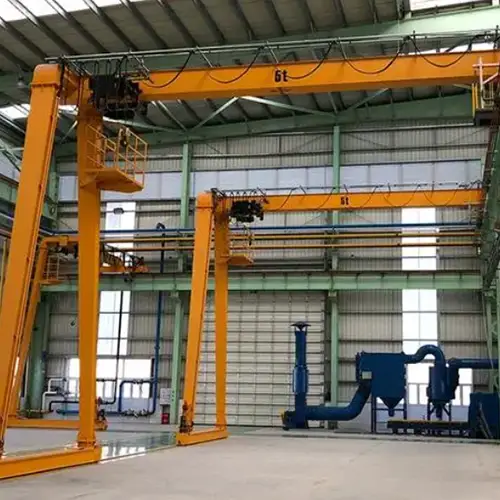
Full Gantry Cranes vs. Half Gantry Cranes: A Buyer's Guide
Full Gantry Cranes vs. Half Gantry Cranes: A Comprehensive Buyer's Guide on Full & Half Gantry Crane's features, advantages, uses, costs & installation
| Crane type | Full gantry crane & Semi gantry crane |
| Crane capacity | 1-20 ton, 3 -320 ton |
| Lifting Height | As your request |
| Crane Span | As customer requirement |
Category: Full& Half Gantry
Your Trusted Half Gantry& Full Gantry Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Full Gantry Cranes vs. Half Gantry Cranes: A Buyer's Guide
Full Gantry Cranes vs. Half Gantry Cranes: A Comprehensive Buyer's Guide on Full & Half Gantry Crane's features, advantages, uses, costs & installation
Full Gantry Cranes vs. Half Gantry Cranes: A Comprehensive Buyer's Guide
In the world of material handling and heavy lifting, the choice of the right crane configuration can make a significant difference in efficiency, safety, and overall productivity. Among the various types of cranes available, gantry cranes have earned a reputation for their versatility and effectiveness. However, within the realm of gantry cranes, two distinct configurations stand out: full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes, also known as semi-gantry cranes.
This comprehensive buyer's guide aims to shed light on the differences, advantages, and considerations associated with these two crane configurations. Whether you're a seasoned professional in the field or new to the world of gantry cranes, understanding the nuances between full gantry and half gantry cranes is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your specific material handling needs.
Before we dive into the details of full gantry and half gantry cranes, let's begin with a brief overview of gantry cranes as a whole. Gantry cranes are a type of material handling equipment characterized by their overhead structure, which includes two or more vertical legs or columns, and a horizontal beam (or girder) that spans the gap between these legs. This overhead structure supports a hoisting mechanism that can move horizontally along the beam, allowing for precise and controlled lifting and positioning of heavy loads.
Gantry cranes come in various configurations, each designed to meet specific requirements and operational conditions. Among these configurations, full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes hold a distinct place due to their unique features and capabilities.
A "half gantry crane" and a "full gantry crane" are two different configurations of gantry cranes used for material handling in industrial applications. These two configurations differ in terms of their support structure and the way they are installed:

Half Gantry Crane:
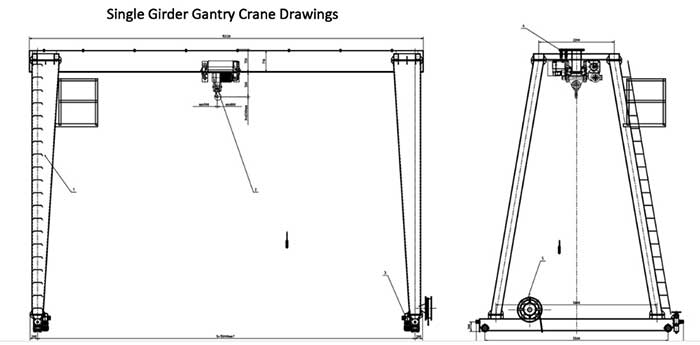
- A half gantry crane, also known as a single-leg gantry crane or semi-gantry crane, has one vertical support leg or column on one side, while the other end of the horizontal beam is supported by a wall, building structure, or existing support.
- It operates on a single runway, which can be installed along a wall or a column-supported structure. The crane can move along the runway using wheels or a rail system.
- Half gantry cranes are often used when there is limited space or when only one side of the lifting area requires material handling. They are known for their versatility and are suitable for various applications, including manufacturing, warehouses, and construction sites.
- While half gantry cranes are efficient and cost-effective for certain tasks, they typically have lower lifting capacities compared to full gantry cranes due to their asymmetric support structure.

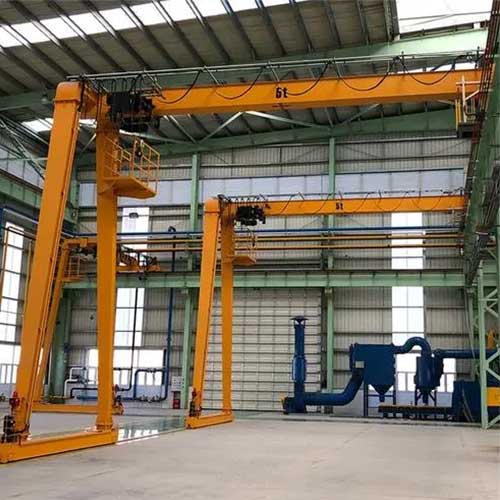
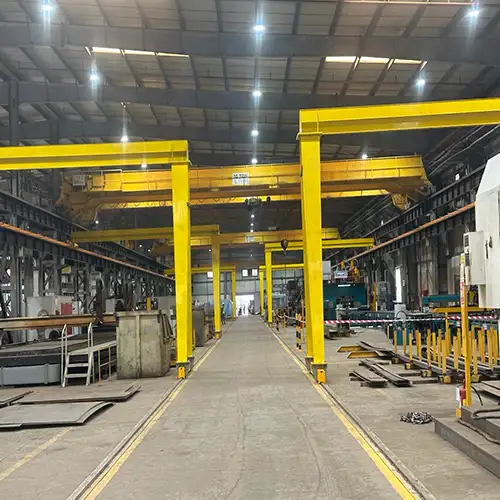
Full Gantry Crane:
- A full gantry crane, also known as a double-leg gantry crane, has two vertical support legs or columns at each end of the horizontal beam. This design creates a complete support structure on both sides.
- Full gantry cranes are known for their enhanced stability and lifting capacity. They are suitable for heavy-duty applications that involve lifting and moving extremely heavy loads with precision.
- These cranes often operate on a dedicated runway system, allowing for maximum coverage of the working area. They are commonly used in industries such as steel production, shipbuilding, and large-scale manufacturing.
- Due to their symmetrical support structure, full gantry cranes can handle much heavier loads compared to half gantry cranes.
In summary, a half gantry crane has one support leg and is often used when space is limited or when only one side of the lifting area requires material handling. In contrast, a full gantry crane has two support legs and is used for heavy-duty lifting tasks that demand high stability and lifting capacity. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the application and available space.
Importance of Choosing the Right Crane Configuration
The choice between a full gantry crane and a half gantry crane is not merely a matter of preference; it has a direct impact on your material handling operations. Selecting the appropriate crane configuration can significantly affect factors such as load capacity, maneuverability, spatial requirements, and cost-effectiveness. Making the right choice can enhance efficiency, improve safety, and contribute to the overall success of your business.
Purpose and Scope of the Guide
The purpose of this buyer's guide is to equip you with the knowledge and insights necessary to make an informed decision when selecting between full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes. We will explore the unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each configuration, helping you assess which one aligns best with your material handling needs. Whether you operate in manufacturing, construction, logistics, or any other industry requiring heavy lifting, this guide will serve as a valuable resource in your decision-making process.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve into the specific attributes of full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes, addressing factors such as load capacity, space requirements, mobility, safety considerations, cost analysis, customization options, industry-specific applications, and much more. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge and confidence to select the crane configuration that optimally suits your operational requirements.
Understanding Gantry Crane Configurations
Gantry cranes are versatile material handling solutions used across a wide range of industries. Their adaptability stems from the availability of different configurations, each designed to meet specific needs. In this section, we'll explore the two primary gantry crane configurations: full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes (also known as semi-gantry cranes).
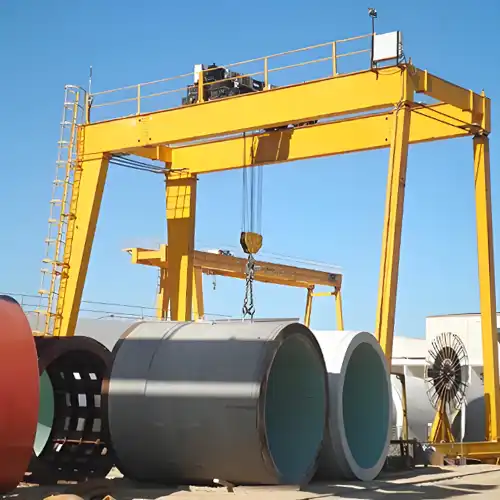
Full Gantry Cranes
Definition and Characteristics:
Full gantry cranes, often referred to as double-leg gantry cranes, are recognized by their symmetrical structure. They feature two vertical support legs or columns positioned at each end of the horizontal beam. This design creates a complete support structure on both sides of the crane.
Key Features:
- Enhanced Stability: The presence of two support legs provides superior stability, allowing full gantry cranes to handle heavy loads with precision.
- High Load Capacity: Due to their robust structure, full gantry cranes boast high load capacities, making them suitable for heavy-duty lifting tasks.
- Wide Span Coverage: These cranes typically operate on dedicated runways, providing extensive coverage of the working area and versatility in load positioning.
- Ideal for Heavy Industries: Full gantry cranes find applications in heavy industries such as steel production, shipbuilding, and large-scale manufacturing.
Typical Applications:
Steel mills and foundries
Shipbuilding and maritime operations
Container handling at ports
Automotive manufacturing
Power plant construction and maintenance

Chinese style half gantry crane
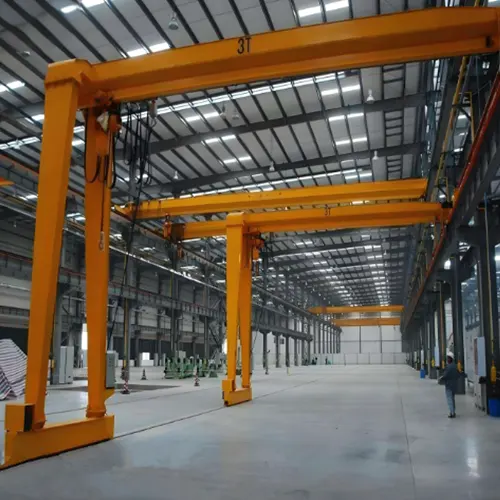
Half Gantry Cranes (Semi-Gantry Cranes)
Definition and Characteristics:
Half gantry cranes, also known as single-leg gantry cranes or semi-gantry cranes, have a distinctive asymmetric structure. They feature a single vertical support leg or column on one side, while the other end of the horizontal beam is supported by a wall, building structure, or existing support.
Key Features:
- Versatility in Limited Spaces: Half gantry cranes are ideal for applications with limited space or when material handling is required on one side of the lifting area.
- Portability: Some half gantry cranes are designed for portability, allowing them to be relocated easily to adapt to changing operational needs.
- Cost-Effective for Lighter Loads: These cranes are cost-effective for tasks involving lighter to moderate loads and temporary use.
- Smaller Footprint: The single-leg design results in a smaller footprint compared to full gantry cranes, making them suitable for compact facilities.
Typical Applications:
Manufacturing facilities with space constraints
Warehouses and distribution centers
Construction sites
Maintenance and repair operations
Small to medium-sized production environments
Understanding the characteristics and applications of full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes is the first step in making an informed decision about which configuration best suits your material handling needs. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into various aspects of these configurations, helping you assess their suitability for your specific requirements.
Lifting Capacity and Load Requirements
Assessing Your Material Handling Needs:
Before choosing between full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes, it's crucial to assess your material handling requirements. Consider the following factors:
- Type of Materials: Determine the types of materials you'll be lifting, whether they are raw materials, finished products, machinery, or other items.
- Weight of Loads: Calculate the maximum weight of the loads you need to lift and transport. Ensure the chosen crane can handle your heaviest loads.
- Frequency of Lifting: Evaluate how often you'll be using the crane and the number of lifts per hour or day.
Load Capacity Considerations:
- Full Gantry Cranes: Full gantry cranes are designed for heavy-duty lifting tasks and offer high load capacities. They are suitable for applications involving extremely heavy loads.
- Half Gantry Cranes: Half gantry cranes have lower load capacities compared to full gantry cranes. They are ideal for lighter to moderate loads and may not be suitable for extremely heavy items.
Examples of Suitable Applications for Each Configuration:
- Full Gantry Cranes: Best suited for industries requiring high lifting capacities, such as steel mills, shipbuilding, and large-scale manufacturing.
- Half Gantry Cranes: Ideal for applications where lighter to moderate loads need to be handled, and space constraints exist, such as manufacturing facilities with limited workspace.
Space and Layout Considerations
Available Workspace and Layout Constraints:
Consider the layout of your workspace and any constraints that may affect crane installation. Take into account:
- Available Floor Space: Assess the available area for crane operation, including clearances for the crane's movement.
- Overhead Clearance: Determine the overhead clearance, considering obstacles such as lights, ducts, and beams.
- Spatial Constraints: Identify any spatial limitations or obstacles that may affect crane movement and load positioning.
Advantages of Each Configuration in Different Space Environments:
- Full Gantry Cranes: Full gantry cranes typically operate on dedicated runways and offer extensive span coverage. They are well-suited for larger working areas with ample space.
- Half Gantry Cranes: Half gantry cranes are advantageous in space-constrained environments where only one side of the lifting area requires material handling. Their smaller footprint makes them suitable for compact facilities.
Mobility and Installation Requirements
Mobility of Half Gantry Cranes: - Half gantry cranes are known for their mobility. Some models are designed for portability, allowing easy relocation to adapt to changing operational needs.
Installation Requirements for Full Gantry Cranes: - Full gantry cranes require a more substantial installation process. This typically involves the construction of dedicated runways or support structures on both ends of the crane.
Suitable Locations for Each Configuration:
- Full Gantry Cranes: Full gantry cranes are typically installed as permanent fixtures in facilities with ample space and dedicated runways.
- Half Gantry Cranes: Half gantry cranes are suitable for both permanent installations and temporary setups, making them versatile for various locations and operational needs.
Stability and Safety
- Stability Features of Full Gantry Cranes: - Full gantry cranes offer enhanced stability due to their symmetrical, two-legged design. This stability is crucial for handling heavy loads with precision and safety.
- Safety Considerations for Half Gantry Cranes: - Half gantry cranes require careful consideration of safety, especially in applications involving unbalanced loads. Operator training and adherence to safety protocols are essential.
- Compliance with Industry Safety Standards: - Regardless of the crane configuration chosen, it's imperative to ensure compliance with industry safety standards and regulations. Both full gantry and half gantry cranes should adhere to safety guidelines to protect personnel and assets.
Understanding the lifting capacity, space requirements, mobility, installation, stability, and safety considerations for full gantry and half gantry cranes is vital in making the right choice for your material handling operations. In the upcoming sections, we will delve into cost analysis, customization options, industry-specific applications, and more to further assist you in your decision-making process.
Cost Analysis and Budgeting
When it comes to selecting between full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes, a comprehensive cost analysis is essential. Understanding the various cost components will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and long-term financial planning. Here, we break down the cost considerations into three main categories: initial investment costs, ongoing operating and maintenance costs, and evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO).
Initial Investment Costs:
- Crane Purchase: The initial purchase price of the crane is a significant portion of the investment. Full gantry cranes, with their higher load capacities and larger structures, generally come with a higher upfront cost compared to half gantry cranes.
- Installation: Consider the costs associated with installing the crane. Full gantry cranes may require more extensive installation work, including the construction of dedicated runways, which can increase installation expenses.
- Foundation and Infrastructure: For full gantry cranes, a robust foundation and supporting infrastructure are necessary, adding to the initial investment. Half gantry cranes may have fewer infrastructure requirements.
Ongoing Operating and Maintenance Costs:
- Energy Consumption: Evaluate the energy consumption of the crane, as this will impact your operational expenses. Full gantry cranes, due to their higher lifting capacities, may have higher energy demands.
- Routine Maintenance: Consider the cost of routine maintenance, including lubrication, inspections, and minor repairs. Full gantry cranes may have more components to maintain.
- Operator Training: Budget for operator training programs to ensure safe and efficient crane operation. Both configurations require trained operators.
Evaluating the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
The TCO is a comprehensive approach to assessing the long-term costs associated with owning and operating a crane. It takes into account the initial investment costs, ongoing operating and maintenance costs, and other factors that may impact your bottom line over the crane's lifespan. Here are some key considerations:
- Downtime Costs: Calculate the potential costs of downtime due to crane maintenance, repairs, or operational issues. Minimizing downtime is crucial for productivity.
- Expected Lifespan: Estimate the expected lifespan of the crane and consider replacement or refurbishment costs at the end of its useful life.
- Resale Value: Investigate the potential resale or trade-in value of the crane at the end of its service life. Some cranes retain value better than others.
- Energy Efficiency: Choose a crane configuration with energy-efficient features to reduce long-term energy costs.
- Operational Efficiency: Consider how the crane's design and features impact efficiency in material handling tasks. Improved efficiency can result in cost savings.
- Safety and Compliance: Investing in safety features and compliance with industry standards can help avoid costly accidents or fines.
- Supplier Support: Assess the level of technical support and after-sales services offered by the crane supplier. Prompt support can minimize downtime and reduce operational costs.
By evaluating the initial investment costs, ongoing operating and maintenance costs, and considering the TCO, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your budget and long-term financial goals. Keep in mind that the TCO approach takes into account the entire lifespan of the crane, ensuring that your investment provides value over time.
Customization and Accessories
In the world of material handling, one size doesn't fit all. Customization options and accessories play a crucial role in tailoring your gantry crane to meet specific operational needs and enhance its functionality. Whether you opt for a full gantry crane or a half gantry crane, the ability to adapt and customize the crane to your requirements is essential.
Custom your full gantry crane

Custom your half gantry crane
Customization Options for Gantry Cranes:
- Hoisting Mechanism: You can choose from various hoisting mechanisms, such as wire rope hoists, chain hoists, or electric winches, depending on your lifting requirements and precision.
- Control Systems: Advanced control systems, including radio remote controls, variable frequency drives (VFDs), and smart automation, can be integrated to improve crane operation and safety.
- Runway Length and Configuration: Customize the length and configuration of the crane's runway to fit your workspace, whether it's a straight runway or one with curves and junctions.
- Load Attachment: Depending on the type of materials you handle, you can select specialized load attachments, such as hooks, magnets, or grabs, for efficient and safe lifting.
- Safety Features: Enhance safety with additional features like overload protection, collision avoidance systems, and emergency stop controls.
- Paint and Finish: Choose coatings and finishes that offer corrosion resistance and durability, ensuring your crane maintains its appearance and functionality over time.
- Variable Speeds: Some cranes offer variable speed options for precise load positioning and efficient material handling.
Common Accessories to Enhance Functionality:
- Load Monitoring Devices: Load cells and load monitoring systems help ensure that the crane operates within safe load limits, preventing overloading.
- Wireless Communication: Wireless communication systems enable real-time monitoring and control of crane operations from a remote location.
- Anti-Collision Systems: Anti-collision systems use sensors and software to prevent collisions between cranes and other structures or equipment in the workspace.
- Maintenance Platforms: Installing maintenance platforms provides safe access for maintenance and inspection tasks, ensuring the crane remains in optimal condition.
- LED Lighting: LED lighting can be added to the crane for improved visibility during nighttime or low-light operations.
- Warning Signals: Audible and visual warning signals alert personnel to the crane's movements, enhancing safety in the workspace.
- Load Spreaders and Lifting Beams: Load spreaders and lifting beams distribute the load evenly, reducing the risk of damage to the load or the crane.
- Weather Protection: Weather-resistant enclosures and covers protect the crane's components from harsh environmental conditions.
- Remote Monitoring: Implement remote monitoring systems that allow you to track crane performance, schedule maintenance, and troubleshoot issues remotely.
- Operator Comfort Features: Enhance operator comfort with features like ergonomic seating, climate control, and noise-reduction measures.
The availability of customization options and accessories empowers you to design a gantry crane system that precisely meets your operational needs. When considering these options, prioritize safety, efficiency, and compatibility with your specific material handling tasks. Working closely with crane suppliers and manufacturers can help you determine the most suitable customizations and accessories for your crane.

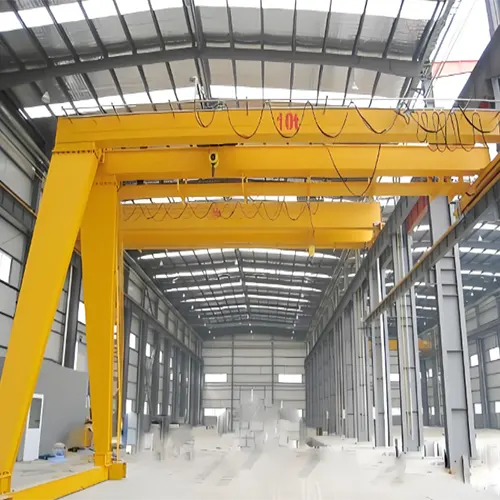
Outdoor gantry crane with full and half gantry crane design
Applications and Industry-Specific Considerations
Understanding the real-world applications and industry-specific considerations for both full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes is crucial in making an informed decision. Each configuration has its strengths and suitability for different industries and tasks.
Real-World Applications for Full Gantry Cranes:
Full gantry cranes are known for their high lifting capacity, stability, and versatility. Here are some real-world applications where full gantry cranes excel:
- Steel Mills and Foundries: Full gantry cranes are commonly used in steel mills and foundries for handling heavy steel coils, ingots, and finished products with precision.
- Shipbuilding and Maritime Operations: Shipyards rely on full gantry cranes to lift and position ship components, including hull sections and engines, during construction and maintenance.
- Container Handling at Ports: Full gantry cranes are the workhorses of container terminals, efficiently loading and unloading containers from ships and trucks.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Automotive plants use full gantry cranes for assembling vehicles, moving heavy machinery, and transporting car bodies along the production line.
- Power Plant Construction and Maintenance: Full gantry cranes play a crucial role in power plant construction, lifting generators, turbines, and heavy equipment into position.
Industry Examples Benefiting from Half Gantry Cranes:
Half gantry cranes, with their adaptability and suitability for confined spaces, find applications across various industries:
- Manufacturing Facilities with Space Constraints: Industries with limited workspace, such as small manufacturing units, benefit from half gantry cranes for efficient material handling.
- Warehouses and Distribution Centers: Half gantry cranes are used for stacking and transporting goods in warehouses, optimizing storage space.
- Construction Sites: Half gantry cranes are ideal for construction projects that require lifting and positioning materials in tight spaces.
- Maintenance and Repair Operations: Industries involved in equipment maintenance and repair utilize half gantry cranes to handle machinery components.
- Small to Medium-Sized Production Environments: Industries with moderate lifting needs appreciate the cost-effective and space-efficient nature of half gantry cranes.
Choosing the Right Configuration
Choosing the right configuration, whether a full gantry crane or a half gantry crane, depends on your specific material handling needs and operational environment. Here are steps to help you make an informed decision:
- Developing a Checklist for Your Specific Needs:
- Clearly define your material handling requirements, including load capacity, frequency of use, available space, and safety considerations.
- Consider the pros and cons of each crane configuration and how they align with your checklist.
- Prioritize key factors such as load capacity, space availability, mobility, and budget constraints based on your checklist.
Consulting with Crane Experts and Suppliers:
- Engage with crane experts and reputable suppliers who can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on your unique needs.
- Request site assessments and feasibility studies to ensure the chosen crane configuration is compatible with your workspace.
- Seek multiple quotes and compare proposals from different suppliers to make a well-informed decision.
By developing a checklist tailored to your specific needs and consulting with experts and suppliers, you can confidently choose the crane configuration that optimally suits your material handling requirements and industry-specific considerations. Making the right choice will positively impact efficiency, safety, and productivity in your operations.
Installation and Maintenance
Once you've selected the appropriate gantry crane configuration for your material handling needs, the next critical steps involve installation and ongoing maintenance. Proper installation ensures safe and efficient crane operation, while regular maintenance preserves the crane's functionality and longevity. In this section, we'll delve into the installation requirements and considerations, as well as maintenance best practices for both full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes.
Installation Requirements and Considerations:
For Full Gantry Cranes:
- Foundation Construction: Full gantry cranes require a robust foundation or runway construction to support the crane's structure and handle the loads. The foundation must be level, stable, and able to withstand the crane's weight and the forces generated during lifting.
- Runway Construction: Establishing dedicated runways with precise alignment is crucial. Runway beams must be securely anchored to support the crane's movement.
- Clearances: Ensure sufficient overhead clearance, both for the crane's vertical movement and for the load being lifted. Account for any obstacles or obstructions in the crane's path.
- Electrical Supply: Provide the necessary electrical supply and power distribution for the crane's electrical components, including motors, control systems, and lighting.
- Safety Measures: Implement safety measures during installation, including fall protection for workers, secure anchor points, and adherence to safety standards and regulations.
For Half Gantry Cranes:
- Foundation or Wall Mounting: Depending on the design, half gantry cranes are either floor-mounted or wall-mounted. Ensure that the floor or wall structure can support the crane's weight and withstand the forces applied during lifting.
- Clearances: Similar to full gantry cranes, consider overhead clearances and any obstructions in the crane's path, especially if it operates near walls or columns.
- Electrical Supply: Provide the necessary electrical supply and power distribution for the crane's electrical components, which may include control panels and festoon systems.
- Operator's Line of Sight: Ensure that the crane operator has a clear line of sight to the load and the entire workspace. This is essential for safe and precise operation.
Maintenance Best Practices for Both Configurations:
- Regular Inspections: Implement a routine inspection schedule to identify wear and tear, loose components, and potential issues. Inspect the hoisting mechanism, electrical systems, structural components, and safety features.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of moving parts, such as gears, wheels, and bearings, is essential to prevent friction, reduce wear, and extend the crane's lifespan.
- Safety Checks: Pay close attention to safety features, including limit switches, emergency stop controls, and overload protection systems. Ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Operator Training: Invest in operator training to ensure that crane operators are knowledgeable about safe operation, load limits, and emergency procedures.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities, inspections, and repairs. Documentation helps track the crane's performance and compliance with safety standards.
- Emergency Response Plan: Develop and communicate an emergency response plan to address unexpected situations or accidents during crane operation.
- Spare Parts Inventory: Keep a stock of essential spare parts to facilitate prompt repairs in case of component failure.
- Suppliers and Service Providers: Establish a relationship with crane suppliers or service providers who can offer technical support, spare parts, and maintenance services.
Proper installation and ongoing maintenance are essential for the safe and efficient operation of both full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes. Regular inspections, adherence to safety standards, and proactive maintenance practices contribute to the crane's reliability and longevity, minimizing downtime and ensuring a high level of safety in your material handling operations.
Supplier Selection and Manufacturer Reputation
Selecting the right supplier and ensuring the manufacturer's reputation aligns with your expectations are pivotal steps in acquiring a gantry crane that meets your material handling needs. This section outlines key considerations for researching reputable manufacturers and evaluating supplier reputation and service.
Researching Reputable Manufacturers:
- Industry Experience: Look for manufacturers with a substantial history and experience in designing and producing gantry cranes. Companies with a proven track record tend to provide reliable products.
- Product Range: Assess the manufacturer's range of crane products. A diverse product portfolio indicates versatility and the ability to cater to various customer needs.
- Certifications and Compliance: Verify that the manufacturer complies with industry standards and holds relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management.
- Customization Capability: Check whether the manufacturer offers customization options to tailor the crane to your specific requirements. A manufacturer that can adapt its products to your needs is valuable.
- References and Case Studies: Request references and review case studies showcasing the manufacturer's successful crane installations. Hearing from satisfied customers provides insight into the manufacturer's capabilities.
Evaluating Supplier Reputation and Service:
- Customer Feedback: Seek customer reviews and testimonials to gauge satisfaction levels with the supplier's products and services. Online platforms, industry forums, and references can be valuable sources of feedback.
- Service and Support: Assess the supplier's commitment to customer support. This includes pre-sale consultations, technical assistance, and after-sales services such as maintenance and spare parts availability.
- Response Time: Evaluate the supplier's responsiveness to inquiries and service requests. Prompt communication is essential, especially during emergency situations.
- Warranty and Guarantees: Review the terms and conditions of warranties and guarantees offered by the supplier. A robust warranty reflects the manufacturer's confidence in their product.
- Local Presence: Consider whether the supplier has a local presence, including service centers and spare parts availability. Local support can expedite maintenance and repairs.
- Price Transparency: Ensure that pricing is transparent and includes all necessary components, installation costs, and any additional fees. Hidden costs can lead to budget overruns.
- References: Request references from the supplier and contact previous clients to inquire about their experiences with the supplier's products and services.
- Contractual Agreements: Carefully review all contractual agreements, including delivery schedules, payment terms, and service commitments. Seek legal counsel if needed to understand the terms thoroughly.
- Scalability: Consider whether the supplier can accommodate future needs, such as additional cranes or upgrades. A supplier that can grow with your business is advantageous.
- Safety Commitment: Assess the supplier's commitment to safety in crane design and manufacturing. Safety features and compliance with safety standards are critical.
- Sustainability Practices: Inquire about the manufacturer's sustainability practices, including energy-efficient designs and responsible sourcing of materials.
Choosing a reputable manufacturer and supplier ensures not only the quality and reliability of your gantry crane but also a positive and long-lasting partnership. Thorough research and due diligence during the selection process are vital to achieving a successful crane installation and ongoing support for your material handling operations.
Conclusion
In the world of material handling, the choice between full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes represents a critical decision that impacts efficiency, safety, and productivity. This guide has provided comprehensive insights into these two crane configurations to help you make informed decisions tailored to your unique needs.
Keypoints:
- Full gantry cranes offer high load capacities, stability, and versatility, making them ideal for heavy-duty industries like steel production and shipbuilding.
- Half gantry cranes are adaptable and space-efficient, making them suitable for industries with limited workspace and lighter to moderate lifting requirements.
- Assess your specific material handling needs, including load capacity, available space, and safety considerations, to determine the most suitable crane configuration.
- Installation and maintenance are crucial aspects of crane ownership. Proper installation ensures safe operation, while regular maintenance preserves crane functionality and longevity.
- Supplier selection is vital. Research reputable manufacturers and evaluate supplier reputation, service, and support to ensure a successful crane acquisition.
- Budgeting should include considerations beyond the initial purchase price, such as ongoing operating costs and the total cost of ownership over the crane's lifespan.
- Customization options and accessories allow you to tailor your crane to your specific needs, enhancing efficiency and safety.
- Consider real-world applications and industry-specific requirements to align your choice of crane configuration with your operational goals.
- Developing a checklist and consulting with experts and suppliers are essential steps in choosing the right crane for your organization.
Encouraging Informed Decision-Making:
Making an informed decision when selecting a gantry crane configuration involves a comprehensive evaluation of your material handling needs, budget, and the expertise of your chosen supplier. Remember that the right crane not only enhances your operations but also contributes to the safety of your personnel and assets.
By following the guidance provided in this guide and seeking expert advice where needed, you can confidently choose the gantry crane configuration that aligns with your goals and ensures the success of your material handling endeavors. Your investment in the right crane will have a lasting and positive impact on your business operations.
This comprehensive guide will provide buyers with the information needed to make an informed choice between full gantry cranes and half gantry cranes based on their specific material handling requirements and operational conditions.
Main Projects
Related Products
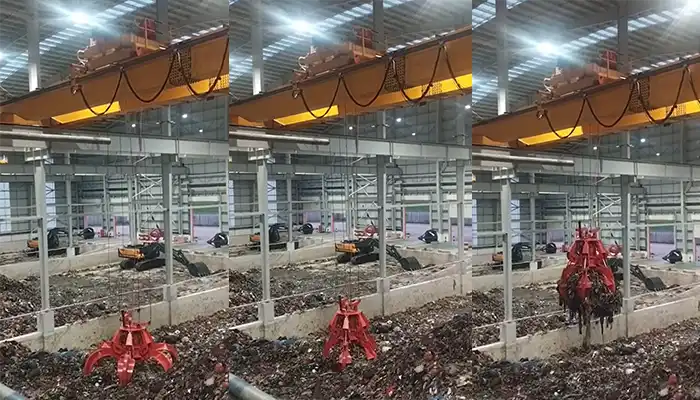

Supplied three grab bucket crane kits to Indonesia, enhancing garbage handling efficiency with high load capacity and reliable performance.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch















