Double Hoist Overhead Cranes | Single Girder vs Double Girder Design
Single girder double hoist & double girder double hoist overhead cranes, comparisons in strengths, limitations & suitability for industrial applications.
Category: Overhead Hoist
Your Trusted Overhead Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Double Hoist Overhead Cranes | Single Girder vs Double Girder Design
Single girder double hoist & double girder double hoist overhead cranes, comparisons in strengths, limitations & suitability for industrial applications.
In industrial settings, the efficient movement of heavy materials is paramount. Overhead cranes, also known as bridge cranes, are pivotal in handling hefty loads by suspending them from a beam that traverses the area. These cranes are categorized based on their configuration, with single girder double hoist and double girder double hoist standing out as two prevalent designs.
Selecting the appropriate overhead crane configuration is crucial for optimizing operations within various industrial environments. The right choice ensures not only enhanced efficiency but also cost-effectiveness and safety in material handling processes.
Single Girder Double Hoist Overhead Cranes
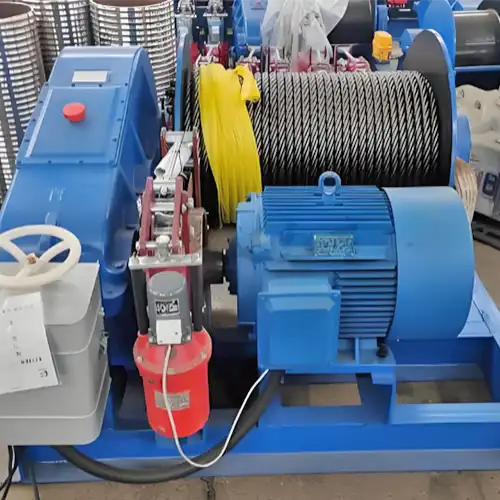
Single girder double hoist overhead cranes consist of a single beam or girder, on which two hoists are mounted, enabling the lifting and movement of loads. These cranes typically operate by running along elevated runways, utilizing the single girder as a support structure.
Strengths
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to their double girder counterparts, single girder double hoist cranes are more economical in terms of initial investment and operational costs.
- Flexibility in smaller spaces: Their design allows for greater maneuverability in confined spaces, making them suitable for facilities with space limitations.
- Ease of installation and maintenance: Their simpler design and fewer components make installation and maintenance more straightforward and cost-effective.
Limitations
- Lower load capacity compared to double girder: Single girder cranes typically have a lower load-bearing capacity compared to double girder cranes, limiting their use for heavier loads.
- Limited height under the hook: The single girder design restricts the lifting height, affecting its usability in environments requiring significant vertical lift.
- Not ideal for heavy-duty operations: Due to their lower load capacity, these cranes are not well-suited for heavy-duty industrial operations.
Industrial Applications
- Warehousing and logistics: Ideal for handling lighter loads and material movement within warehouse and logistics environments.
- Light to medium manufacturing processes: Suitable for manufacturing operations involving moderate load lifting and movement, where heavy-duty capabilities are not essential.
Single girder double hoist overhead cranes find their niche in industries where cost-effectiveness, space flexibility, and moderate load handling are prioritized over heavy-duty lifting capabilities.
Types of Overhead Double Hoist Cranes
Single girder overhead double hoist cranes come in various configurations, designed to accommodate different lifting needs and operational requirements. Here are a few types:

Top Running Single Girder Double Hoist Crane:
Twin Hoist Bridge Crane: This type of crane consists of a single girder with two hoists mounted on it, allowing for lifting two loads independently or synchronously. It operates along a fixed overhead runway.

Top Running Double Girder Double Hoist Crane: - Twin Hoist Bridge Crane: This crane configuration involves two hoists on each girder, allowing for independent or synchronized lifting of heavy loads. It operates on a fixed overhead runway.
