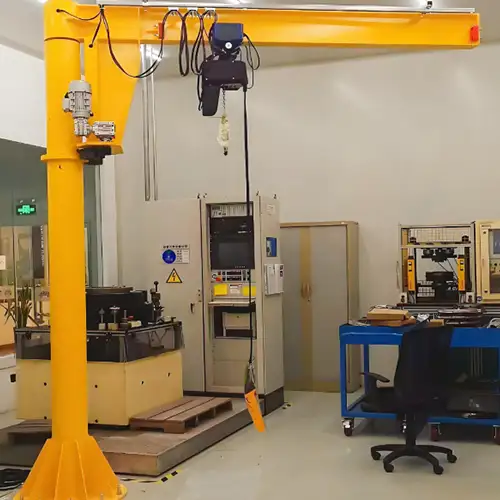
Quick Guide: Choose Right Overhead Crane for CNC Material Supply
Select the right hoisting crane based on material type, weight, space, and use frequency to optimize CNC fiber laser cutting efficiency.Get your design!
Category: Featured
Your Trusted Overhead Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Quick Guide: Choosing the Right Overhead Crane for CNC Material Supply
Select the ideal crane based on material type, weight, space, and use frequency to optimize CNC fiber laser cutting efficiency.
Choosing the right overhead crane for supplying materials to CNC fiber laser cutting machines depends on several key factors, including the type of material, its weight, the workshop layout, and the frequency of crane use. Here’s a simplified guide to help you make the best choice for your operation:
Assess the Material Type and Weight
Choosing the right crane for material handling begins with understanding the type and weight of the materials being moved. The type of material and its weight directly influence the crane capacity, lifting method, and safety considerations. Here are the key categories of materials and the appropriate cranes for each:
Light to Medium Loads (e.g., metal sheets, light plates, small pipes)
For materials that are relatively lightweight but still require regular handling, it’s important to choose a crane that is both compact and capable of performing repetitive tasks efficiently.Capacity Range for Light to Medium Loads: Up to 5-10 tons. Both jib cranes and workstation cranes offer effective solutions for handling lighter materials and optimizing workflow in tight spaces.
Recommended Cranes:
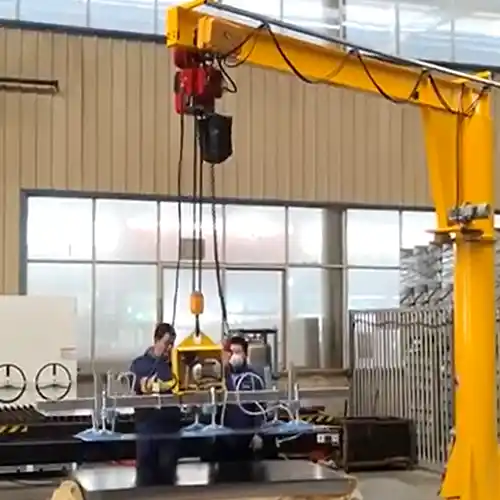
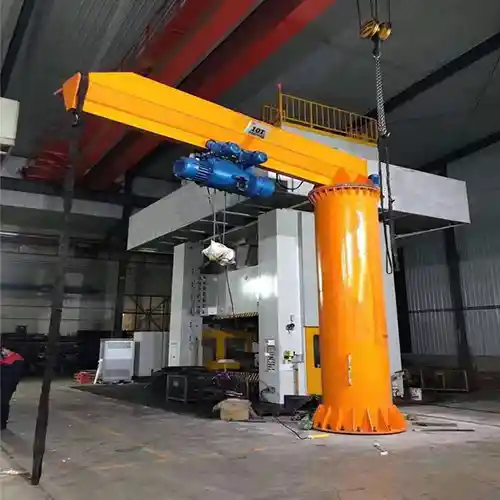
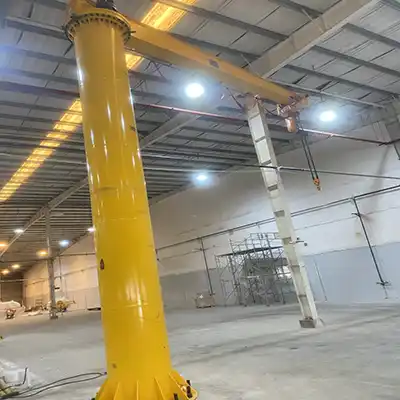
Jib Cranes:
- Features: Jib cranes are ideal for smaller-to-medium loads, especially in confined spaces. They have a rotating arm that allows for easy movement of materials within a defined area, making them perfect for localized loading and unloading operations.
- Capacity: Typically range from 0.5 tons to 5 tons. Larger jib cranes can handle up to 10 tons, but they are usually better suited for smaller, frequent lifts.
- Applications: Jib cranes are often used to lift sheets of metal, smaller pipes, or plates from storage racks to CNC machines or other processing areas. Their compact design makes them ideal for workshops with limited space.
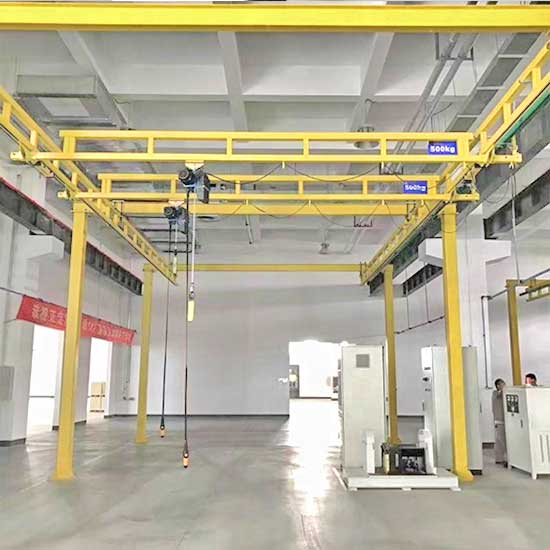
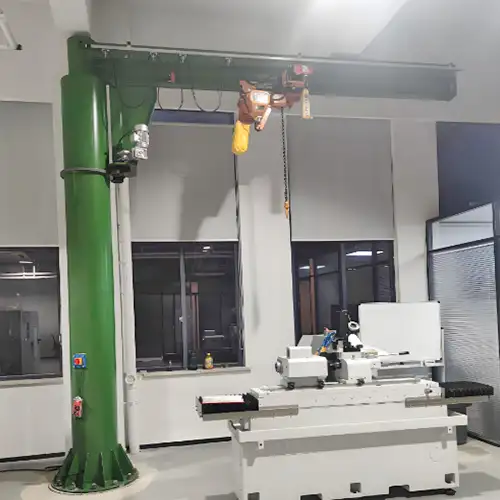
Workstation Cranes:
- Features: Lightweight and modular, workstation cranes are perfect for frequent handling of lighter loads. These cranes are easy to install and can be customized for specific tasks, making them highly flexible.
- Capacity: Commonly handle loads ranging from 0.5 tons to 10 tons, depending on the specific design and requirements.
- Applications: Workstation cranes are commonly used in high-turnover, repetitive lifting tasks in small to medium-sized workshops. They are often used to move light metal sheets or parts to and from CNC fiber laser cutting machines or other production areas.
Here’s a detailed comparison table between Jib Cranes and Workstation Cranes, highlighting their features, similarities, and differences:
| Feature | Jib Cranes | Workstation Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Compact design, ideal for confined spaces | Lightweight, modular design, easy to install |
| Mounting Type | Can be floor-mounted, wall-mounted, or pillar-mounted | Typically ceiling-mounted or fixed to a support column |
| Capacity | 0.5 tons to 5 tons (up to 10 tons for larger versions) | 0.5 tons to 10 tons |
| Range of Motion | Rotating arm, often has limited travel distance | Flexible, often has overhead or rail travel |
| Lifting Height | Low to medium lifting height (depends on mounting) | Varies based on the crane design and height requirements |
| Applications | Handling small-to-medium metal sheets, pipes, plates | Frequent handling of lighter loads in small-to-medium workshops |
| Localized loading and unloading in small workshops | Moving light parts to and from CNC machines or other workstations | |
| Ideal for confined, hard-to-reach areas | Suitable for high-turnover, repetitive lifting tasks | |
| Flexibility | Ideal for localized material handling in tight spaces | Highly flexible for adapting to various lifting tasks |
| Space Requirements | Suitable for workshops with limited space | Suited for areas with moderate space requirements |
| Installation | Easy to install and can be customized | Easy to install and can be adjusted as needed |
| Mobility | Limited range of movement, usually fixed position | Can be designed for easy movement within a workspace |
| Cost | Cost-effective, generally cheaper than larger cranes | Affordable, though costs may increase with capacity |
Key Similarities:
- Both cranes are ideal for handling lighter materials, typically ranging from 0.5 tons to 10 tons.
- Both cranes are designed for use in workshops where space is a consideration.
- Both types of cranes are modular and easy to install, making them a good choice for small to medium-sized operations.
- Both can handle high-turnover, repetitive lifting tasks, improving operational efficiency in workshops.
Key Differences:
- Design and Mobility: Jib cranes feature a rotating arm and are often stationary, making them ideal for localized material handling in confined spaces. Workstation cranes, on the other hand, can be more versatile and mobile within a workshop, making them better suited for tasks that require more flexibility.
- Capacity and Application: Jib cranes typically handle lighter loads (up to 5 tons, though larger versions can handle up to 10 tons), making them suitable for tasks like lifting metal sheets or small pipes. Workstation cranes can handle loads up to 10 tons and are often used for high-turnover tasks like moving light parts and metal sheets to and from CNC machines.
- Space and Installation: Jib cranes are ideal for tight spaces and can be mounted in a variety of configurations (floor, wall, pillar). Workstation cranes are more flexible in terms of installation but generally require a bit more space to operate efficiently within the workshop.
This table helps to compare the capabilities of Jib Cranes and Workstation Cranes, allowing you to choose the best crane for specific lifting tasks in workshops.
Heavy Loads (e.g., large metal plates, heavy pipes, beams)
When handling heavier materials, the crane must have both the capacity and structural strength to safely move large, bulky items. These materials require cranes that offer high load capacities and are designed for stability during lifting.
Recommended Cranes:
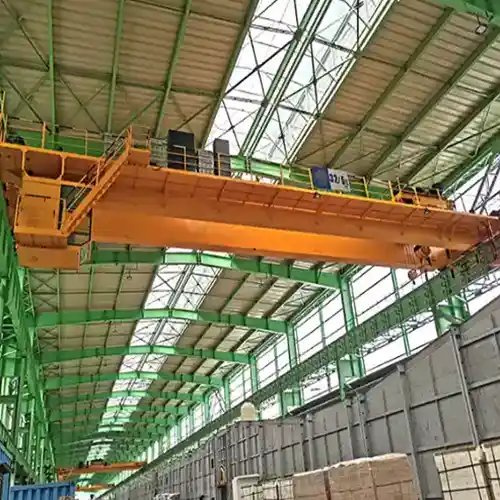
Bridge Cranes:
- Features: Ceiling-mounted bridge cranes are highly efficient for heavy-duty material handling. These cranes feature a span that runs along parallel tracks mounted on the ceiling, allowing for wide coverage of large areas and heavy lifting capabilities.
- Capacity: Bridge cranes typically handle loads from 10 tons to 100 tons or more, depending on the specific model and application. High-capacity versions can manage extremely heavy loads in manufacturing plants or warehouses.
- Applications: These cranes are commonly used to move large metal plates, heavy pipes, structural beams, and other massive components that require lifting and precise placement in CNC cutting or fabrication areas.
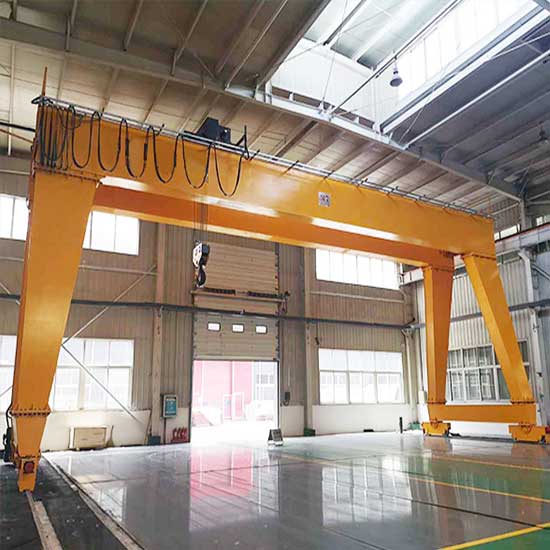
Gantry Cranes:
- Features: Gantry cranes are freestanding, versatile systems that don’t require ceiling tracks. They can be used indoors or outdoors and are suitable for large or heavy materials. Gantry cranes often come with adjustable height and width, making them flexible for a range of lifting tasks.
- Capacity: Gantry cranes are capable of handling loads from 10 tons to over 100 tons, depending on the specific design and purpose.
- Applications: They are ideal for lifting heavy, oversized materials like structural beams, long metal pipes, or large slabs of metal, especially in areas where overhead structures (like ceiling beams) are not feasible or desired.
Here’s a more detailed comparison table between Bridge Cranes and Gantry Cranes, emphasizing their similarities and differences:
| Feature | Bridge Cranes | Gantry Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Mounting Type | Ceiling-mounted or facility-mounted | Freestanding, does not require ceiling tracks |
| Track Type | Runs along parallel tracks mounted on ceiling or facility | Can run on ground-level tracks or be supported by legs |
| Coverage Area | Provides wide coverage of large indoor spaces | Versatile, suitable for both indoor and outdoor use |
| Flexibility | Limited to the area defined by the ceiling tracks | Highly flexible, adjustable height, and width |
| Load Handling | Ideal for heavy-duty material handling, especially in large facilities | Suitable for heavy lifting, especially in large outdoor areas or where overhead structures are not available |
| Space Requirements | Requires sufficient ceiling height and free space for track installation | Requires ground-level space for setup, no ceiling space required |
| Capacity | 10 tons to 100 tons or more, depending on model and application | 10 tons to over 100 tons, depending on design and application |
| Lifting Height | Typically higher lifting height, constrained by ceiling height | Adjustable lifting height based on the crane design |
| Mobility | Fixed, limited mobility within the defined track area | Mobile, able to move along tracks or across large open spaces |
| Applications | Moving large metal plates, heavy pipes, beams, and massive components | Lifting heavy materials such as structural beams, long metal pipes, and slabs |
| Ideal for CNC cutting or fabrication areas with heavy-duty requirements | Often used in areas where ceiling-mounted structures are not feasible | |
| Works best in environments where maximum lifting height is required | Can handle large, long, or oversized components | |
| Installation Complexity | Requires proper installation of ceiling or facility tracks | Easier to install, no requirement for ceiling tracks |
| Cost | Typically more expensive due to installation and infrastructure costs | Often more cost-effective, especially in open or outdoor spaces |
Key Similarities:
- Both are ideal for handling large and heavy materials.
- Both types of cranes can handle capacities from 10 tons to over 100 tons, depending on the specific design.
- Both are used in industrial environments that require precise and heavy lifting.
- Both offer flexibility in handling large components, though the extent of mobility and space constraints vary.
Key Differences:
- Mounting and Space: Bridge cranes are ceiling or facility-mounted and require sufficient overhead space, whereas gantry cranes are freestanding and don’t require ceiling installations, allowing them to be more flexible in outdoor or space-constrained environments.
- Flexibility in Installation: Bridge cranes require fixed track installations on the ceiling, while gantry cranes can be set up with ground-level tracks and adjusted in height and width to suit varying lifting needs.
- Lifting Height: Bridge cranes generally offer higher lifting heights but are limited by the ceiling, whereas gantry cranes offer adjustable heights, making them more adaptable in different spaces.
- Mobility: Bridge cranes operate within the confines of their fixed tracks, limiting their movement, while gantry cranes are more mobile and can be used in larger, more open areas.
This table gives a clearer and more detailed understanding of the similarities and differences between Bridge Cranes and Gantry Cranes, helping you choose the right crane for specific operational needs.
Capacity Range for Heavy Loads: 10 tons to 100+ tons. Both bridge and gantry cranes provide the necessary lifting power for large, heavy materials, ensuring safe and efficient handling.
Delicate or Thin Materials (e.g., polished surfaces, thin sheets)
Handling delicate materials requires specialized equipment to prevent damage, such as scratches, bends, or deformations. Cranes with non-contact lifting systems are ideal for these applications, offering precise control without physically touching the material.
Recommended Cranes:
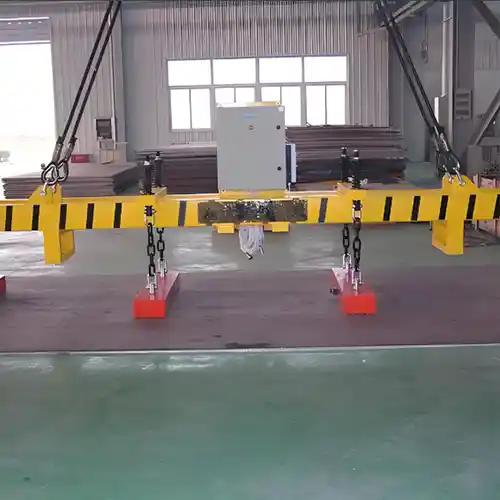
Cranes with Magnetic Lifters
Features:
- Non-contact lifting system that uses magnetic force for material handling.
- Designed for ferrous materials, such as steel, iron, and other metals that are magnetically attracted.
- Powerful lifting capabilities, making them ideal for heavy loads and large components.
- Prevents material surface damage as there is no physical contact between the crane and the material being lifted.
Capacity:
- Typically handles loads ranging from 1 ton to 10 tons or more, depending on the specific steel plate lifter type and the nature of the material being lifted.
- Custom systems may be available for higher capacity applications, especially for specialized industrial needs.
Applications:
- Commonly used in handling large metal sheets, structural beams, and heavy metal components.
- Essential in CNC workshops where precise and heavy lifting of ferrous materials is required, ensuring no direct contact with the material.
- Widely employed for loading and unloading materials for CNC fiber laser cutting machines, ensuring that there is no risk of surface damage during the process.
Cranes with Vacuum Lifters
Features:
- Non-contact system that utilizes suction force to lift materials.
- Ideal for non-ferrous materials, including aluminum, glass, plastics, and other delicate surfaces.
- Gentle handling ensures minimal risk of damage or deformation, especially with fragile or easily scratched materials.
Capacity:
- Typically handles lighter loads, with capacities ranging from 0.5 tons to 5 tons.
- Higher capacity options may be available for specific applications, though these systems are generally best suited for lightweight materials.
Applications:
- Perfect for handling thin metal sheets, polished surfaces, glass, and delicate or fragile materials that require careful handling.
- Widely used in CNC workshops where surface integrity is crucial, and materials need to be handled without physical contact.
- Ensures damage-free transport of delicate parts during loading and unloading, especially in environments where precision and material care are of paramount importance.
This format provides a clear breakdown of each crane type's features, capacity, and primary applications, helping you choose the most appropriate lifting system for your materials and operational requirements.
Magnetic Lifters can generally handle heavier loads than Vacuum Lifters because magnetic systems are typically used for lifting ferrous materials like steel, which are often heavier. On the other hand, Vacuum Lifters are usually best suited for lighter, non-ferrous materials or delicate surfaces.
Capacity Range for Delicate or Thin Materials: 0.5 tons to 5 tons. Non-contact lifting solutions such as magnetic or vacuum lifters are optimal for preventing damage during the handling of sensitive materials.
Here’s an expanded comparison table with more similarities and differences between Cranes with Magnetic Lifters and Cranes with Vacuum Lifters:
| Crane Type | Cranes with Magnetic Lifters | Cranes with Vacuum Lifters |
|---|---|---|
| Features | Non-contact lifting using magnetic force. | Non-contact lifting using suction force. |
| Ideal for lifting ferrous materials like steel, iron, and other metals. | Ideal for handling non-ferrous or delicate materials (e.g., glass, aluminum, plastics). | |
| Strong lifting power for heavier loads. | Best for lightweight or fragile materials with smooth surfaces. | |
| Requires a ferrous material to create a magnetic bond. | Requires a sealed, smooth surface to create suction. | |
| Can lift larger, thicker materials without causing damage. | Can handle more delicate or thin materials without leaving marks. | |
| Capacity | 1 ton to 10 tons (or more, depending on the lifter type and application). | 0.5 tons to 5 tons (custom options for higher capacities). |
| Applications | Handling large metal sheets, beams, and other heavy ferrous materials. | Handling thin metal sheets, polished surfaces, glass, and delicate materials. |
| Used in CNC workshops for precise material handling, reducing risk of damage. | Common in CNC operations for sensitive materials, ensuring damage-free handling. | |
| Ideal for heavy-duty material movement in manufacturing environments. | Often used for lifting delicate or easily scratched materials in fabrication areas. | |
| Perfect for scrap handling and metal component lifting in large factories. | Excellent for high-precision tasks where contact must be minimized (e.g., in the electronics or glass industries). | |
| Surface Requirements | Requires ferrous materials (steel, iron) for magnetic attraction. | Requires smooth, sealed surfaces for the suction grip. |
| Effect on Material | Can cause magnetic field impact on sensitive electronic components if not shielded. | No risk of magnetic interference, making it safe for delicate electronics. |
| Safety Features | Reduces manual labor and material handling injuries, especially with heavy materials. | Ensures safe handling of delicate materials, reducing risk of scratches or damage. |
| Energy Source | Powered by electricity or permanent magnets (depending on the design). | Powered by air vacuum systems (requires air compressors). |
| Operation Speed | Faster for handling larger, denser loads due to strong magnetic force. | Slower compared to magnetic lifters due to the time needed for suction to grip. |
| Ease of Use | Simple operation for heavy loads but requires careful handling of materials. | Easy to operate but requires regular maintenance of vacuum systems. |
| Cost | Generally more affordable for heavy-duty lifting needs. | Slightly higher cost due to the vacuum system and precision components. |
Key Similarities:
- Non-contact Handling: Both crane types provide non-contact lifting, ensuring materials are not physically touched, which reduces the risk of damage.
- Increased Safety: Both systems are designed to reduce manual labor and improve safety by minimizing material handling injuries.
- Precision Handling: Both types allow for more precise handling of materials, especially in environments where accuracy is crucial.
Key Differences Between Magnetic and Vacuum Lifters
Material Compatibility:
- Magnetic Lifters: Specifically designed for lifting ferrous materials such as steel, iron, and other magnetic metals.
- Vacuum Lifters: Ideal for non-ferrous and delicate materials like glass, aluminum, plastics, and thin metal sheets, where a non-contact lift is crucial.
Load Capacity:
- Magnetic Lifters: Can handle heavier loads, typically ranging from 1 ton to 10 tons or more, making them suitable for large, dense materials.
- Vacuum Lifters: Generally limited to lifting lighter loads, ranging from 0.5 tons to 5 tons, although custom options may handle slightly heavier materials.
Surface Requirements:
- Magnetic Lifters: Require a ferrous surface to create a magnetic bond, which limits their application to ferrous materials only.
- Vacuum Lifters: Need a smooth, non-porous surface for the suction to form a secure grip, offering versatility with a wider range of materials.
Cost & Maintenance:
- Magnetic Lifters: More cost-effective, especially when handling large volumes of heavy-duty materials. They have lower maintenance needs compared to vacuum systems.
- Vacuum Lifters: Tend to be more expensive due to the sophisticated vacuum technology and require regular maintenance to ensure optimal operation.
Speed of Operation:
- Magnetic Lifters: Operate faster, particularly with heavy materials, as the magnetic bond is almost instantaneous.
- Vacuum Lifters: May be slower as it takes time to establish the vacuum seal, particularly for large or irregularly shaped items.
This comparison highlights the unique advantages and limitations of each lifting system, guiding you to choose the most suitable crane system based on material type, load capacity, operational speed, and cost-effectiveness in your specific manufacturing or workshop environment.
Summary of Material Type and Weight Assessment
- Light to Medium Loads: Jib cranes and workstation cranes are best for small to medium-sized materials like metal sheets, small pipes, and light plates, with capacities typically ranging from 0.5 tons to 10 tons.
- Heavy Loads: Bridge cranes and gantry cranes are the best choices for lifting large, heavy materials like metal plates, beams, and pipes, with capacities ranging from 10 tons to 100+ tons.
- Delicate or Thin Materials: For delicate materials, cranes with magnetic or vacuum lifters are ideal for non-contact lifting, with capacities typically ranging from 0.5 tons to 5 tons.
By assessing the material type and weight, businesses can choose the crane that best suits their material handling needs, ensuring efficiency, safety, and minimal material damage in CNC fiber laser cutting operations.
Consider the Workshop Layout
When selecting the right crane for your CNC workshop, the available space plays a crucial role in determining the most suitable option. Here’s how different crane types perform in various space conditions:
Limited Space (Narrow Aisles or Low Ceilings)
In workshops with space constraints, such as narrow aisles or low ceilings, selecting the right crane is crucial. The crane must be able to operate effectively in tight areas without compromising performance, efficiency, or safety.
Jib Cranes
Features:
- Compact design with a rotating arm, perfect for localized material handling in confined spaces.
- Can be mounted on a pillar or wall, offering flexibility in installation.
Advantages:
- Easy to install and operate, with minimal overhead space requirements.
- Ideal for lifting small to medium-sized materials in tight spaces.
- Efficient for lifting loads at lower heights (typically up to 6 meters), making it perfect for handling materials at ground level or in low-ceiling workshops.
Applications:
- Used for moving small metal plates, sheets, pipes, and components to and from CNC machines, storage racks, or processing areas.
- Ideal for workshops with limited space, allowing workers to lift and position materials with precision in areas with narrow aisles or low headroom.
Workstation Cranes
Features:
- Lightweight, modular, and customizable design, which can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the workshop.
- Easily reconfigurable, making it suitable for workshops with frequently changing layouts or tasks.
Advantages:
- Highly flexible, offering a range of lifting capacities (typically up to 5 tons).
- Suitable for small to medium-sized spaces, enabling easy movement of materials across different workstations.
- Simple to install and relocate, providing a cost-effective solution for frequent lifting operations.
Applications:
- Best for repetitive, frequent lifting tasks, such as transferring light to medium-sized metal sheets, components, or smaller parts in CNC machining areas.
- Common in small to medium-sized workshops, providing an easy way to load and unload materials from CNC machines, lathes, or other manufacturing equipment.
Here are the tables for the Jib Cranes and Workstation Cranes with more specific details:
| Jib Cranes | Workstation Cranes |
|---|---|
| Features | Features |
| Compact design with a rotating arm. | Lightweight, modular, and customizable. |
| Mounted on a pillar or wall for flexibility. | Can be easily reconfigured based on workshop needs. |
| Advantages | Advantages |
| Easy to install and operate in limited spaces. | High flexibility for lifting light to medium loads. |
| Suitable for small to medium materials. | Can be relocated or reconfigured easily. |
| Efficient for lifting loads at lower heights. | Ideal for frequent, repetitive lifting tasks. |
| Applications | Applications |
| Handling small metal plates, sheets, pipes. | Transferring metal sheets, components, and parts. |
| Moving materials to/from CNC machines or racks. | Common in small-to-medium workshops with tight spaces. |
| Perfect for areas with limited headroom or narrow aisles. | Used for frequent lifting in small and medium-sized workshops. |
This table format compares the Jib Cranes and Workstation Cranes side by side, making it easier to understand their key features, advantages, and applications in workshops with limited space.
Larger Spaces (Open Workshops with High Ceilings)
In large workshops or facilities with high ceilings and ample space, cranes with higher lifting capacities and long spans can significantly improve operational efficiency. These cranes provide the ability to cover larger areas and handle heavier materials with ease.
Bridge Cranes
Features:
- Ceiling-mounted or facility-mounted with high lifting height and long spans.
- Wide coverage area that allows handling of heavy materials over long distances.
Advantages:
- Ideal for spacious workshops with greater clearance, offering high lifting height for heavy material movement.
- Provides wide coverage for handling large, bulky materials across vast distances.
- Efficient for high-volume lifting in industrial environments requiring heavy-duty capacity.
Applications:
- Handling large metal sheets, heavy beams, and other bulky materials in CNC cutting or fabrication areas.
- Commonly used in factories, warehouses, or large manufacturing plants where significant lifting heights and spans are needed.
Gantry Cranes
Features:
- Freestanding design, which does not require ceiling tracks or overhead support structures.
- Adjustable height and capacity, making them versatile for different lifting tasks.
- Suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, perfect for environments with or without overhead beams.
Advantages:
- Ideal for spaces with no ceiling beams, providing flexibility to operate in various locations, including outdoor facilities.
- Can travel along rails and cover large areas, offering great mobility.
- Capable of handling large lifting capacities for heavy and oversized materials.
Applications:
- Handling large structural beams, long metal pipes, and oversized components in both indoor workshops and outdoor yards.
- Frequently used in shipping yards, outdoor fabrication sites, and construction projects, where high mobility and large load handling are crucial.
| Limited Space | Larger Spaces |
|---|---|
| Recommended Cranes | Recommended Cranes |
| Jib Cranes, Workstation Cranes | Bridge Cranes, Gantry Cranes |
| Key Benefits | Key Benefits |
| Compact Design: Ideal for small-to-medium-sized spaces, allowing for efficient material handling in confined areas. | Higher Lifting Height: Suitable for high-ceiling workshops, offering substantial vertical lifting capabilities for large loads. |
| Flexibility: Easy to install and relocate, adaptable to frequently changing layouts and tasks. | Long Spans: Capable of spanning large distances, maximizing operational coverage and handling heavy materials across extensive areas. |
| Ease of Use: Simple operation that reduces the need for extensive training or setup time. | Heavy Load Handling: Designed for handling larger, heavier materials like beams, metal sheets, and machinery components. |
| Low Ceiling Compatibility: Ideal for areas with low ceilings or limited headroom, ensuring safe lifting in tight spaces. | Increased Productivity: High lifting capacity and wide coverage contribute to faster, more efficient operations, reducing downtime. |
| Space Efficiency: Minimal space is required overhead or on the floor, making it perfect for workshops with narrow aisles or space constraints. | Versatility: Gantry cranes are freestanding and can be used both indoors and outdoors, while bridge cranes are ceiling-mounted for optimized space utilization. |
| Localized Handling: Efficient at lifting small-to-medium materials to and from workstations or CNC machines in compact environments. | Open Space Compatibility: Ideal for large, open workshops or outdoor areas where overhead support structures (like ceiling beams) may be unavailable or impractical. |
For limited space environments, Jib Cranes and Workstation Cranes are ideal for smaller, high-turnover tasks. For larger spaces, Bridge Cranes and Gantry Cranes are best suited for handling heavier loads with high lifting capacities and wide coverage.
Evaluate Operational Frequency
When evaluating crane types for different operational frequencies, it's important to consider both the volume of material handling and the weight of loads being moved. Frequent use requires robust, high-capacity cranes that can handle continuous operation without experiencing downtime, while occasional use focuses on lighter, more specialized lifting tasks.
Frequent Use (High-Volume Material Handling)
Recommended Cranes:
Bridge Cranes
- Features: Designed for continuous, high-duty cycles with high lifting capacities and long spans. They can be ceiling-mounted or facility-mounted, allowing them to cover large areas.
- Advantages: Built for heavy-duty, frequent operations, bridge cranes are ideal for environments where lifting loads are continuous and high-capacity. Their versatility in lifting both light and heavy materials makes them highly efficient in manufacturing and large workshops.
- Applications: Widely used in large workshops, manufacturing facilities, and distribution centers for moving heavy materials such as metal sheets, beams, or components. The ability to span long distances and handle heavy loads over long periods of time makes them ideal for CNC workshops and large-scale production lines.
Gantry Cranes
- Features: Freestanding and often used outdoors or in spaces without overhead structural support. Adjustable height and span for flexibility in material handling.
- Advantages: Gantry cranes can be moved across a large area, which is ideal for high-frequency operations in outdoor environments or spacious indoor workshops. They are rugged and designed to handle large, heavy materials over a long operational lifespan.
- Applications: Common in industries like steel manufacturing, shipping yards, or large factories where heavy loads are handled continuously. They are well-suited for lifting large equipment, long metal beams, or heavy components that require frequent repositioning.
Workstation Cranes
- Features: Modular, lightweight, and flexible cranes designed for repetitive, fast handling in smaller spaces.
- Advantages: Workstation cranes are ideal for high-frequency lifting of lighter loads, providing fast, efficient material handling with minimal downtime. Their modular nature makes them easy to install and move, offering flexibility for various tasks.
- Applications: Frequently used in smaller to medium-sized workshops where lighter loads, such as metal sheets, small parts, or components, need to be moved quickly and repeatedly from one workstation to another. Workstation cranes are commonly seen in CNC machining areas, assembly lines, and parts manufacturing where repetitive tasks are common.
Occasional Use (Lower Load Handling Frequency)
Recommended Cranes:
Jib Cranes
- Features: Compact, easy-to-install cranes with a rotating arm, often mounted on a pillar or wall. Ideal for localized lifting tasks with minimal space requirements.
- Advantages: Jib cranes excel in environments where occasional, precise lifting is needed for lighter loads. They provide excellent reach and flexibility in confined spaces and are ideal for tasks that do not require continuous operation.
- Applications: Common in workshops with limited space or low ceilings, jib cranes are perfect for handling materials like small metal plates, pipes, or components. They are often used for loading/unloading parts to and from machines such as CNC equipment, especially when the lifting frequency is not as high.
Monorail Cranes
- Features: A rail-mounted lifting system that moves materials along a fixed path, typically used for linear or semi-linear material handling.
- Advantages: Monorail cranes are ideal for occasional, linear material movement. They are simple to install and require minimal maintenance. With a fixed path, they offer reliable, low-maintenance lifting for occasional use where a dedicated, high-frequency system is not required.
- Applications: Monorail cranes are commonly used in environments where materials need to be moved in one direction, such as in small to medium-sized workshops for loading/unloading parts or materials from one station to another. They are often used in assembly lines or areas with limited space, providing efficient movement without the complexity of larger cranes.
| Operational Frequency | Recommended Cranes |
|---|---|
| Frequent Use (High-Volume) | Bridge Cranes: High-capacity, high-duty, versatile for large areas. Gantry Cranes: Freestanding, rugged, and ideal for large outdoor or indoor areas. Workstation Cranes: Modular, efficient for fast, repetitive tasks in small-to-medium spaces. |
| Occasional Use (Low-Volume) | Jib Cranes: Compact, ideal for occasional, precise lifting in tight spaces. Monorail Cranes: Simple, linear material movement ideal for light, occasional handling tasks. |
This approach ensures the crane you select aligns with your operational needs, optimizing both efficiency and safety. High-volume environments require heavy-duty, reliable systems like bridge and gantry cranes, while occasional, lighter lifting tasks are well-suited for jib or monorail cranes.
Space for Crane Travel
When selecting a crane, considering the travel distance and the layout of your workshop or facility is crucial. The type of crane needed will depend on whether the material needs to be moved across long distances in large areas or within confined, short-range spaces.
Long Travel Distance (Large Workshops or Outdoor Areas)
Recommended Cranes:
Bridge Cranes
- Features: Bridge cranes can cover expansive areas with their long spans and high lifting capacities. Mounted on rails, they travel along a fixed overhead track, providing the ability to move materials across wide, open spaces.
- Advantages: Ideal for large workshops, manufacturing facilities, and outdoor yards where heavy materials need to be transported over long distances. With their ability to lift and move materials across vast areas, bridge cranes are highly effective in operations that require both height and span.
- Applications: Used in large factories, steel mills, and shipping yards where materials such as heavy beams, metal sheets, and large machinery need to be moved over considerable distances. Their long travel distance makes them suitable for manufacturing processes that involve large-scale production lines or complex handling systems.
Gantry Cranes
- Features: Freestanding cranes that can be used both indoors and outdoors, gantry cranes offer adjustable height and span, making them versatile for large, open areas.
- Advantages: Gantry cranes are ideal for large or open spaces where overhead structures are not available. Their mobility allows them to travel across the facility, making them perfect for both indoor and outdoor environments. They can be equipped with high lifting capacities and can cover long travel distances.
- Applications: Commonly used in large outdoor areas such as construction sites, shipping yards, and steel production plants, gantry cranes are ideal for handling heavy or oversized materials, structural beams, or long metal pipes. They are also suitable for industries where flexibility in crane movement is essential.
Short Travel Distance (Small Workshops or Confined Areas)
Recommended Cranes:
Monorail Cranes
- Features: Monorail cranes are designed for moving materials along a single fixed path, typically in a linear direction. These cranes are excellent for short-range material transport, often within a limited area.
- Advantages: They are simple, efficient, and cost-effective for small workshops or areas where materials need to be moved only in one direction. The ability to move materials along a straight path means minimal installation space and a simple, low-maintenance system.
- Applications: Monorail cranes are commonly used in smaller workshops, assembly lines, or warehouses where materials need to be moved along a fixed path. Ideal for tasks such as moving small components between stations or from storage to processing areas.
Workstation Cranes
- Features: Modular and lightweight, workstation cranes are designed for easy movement in confined spaces. They are often installed for tasks that require minimal travel and precise material positioning.
- Advantages: Workstation cranes provide an efficient solution for handling materials in tight spaces. Their modular design allows for reconfiguration and installation in areas with limited headroom or restricted floor space. They are often used for handling lighter loads over short distances.
- Applications: Ideal for small-to-medium-sized workshops, workstation cranes are perfect for moving small metal sheets, components, or tools from one workstation to another. They provide quick and efficient movement over short distances, making them ideal for repetitive lifting tasks in confined spaces like CNC machining or assembly lines.
| Travel Distance | Recommended Cranes |
|---|---|
| Long Travel Distance | Bridge Cranes: Long spans, ideal for large workshops and outdoor areas. Gantry Cranes: Versatile, freestanding, ideal for large indoor and outdoor areas with flexible movement. |
| Short Travel Distance | Monorail Cranes: Ideal for short, linear material movement in confined spaces. Workstation Cranes: Modular, efficient for handling light loads over small distances in tight spaces. |
This classification helps in choosing cranes based on the spatial constraints of your facility, ensuring maximum efficiency in material handling based on the required travel distance. For large areas, bridge and gantry cranes offer flexibility and long-range operation, while monorail and workstation cranes excel in confined spaces with shorter travel distances.
Additional Considerations
When selecting a crane system for your workshop or facility, it's important to consider more than just the load capacity or travel distance. Key factors such as safety features and ease of maintenance play a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations and prolonging the lifespan of your equipment.
Safety Features
Safety should always be a top priority when selecting a crane, especially when handling hazardous or delicate materials. Cranes with integrated safety features can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and ensure the safe handling of materials in the workplace.
- Overload Protection: Cranes equipped with overload protection prevent lifting beyond the maximum rated capacity, reducing the risk of structural damage to the crane and injuries to operators.
- Emergency Stops: Emergency stop systems are essential for quickly halting crane operations in case of a malfunction, preventing accidents and ensuring the safety of personnel.
- Magnetic and Vacuum Lifters: These non-contact lifting systems provide safer handling of fragile materials like glass, aluminum, or polished surfaces. The use of magnetic or vacuum lifters eliminates the risk of surface damage or contamination, ensuring materials are moved without direct physical contact.
- Anti-Collision Systems: For cranes with high mobility or multiple cranes operating in the same area, anti-collision systems help prevent accidents by detecting obstacles and avoiding collisions.
Recommended Cranes for Enhanced Safety:
- Cranes with Magnetic Lifters: These cranes provide non-contact lifting for ferrous materials, minimizing the risk of damage to the material's surface. Ideal for environments where safety and surface integrity are critical.
- Cranes with Vacuum Lifters: These cranes offer gentle handling of non-ferrous, delicate materials such as glass or thin metal sheets, ensuring safe and damage-free lifting operations.
- Bridge Cranes and Gantry Cranes: These cranes can be equipped with advanced safety systems such as load limiters, collision avoidance, and emergency stop functions to ensure safety during heavy-duty operations.
Ease of Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping cranes running smoothly and avoiding costly downtime. Some cranes are easier to maintain than others, depending on their design, complexity, and the environment in which they are used.
- Modular Design: Cranes with a modular design, such as workstation cranes, are easier to maintain due to their simpler components and the ability to replace parts individually. This design also allows for flexibility in upgrading or modifying the crane as needs change.
- Accessibility: Cranes with easy-to-access components (e.g., electrical systems, hoist mechanisms) simplify the inspection and repair process, reducing the time and effort needed for maintenance.
- Durability: Cranes designed for heavy-duty environments, such as bridge or gantry cranes, often require more robust maintenance schedules. Regular inspections of high-load components (like lifting motors and travel systems) are crucial to ensure their longevity.
- Remote Diagnostics: Modern cranes with remote diagnostic capabilities allow for real-time monitoring of the crane’s performance, helping detect and address potential issues before they lead to costly repairs.
Recommended Cranes for Easy Maintenance:
- Workstation Cranes: Due to their simple, modular design, workstation cranes are generally easier to maintain and service. Their components are typically accessible, and parts can be replaced with minimal downtime.
- Gantry Cranes: Gantry cranes can be maintained easily because of their open structure and modular components. They are also easier to service in outdoor environments compared to more complex overhead systems.
- Bridge Cranes: While these cranes may require more frequent and detailed maintenance due to their larger size and complexity, those equipped with advanced monitoring systems can help detect issues early and streamline the maintenance process.
| Consideration | Recommended Cranes | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Safety Features | Magnetic Lifter Cranes: Non-contact lifting of ferrous materials. Vacuum Lifter Cranes: Safe handling of fragile materials. Bridge & Gantry Cranes: Equipped with overload protection, emergency stops, and anti-collision systems. | Ensures safe handling, minimizes damage, and reduces risks during operations. |
| Ease of Maintenance | Workstation Cranes: Modular design, easy to maintain. Gantry Cranes: Freestanding and open design for easy access. Bridge Cranes: Equipped with monitoring systems for easy diagnostics. | Simplifies maintenance processes, reduces downtime, and prolongs crane lifespan. |
By considering these additional factors, you can select a crane system that not only fits your operational needs but also promotes safety and reduces maintenance efforts, ensuring smooth and efficient material handling operations in the long run.
Quick Guide on Crane Selection for Specific Objects Handled
Choosing the right crane for your specific materials is essential to ensure safe, efficient, and precise handling. Here's a streamlined guide to help you match cranes with different objects commonly handled in CNC workshops, fabrication areas, and industrial environments.
Thick Steel/Aluminum Plates
- Recommended Cranes: Overhead Bridge Cranes, Gantry Cranes
- Typical Capacity: 5 to 30 tons
- Material Size & Weight: Large, flat plates; 100 kg to 10,000 kg
- Features: Heavy-duty handling, wide spans for large areas, precise control for heavy loads. Ideal for construction, fabrication, and machinery.
Long Pipes or Beams
- Recommended Cranes: Gantry Cranes, Monorail Cranes
- Typical Capacity: 1 to 20 tons
- Material Size & Weight: Long, cylindrical or rectangular shapes; 200 kg to 5,000 kg
- Features: Flexibility in movement, adjustable height for proper lifting angles. Perfect for linear material handling in tight or large spaces.
Small Precision Parts
- Recommended Cranes: Jib Cranes, Workstation Cranes
- Typical Capacity: 0.25 to 2 tons
- Material Size & Weight: Compact components; 0.5 kg to 500 kg
- Features: High precision and localized movement, ideal for small loads and confined spaces. Provides easy access to CNC machines or workstations.
Delicate Metal Sheets
- Recommended Cranes: Semi-Automatic Cranes with Lifters
- Typical Capacity: 1 to 10 tons
- Material Size & Weight: Thin, large sheets; 50 kg to 1,000 kg
- Features: Non-contact lifting with magnetic or vacuum lifters. Designed to prevent surface damage during lifting, ideal for delicate materials.
Large Industrial Panels
- Recommended Cranes: Overhead Bridge Cranes
- Typical Capacity: 5 to 20 tons
- Material Size & Weight: Large, rigid panels; 500 kg to 8,000 kg
- Features: Overhead clearance, strong lifting power, precise control for heavy-duty industrial handling. Common in manufacturing and assembly lines.
Lightweight Metal Sheets
- Recommended Cranes: Workstation Cranes
- Typical Capacity: 0.5 to 2 tons
- Material Size & Weight: Thin, flexible sheets; 50 kg to 500 kg
- Features: Compact design, modular, perfect for frequent and repetitive lifting in tight spaces. Ideal for small fabrication tasks or loading/unloading CNC machines.
Additional Considerations:
- Customization: Crane capacities can be adjusted to accommodate specific material weights and sizes. Custom solutions ensure optimal performance for unique handling needs.
- Safety Features: Modern cranes come equipped with overload protection, anti-sway systems, and precision controls to ensure safe lifting, especially for heavy or delicate materials.
- Automation: Many overhead cranes, particularly bridge cranes, can be automated to increase operational efficiency, reduce manual handling, and improve workflow in busy environments.
This quick guide is designed to help you understand the general crane options best suited for various materials. For specific applications, capacities, or configurations, please reach out for personalized advice.
| Material & Size/Weight | Crane Type & Capacity | Features |
|---|---|---|
Thick Steel/Aluminum Plates Large, flat plates100 kg to 10,000 kg | Overhead Bridge or Gantry Cranes 5 to 30 tons | Heavy-duty handling for large sheets or plates, wide spans for large areas, precise control for heavy loads. |
Long Pipes or Beams Long, cylindrical shapes200 kg to 5,000 kg | Gantry or Monorail Cranes 1 to 20 tons | Versatile lifting for long and heavy materials, requires adjustable height for flexibility in lifts. |
Small Precision Parts Small and compact0.5 kg to 500 kg | Jib or Workstation Cranes 0.25 to 2 tons | High precision and localized movement, ideal for small loads in confined spaces, minimal workspace interference. |
Delicate Metal Sheets Flat, thin sheets50 kg to 1,000 kg | Semi-Automatic Cranes with Lifters 1 to 10 tons | Non-contact lifting (magnetic/vacuum lifters) to avoid surface damage, ideal for fragile materials requiring lightweight handling. |
Large Industrial Panels Large, flat panels500 kg to 8,000 kg | Overhead Bridge Cranes 5 to 20 tons | Heavy-duty lifting for large industrial components, precision control, and overhead clearance. |
Lightweight Metal Sheets Thin, flat sheets50 kg to 500 kg | Workstation Cranes 0.5 to 2 tons | Compact, modular design, ideal for frequent, repetitive lifting in tight spaces, efficient for lightweight loads. |
Important Notes:
- For Reference Only: The capacities and crane types listed above are general recommendations based on typical material types, sizes, and weights. Specific requirements may vary depending on your unique application, so it’s always advisable to contact us directly for customized recommendations.
- Customized Solutions Available: Cranes can be designed or customized to handle materials that may fall outside the typical ranges, ensuring optimal performance for your operations. Our team will be happy to provide tailored solutions based on your precise needs.
- Safety and Compliance: All crane systems are equipped with safety features such as overload protection, precision control, and anti-sway mechanisms. Additionally, cranes can be integrated with automation systems to further streamline workflows and improve operational efficiency.
- Capacity Adjustments: The weight capacity of a crane can be customized based on the size, type, and frequency of materials being lifted, as well as any other operational specifications (e.g., lifting height, speed, and environment).
- Material Handling and Automation: Many of the recommended crane systems can be integrated with vacuum or magnetic lifters for delicate material handling, or with automation technology to further increase productivity and reduce manual handling.
For more information or to discuss your specific material handling needs, feel free to get in touch with our experts for advice and assistance.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Crane for CNC Fiber Laser Cutting
To choose the most suitable overhead crane for your CNC fiber laser cutting operations, consider the following factors:
- Material Type & Weight: Ensure the crane's lifting capacity aligns with the material's size and weight. Heavy-duty materials, like thick steel plates, require steel plate handling cranes with higher lifting capacities.
- Space Constraints: Account for the layout of your workshop. If space is limited, opt for compact crane systems that provide maximum flexibility in tight areas.
- Frequency of Use: Choose a crane system that fits the demands of your production schedule. High-volume operations benefit from heavy-duty cranes, while low-frequency tasks may require lighter, more precise systems.
- Crane Capacity: Always prioritize the crane's lifting capacity to ensure it can handle the load safely without compromising performance or efficiency.
By taking these factors into account, you can optimize your material handling process for improved safety, productivity, and long-term efficiency. Contact us to get your customized lifting crane for your cnc workshop material handling .
Main Projects
Related Products
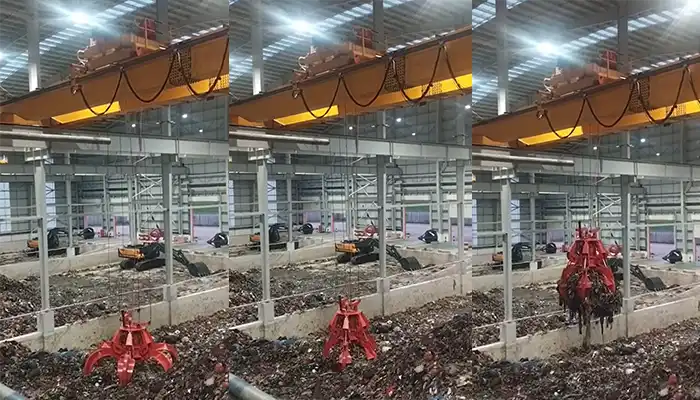

Supplied three grab bucket crane kits to Indonesia, enhancing garbage handling efficiency with high load capacity and reliable performance.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch