Electric Hoist 20 Ton & Manual Hoist 20 Ton Trinidad and Tobago
20 ton electric hoist 70 m lifting height & 20 ton manual chain hoist 5 & 10 m lifting height, engineered for heavy lifting for sale Trinidad and Tobago.
| Electric Hoist | 20 Ton 70 Meter lifting Height |
| Manual Hoist | 20 Ton 5 M & 10 M lifting height |
Category: Featured
Your Trusted Electric Hoists and Manul Hoist Manufacturer & Supplier
Electric Hoists 20 Ton & Manual Hoists 20 Tons for Sale Trinidad and Tobago
Discover durable 20-ton electric hoists and manual hoists, engineered for heavy lifting needs, available now in Trinidad and Tobago. Get your 20 ton hoist!
This case study explores the current market for electric and manual hoists with a 20-ton capacity in Trinidad and Tobago. The focus is on understanding the specifications, applications, and availability of these hoists, which are crucial for various industrial and construction operations. By examining both electric and manual hoists, this study aims to offer a comprehensive view of their roles in the local market and how they meet the demands of different sectors.
Electric hoists, known for their efficiency and automation, and manual hoists, valued for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, are both essential tools in material handling. In Trinidad and Tobago, where industrial and construction activities are growing, selecting the right type of hoist can significantly impact operational efficiency and safety. This case study provides a detailed look at the features and benefits of these hoists, helping stakeholders make informed decisions based on their specific needs and conditions.
The objective of this case study is to deliver in-depth insights into two types of hoists: electric and manual, each with a 20-ton capacity, as available in Trinidad and Tobago. The study aims to:
- Detail Specifications: Provide a clear understanding of the technical specifications for both electric and manual hoists, including lifting capacities, heights, and power requirements.
- Examine Applications: Explore the various applications of these hoists in different industrial and construction environments, highlighting their practical uses and advantages.
- Assess Availability: Review the availability of these hoists in Trinidad and Tobago, including local suppliers, distributors, and potential lead times for procurement.
- Compare Performance: Offer a comparative analysis of electric versus manual hoists, focusing on performance, cost, and operational factors to help users determine the best fit for their specific needs.
By achieving these objectives, the case study will provide valuable information to businesses and professionals in Trinidad and Tobago, aiding in the selection and acquisition of the most suitable hoisting solutions for their operations.

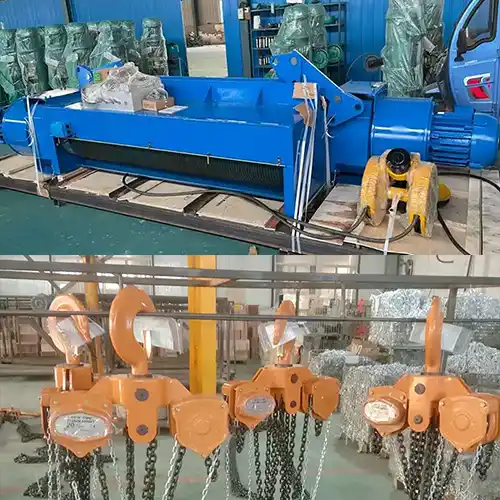
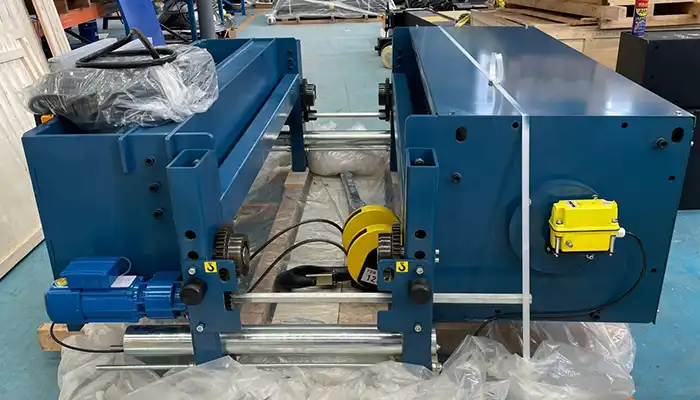
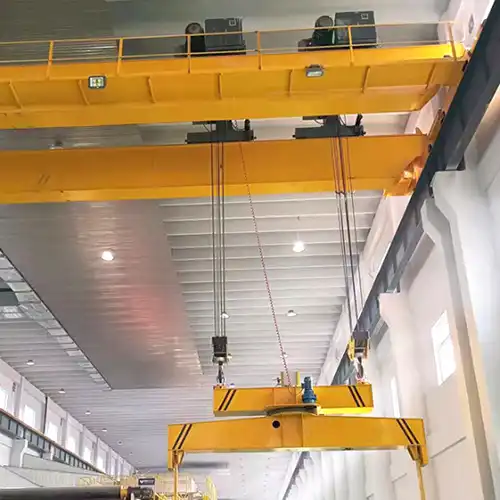
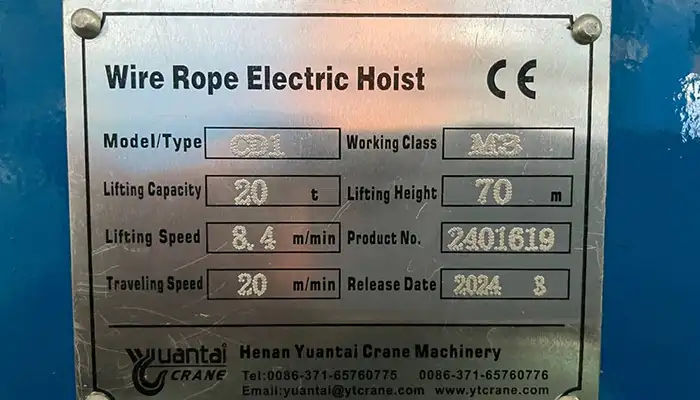
Electric Hoist Type: CD type single girder electric wire rope hoist .
- Hoist capacity: 20T- .
- Hoist LIfting Height : 70M .
- Power supply: 440V60HZ3P;
- Manual Hoists 20 Ton for sale Trinidad and Tobago .
- Main Specifications of 20 ton Manual Chain hoists .
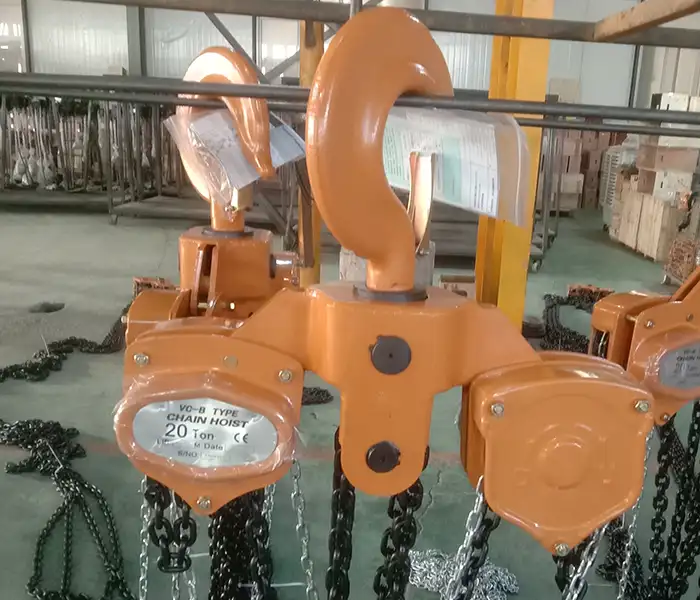

Hoist Type:VC-B Manual Hoist with Hand-Pulled Operation .
- Hoist capacity: 20 tons,
- Lifting Height:10 meters,
- Quantity : 4 units;
Hoist Type:HSZ Manual Hoist with Hand-Pulled Operation:
- Hoist capacity: 5 tons,
- Lifting Height: 5 meters,
- Quantity: 10 units.
Electric Hoists 20 Ton for Sale in Trinidad and Tobago
- Overview of Electric Hoists Electric hoists are essential lifting devices used to handle heavy loads efficiently and safely in various industrial and construction settings. They are powered by electricity, which allows them to lift and lower loads with precision and speed, reducing the need for manual effort. Electric hoists are known for their reliability, automation capabilities, and ability to handle substantial weights, making them ideal for tasks that require consistent performance and high safety standards.
- Importance in Industrial Settings In industrial settings, electric hoists play a crucial role in material handling and equipment operation. They are commonly used in factories, warehouses, construction sites, and other environments where heavy materials need to be moved or positioned. Their automation features help streamline operations, enhance productivity, and minimize the risk of injury associated with manual lifting. Electric hoists are designed to meet rigorous standards, ensuring they can withstand the demands of heavy-duty applications.
- Market Demand and Application in Trinidad and Tobago In Trinidad and Tobago, the demand for electric hoists is driven by a growing industrial and construction sector. As infrastructure projects and industrial activities expand, there is an increasing need for reliable lifting solutions capable of handling large loads. Electric hoists with a 20-ton capacity are particularly valuable in this context, as they provide the necessary strength and efficiency for demanding tasks.
Key applications in Trinidad and Tobago include:
- Construction Sites: For lifting and placing heavy materials such as steel beams, concrete blocks, and machinery.
- Manufacturing Facilities: To move large components and equipment during assembly, maintenance, or production processes.
- Warehousing: For handling and positioning bulky items, improving storage and retrieval operations.
- Port Operations: In dockyards and shipping facilities, where heavy cargo needs to be moved efficiently.
Overall, the availability of 20-ton electric hoists in Trinidad and Tobago meets the growing needs of these sectors, supporting enhanced operational efficiency and safety.

Main Specifications of 20 Ton Electric Hoists Cases for Your Reference
- Hoist Type: CD Type Single Girder Electric Wire Rope Hoist. The CD type electric hoist is designed for single girder cranes, using a wire rope mechanism to lift and lower loads. This type of hoist is well-suited for various industrial applications where precise and reliable lifting is required.
- Hoist Capacity: 20 Tons. With a capacity of 20 tons, this hoist can handle substantial loads, making it ideal for heavy-duty tasks in industrial and construction environments. The high capacity ensures it can support significant weight without compromising safety or performance.
- Lifting Height: 70 Meters. The hoist offers an impressive lifting height of 70 meters, allowing it to reach elevated points and handle tall structures. This extended height capability is beneficial for applications requiring lifting to significant heights, such as in high-rise construction or large warehouses.
- Power Supply: 440V, 60Hz, 3-Phase. The hoist operates on a power supply of 440V, 60Hz, 3-phase, which is standard for many industrial settings. This power configuration supports the hoist's robust performance and ensures compatibility with typical industrial electrical systems.
Key Features:
- High Lifting Capacity: The 20-ton capacity is suitable for handling large and heavy materials, making the hoist ideal for demanding operations where strength and reliability are crucial.
- Extended Lifting Height: The 70-meter lifting height allows for versatility in applications, enabling the hoist to manage tall structures and extensive lifting tasks efficiently.
- Efficient Power Supply: The 440V, 60Hz, 3-phase power supply ensures consistent and efficient operation, meeting the power demands of industrial-grade lifting while enhancing overall performance.
These specifications make the 20-ton electric hoist a valuable asset for industries in Trinidad and Tobago that require high-performance lifting solutions for heavy loads and tall applications.
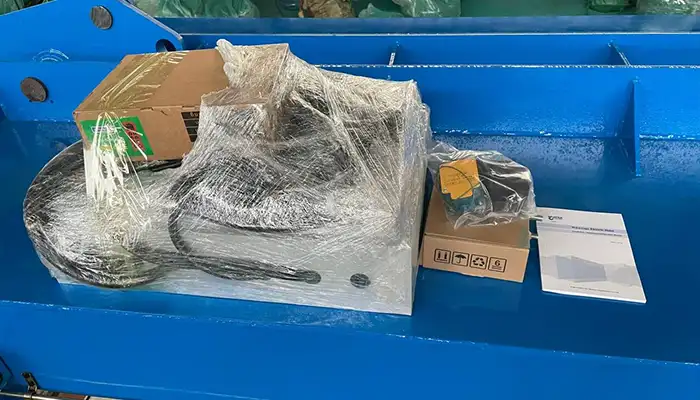

Advantages
- Increased Efficiency and Speed Compared to Manual Hoists: Electric hoists significantly enhance operational efficiency and speed. Unlike manual hoists, which rely on physical effort to lift and lower loads, electric hoists operate with the push of a button. This automation allows for faster and more consistent movement of heavy materials, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity in industrial and construction tasks.
- Enhanced Safety Features and Automation: Electric hoists come equipped with advanced safety features such as overload protection, automatic braking systems, and emergency stop functions. These features help prevent accidents and ensure safe operation even under heavy loads. The automation in electric hoists also reduces the risk of human error, contributing to a safer working environment and minimizing the potential for injuries associated with manual handling.
- Reduced Labor Requirements: By automating the lifting process, electric hoists reduce the need for manual labor. This not only lowers labor costs but also decreases the physical strain on workers. With fewer personnel required for lifting tasks, companies can allocate their workforce to other critical functions, optimizing labor resources and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Applications
Use Cases in Various Industries
- Construction: Electric hoists are extensively used in construction for lifting and positioning heavy materials such as steel beams, concrete slabs, and prefabricated components. They are ideal for tasks such as assembling high-rise structures, moving large construction equipment, and hoisting materials to elevated levels on job sites. Their efficiency and capacity make them crucial for maintaining productivity and meeting tight deadlines.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing facilities, electric hoists are employed to move large parts, components, and machinery during assembly, maintenance, and production processes. They streamline workflows by facilitating the handling of heavy and bulky items, improving assembly line efficiency, and reducing manual handling requirements. This ensures smooth operation and enhances productivity in manufacturing environments.
- Mining: Electric hoists play a vital role in mining operations where they are used to transport heavy equipment, ore, and other materials from deep underground to the surface. Their high lifting capacity and reliability are essential for handling the demanding conditions in mining environments, where efficiency and safety are paramount.
Benefits of Electric Hoists in Handling Heavy Loads
- Enhanced Lifting Capability: Electric hoists offer substantial lifting capacities, allowing them to handle heavy loads that would be challenging or unsafe with manual hoists. This capability is crucial for industries where moving large and heavy materials is a routine task.
- Precision and Control: Electric hoists provide precise control over lifting and lowering movements, which is essential for tasks requiring accurate positioning of heavy items. This precision helps in minimizing the risk of damage to materials and structures.
- Improved Efficiency: The automation of electric hoists speeds up the lifting process compared to manual methods. This increased efficiency translates to faster completion of tasks, reduced operational downtime, and enhanced overall productivity.
- Reduced Physical Strain: By eliminating the need for manual effort in lifting and moving heavy loads, electric hoists reduce physical strain on workers. This contributes to a safer working environment and minimizes the risk of injury associated with manual handling.
Overall, electric hoists are invaluable in various industries for their ability to efficiently and safely handle heavy loads, improve operational productivity, and enhance workplace safety.
Manual Hoists 20 Ton for Sale in Trinidad and Tobago
Overview of Manual Hoists Manual hoists are simple yet effective lifting devices that rely on human power to operate. They typically use a chain or rope mechanism to lift and lower loads, requiring manual effort through a hand wheel or pull chain. Manual hoists are valued for their straightforward design, durability, and cost-effectiveness. They are commonly used in environments where electric power is unavailable or where manual control is preferred.
- Applications Manual hoists are versatile and can be used across various applications:
- Construction: Ideal for lifting materials in locations where electric power is not accessible or for smaller-scale lifting tasks.
- Maintenance: Useful for adjusting or moving equipment in facilities without permanent lifting setups.
- Warehousing: Practical for handling items in areas where power hoists might be impractical or unnecessary.
Market Demand and Relevance in Trinidad and Tobago In Trinidad and Tobago, the market for manual hoists is driven by their practicality and affordability. Many industries in the region, including construction, manufacturing, and small-scale operations, benefit from manual hoists due to their simplicity and reliability.
Key factors contributing to their relevance in Trinidad and Tobago include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Manual hoists offer a more budget-friendly option compared to electric hoists, making them an attractive choice for businesses with limited resources or smaller-scale operations.
- Power Availability: In areas where electrical infrastructure may be less reliable or where temporary lifting solutions are needed, manual hoists provide a viable alternative.
- Ease of Use and Maintenance: The simplicity of manual hoists means they require less maintenance and are easy to operate, which is beneficial in a variety of settings.
Overall, manual hoists remain an important lifting solution in Trinidad and Tobago, offering practical benefits for diverse applications and contributing to the efficiency and effectiveness of material handling operations.
Main Specifications of 20 Ton Manual Chain Hoists
VC-B Manual Hoist:
- Type: Hand-pulled operation. The VC-B manual hoist operates through a hand-pulled chain mechanism, allowing users to lift and lower loads manually with a chain wheel or handle.
- Capacity: 20 tons. This hoist is capable of handling heavy loads up to 20 tons, making it suitable for demanding lifting tasks in various industrial and construction settings.
- Lifting Height: 10 meters. The VC-B hoist provides a lifting height of 10 meters, allowing for effective handling of taller loads and materials.
- Quantity: 4 units. A total of 4 units of the VC-B manual hoist are available, providing multiple options for meeting lifting needs in different locations or projects.
HSZ Manual Hoist:
- Type: Hand-pulled operation. The HSZ manual hoist also uses a hand-pulled chain mechanism, offering manual control for lifting and lowering tasks.
- Capacity: 5 tons. With a capacity of 5 tons, this hoist is suitable for lighter lifting tasks compared to the VC-B model, making it ideal for smaller loads and less demanding applications.
- Lifting Height: 5 meters. The HSZ hoist provides a lifting height of 5 meters, which is effective for moderate-height lifting tasks.
- Quantity: 10 units. There are 10 units of the HSZ manual hoist available, accommodating various lifting needs and providing flexibility for different applications.
These manual chain hoists offer reliable and cost-effective solutions for lifting heavy and moderate loads, with their specifications tailored to meet a range of operational requirements in Trinidad and Tobago.
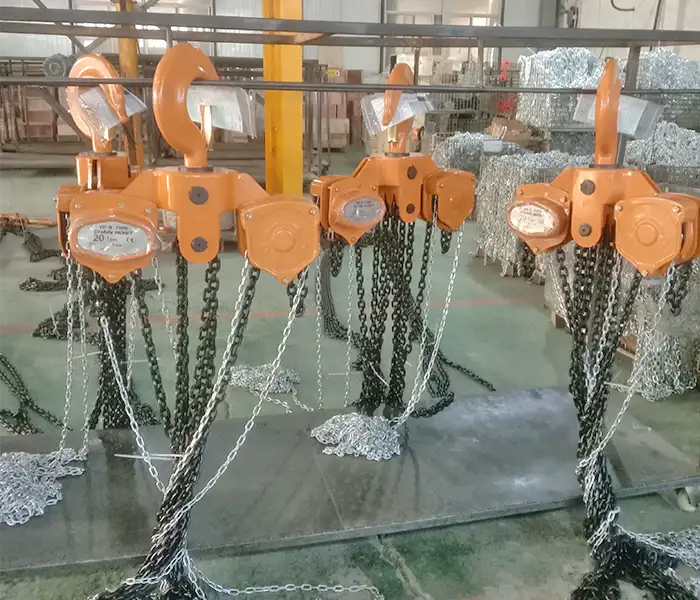

20 ton manual chain hoist and chain block for sale
20 ton manual hoist trolley
Advantages
- Simplicity of Operation and Maintenance: Manual hoists are known for their straightforward design, which translates to ease of operation. Users can handle lifting tasks with minimal training, and the manual control allows for precise load handling. Maintenance is also simplified due to the lack of complex electrical components, leading to fewer breakdowns and lower maintenance costs.
- Cost-Effective for Specific Applications: Manual hoists offer a budget-friendly solution for lifting needs. They are often more affordable than electric hoists, making them a cost-effective choice for operations where high-frequency lifting or heavy-duty performance is not required. This makes them suitable for smaller projects or businesses with limited budgets.
- No Need for External Power Sources: One of the key benefits of manual hoists is that they do not require an external power source. This makes them ideal for use in environments where electrical power is unreliable or unavailable. Manual hoists can be used in remote locations or during power outages, offering flexibility and reliability without the need for electrical infrastructure.
Applications
- Suitable for Environments Where Electric Power is Not Available: Manual hoists are particularly advantageous in locations where access to electric power is limited or non-existent. Their reliance on manual operation makes them ideal for remote sites, temporary setups, or areas with unreliable electrical supply. This adaptability ensures that lifting operations can continue even in challenging environments where electrical infrastructure is not feasible.
- Use Cases in Smaller-Scale or More Accessible Lifting Tasks: Manual hoists excel in smaller-scale lifting tasks where the volume of material handling is manageable and does not require the high-speed operation of electric hoists. They are well-suited for applications such as:
- Workshop and Maintenance Tasks: Lifting equipment or parts for maintenance and adjustments where heavy lifting is needed but power availability is not a concern.
- Construction Sites: Handling materials like tools, small machinery, or building components in areas with limited access to electric power.
- Warehousing and Storage: Moving and positioning lighter loads or smaller quantities of goods in environments where electrical hoisting solutions may not be practical or necessary.
- Portable Applications: Tasks that require a hoist to be easily transported or set up in various locations, such as during small-scale construction or repair jobs.
- Overall, manual hoists offer practical solutions for diverse lifting tasks, particularly in settings where simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and independence from electrical power are valued.
Comparison of Electric and Manual Hoists
Performance
Speed and Efficiency Differences
- Electric Hoists: Electric hoists are designed for high-speed lifting and lowering, significantly outperforming manual hoists in terms of speed and operational efficiency. They are capable of handling continuous and rapid lifting tasks, which is essential in high-demand industrial and construction environments. The automation provided by electric hoists allows for precise control and quick adjustments, leading to faster completion of lifting operations and increased overall productivity.
- Manual Hoists: Manual hoists operate at a slower pace, as they rely on human effort to lift and lower loads. This manual operation limits their speed compared to electric hoists. While they are effective for occasional or less frequent lifting tasks, they may not match the efficiency required for high-volume or time-sensitive operations. The speed of lifting with manual hoists depends on the operator's effort and physical condition, which can vary.
Suitability for Different Lifting Requirements
- Electric Hoists: Electric hoists are highly suitable for tasks that require high lifting capacities, extended lifting heights, and frequent use. They excel in environments where continuous and precise lifting is necessary, such as in large-scale construction sites, manufacturing facilities, and industrial operations. Their ability to handle heavy loads quickly and consistently makes them ideal for demanding applications where efficiency and speed are critical.
- Manual Hoists: Manual hoists are best suited for lighter and less frequent lifting tasks where power availability is limited or cost constraints are a concern. They are effective in smaller-scale applications or environments where the lifting volume does not justify the investment in electric hoists. Manual hoists are also useful in situations where simplicity and portability are valued, such as in workshops, smaller construction projects, or temporary setups.
In summary, while electric hoists offer superior speed and efficiency, making them ideal for high-demand applications, manual hoists provide a cost-effective and practical solution for less frequent, smaller-scale tasks. The choice between electric and manual hoists depends on specific lifting requirements, including the volume, frequency, and environment of the operation.
Cost Considerations
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Operational Costs
Electric Hoists:
- Initial Investment: Electric hoists generally have a higher upfront cost due to their complex components, advanced technology, and the need for electrical infrastructure. The initial investment includes not only the cost of the hoist itself but also installation, wiring, and potential upgrades to power supply systems.
- Long-Term Operational Costs: Despite the higher initial cost, electric hoists can be cost-effective in the long run due to their efficiency and speed. They reduce labor costs by automating lifting processes and can handle high volumes of work without additional manpower. However, their long-term operational costs include electricity consumption and potential costs associated with repairs or replacements of electrical components.
Manual Hoists:
- Initial Investment: Manual hoists have a lower initial cost compared to electric hoists. They require minimal infrastructure and installation expenses, making them a more budget-friendly option for businesses with lower lifting demands or limited capital.
- Long-Term Operational Costs: Manual hoists have minimal ongoing operational costs, as they do not require electricity or complex maintenance. Their operational costs are mainly related to periodic maintenance and occasional repairs, which are typically lower than those of electric hoists. However, the cost of labor for manual operation must be considered, especially if the hoist is used frequently.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
Electric Hoists:
- Maintenance: Electric hoists require regular maintenance to ensure their components—such as motors, gears, and control systems—function correctly. This may involve inspections, lubrication, and electrical system checks. Maintenance is crucial to prevent breakdowns and ensure safe operation.
- Repair Costs: Repairing electric hoists can be more costly due to the need for specialized parts and technical expertise. Electrical components and control systems can be expensive to repair or replace, potentially leading to higher costs over time.
Manual Hoists:
- Maintenance: Manual hoists have simpler mechanisms and typically require less frequent maintenance. Routine checks focus on the condition of the chains or ropes, lubrication, and ensuring that the hoist is functioning smoothly.
- Repair Costs: Repair costs for manual hoists are generally lower due to their straightforward design and fewer components. Replacement parts, if needed, are often less expensive compared to those for electric hoists. However, manual hoists may require more frequent inspection to ensure reliable performance.
In summary, while electric hoists involve a higher initial investment and potentially higher repair costs, they offer long-term efficiency and reduced labor costs. Manual hoists are more cost-effective initially and have lower operational and repair costs but may involve higher labor costs for manual operation. The choice between the two should be based on budget constraints, lifting requirements, and long-term operational needs.
Operational Factors
Ease of Use
- Electric Hoists: Electric hoists are generally easier to use due to their automated operation. Operators can control the hoist with simple push-button controls, which streamline the lifting and lowering process. This ease of use reduces the physical effort required and allows for precise control of the load. The automation also minimizes manual intervention, leading to fewer errors and a more consistent lifting performance.
- Manual Hoists: Manual hoists require physical effort from the operator to lift and lower loads using a hand wheel or pull chain. While the design is straightforward, the process can be labor-intensive and less efficient compared to electric hoists. Operators need to manually exert force to handle the load, which can be physically demanding, especially for heavier loads or prolonged use. The ease of use is influenced by the operator's physical strength and endurance.
Training Requirements for Operators
- Electric Hoists: Training for electric hoists typically involves familiarizing operators with the control systems, safety features, and proper handling procedures. Because electric hoists are automated, training can be relatively brief, focusing on understanding the operational controls, safety protocols, and emergency procedures. The learning curve is usually shorter compared to manual hoists, making it easier for operators to become proficient quickly.
- Manual Hoists: Training for manual hoists involves educating operators on the proper techniques for manually lifting and lowering loads, including how to use the hand wheel or pull chain effectively. Operators must be trained to handle the physical demands of manual hoisting and to perform tasks safely. Training may also cover maintenance procedures to ensure the hoist remains in good working condition. The physical nature of manual hoisting can lead to a longer training period, as operators need to develop the strength and skills required for efficient operation.
In summary, electric hoists offer greater ease of use and require less training due to their automated nature and simple controls. Manual hoists, while straightforward, involve more physical effort and a potentially longer training period to ensure operators can manage the manual lifting process effectively. The choice between the two should consider the operational context, including the level of automation desired and the physical demands on the operators.
Market Insights for Trinidad and Tobago
Demand Analysis
- Current Market Trends for Hoists in Trinidad and Tobago The market for hoists in Trinidad and Tobago is influenced by various factors including industrial growth, infrastructure development, and economic conditions. Key trends include:
- Growing Infrastructure Projects: Increased investment in infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and commercial buildings, drives demand for both electric and manual hoists. These projects require reliable lifting solutions for material handling and construction tasks.
- Industrial Expansion: The expansion of industries such as manufacturing, mining, and energy contributes to the demand for heavy-duty hoists. Electric hoists are particularly sought after for their efficiency in high-volume and continuous lifting operations.
- Economic Considerations: Economic factors, including budget constraints and cost management, influence the choice between electric and manual hoists. Businesses and contractors may opt for manual hoists for smaller-scale or budget-sensitive projects, while larger operations invest in electric hoists for greater efficiency.
- Focus on Safety and Automation: There is a growing emphasis on safety and automation in industrial operations. Electric hoists are preferred for their advanced safety features and automation, aligning with industry trends towards enhanced operational safety and productivity.
Key Industries and Sectors Utilizing These Hoists
- Construction: Hoists are extensively used in construction projects for lifting materials, equipment, and tools. Both electric and manual hoists play crucial roles in various stages of construction, from foundation work to structural assembly.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, hoists are employed for handling heavy components and materials within production facilities. Electric hoists are favored for their speed and reliability in managing high volumes of lifting tasks.
- Mining: The mining sector utilizes hoists for moving heavy loads, including mining equipment and extracted materials. The rugged environment often necessitates robust and reliable hoisting solutions, including both electric and manual types.
- Energy Sector: In the energy sector, hoists are used for maintenance and installation of heavy machinery and equipment. Electric hoists are often used for their efficiency and ability to handle substantial loads.
Supplier and Distributor Information
- Overview of Local Suppliers and Distributors Trinidad and Tobago has a range of local suppliers and distributors specializing in hoisting equipment. These entities offer various hoist models, including electric and manual types, and provide services such as sales, maintenance, and support. Key suppliers and distributors typically include:
- Industrial Equipment Suppliers: Companies specializing in industrial equipment and machinery offer a selection of hoists suitable for different applications. They provide comprehensive solutions, including product recommendations and technical support.
- Construction and Maintenance Supply Stores: Local stores focused on construction and maintenance supplies often stock manual and electric hoists. They cater to the needs of contractors and maintenance professionals with readily available products and support.
- Specialized Distributors: Some distributors focus exclusively on hoisting and lifting equipment, offering expertise in selecting the right hoist for specific applications. They provide detailed information on product specifications, safety features, and customization options.
Availability and Lead Times for Procurement
- Stock Availability: Local suppliers generally maintain an inventory of popular hoist models, including 20-ton electric and manual hoists. Availability may vary based on demand and supplier stock levels.
- Lead Times: Lead times for procurement can vary depending on the type of hoist, customization requirements, and supplier efficiency. Electric hoists may have longer lead times due to their complexity and need for specific electrical components. Manual hoists typically have shorter lead times due to their simpler design and fewer parts.
- Delivery and Support: Suppliers often offer delivery services and post-purchase support, including installation and maintenance. The responsiveness of suppliers and distributors can influence the overall procurement experience, ensuring timely delivery and reliable service.
In summary, the market for hoists in Trinidad and Tobago is driven by industrial growth and infrastructure development. Understanding local suppliers, their offerings, and procurement timelines is crucial for making informed decisions and ensuring efficient acquisition of hoisting equipment.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Findings
Specifications and Advantages of Both Electric and Manual Hoists
- Electric Hoists: The 20-ton electric hoists are designed with a CD type single girder configuration, offering a lifting height of 70 meters and powered by a 440V, 60Hz, 3-phase supply. They are known for their high-speed operation, efficiency in handling large loads, and enhanced safety features. These hoists are ideal for high-demand industrial and construction environments where continuous and precise lifting is required. The benefits include increased efficiency, automation, and reduced labor requirements, making them suitable for large-scale operations and projects with frequent lifting needs.
- Manual Hoists: The 20-ton manual hoists include the VC-B model with a 10-meter lifting height and the HSZ model with a 5-meter lifting height. Both are operated manually, requiring physical effort to lift and lower loads. Manual hoists are simpler and more cost-effective, especially in environments where electric power is unavailable or where lifting needs are less frequent. Their advantages include ease of maintenance, cost-effectiveness, and no reliance on external power sources, making them suitable for smaller-scale applications and locations with limited access to electricity.
Applications and Market Suitability
- Electric Hoists: Given their high capacity, efficiency, and automation, electric hoists are well-suited for environments that demand high performance and continuous operation. They are particularly effective in large-scale construction projects, manufacturing plants, and industrial settings where speed and automation are crucial. Their higher initial investment is justified by their long-term operational efficiency and reduced labor costs.
- Manual Hoists: Manual hoists offer a practical and economical solution for lifting needs where electricity is not readily available or where the lifting volume does not warrant the investment in electric hoists. They are ideal for small to medium-sized projects, maintenance tasks, and environments where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. Their lower initial cost and minimal operational expenses make them a viable option for various applications, including construction sites and workshops with intermittent lifting needs.
In conclusion, both electric and manual hoists have distinct advantages that cater to different operational requirements. Electric hoists excel in high-demand, industrial settings, while manual hoists offer a reliable and budget-friendly solution for more localized or less frequent lifting tasks. Understanding the specific needs of a project and the local market conditions in Trinidad and Tobago can guide the selection of the most appropriate hoisting equipment to achieve optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Main Projects
Related Products
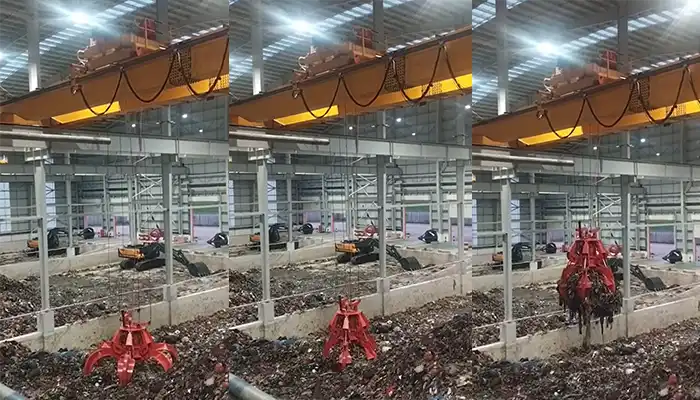

Supplied three grab bucket crane kits to Indonesia, enhancing garbage handling efficiency with high load capacity and reliable performance.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch