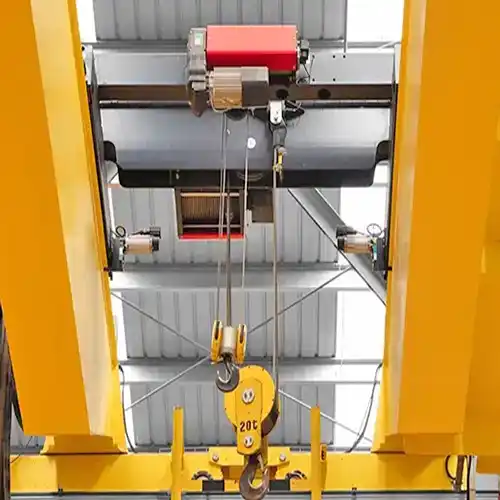
Double Girder Double Hoist Overhead Cranes
Double girder double hoist overhead cranes are designed with two girders or beams, each supporting a hoist mechanism for lifting and transporting heavy loads. This configuration provides robust support and stability for handling substantial weights across longer spans.
Strengths
- Higher load capacity: Double girder cranes excel in lifting heavier loads, offering superior load-bearing capabilities compared to single girder cranes.
- Increased lifting height: The design allows for greater hook height, facilitating the handling of materials requiring elevated positioning.
- Suitable for heavy-duty operations: Well-suited for rigorous industrial settings that demand the handling of substantial and bulky materials regularly.
Limitations
- Higher initial cost: Double girder double hoist cranes typically involve a higher initial investment due to their heavier construction and increased load capacities.
- More complex installation and maintenance: Their design complexity makes installation and maintenance more intricate, potentially leading to higher ongoing costs.
Requires more overhead space: Due to their structural design, these cranes necessitate more vertical space, limiting their suitability in areas with height constraints.
Industrial Applications
- Heavy manufacturing and construction: Ideal for heavy-duty lifting and movement in manufacturing settings involving large machinery or components.
- Foundries and steel mills: Crucial in handling massive loads such as molten metal or heavy steel materials in demanding industrial environments.
Double girder double hoist overhead cranes are the preferred choice in industries where heavy lifting, extended reach, and robustness are imperative for operational efficiency. Their ability to handle substantial weights and larger spans makes them indispensable in heavy industrial applications.
The comparative analysis between single girder double hoist and double girder double hoist overhead cranes will be further explored to understand the nuanced differences and their suitability across various industrial domains.
Comparative Analysis between Single Girder Double Hoist and Double Girder Double Hoist Overhead Cranes
Load Capacity and Lifting Height
- Single Girder Double Hoist Cranes: These cranes offer moderate load capacity and have limitations in lifting height due to their structural design. They are suitable for light to medium loads.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Cranes: Exhibiting significantly higher load capacity and increased lifting height capabilities, they excel in handling heavier loads and materials that require greater elevation.
Space and Installation Requirements
- Single Girder Double Hoist Cranes: Known for their flexibility in smaller spaces, these cranes require less overhead space, making them ideal for facilities with space constraints. Their installation is relatively simpler compared to double girder cranes.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Cranes: These cranes demand more overhead space due to their design, limiting their feasibility in facilities with height limitations. Additionally, their installation is more complex, requiring careful planning and structural considerations.
Cost Analysis
- Single Girder Double Hoist Cranes: These cranes are more cost-effective in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance due to their simpler design and lower load capacities.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Cranes: Despite their higher initial cost, these cranes offer superior load capacities and are more suitable for heavy-duty operations, potentially offering cost efficiencies in handling heavier materials over time.
Maintenance and Operational Efficiency
- Single Girder Double Hoist Cranes: Their simpler design translates into easier maintenance and lower operational complexities. They are efficient in handling lighter loads with reduced operational costs.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Cranes: While they require more intricate maintenance due to their complexity, these cranes offer high operational efficiency in heavy-duty applications, ensuring seamless handling of substantial loads.
Suitability for Different Industrial Environments
- Single Girder Double Hoist Cranes: Primarily suitable for warehousing, logistics, and light to medium manufacturing operations where cost-effectiveness and flexibility in smaller spaces are paramount.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Cranes: Excelling in heavy manufacturing, construction, foundries, and steel mills, these cranes are indispensable for handling massive loads and demanding industrial environments requiring robust lifting capabilities.
Understanding these comparative aspects is crucial in determining the most appropriate overhead crane configuration tailored to specific industrial needs, considering factors such as load requirements, space constraints, budget considerations, and operational demands. Such insights aid decision-makers in selecting the optimal overhead crane for their respective industries, ensuring enhanced efficiency and safety in material handling processes.
Double Hoist Gantry Cane Single Girder vs. Double Girder
Single Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes
Single girder double hoist gantry cranes are a type of overhead crane that operates on a gantry structure, with a single girder supporting two hoists for lifting and transporting loads. These cranes are versatile and commonly used in outdoor settings or where overhead runways are impractical. Components typically include:
- Girder: A single beam supporting the hoists and providing structural support.
- Hoists: Two hoisting mechanisms mounted on the girder, allowing simultaneous lifting and movement of loads.
- End Carriages: Support structures attached to the girder, enabling the crane's movement along the gantry runway.
- Gantry Legs: Vertical columns or supports that provide stability to the crane structure.
Strengths
Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Single girder double hoist gantry cranes are relatively easier to install compared to some other crane configurations due to their simpler design and fewer components. Their maintenance is also less complex, requiring less downtime and cost for upkeep and repairs.
Limitations
Specific limitations of single girder double hoist gantry cranes may include:
- Lower Load Capacity: These cranes may have a limited load capacity compared to some double girder configurations, making them less suitable for handling extremely heavy loads.
- Height Restrictions: Similar to other single girder cranes, the height under the hook may be limited, affecting the vertical lifting capability.
Industrial Applications
Single girder double hoist gantry cranes find applications in various industries, including:
- Shipbuilding Yards: Used for handling components and materials during ship construction and maintenance due to their outdoor flexibility and ease of installation.
- Construction Sites: These cranes are utilized for lifting and transporting materials in construction projects where overhead runways may not be feasible.
- Outdoor Storage Yards: Ideal for moving materials in open-air storage facilities due to their outdoor suitability and ease of maintenance.
Their adaptability to outdoor environments, combined with ease of installation and maintenance, makes single girder double hoist gantry cranes advantageous in various industries requiring moderate lifting capacities and flexibility in outdoor settings.
Types of Double Hoist Gantry Cranes
Single girder gantry cranes with double hoists come in various configurations to cater to different lifting needs in industrial settings. Here are some common types:

Single Girder Gantry Crane with Double Hoists: - Twin Hoist Gantry Crane: This type features a single girder design with two hoists mounted on it, allowing for independent or simultaneous lifting of loads. It operates along a fixed overhead runway on a gantry frame.
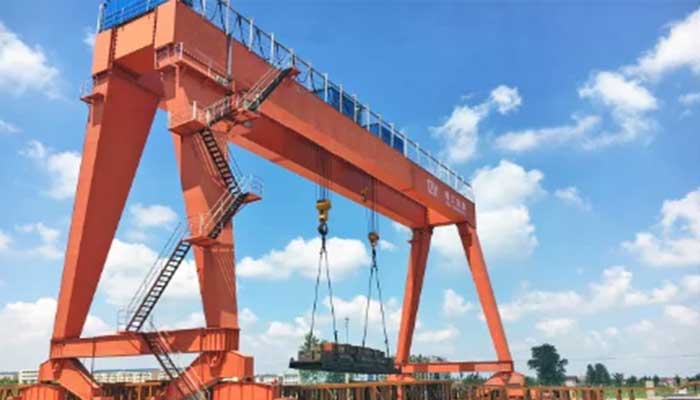

Box Girder Gantry Crane with Dual Hoists:
- Description: A heavy-duty gantry crane featuring box-shaped girders for increased strength and stability. The dual hoists are mounted on each girder, enabling efficient handling of extremely heavy loads.
- Applications: Ideal for industrial settings requiring robust lifting capacities, such as foundries, steel mills, and heavy manufacturing plants.
Each of these single girder gantry cranes with double hoists serves distinct purposes, offering advantages in terms of load handling, space utilization, and adaptability to various industrial environments. The choice of a specific type depends on factors such as available space, load requirements, installation preferences, and specific operational needs within an industry.
Double Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes
Double girder double hoist gantry cranes are robust overhead cranes that operate on a gantry structure, utilizing two girders to support two hoists for lifting and transporting heavy loads. These cranes are designed to handle substantial weights and are commonly used in outdoor environments or locations where heavy-duty lifting is required. Components typically include:
- Girders: Two parallel beams providing structural support and accommodating the hoisting mechanisms for lifting loads.
- Hoists: Dual hoisting mechanisms attached to each girder, allowing for independent or synchronized lifting and movement of heavy loads.
- End Carriages: These support the girders and facilitate the crane's movement along the gantry runway.
- Gantry Legs: Sturdy columns or supports that provide stability and support the entire crane structure.
Strengths
Double girder double hoist gantry cranes offer several strengths:
- Higher Load Capacity: These cranes are designed for heavy lifting and have significantly higher load capacities compared to single girder configurations, making them suitable for handling substantial weights.
- Increased Lifting Height: The dual girder design allows for increased lifting heights, enabling the handling of materials that require elevated positioning.
- Suitable for Heavy-Duty Operations: These cranes excel in heavy-duty industrial settings where robust lifting capabilities and higher load capacities are essential.
Limitations
Specific limitations of double girder double hoist gantry cranes may include:
- Higher Initial Cost: Due to their heavy-duty construction and higher load capacities, these cranes often involve a higher initial investment compared to some other crane configurations.
- Complex Installation and Maintenance: The complexity of the design can result in more intricate installation requirements and maintenance procedures, potentially leading to higher ongoing costs.
Industrial Applications
Double girder double hoist gantry cranes find applications in industries requiring heavy lifting and robust operations, including:
- Steel Mills and Foundries: Used for handling heavy materials like molten metal, ingots, and heavy machinery due to their ability to handle substantial weights.
- Construction Sites: Ideal for lifting and transporting large and bulky materials in construction projects that demand heavy lifting capacities.
- Industrial Manufacturing Facilities: These cranes are employed in manufacturing settings that involve large-scale production and handling of heavy components or machinery.
Due to their ability to handle heavy loads, increased lifting heights, and robustness, double girder double hoist gantry cranes are indispensable in industries where heavy-duty lifting capabilities are crucial for operational efficiency and safety.
Each type of gantry crane with dual hoists has distinct features suited for specific industrial applications, offering varying degrees of strength, mobility, and load-handling capabilities. The selection of a particular type depends on the operational requirements, load specifications, and environmental conditions of the specific industry or facility.
Comparative Analysis between Single Girder Double Hoist and Double Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes
Load Capacity and Lifting Height
- Single Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: These cranes generally offer moderate load capacities suitable for light to medium lifting operations. They may have limitations in lifting height due to the single girder design, restricting their vertical reach.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: In contrast, these cranes excel in load capacity, handling significantly heavier weights compared to their single girder counterparts. Additionally, the double girder design allows for increased lifting heights, facilitating the handling of materials requiring elevated positioning.
Space and Installation Requirements
- Single Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: Known for their flexibility in smaller spaces, these cranes require less overhead space and can be installed more easily due to their simpler design and fewer components.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: Due to their heavier construction and larger dimensions, these cranes demand more overhead space for installation. Additionally, their complex design makes the installation process more intricate and potentially time-consuming.
Cost Analysis
- Single Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: These cranes are generally more cost-effective in terms of both initial investment and ongoing maintenance due to their simpler design and lower load capacities.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: Despite their higher initial cost, these cranes offer higher load capacities, making them more suitable for heavy-duty operations. Over time, they might prove cost-efficient in handling heavier materials.
Maintenance and Operational Efficiency
- Single Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: Their simpler design translates to easier maintenance and lower operational complexities. They excel in handling lighter loads with reduced operational costs.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: While they require more intricate maintenance due to their complexity, these cranes offer high operational efficiency in heavy-duty applications, ensuring seamless handling of substantial loads.
Suitability for Different Industrial Environments
- Single Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: Primarily suitable for warehousing, logistics, and light to medium manufacturing operations where cost-effectiveness and flexibility in smaller spaces are essential.
- Double Girder Double Hoist Gantry Cranes: Excelling in heavy manufacturing, construction, foundries, and steel mills, these cranes are indispensable for handling massive loads and demanding industrial environments requiring robust lifting capabilities.
Understanding these comparative aspects aids in choosing the most suitable gantry crane configuration aligned with specific industrial needs, considering factors such as load requirements, space constraints, budget considerations, and operational demands. Such insights ensure enhanced efficiency and safety in material handling processes across diverse industrial settings.
How to Select A Suitable Double Hoist Cranes ?
Selecting a suitable double hoist crane involves assessing various factors to ensure it aligns with your specific industrial requirements. Here are steps to consider:
- Understand Your Lifting Needs: Determine the maximum weight and dimensions of the loads you'll be handling. Evaluate if the loads require simultaneous lifting, different lifting speeds, or if they demand specialized handling.
- Consider the Working Environment: Assess the available space, including ceiling height and floor area. Ensure the crane's dimensions align with the available space and take into account any obstacles or structural limitations.
- Evaluate the Hoisting Capacity and Lifting Height: Double hoist cranes offer increased lifting capacity and height. Ensure the crane's specifications match or exceed your lifting requirements without compromising safety.
- Review Speed and Control Requirements: Determine if you need variable speed controls, precise positioning, or synchronized movement between hoists. Some operations might require customized control systems for optimal efficiency.
- Factor in Safety Features: Ensure the crane meets safety standards and includes features like overload protection, emergency stop systems, limit switches, and anti-collision devices to prevent accidents.
- Assess Maintenance Requirements: Consider the maintenance needs of the crane. Some systems might require more frequent or specialized maintenance due to their complexity.
- Compare Different Manufacturers and Models: Research reputable manufacturers and their crane models. Compare specifications, reliability, warranties, and after-sales services to make an informed decision.
- Seek Expert Advice: Consult with crane specialists or engineers who can assess your requirements and recommend the most suitable double hoist crane for your operations.
- Consider Long-Term Costs: While upfront costs are essential, also consider the crane's lifecycle costs. A more expensive crane might prove cost-effective in the long run due to increased efficiency, lower maintenance, and fewer downtime issues.
- Customization and Adaptability: Ensure the crane can be customized to fit specific needs. Additionally, check if it can adapt to future changes or expansions in your operations.
- Compliance and Regulations: Ensure the chosen crane meets industry standards and local regulations to avoid any legal or safety issues.
By carefully evaluating these factors and conducting thorough research, you can select a suitable double hoist crane that aligns with your operational needs, enhances productivity, and ensures safety in your workplace.
Wrap it Up,
In summary, the comparison between single girder double hoist and double girder double hoist overhead cranes reveals distinct differences and some similarities:
Differences:
- Load Capacity and Lifting Height: Double girder cranes offer higher load capacities and increased lifting heights compared to single girder cranes.
- Space and Installation Requirements: Single girder cranes are more flexible in smaller spaces and have simpler installation needs, while double girder cranes demand more overhead space and complex installation.
- Cost Analysis: Single girder cranes are more cost-effective initially and in maintenance, whereas double girder cranes have higher initial costs but offer higher load capacities for heavy-duty operations.
- Maintenance and Operational Efficiency: Single girder cranes are easier to maintain but may lack efficiency in heavy-duty applications, whereas double girder cranes require more maintenance but excel in heavy lifting.
- Suitability for Different Industrial Environments: Single girder cranes are suitable for lighter operations like warehousing, while double girder cranes shine in heavy industries such as steel mills and foundries.
Similarities:
- Both configurations have hoists mounted on girders for lifting loads.
- Each type has its own strengths and limitations, catering to diverse industrial requirements.
Factors Influencing the Choice between the Two Configurations
Several factors influence the selection between single girder double hoist and double girder double hoist overhead cranes:
- Load Requirements: For heavier loads, double girder cranes are preferred due to their higher load capacities.
- Space Constraints: Facilities with limited overhead space might opt for single girder cranes due to their flexibility.
- Budget Considerations: Initial investment and long-term operational costs influence the choice, with single girder cranes being more cost-effective initially.
- Operational Demands: Heavy-duty applications demand the robustness and higher load capacities of double girder cranes.
Final Recommendations for Various Industrial Applications
- For Warehousing and Light Manufacturing: Single girder double hoist overhead cranes offer cost-effective solutions with flexibility in smaller spaces.
- For Heavy Manufacturing, Foundries, and Steel Mills: Double girder double hoist overhead cranes are recommended for their ability to handle heavy loads and rigorous industrial operations effectively.
Related Products

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch