk. For example, if the LC is issued in a foreign currency, sudden changes in exchange rates could reduce the value of the final payment receive To mitigate this risk, both parties can consider currency hedging strategies or agree on a fixed exchange rate to avoid unpredictable fluctuations.
Importance: Managing currency risks is especially important for crane manufacturers operating in multiple markets, as it helps avoid unexpected financial shortfalls. By agreeing to lock in a specific exchange rate or using hedging instruments, both the buyer and seller can protect themselves from unfavorable currency shifts.
Actionable Tip: Discuss exchange rate risks with the buyer and your bank before issuing the L If possible, agree to a fixed exchange rate or consider using hedging strategies to protect against currency fluctuations. This ensures that both parties are clear on the financial terms and can avoid surprises when it comes time for payment.
By implementing these strategies, both buyers and sellers in crane transactions can minimize the risks associated with Letters of Credit, ensuring smoother and more secure international trade. Whether it's through careful planning of payment terms, working with trusted banks, or managing currency risks, these proactive steps will help mitigate common issues that arise in crane orders and ensure timely and accurate payments.
Case Studies of LC Issues and Resolutions
Case Study 1: Delay Due to Late Issuance of LC
Problem: A crane manufacturer in the UK faced production delays due to the buyer's late issuance of the Letter of Credit (LC). The delay in receiving the LC prevented the manufacturer from securing the necessary materials and starting production on time, risking project deadlines and customer relationships.
Solution:
- The manufacturer and buyer revised the project timeline to accommodate the LC delay.
- Partial payments were negotiated based on production milestones, helping to keep the cash flow stable and allowing the manufacturer to proceed with the procurement of critical materials.
- The buyer agreed to expedite the LC process in the future to prevent further delays.
Outcome:
- The manufacturer was able to continue production despite the delay, minimizing disruptions.
- Both parties ensured better alignment and communication moving forward, preventing further issues related to late LC issuance.
Case Study 2: Non-Compliance with LC Terms
Problem: A European crane manufacturer experienced delays in payment due to discrepancies between the documents submitted and the terms outlined in the L The issuing bank rejected the payment because the bill of lading did not match the required terms, causing a significant delay.
Solution:
- The seller and buyer worked together to clarify document requirements and correct discrepancies.
- The manufacturer resubmitted the correct documentation and ensured future document submissions would strictly adhere to LC terms.
- Both parties implemented a more thorough internal document review process before submitting documents for future LC transactions.
Outcome:
- The payment was successfully processed after document correction.
- The internal review process for LCs was strengthened, reducing the risk of similar issues in the future.
Case Study 3: Currency Fluctuations and Payment Delays
Problem: A crane manufacturer in the US faced financial difficulties due to currency fluctuations. The buyer, based in South America, experienced a devaluation of their local currency, causing discrepancies in the final payment amount when converting the payment from USD to Brazilian Reals (BRL).
Solution:
- The manufacturer and buyer agreed to a fixed exchange rate at the time of contract signing, ensuring the agreed payment would remain unaffected by currency fluctuations.
- They also explored currency hedging options through their banks to protect future transactions from exchange rate risks.
Outcome:
- The fixed exchange rate ensured that both parties received the agreed-upon payment.
- The buyer and seller avoided further currency-related payment issues, ensuring smoother transactions in future contracts.
These case studies illustrate the common issues associated with Letters of Credit in crane transactions, such as delayed LC issuance, non-compliance with document terms, and currency fluctuations. By adopting strategies such as partial payments, strict document reviews, and fixed exchange rates, companies can successfully mitigate these risks and ensure more secure and timely crane orders.
Best Practices for Securing Crane Orders with LCs
Building Strong Relationships with Banks
Importance of Long-Term Relationships:
- Establishing a strong, ongoing relationship with reputable banks is critical for streamlining LC processes.
- Trusted banks provide expert advice, reduce delays in issuing or confirming LCs, and help resolve potential issues quickly, ensuring that crane manufacturers and buyers can maintain a smooth cash flow.
How It Helps:
- A solid banking relationship can lead to faster approvals and fewer document rejections, as banks become familiar with the needs and requirements of the business.
- Banks can also offer customized solutions to suit the unique needs of large-scale crane transactions, such as flexible payment terms or advice on hedging against currency risks.
Regular Monitoring of LC Status
Why It’s Important:
- Continuous monitoring of the LC and related documents is essential to ensure that there are no unexpected issues or discrepancies that could cause delays.
- Delays in submitting required documents or failing to meet deadlines can result in halted production or payment delays.
Best Practices:
- Establish a clear timeline for submitting documents and ensure they are checked well in advance of the LC deadline.
- Regularly follow up with the bank to track the status of the LC, confirming any required documents and ensuring that everything is in compliance with the terms set out.
Actionable Tip:
- Implement an internal system or team responsible for tracking the progress of LCs, ensuring deadlines are met and payments processed on time.
Transparent Communication Between Buyer and Seller
Why Communication Matters:
- Clear and open communication between the buyer and seller is crucial in avoiding misunderstandings related to LC terms, payment schedules, and production timelines.
- It ensures that both parties are aligned on the requirements and expectations, reducing the chance of disputes or delays during the production and delivery process.
Best Practices:
- Schedule regular check-ins or meetings with the buyer to discuss the LC terms and review any changes or updates.
- Share timely updates on production progress, shipment schedules, and any potential delays, ensuring that both parties remain informed and prepare
Actionable Tip:
- Maintain clear documentation of all communication with the buyer to ensure transparency and avoid miscommunication about the LC or production process.
Ensuring Legal and Trade Compliance
Why Compliance Is Critical:
- Ensuring that both the LC and the contract comply with international trade regulations and laws is vital to avoid legal issues or delays in payment.
- Legal and trade compliance guarantees that the transaction is executed according to global standards, reducing the risk of disputes and financial penalties.
Best Practices:
- Work with a trade lawyer or legal expert to review both the LC terms and the contract to ensure all legal and regulatory requirements are met.
- Stay informed on the latest international trade regulations, especially those related to exports and imports of industrial equipment like cranes, to ensure full compliance throughout the transaction.
Actionable Tip:
- Always consult with a trade lawyer before finalizing any contract or LC, particularly for large and complex crane orders that involve cross-border transactions.
By following these best practices, crane manufacturers and buyers can significantly improve the efficiency and security of their Letter of Credit transactions. Establishing strong relationships with banks, actively monitoring the LC status, ensuring transparent communication, and maintaining legal compliance all contribute to securing crane orders and mitigating the payment risks associated with large-scale, international transactions.
Conclusion
Recap of the Importance of LCs in Crane Trade
- Security for Both Parties: LCs play a critical role in providing financial security for both the buyer and the seller in crane transactions.
- Payment Assurance: For manufacturers, LCs guarantee timely payment once the terms are met, reducing the risk of non-payment. For buyers, LCs ensure that payments are made only after receiving the correct products or services.
- International Trade Confidence: In the crane industry, where transactions are often high-value and international, LCs provide confidence and reduce the risk of disputes between the parties involve
In summary, Letters of Credit are essential tools for securing payments and ensuring smooth international crane trade, protecting both buyers and sellers from financial uncertainties.
Final Thoughts on Mitigating Risks
Proactive Risk Management: By understanding common LC risks, manufacturers can apply best practices to mitigate delays and ensure timely payments.
Best Practices Include:
- Clear agreements on terms and documents.
- Timely issuance and confirmation of LCs.
- Regular monitoring of LC status to avoid last-minute issues.
- Thorough review of LC terms to ensure compliance.
Strategies to Avoid Delays: Adopting these best practices, along with effective communication and strong partnerships, will help prevent disruptions in the crane production and delivery process.
In conclusion, mitigating payment risks requires a proactive approach, focusing on clear communication and timely actions.
Call to Action
- Collaboration is Key: Crane manufacturers and buyers should work closely together, focusing on timely LC issuance, clear communication, and proper documentation.
- Securing Successful Transactions: By ensuring that LC terms are well-defined and understood, both parties can navigate the complexities of international transactions and avoid payment delays.
- Adopting Proactive Strategies: Manufacturers should stay informed, closely monitor the LC process, and establish strong relationships with trusted banks to ensure smooth crane orders.
In summary, a collaborative, proactive approach to managing LCs will ensure successful, risk-free crane transactions, benefiting both buyers and sellers in the long term.
Key Takeaways
Securing Crane Orders with LCs:
Letters of Credit (LC) are vital tools for ensuring timely payments and providing financial security for both buyers and sellers in crane transactions. They help mitigate risks associated with large, international orders.
Common Payment Risks:
- Delayed Issuance: A late LC can halt production and cause delivery delays.
- Non-Compliance: Discrepancies between LC terms and submitted documents can lead to payment rejections.
- Currency Fluctuations: Changes in exchange rates may create payment discrepancies and additional costs.
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
- Careful Planning: Clearly define terms and documents required to avoid issues.
- Open Communication: Maintain ongoing discussions between buyer and seller to ensure alignment.
- Best Practices: Timely LC issuance, regular monitoring, and thorough review of terms are essential for minimizing risks and ensuring smooth transactions.