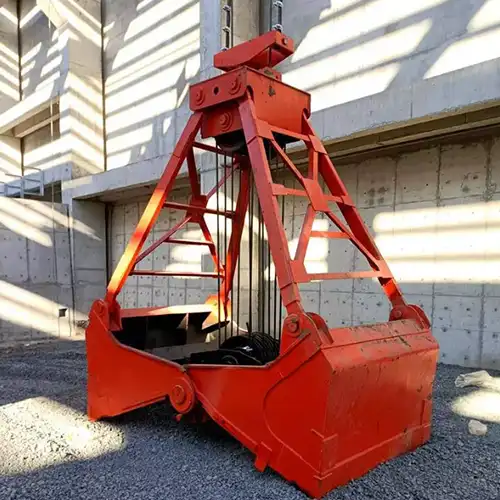
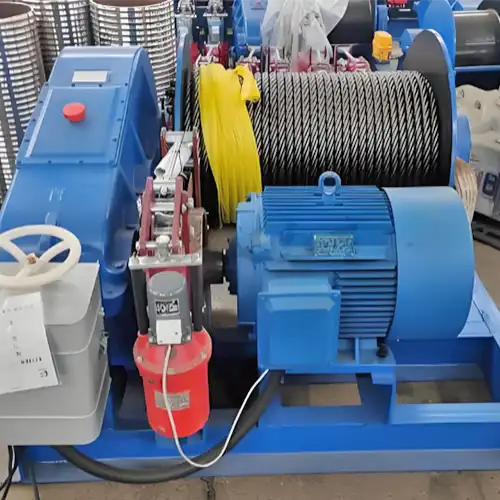
How to Get a Customized Grab Bucket for Your Cranes
Learn about custom crane grabs with these 9 key questions to ensure you get the perfect design for your needs. Clamshell grab & orange peel grab for sale.
Category: Grab Crane
Your Trusted Overhead Grab Bucket Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
How to Get a Customized Grab Bucket for Your Cranes
Learn how to get a customized grab bucket for your cranes by defining requirements, ensuring compatibility, and consulting manufacturers.
Choosing the right grab bucket for your crane is crucial for efficient material handling and smooth operations. A customized grab bucket is tailored to handle specific types of materials, match your crane’s capabilities, and meet the demands of your work environment. This ensures not only improved performance but also enhanced safety and productivity. Whether you're working with bulk materials, scrap metal, or delicate items, having a grab bucket that fits your exact needs can make a significant difference in operational efficiency.
This guide aims to help you navigate the process of acquiring a customized grab bucket for your crane. It will cover key steps and considerations, from defining your material handling requirements to choosing the right type of bucket and ensuring compatibility with your crane. By following these guidelines, you’ll be able to make informed decisions and secure a grab bucket that aligns perfectly with your operational needs, leading to optimized performance and reduced downtime.

Common Types of Grab Buckets for Cranes
There are various types of bucket grabs designed to meet specific needs. Bucket grabs are designed for various material handling needs, and different types are tailored for specific applications. Click to leanr more on 12 types of grab buckets, single girder grab bucket overhead cranes and gantry cranes
Define Your Requirements
Material Handling Needs
Type of Materials: Start by identifying the types of materials your grab bucket will need to handle. This can include a variety of materials such as:
Bulk Goods
Bulk goods such as sand, gravel, and grain require grab buckets specifically designed for handling loose and granular materials. The main considerations for these materials include:
Sealing Capabilities:
- Preventing Spillage: The grab bucket must have good sealing capabilities to prevent spillage during lifting and transportation. Effective sealing ensures that materials are not lost, which is crucial for maintaining efficiency and reducing waste.
- Edge Design: Buckets designed for bulk goods often have specialized edges and seals that close tightly to keep fine particles contained.
- Wear Resistance: Since these materials can be abrasive, the bucket should be made from wear-resistant materials to withstand prolonged use without significant degradation.
Efficient Handling:
- Volume Capacity: The bucket should have a sufficient volume capacity to handle large quantities of material in each load, optimizing the number of trips and reducing operational time.
- Smooth Interior Surfaces: To ensure that materials flow out easily when being emptied, the interior surfaces of the bucket should be smooth, preventing materials from sticking and causing delays.
Heavy Materials
Heavy materials, such as scrap metal, rocks, and construction debris, require grab buckets that are robust and durable to withstand the significant forces involved in lifting and transporting these loads. Key features include:
Robust Construction:
- High-Strength Materials: The bucket should be constructed from high-strength materials, such as reinforced steel, to withstand the heavy loads and impacts encountered during use.
- Reinforcements: Additional reinforcements, such as ribs and gussets, can help distribute stress and prevent structural failure under heavy loads.
- Thick Walls: Thicker walls provide greater resistance to dents and deformations caused by handling heavy and sharp materials.
Durability:
- Wear and Tear Resistance: The bucket should have a high resistance to wear and tear, especially in areas that come into direct contact with the materials. This includes reinforced edges and wear plates.
- Shock Absorption: Features like shock absorbers or dampening systems can help reduce the impact forces on the bucket and the crane, extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Specialized Items
Specialized items, such as aggregates, logs, and waste, have unique handling requirements that necessitate specific bucket designs. Considerations for these materials include:
Aggregates:
- Minimizing Degradation: Aggregates, such as crushed stone or concrete, require a bucket design that minimizes material degradation during handling. This can involve smooth interior surfaces and gentle handling mechanisms to preserve the quality of the materials.
- Proper Sizing: The bucket should be appropriately sized to handle the typical volume of aggregates without causing excessive wear on the crane or bucket.
Logs:
- Secure Grasp: Handling logs requires a bucket that can securely grasp irregular shapes. This typically involves using grapples or claws that can adapt to different log sizes and shapes.
- Non-Slip Features: The bucket should have non-slip surfaces or teeth to prevent logs from slipping during lifting and transport.
- Protection from Damage: To avoid damaging the logs, the bucket might include padding or other protective features that cushion the logs and prevent splitting or chipping.
Waste:
- Versatility: Waste materials can vary widely in size, shape, and composition, so the bucket needs to be versatile enough to handle different types of waste efficiently.
- Containment: For handling waste, the bucket should have containment features, such as high sides and lids, to prevent materials from spilling or escaping during transport.
- Easy Cleaning: Given the nature of waste materials, the bucket should be easy to clean and maintain, reducing downtime and ensuring hygienic operation.
By understanding the specific requirements for handling bulk goods, heavy materials, and specialized items, you can select a grab bucket that is optimally designed for your needs, ensuring efficient and reliable material handling.
The type of material will influence the grab bucket's design, including its shape, size, and opening mechanism. Different materials have distinct handling characteristics, and the bucket must be tailored to address these specific needs to ensure efficient and safe operations.
Material Size and Density:
Material Size
The physical dimensions of the materials being handled can vary greatly, and selecting a grab bucket that accommodates these variations is crucial for effective and safe material handling.
Handling Larger or Irregularly Shaped Items:
- Wider Opening: Materials such as boulders, large rocks, or scrap metal pieces often have irregular shapes and significant sizes. A grab bucket with a wider opening is essential to fully grasp and secure these items.
- Reinforced Structure: The bucket must have a reinforced structure to handle the stresses associated with lifting and transporting large and irregular items. Reinforcements might include additional ribs, thicker walls, and high-strength materials.
- Secure Handling: Ensuring that the grab bucket can fully open and close around these items is critical. This requires precision in the design of the bucket’s jaws or tines to ensure a firm grip without risking slippage or dropping of the load.
Customization for Specific Sizes:
- Adjustable Mechanisms: Some grab buckets feature adjustable mechanisms that can adapt to different material sizes, providing versatility for various applications.
- Specialized Designs: For specific industries, such as logging or scrap metal recycling, specialized grab bucket designs are available that cater to the unique requirements of the materials being handled.
Material Density
Material density, typically measured in tons per cubic meter (ton/m³), significantly impacts the design and operational requirements of the grab bucket.
Handling Heavier Materials:
- Capacity Adjustment: For materials with high density, such as metals or dense minerals, the grab bucket's lifting capacity must be adjusted accordingly. The bucket should be capable of handling substantial weight without compromising structural integrity.
- Load Calculation: Multiply the volume of the material by its density to determine the total weight. This calculation is crucial for selecting a bucket with the appropriate capacity. For example, if handling 2 cubic meters of a material with a density of 3 tons per cubic meter, the bucket must be designed to lift at least 6 tons.
- Structural Reinforcements: To accommodate high-density materials, the bucket should have additional structural reinforcements. This might include using thicker steel, reinforcing critical stress points, and ensuring robust welding and construction techniques.
Design Considerations:
- Weight Distribution: Proper weight distribution within the bucket is essential to prevent uneven loading, which can strain the crane and the bucket. A well-designed bucket will evenly distribute the material’s weight to maintain stability during lifting.
- Safety Margins: Incorporate safety margins in the bucket’s design to account for unexpected load increases or variations in material density. This ensures that the bucket can handle slightly higher loads without risking failure.
- Dynamic Loads: Consider the dynamic loads that occur during lifting and transportation. The bucket must be designed to withstand not only the static weight of the materials but also the additional forces generated by movement and handling.
By taking into account the size and density of the materials, you can select or design a grab bucket that meets the specific requirements of your operation. This ensures safe, efficient, and reliable material handling, minimizing the risk of equipment failure and optimizing the performance of your material handling system.
Volume to Weight Ratio
Ensuring the grab bucket can hold a sufficient volume of material while staying within the crane's lifting capacity is essential for safe and efficient operations.When determining material size and density, consider factors such as:
Balancing Volume and Weight:- Material Volume Calculation: Start by calculating the volume of the material to be handled, typically measured in cubic meters (m³). This helps determine how much material the bucket needs to hold per load.
- Weight Calculation: Multiply the volume by the material’s density (tons per cubic meter) to get the total weight of the load. For example, handling 1 m³ of a material with a density of 2 tons/m³ results in a load weight of 2 tons.
- Crane Capacity Check: Ensure that the calculated weight is within the crane's lifting capacity. If the weight exceeds the crane’s limit, reduce the volume of material per load or use a different bucket.
Optimizing Capacity:
- Efficient Design: Choose a bucket design that maximizes the volume it can hold without compromising structural integrity. This includes considering the shape and dimensions of the bucket to optimize space usage.
- Load Distribution: Ensure the bucket is designed to distribute the load evenly, preventing imbalances that could affect the crane’s stability.
Structural Strength
The grab bucket must be constructed from materials capable of withstanding the wear and tear associated with heavy or abrasive materials to ensure longevity and reliability.
Material Selection:
- High-Strength Materials: Use high-strength steel or other durable materials that can handle the physical stresses of heavy loads. These materials should be resistant to bending, breaking, and wear.
- Abrasion Resistance: For handling abrasive materials like gravel, sand, or scrap metal, the bucket should be made from or lined with abrasion-resistant materials to minimize wear and extend its lifespan.
- Corrosion Resistance: If the bucket will be exposed to harsh environmental conditions, consider corrosion-resistant coatings or materials to prevent rust and degradation.
Reinforcements:
- Ribs and Gussets: Incorporate reinforcements such as ribs and gussets into the bucket’s design to enhance structural strength. These reinforcements help distribute stress and prevent deformation.
- Thicker Walls: Use thicker material in areas that experience the most wear and tear, such as the bucket’s edges and bottom.
Opening and Closing Mechanism
The mechanism for opening and closing the grab bucket should be robust enough to handle the forces exerted by dense or heavy materials without failure.
Mechanism Design:
- Hydraulic Systems: Hydraulic opening and closing systems provide the necessary force to handle heavy and dense materials. Ensure the hydraulic components are rated for the expected loads and pressures.
- Mechanical Systems: For buckets with mechanical systems, use high-quality gears, chains, or cables that can withstand significant force without breaking or stretching.
- Wear-Resistant Components: Components of the mechanism, such as pins, bushings, and joints, should be made from wear-resistant materials to ensure smooth operation and longevity.
Maintenance and Inspection:
- Regular Maintenance: Implement a regular maintenance schedule to check and service the opening and closing mechanism. This includes lubricating moving parts, inspecting for wear, and replacing any worn components.
- Safety Checks: Conduct safety checks before each use to ensure the mechanism operates correctly and safely. This includes verifying the integrity of hydraulic lines, checking for leaks, and testing the mechanical components.
By carefully considering the volume to weight ratio, structural strength, and opening and closing mechanism, you can select or design a grab bucket that meets your specific material handling needs. This ensures safe, efficient, and reliable operations, reducing the risk of equipment failure and optimizing performance.
Operational Conditions:
Frequency of Use: Determine how often the grab bucket will be used on a daily basis. High-frequency operations may require a more durable and heavy-duty bucket to withstand constant use. If the bucket will be used intermittently, a less robust design might suffice. Understanding your operational frequency helps in selecting a bucket that offers the right balance between durability and cost.
Environmental FactorsAssessing the environment where the grab bucket will be used is crucial for selecting the right design and materials. Here are key environmental factors to consider:
Outdoor vs. Indoor: When determining whether the grab bucket will be used in an outdoor or indoor environment, it’s essential to understand the specific challenges each setting presents.
- Outdoor Environments: Using a grab bucket outdoors exposes it to various weather conditions such as rain, snow, extreme temperatures, and UV radiation. These conditions can lead to corrosion, wear, and material degradation over time. To combat these issues, the grab bucket should be equipped with appropriate coatings or materials that resist corrosion and wear from moisture and chemicals. Additionally, UV-resistant materials are crucial to prevent damage from prolonged sun exposure. For environments with heavy rainfall or frequent wet conditions, the bucket design should incorporate effective drainage systems to prevent water accumulation and related issues such as rust or weakening of structural components.
- Indoor Environments: While indoor environments typically offer more controlled conditions, they still require specific considerations. Temperature and humidity levels can vary significantly, and the grab bucket should be designed to handle these variations without compromising performance. For example, in industrial settings where temperature fluctuations are common, the materials used must maintain their structural integrity and performance. Additionally, certain indoor environments, such as food processing or pharmaceutical plants, demand high standards of cleanliness and hygiene. In such cases, the grab bucket may need to be made from materials that are easy to clean and sanitize, ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards.
Temperature Variations:
The grab bucket’s performance and material integrity can be significantly affected by extreme temperature variations. Therefore, it’s important to consider the operating temperature range and select materials accordingly.
- High Temperatures: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can weaken the materials used in the grab bucket and reduce its load capacity. For operations involving high temperatures, materials that retain their strength and durability under heat, such as high-temperature steel alloys, should be used. These materials ensure that the bucket can handle the stresses of high-temperature environments without degrading or failing.
- Low Temperatures: In extremely cold environments, materials can become brittle and more prone to cracking. To prevent this, materials that remain flexible and strong at low temperatures, such as certain types of stainless steel, are preferable. These materials ensure that the grab bucket maintains its functionality and safety even in freezing conditions.
- Thermal Expansion: Temperature fluctuations can cause materials to expand and contract, which may lead to structural issues or malfunctions if not properly accounted for in the design. The grab bucket should be designed to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction, ensuring that all components fit together securely and operate smoothly despite temperature changes.
By thoroughly assessing these environmental factors, you can ensure that the grab bucket you choose is well-suited to your specific operational needs. This detailed understanding leads to more efficient, reliable, and safe material handling, ultimately optimizing performance and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Select the Type of Grab Bucket
Types of Grab Buckets:
- Clamshell Buckets: These buckets are designed with two hinged shells that open and close to scoop up and release materials. They are ideal for handling bulk materials such as sand, gravel, and coal. The clamshell design allows for efficient loading and unloading of loose, granular materials. They come in various sizes and configurations, including single and double clamshell types, depending on the volume and type of material.
- Grapple Buckets: Grapple buckets are equipped with grappling arms or jaws that can grab, lift, and move a wide range of materials. They are highly versatile and suitable for handling various materials including logs, scrap metal, and demolition debris. Their design allows for precise control and manipulation of irregularly shaped or heavy materials, making them ideal for diverse applications.
- Specialty Buckets: These are custom-designed buckets tailored for specific applications or materials. They include buckets designed for hazardous materials, such as chemicals or radioactive substances, which require specialized features for safe handling. Specialty buckets can also include designs for unique material types or handling conditions, ensuring that the bucket meets very specific operational requirements.
Mechanical vs. Hydraulic:
- Mechanical: Mechanical grab buckets operate through a system of gears, cables, or chains, and are typically simpler in design. They are cost-effective and suitable for applications where high precision and frequent adjustments are not required. Mechanical buckets are often chosen for their durability and lower maintenance costs, making them a practical option for straightforward material handling tasks.
- Hydraulic: Hydraulic grab buckets use hydraulic cylinders to control the opening and closing of the bucket. This type offers greater efficiency and versatility, allowing for smoother operation and better control over the material handling process. Hydraulic buckets are ideal for tasks requiring precise handling or where the material being moved is particularly heavy or challenging. They are also well-suited for high-frequency operations due to their robustness and ability to handle a wide range of materials with varying densities.
Choosing the right type of grab bucket depends on the specific materials you handle, the operational environment, and the level of control and efficiency you need. By selecting the appropriate type and mechanism, you ensure that the grab bucket enhances your crane’s performance and meets your operational needs effectively.
Assess Crane Specifications
Crane Type:
- Overhead Crane: Overhead cranes are designed for lifting and moving materials horizontally within a facility. They are typically used in manufacturing plants, warehouses, and workshops where materials need to be moved across a defined area. When selecting a grab bucket for an overhead crane, ensure that the bucket’s size and weight are compatible with the crane’s lifting mechanism and operational range.
- Gantry Crane: Gantry cranes are commonly used in large-scale operations, including outdoor environments like construction sites or ports. They feature a bridge supported by two or more legs and can travel along rails or tracks. When choosing a grab bucket for a gantry crane, consider the bucket’s ability to handle heavy loads and its durability under varying environmental conditions.
- Crawler Crane: Crawler cranes are known for their mobility and ability to handle heavy lifting on different terrains. They are equipped with tracks instead of wheels, which provide stability and flexibility in challenging environments. For crawler cranes, select a grab bucket that complements the crane’s lifting capacity and can withstand the rugged conditions typical of construction or industrial sites.
Crane Lifting Capacity:
Ensure that the grab bucket you choose matches the lifting capacity of your crane. The crane’s lifting capacity determines the maximum weight it can safely handle, which directly impacts the size and strength of the grab bucket required.
Bucket Capacity
The capacity of the grab bucket must be carefully matched to the crane's lifting capabilities to ensure safe and efficient operation. If the grab bucket's capacity exceeds the crane's lifting limit, it can lead to mechanical failure, increased maintenance costs, and potentially dangerous working conditions. On the other hand, a bucket with insufficient capacity may result in inefficient operations, as it would require more cycles to move the same amount of material, increasing wear and tear on both the bucket and the crane.
When determining the appropriate bucket capacity, consider the following factors:
- Crane’s Lifting Capacity: The maximum load that the crane can safely lift and maneuver must be known. This includes not just the weight of the material but also the weight of the grab bucket itself.
- Material Density: The density of the material being handled will affect the total weight of the load. For example, materials like wet sand or scrap metal are much denser than materials like dry grain or wood chips, affecting how much volume can be safely lifted without exceeding weight limits.
- Operational Efficiency: A bucket that is too small for the crane's capacity can lead to inefficiencies, as more lifts will be required to move the same volume of material. This increases the operational time and the wear on the equipment, potentially leading to higher maintenance costs and shorter equipment lifespan.
- Load Distribution: Even distribution of the load is crucial to maintaining the stability and safety of the lifting operation. A bucket that is too large might not evenly distribute the weight, leading to an unbalanced load that can cause tipping or swaying during lifting.
Compatibility Check
Ensuring that the grab bucket is compatible with the crane's hook or lifting system is vital for a secure and efficient connection. This involves several key considerations:
- Attachment Mechanism: The type of attachment mechanism, whether it's a hook, flange, or a custom mount, must match the crane's lifting system. This ensures that the grab bucket can be securely attached and easily detached as needed.
- Dimensions and Weight: The dimensions and weight of the grab bucket must be appropriate for the crane’s lifting system. If the bucket is too heavy or too large, it may not fit properly or could strain the crane's mechanisms, leading to potential failures or unsafe conditions.
- Mounting Options: Verify that the mounting options on the grab bucket are compatible with the crane. This includes checking the size and shape of the mounting points, as well as ensuring that any quick-release or locking mechanisms function correctly with the crane's existing setup.
- Hydraulic and Electrical Connections: For buckets that use hydraulic or electrical systems for opening and closing mechanisms, ensure that the connections are compatible with the crane’s systems. This includes matching hydraulic pressure and flow requirements, as well as ensuring that electrical connections meet the necessary voltage and control standards.
- Load Stability: The bucket should be designed to maintain load stability during lifting and maneuvering. This involves considering the bucket's shape, center of gravity, and any additional stabilizing features that can prevent load shifting or swinging.
By carefully matching the grab bucket’s capacity and ensuring compatibility with the crane’s lifting system, you can avoid mechanical failures, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain safe working conditions. This thorough evaluation helps in selecting a grab bucket that maximizes the performance and longevity of both the bucket and the crane, contributing to a safer and more productive work environment.
By accurately assessing your crane’s specifications and matching them with the appropriate grab bucket, you ensure that both the crane and bucket operate effectively and safely within their intended parameters. This alignment is crucial for optimizing performance and maintaining operational efficiency.
Determine Bucket Capacity and Size
Capacity Requirements:
Volume and Weight of Materials
To ensure the grab bucket can efficiently and safely handle the materials in your operations, it is essential to start by calculating the volume and weight of the materials. This involves a few critical steps:
Measuring Volume: Determine the amount of material in cubic meters (m³) or another relevant unit. This measurement can be obtained by calculating the dimensions of the material pile or container. For example, if you are handling bulk goods like sand or gravel, measure the length, width, and height of the material pile to calculate its volume.
Determining Density: Density is typically measured in tons per cubic meter (ton/m³) and varies depending on the type of material. Common material densities include:
- Sand: Approximately 1.6-1.8 ton/m³
- Gravel: Approximately 1.4-1.7 ton/m³
- Scrap Metal: Approximately 0.5-2.0 ton/m³ (depending on the type and compactness)
- Aggregates: Approximately 1.5-1.7 ton/m³
Calculating Total Weight: Multiply the volume of the material by its density to get the total weight the grab bucket needs to handle. For example, if you have 5 cubic meters of sand with a density of 1.8 ton/m³, the total weight would be:
- Total Weight = Volume × Density = 5 m 3 × 1.8 ton/m 3 = 9 tons
Account for Variations: Consider any variations in material density or volume that may occur during operations. Ensure the grab bucket can handle the maximum expected weight to avoid overloading and ensure safe operation.
Bucket Capacity
Selecting the right grab bucket capacity is critical for efficient material handling and to avoid operational issues. Here's how to determine the appropriate capacity:
- Maximum Load Handling: The grab bucket should have a capacity sufficient to handle the maximum load of material you intend to move. For example, if your operations involve lifting large quantities of sand or scrap metal, ensure the bucket can accommodate these volumes without straining its structure or exceeding the crane's lifting capacity.
- Avoiding Overload: Ensure the grab bucket's capacity aligns with the crane's lifting capabilities. Overloading the bucket can lead to mechanical failures and unsafe working conditions. For instance, if your crane has a lifting capacity of 10 tons, the bucket and its contents should not exceed this limit.
- Efficiency Considerations: A bucket with too little capacity may result in multiple trips to move the same amount of material, leading to inefficient operations and increased wear on the bucket and crane. Conversely, a bucket with excessive capacity might be unnecessarily costly, cumbersome, and harder to maneuver, potentially reducing operational efficiency.
- Structural Strength: Ensure the grab bucket's design can handle the maximum load without compromising its structural integrity. This includes considering the materials used in the bucket's construction, such as high-strength steel, and the quality of the welding and joints.
- Operational Conditions: Consider the specific operational conditions, such as the frequency of use and the type of materials being handled. A grab bucket used in high-frequency operations with heavy materials should be designed for durability and long-term use.
- Future Needs: Anticipate any potential increases in material handling needs. Choosing a grab bucket with a slightly higher capacity than currently required can provide flexibility for future growth or changes in operations without the need for immediate equipment upgrades.
By accurately calculating the volume and weight of materials and selecting a grab bucket with the appropriate capacity, you ensure efficient, safe, and cost-effective material handling. This careful planning helps maximize the performance and lifespan of both the grab bucket and the crane, contributing to a more productive and reliable operation.
Size Considerations:
Matching Crane’s Lifting Capacity
Ensuring that the grab bucket matches the crane’s lifting capacity is essential for maintaining safe and effective operation. The alignment of the bucket size and weight with the crane's capabilities involves several considerations:
- Crane Specifications: Begin by reviewing the crane’s maximum lifting capacity, which includes both the weight of the grab bucket and the material it will carry. For instance, if a crane has a lifting capacity of 10 tons, the combined weight of the bucket and its load should not exceed this limit.
- Bucket Weight: The weight of the empty grab bucket must be factored into the total lifting calculation. A heavy bucket can significantly reduce the amount of material that can be safely lifted. For example, if the bucket weighs 1 ton and the crane’s capacity is 10 tons, the maximum weight of the material should not exceed 9 tons.
- Load Distribution: Ensure that the grab bucket distributes the load evenly to avoid uneven stress on the crane. An unbalanced load can cause tipping or swaying, leading to mechanical issues or safety hazards. The bucket design should support stable and secure lifting.
- Operational Efficiency: While a bucket that is too large or heavy for the crane can cause safety issues, a bucket that is too small might underutilize the crane’s full lifting potential. This can lead to inefficiencies, as more trips will be needed to move the same amount of material. Optimizing the bucket size within the crane’s capacity ensures both safety and efficiency.
Operational Needs
The grab bucket's design must align with the specific operational needs and environment in which it will be used. This includes considering space constraints, material types, and the nature of the tasks performed.
Space Constraints: In environments with limited space, maneuverability becomes a critical factor. For example, in tight spaces such as warehouses or confined construction sites, a smaller grab bucket may be more practical, even if it means handling less material per load. A smaller bucket can navigate narrow aisles and tight corners more easily, reducing the risk of collisions or damage to surroundings.
Material Types: Different materials require different bucket designs to ensure effective handling:
- Irregularly Shaped Items: For handling materials like scrap metal or demolition debris, which often have irregular shapes and sizes, a grab bucket with a wider opening or specialized jaws may be necessary. This design ensures the bucket can securely grasp and lift these items without dropping or damaging them.
- Large Items: If the operation involves lifting large items, such as logs or boulders, the bucket must be designed to accommodate these dimensions. This might include features like extended arms or reinforced edges to handle the additional stress.
- Bulk Materials: For materials like sand, gravel, or grain, the bucket should have a design that prevents spillage and maximizes load capacity. Features such as tight-sealing jaws or curved sides can help contain the material during lifting and transport.
Practical Considerations
- Ease of Maintenance: Choose a bucket that is easy to maintain and repair. Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and reliability of the equipment. Consider designs that allow for easy access to critical components, such as hydraulic systems or attachment points.
- Durability: The grab bucket should be constructed from durable materials that can withstand the operational demands, including frequent use and exposure to harsh conditions. High-strength steel and reinforced joints can help extend the bucket’s lifespan.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While ensuring the bucket meets all operational needs and safety standards, it’s also important to consider the cost. Balance the initial investment with the long-term benefits of efficiency, durability, and reduced maintenance costs.
- Future Expansion: Consider potential future needs when selecting a grab bucket. Choosing a slightly larger or more versatile bucket can provide flexibility for future growth or changes in operational requirements, saving costs on future upgrades.
By carefully matching the grab bucket’s size and design to the crane’s lifting capacity and the specific operational needs, you ensure a safe, efficient, and cost-effective material handling process. This thorough evaluation helps in selecting the right equipment that maximizes productivity while maintaining safety and durability.
Choose the Power Source
Hydraulic System:
- Smooth Operation and Control: Hydraulic grab buckets are powered by hydraulic cylinders that provide precise control over the bucket’s opening and closing mechanisms. This system allows for smooth and adjustable operation, making it ideal for tasks requiring careful handling of materials. Hydraulic systems can easily handle a variety of materials and provide consistent performance even under heavy loads.
- Versatility: Hydraulic grab buckets are versatile and can be adapted to different material types and handling conditions. The hydraulic system can be fine-tuned to accommodate specific operational needs, such as varying grip strength and opening speed. This adaptability is beneficial for operations involving diverse materials or where precision is crucial.
- Efficiency: Hydraulic systems are generally more efficient for high-frequency operations or environments where quick adjustments and reliable performance are necessary. They tend to have higher operational speeds and can handle larger or heavier loads compared to mechanical systems.
Mechanical System:
- Simplicity and Cost: Mechanical grab buckets operate through a system of gears, cables, or chains. They are often simpler in design, which can make them more cost-effective compared to hydraulic systems. This simplicity also translates to potentially lower maintenance and repair costs.
- Durability: Mechanical systems are robust and durable, suitable for applications where extreme precision is not required. They are less complex, which can lead to fewer points of failure and greater longevity under consistent use.
- Limitations: While mechanical systems are straightforward, they may lack the flexibility and control offered by hydraulic systems. Mechanical grab buckets might not be as well-suited for handling delicate or varied materials and may not perform as efficiently in high-frequency or high-precision tasks.
When choosing the power source for your grab bucket, consider the nature of your material handling tasks and the operational demands of your environment. Hydraulic systems offer greater control and efficiency for diverse and demanding applications, while mechanical systems provide a cost-effective and durable solution for simpler, less variable tasks.
Review Safety and Durability Features
Safety Features:
- Safety Locks: Ensure that the grab bucket is equipped with reliable safety locks to prevent accidental opening or closure during operation. Safety locks are crucial for maintaining control over the material being handled and for protecting operators and equipment from unexpected movements. Look for features such as automatic locking mechanisms that engage when the bucket is not in use or during transport.
- Reliable Controls: The grab bucket should have intuitive and dependable controls, whether hydraulic or mechanical. Reliable controls enable precise operation, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing safety. For hydraulic systems, ensure that controls are well-designed to provide smooth and predictable movements. For mechanical systems, check that the control mechanisms are robust and easy to operate under various conditions.
Durability:
- Material Quality: The construction materials of the grab bucket significantly impact its durability. High-quality, wear-resistant materials such as reinforced steel or hardened alloys help ensure the bucket can withstand the rigors of daily use, especially when handling heavy or abrasive materials. Check for features like reinforced edges and robust welds that contribute to the bucket's strength and longevity.
- Maintenance Needs: Evaluate the grab bucket’s design for ease of maintenance and repair. A bucket that is easy to inspect, clean, and service will have lower long-term maintenance costs and reduce downtime. Look for design features that facilitate quick access to key components, such as removable covers or modular parts. Consider the availability of spare parts and the manufacturer’s support for maintenance and repairs.
By thoroughly reviewing these safety and durability features, you can ensure that the grab bucket not only performs effectively but also maintains high safety standards and longevity. Prioritizing these aspects will help safeguard your operations and maximize the return on your investment.
Consult with Manufacturers or Suppliers
Technical Consultation:
- Discuss Your Specific Needs: Engage in a detailed discussion with manufacturers or suppliers about your unique material handling requirements. Provide comprehensive information about the types of materials, operational conditions, crane specifications, and any specific challenges you face. This consultation helps manufacturers understand your needs and recommend the most suitable grab bucket design and features. They can offer valuable insights into the best types of buckets, power systems, and safety features based on your operational context.
- Get Recommendations: Based on your input, ask for expert recommendations on the best grab bucket options. Manufacturers can suggest specific models or customizations that fit your requirements, considering factors such as material types, load capacities, and environmental conditions. Their expertise can guide you in selecting a bucket that enhances performance and efficiency while meeting safety standards.
Quotation and Technical Drawings:
- Request Detailed Quotes: Obtain detailed quotations from manufacturers or suppliers. The quote should include the cost of the grab bucket, any customization options, shipping and delivery charges, and potential additional costs for installation or maintenance. A comprehensive quote helps you understand the total investment required and compare different options effectively.
- Obtain Technical Drawings: Request technical drawings and specifications for the proposed grab bucket. These drawings provide detailed information about the bucket’s dimensions, design features, and compatibility with your crane. Reviewing these drawings allows you to verify that the bucket will fit your operational needs and ensure it meets all technical requirements before making a final decision.
By consulting with manufacturers or suppliers and obtaining detailed quotations and technical drawings, you ensure that you make an informed decision when selecting a grab bucket. This process helps align the bucket’s design and features with your operational needs and budget, leading to a more effective and efficient material handling solution.
Verify Compatibility and Installation
Crane Compatibility
Ensuring that the grab bucket is compatible with your crane’s attachment system is essential for secure and efficient operation. This compatibility involves several critical checks and considerations:
Verify Fitment with Crane’s Attachment System:
- Mounting Brackets: Check that the grab bucket’s mounting brackets are designed to fit your crane’s lifting equipment. The brackets should be of the correct size and shape to align perfectly with the crane’s attachment points. This ensures that the bucket can be securely attached and detached as needed.
- Hooks and Connection Mechanisms: The hooks or other connection mechanisms on the grab bucket must match those on the crane. This includes verifying the dimensions, load ratings, and compatibility of any locking mechanisms or quick-release systems. Proper fitment ensures that the bucket will not become dislodged during operation, which could lead to accidents or damage.
Proper Fitment for Secure Operation:
- Alignment: Ensure that all attachment points on the grab bucket align precisely with those on the crane. Misalignment can lead to uneven load distribution, causing stress on the crane’s structure and potentially leading to mechanical failure.
- Weight Distribution: The weight of the grab bucket, when empty and fully loaded, should be evenly distributed when attached to the crane. An uneven load can cause the crane to tip or become unstable, posing safety risks.
Operational Issues and Safety Hazards:
- Preventing Detachment: Secure attachment mechanisms are crucial to prevent the grab bucket from detaching during lifting operations. This involves ensuring that all connection points are robust and can withstand the forces encountered during normal use.
- Mechanical Failures: Any discrepancies in the attachment system can lead to mechanical issues, such as wear and tear on parts that are not designed to work together. This can shorten the lifespan of both the grab bucket and the crane, leading to increased maintenance costs and downtime.
Discuss Adjustments or Customizations:
- Manufacturer Consultation: If there are any discrepancies or concerns about the attachment system, discuss these with the manufacturer. They can provide guidance on potential adjustments or customizations to ensure a perfect fit. Customizations might include modifying the mounting brackets, reinforcing connection points, or adjusting the dimensions of the attachment mechanisms.
- Custom Solutions: In some cases, it might be necessary to develop custom solutions to achieve optimal compatibility. This could involve designing bespoke mounting systems or incorporating specialized adapters that bridge any gaps between the crane and the grab bucket’s attachment points.
Testing and Verification:
- Initial Testing: Once the grab bucket is attached to the crane, conduct initial testing to verify the fitment and secure operation. This testing should include lifting operations with varying loads to ensure that the attachment system performs correctly under different conditions.
- Regular Inspections: Implement a routine inspection schedule to regularly check the attachment system for signs of wear, misalignment, or other issues. Early detection of potential problems allows for timely maintenance and repairs, ensuring continued safe and efficient operation.
By meticulously verifying that the grab bucket fits with your crane’s attachment system, you ensure secure and reliable operations. This attention to detail helps prevent operational issues and safety hazards, contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of your material handling equipment.
Installation Process
Ensuring a smooth and successful installation of your grab bucket involves a series of detailed steps and checks. Proper installation is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of the grab bucket and crane system.
Confirm Installation Requirements and Procedures
Review Requirements:
- Tools and Equipment: Understand the specific tools and equipment needed for installation. This may include wrenches, alignment tools, lifting gear, and safety equipment. Ensure all necessary tools are available and in good working condition before beginning the installation process.
- Installation Steps: Familiarize yourself with the detailed steps involved in mounting the grab bucket onto the crane. This typically includes positioning the crane, aligning the grab bucket, attaching mounting brackets, securing bolts, and connecting any hydraulic or electrical systems.
Prepare for Installation:
- Site Preparation: Ensure the installation site is prepared, with adequate space and safety measures in place. Clear the area of any obstacles and ensure proper lighting and ventilation.
- Team Coordination: Assign roles and responsibilities to the installation team. Ensure that each team member understands their tasks and the overall installation plan.
Check for Installation Support
Manufacturer Support:
- On-Site Assistance: Determine if the manufacturer or supplier offers on-site installation services. Professional installation support can ensure that the grab bucket is installed correctly and safely.
- Installation Guides: If on-site support is not available, request detailed installation guides or manuals from the manufacturer. These guides should include step-by-step instructions, diagrams, and safety warnings to assist with the installation process.
Team Expertise:
- Training and Experience: Ensure that your installation team has the necessary expertise and training to handle the installation. Team members should be familiar with the crane’s operation, safety protocols, and the specific requirements of the grab bucket.
- Resource Availability: Confirm that your team has access to all required resources, including technical support from the manufacturer, if needed. Having a direct line of communication with the supplier can be invaluable for troubleshooting any issues that arise during installation.
Inspection and Testing
Post-Installation Inspection:
- Alignment and Secure Attachment: Conduct a thorough inspection to ensure that the grab bucket is properly aligned and securely attached to the crane. Check all bolts, brackets, and connections for tightness and integrity.
- Functionality Check: Verify that all mechanical and hydraulic systems are connected correctly and functioning as intended. This includes checking for proper fluid levels, pressure settings, and electrical connections.
Operational Testing:
- Empty Test Runs: Perform initial test runs with the grab bucket empty to check for smooth operation. Pay attention to any unusual noises, vibrations, or misalignments that could indicate installation issues.
- Loaded Test Runs: Gradually introduce loads to the grab bucket, starting with lighter weights and progressing to the maximum intended load. Monitor the bucket’s performance, including its ability to grasp, lift, and release materials effectively.
- Safety Feature Check: Ensure all safety features, such as emergency stop mechanisms and load limiters, are functional. Test these features under controlled conditions to confirm they work as expected.
Final Verification:
- Operational Readiness: Confirm that the grab bucket operates smoothly with the crane, handling materials as required without any issues. Address any identified problems or adjustments needed to optimize performance.
- Documentation: Document the installation process, including any adjustments made and test results. This documentation can be useful for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
By thoroughly preparing for the installation, utilizing available support, and conducting comprehensive inspections and tests, you can ensure that your grab bucket is installed correctly and operates safely and efficiently. This meticulous approach helps maximize the performance and longevity of your equipment while maintaining a safe working environment.
By verifying compatibility and understanding the installation process, you ensure that the grab bucket is correctly integrated with your crane, leading to efficient and safe material handling operations. Proper installation and fitment are essential for maximizing the performance and longevity of the grab bucket.
Finalize Order and Delivery
Shipping Terms
Ensuring clear and comprehensive shipping terms is essential for the smooth delivery of your grab bucket. Specifying the terms and understanding the responsibilities of both the seller and the buyer can help avoid misunderstandings and additional costs.
Specify Terms Such as CFR (Cost and Freight)
Define Shipping Terms:
- CFR (Cost and Freight): If you choose CFR, the seller is responsible for the cost of shipping the grab bucket to the specified destination port. This includes arranging transportation and covering freight charges up to the destination port.
- Buyer Responsibilities: Under CFR terms, the buyer is responsible for insurance and unloading costs once the grab bucket arrives at the destination port. This means you need to arrange for insurance coverage to protect the shipment during transit and plan for unloading upon arrival.
Contract Clarity:
- Detailed Agreement: Ensure that all shipping terms, including CFR, are clearly outlined in the purchase contract. This should include specific responsibilities of both parties, costs covered by the seller, and any additional costs that the buyer needs to manage.
- Avoid Misunderstandings: Clearly define who is responsible for each aspect of the shipping process to avoid misunderstandings or disputes. This includes specifying who handles customs clearance, documentation, and any potential issues that may arise during transit.
Communication with Supplier:
- Shipping Preferences: If you have specific shipping preferences or requirements, communicate these to the supplier in advance. This could include preferred shipping routes, carriers, or handling instructions.
- Accommodation of Requirements: Ensure the supplier is aware of and can accommodate your shipping requirements. Confirm that any special arrangements are documented in the contract.
Destination Port
Accurate Information:
- Provide Destination Port: Clearly provide the name and location of the destination port where the grab bucket will be shipped. This information is crucial for the seller to arrange transportation and ensure the shipment reaches the correct location.
- Double-Check Details: Verify all details about the destination port, including port codes and any specific handling instructions. This helps avoid confusion and ensures smooth delivery.
International Shipping Considerations:
- Customs Documentation: For international shipments, ensure all necessary customs documentation is prepared and handled correctly. This includes import permits, shipping manifests, and any other required paperwork.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with the customs regulations and requirements of the destination country. Ensure that all regulations are followed to avoid delays or additional costs due to non-compliance.
- Handling Delays: Be prepared for potential delays at the destination port due to customs inspections or other regulatory checks. Factor in these potential delays when planning your project timeline.
Coordination with Logistics:
- Transportation Arrangements: Coordinate with your logistics provider to arrange for transportation from the destination port to your final location. This includes planning for unloading, storage, and any further transportation needed.
- Inspection and Receiving: Plan for a thorough inspection of the grab bucket upon arrival at the destination port. Check for any damages or discrepancies and address any issues promptly with the supplier or shipping company.
By specifying clear shipping terms and providing accurate information about the destination port, you ensure a smooth and efficient delivery process for your grab bucket. This careful planning helps avoid unexpected costs and delays, ensuring your project stays on schedule and within budget.
Delivery Timeline
Ensuring a well-coordinated delivery timeline is crucial for aligning the arrival of your grab bucket with your operational needs and project schedules. Effective communication and planning with the manufacturer or supplier can help manage expectations and mitigate potential delays.
Discuss and Agree on Delivery Schedules
Establish Clear Timelines:
- Production Lead Time: Discuss and confirm the expected lead time for the production of the grab bucket. This includes the time needed for manufacturing, quality checks, and any customizations.
- Shipping Duration: Understand the shipping duration from the manufacturer’s location to the destination port. This varies based on the mode of transport (air, sea, or land) and the distance involved.
- Potential Delays: Identify any potential delays that could affect the delivery schedule. These could include production delays, shipping disruptions, or customs clearance issues. Plan for contingencies to manage these delays.
Alignment with Operational Needs:
- Project Timelines: Ensure that the delivery schedule aligns with your project timelines. The grab bucket should arrive when needed, without causing delays to your operations or project milestones.
- Expected Date of Arrival: Confirm the expected date of arrival of the grab bucket. This date should be clearly communicated and agreed upon with the supplier.
Delivery Milestones:
- Progress Updates: Agree on regular progress updates from the supplier. These updates can include key milestones such as the completion of production, dispatch from the factory, arrival at the destination port, and final delivery.
- Milestone Tracking: Use these milestones to track the delivery process and stay informed about the progress. This helps you anticipate any potential issues and manage them proactively.
Plan for Receipt and Inspection
Coordinate Receipt:
- Team Coordination: Plan and coordinate with your team for the receipt of the grab bucket upon delivery. Ensure that there are designated personnel to receive and handle the bucket.
- Inspection Process: Develop a thorough inspection process to check for any damage or discrepancies. This should include a visual inspection for any physical damage and a verification of all specifications and components.
Handling Discrepancies:
- Document Findings: Document any issues or discrepancies found during the inspection. This documentation is crucial for addressing any claims with the supplier or shipping company.
- Prompt Resolution: Promptly communicate any issues with the supplier to ensure a smooth resolution. This might involve repairs, replacements, or adjustments to the equipment.
Proper Storage:
- Storage Preparation: Ensure that there is adequate space and conditions for storing the grab bucket until installation. Proper storage helps protect the bucket from environmental damage and maintains its readiness for use.
- Handling Instructions: Follow any specific handling instructions provided by the manufacturer to avoid damage during storage and subsequent installation.
Communication with Supplier:
- Feedback Loop: Maintain open communication with the supplier throughout the receipt and inspection process. Provide feedback on the condition of the grab bucket and any issues encountered.
- Supplier Support: Utilize any support or assistance offered by the supplier during this phase. This could include technical support, guidance on installation, or help with addressing any issues.
By discussing and agreeing on delivery schedules and planning for the receipt and inspection of the grab bucket, you can ensure a seamless delivery process. This approach minimizes disruptions to your operations and ensures that the equipment is ready for use as soon as it arrives.
By finalizing the order and delivery details with clear terms and schedules, you ensure a seamless procurement process for your grab bucket. This careful planning helps to avoid delays and ensures that the grab bucket arrives on time and in good condition, ready for installation and use.
Conclusion
Securing a customized grab bucket for your crane involves several critical steps. Begin by defining your material handling needs and operational conditions to ensure that the bucket matches your requirements. Choose the right type of grab bucket and power source based on the materials you handle and the operational demands. Assess your crane’s specifications to ensure compatibility with the bucket’s size and capacity. Review essential safety and durability features to guarantee reliable performance and safety. Consult with manufacturers or suppliers for technical advice and detailed quotations. Verify compatibility with your crane’s attachment system and understand the installation process. Finally, finalize the order by specifying shipping terms and agreeing on a delivery timeline.
It is essential to align the grab bucket with your specific operational requirements to maximize efficiency and safety. A well-chosen grab bucket not only enhances the effectiveness of your material handling processes but also ensures safe operation and durability. By following these steps, you ensure that your grab bucket will meet your operational needs and contribute to the overall success of your crane operations. Prioritizing these considerations will lead to a more effective and cost-efficient material handling solution.
Related Products
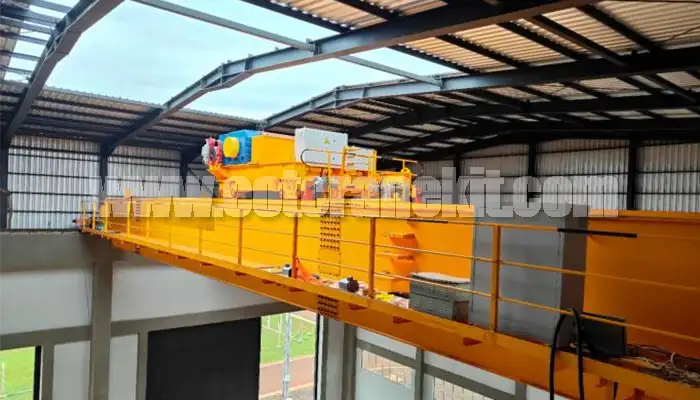

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch