Wall-Mounted Cantilever Jib Cranes in Confined Spaces, Safety Considerations for Operating
Essential safety considerations for operating wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes in confined spaces, including protocols, best practices, and hazard mitigation.
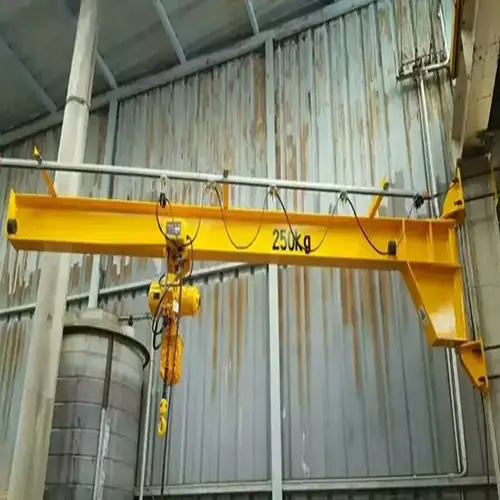
| Crane type | Wall mounted cantilever crane |
| Crane Capacity | 0.25 ton to 5 ton |
| Crane Span | As customer requirement |
| Lifting height | As custom requirement |
Category: Low Built Cranes & Hoists
Your Trusted Overhead Wall Cantilever Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Wall-Mounted Cantilever Jib Cranes in Confined Spaces – Safety Considerations for Operating
Key safety protocols and best practices for operating wall-mounted jib cranes in limited or confined spaces, including common hazards and how to mitigate them.
Essential safety considerations for operating wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes in confined spaces, including protocols, best practices, and hazard mitigation.

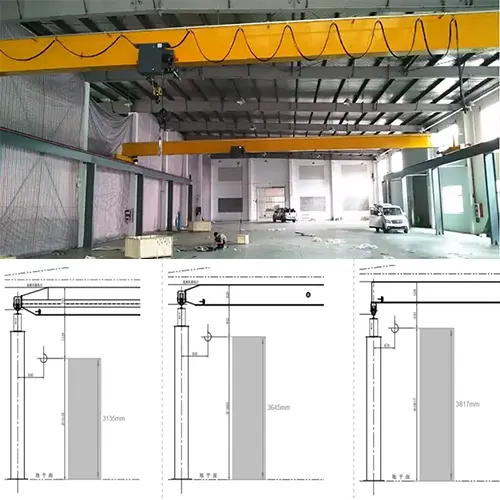
Overview of Wall-Mounted Cantilever Jib Cranes
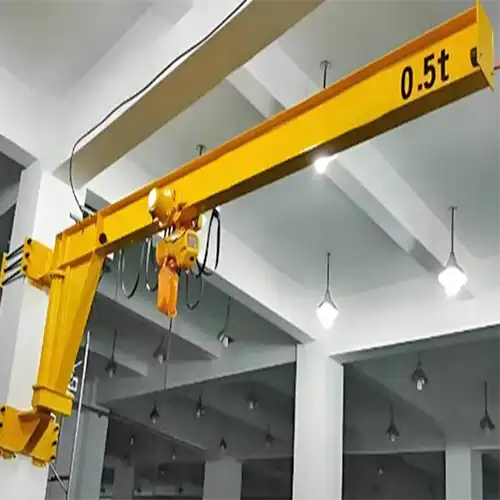
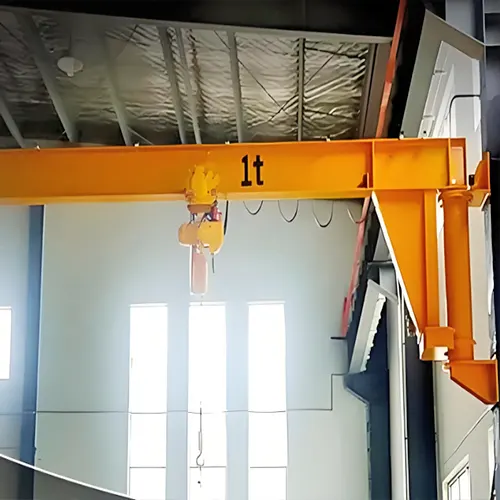
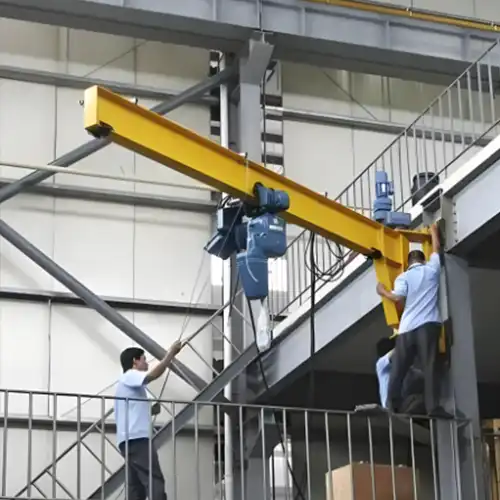
Wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes are versatile lifting solutions designed to be mounted on walls, providing a robust and space-efficient option for material handling. These cranes feature a horizontal arm that extends outward from a vertical support, allowing for precise and controlled lifting and positioning of loads. They are commonly used in various industrial settings, including warehouses, manufacturing plants, and maintenance areas.
In confined spaces, these cranes offer significant advantages due to their compact design. They maximize usable space by extending vertically and horizontally from a fixed point, making them ideal for environments where floor space is limited. Their ability to provide flexible load handling while occupying minimal floor area makes them especially useful in cramped or restrictive working environments.
Importance of Safety in Confined Spaces
Operating wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes in confined spaces presents unique challenges and risks. Confined spaces are typically characterized by limited access, restricted movement, and potentially hazardous conditions. These constraints can make it difficult to maneuver equipment and conduct operations safely.
Key challenges include restricted clearance, which can complicate crane movement and load placement, and the potential for structural obstructions that may interfere with crane operation. Additionally, confined spaces may limit the ability to quickly respond to emergencies or provide adequate ventilation, increasing the risk of accidents or equipment malfunctions.
Safety protocols are critical in such environments to mitigate these risks. Proper safety measures help prevent accidents, ensure the well-being of operators and personnel, and maintain efficient and reliable crane operation. Adhering to safety guidelines is essential for managing the complexities of confined spaces and ensuring that operations are conducted safely and effectively.
Key Safety Protocols
Pre-Operation Safety Checks
Before using a wall-mounted cantilever jib crane, it's crucial to conduct thorough pre-operation safety checks to ensure the equipment is safe and functional. This involves inspecting crane components for signs of wear and damage, such as frayed cables, cracked or bent parts, and rust. Regular checks help identify any issues that could affect the crane's performance or pose safety risks.
Additionally, proper installation and secure mounting are essential. Verify that the crane is installed according to manufacturer specifications and is firmly attached to the wall or support structure. Ensuring that all bolts, anchors, and supports are in place and properly tightened helps prevent equipment failure and maintains stability during operation.
Operator Training and Certification
Specialized training for confined space operations is vital for crane operators. This training should cover the specific challenges of working in confined areas, including maneuvering the crane within restricted spaces and handling potential hazards. Operators must be well-versed in the unique safety protocols associated with confined spaces to ensure safe and effective crane use.
Certification requirements for crane operators vary by region and industry, but generally include formal training and testing. Operators should pursue relevant certifications and stay current with industry standards. Ongoing education is also important to keep up with new safety practices and technological advancements, ensuring that operators are always prepared for safe operation.
Load Handling Procedures
Proper load handling is crucial for maintaining safety and operational efficiency. Techniques for securing loads include using appropriate rigging equipment, such as slings and hooks, and ensuring that loads are evenly distributed to prevent shifting or tipping. Securely fastening loads reduces the risk of accidents and ensures safe transportation.
Accurately calculating load limits is also essential. Operators must be aware of the crane's maximum capacity and ensure that loads do not exceed this limit. Overloading the crane can lead to equipment failure, potential accidents, and damage to the crane. Adhering to load limits and avoiding overloading is critical for maintaining safe and reliable crane operation in confined spaces.
Best Practices for Confined Spaces
Workspace Evaluation
Evaluating the workspace is a fundamental step in ensuring safety when operating wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes in confined spaces. Begin by assessing space constraints, including the dimensions of the area and the required clearance for the crane's movement. Proper evaluation helps determine if the crane can maneuver effectively and safely handle loads without obstruction.
Identifying potential hazards within the confined area is also crucial. This involves looking for obstacles such as structural supports, overhead components, or other equipment that may interfere with crane operation. Recognize any environmental risks, such as poor ventilation or limited access, which could affect both the crane's operation and the safety of personnel working nearby.
Communication and Coordination
Effective communication between crane operators and ground personnel is essential for safe operations in confined spaces. Establish clear lines of communication to ensure that everyone involved is aware of the crane's movements and load handling. This helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures that operations run smoothly.
Setting up clear signals and procedures is vital for confined space operations. Develop a system of hand signals or radio communications to coordinate actions between the crane operator and other team members. Establishing standardized procedures for lifting, moving, and positioning loads ensures consistency and reduces the risk of errors or accidents.
Emergency Preparedness
Preparing for emergencies is critical when working in confined spaces. Develop and practice emergency response plans tailored to the specific risks of the confined area. Ensure that all personnel are familiar with the procedures and know their roles in case of an emergency.
Quick access to emergency equipment and exit routes is essential for effective response. Make sure that emergency equipment, such as first aid kits and fire extinguishers, is readily available and accessible. Clearly mark exit routes and ensure they are unobstructed to facilitate swift evacuation if necessary. Regular drills and reviews of emergency procedures help ensure that everyone is prepared to act quickly and safely in a crisis.
Common Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
Limited Clearance and Space Constraints
Managing tight spaces and restricted movement is a key challenge when operating wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes in confined environments. To navigate these constraints, operators should carefully plan crane movements and load placements to avoid collisions with walls, equipment, or other obstacles.
Using spotters and other aids can significantly enhance safety in these settings. Spotters help guide the crane operator by providing real-time feedback on clearance and positioning. Additional aids, such as mirrors or cameras, can offer better visibility of the surrounding area, assisting in maneuvering the crane safely within the confined space.
Obstacles and Structural Interferences
Identifying and avoiding obstacles in the operating area is crucial for safe crane operation. Before beginning any lifting or movement, inspect the area for potential obstructions like structural supports, beams, or other equipment. Planning the crane's path and load placement helps minimize the risk of interference.
Adapting crane movements to avoid structural interference involves adjusting the crane's positioning and trajectory to navigate around obstacles. Ensure that the crane arm and load do not come into contact with any structures or equipment. This careful planning helps prevent accidents and maintains the safety of the operation.
Electrical and Mechanical Hazards
Ensuring proper maintenance and inspection of electrical components is essential for preventing electrical hazards. Regularly check wiring, controls, and power supplies for signs of wear or damage. Proper maintenance helps avoid electrical failures that could lead to accidents or equipment malfunctions.
Safeguarding against mechanical failures is equally important. Conduct routine inspections and maintenance on mechanical parts, such as gears, cables, and bearings, to ensure they are functioning correctly and are properly lubricated. Addressing any issues promptly helps prevent breakdowns and maintains the crane's reliability and safety.
Case Studies and Examples
Successful Implementations
Wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes have proven effective in various confined spaces across different industries. For example, in a manufacturing plant with limited floor space, a wall-mounted cantilever jib crane was installed to optimize material handling. The crane's compact design allowed it to navigate tight aisles and overhead spaces, facilitating efficient movement of parts without requiring additional floor space.
In another case, a warehouse with narrow storage aisles utilized wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes to handle heavy pallets. The cranes' ability to extend and rotate allowed for precise placement of goods into high shelves, improving operational efficiency and reducing the need for additional equipment.
Lessons Learned
Several key takeaways from past implementations highlight the importance of thorough planning and continuous improvement:
- Pre-Operation Planning: Detailed space evaluations and planning were essential to successfully integrating the cranes into confined environments. This included precise measurements and anticipating potential obstacles.
- Operator Training: Comprehensive training for crane operators was crucial in ensuring safe and efficient use of the cranes in tight spaces. Ongoing education helped operators adapt to the specific challenges of confined environments.
- Regular Maintenance: Continuous maintenance and inspection practices were necessary to address wear and prevent mechanical failures. Implementing a routine maintenance schedule helped in identifying issues before they led to significant problems.
- Safety Protocols: Adhering to established safety protocols, including effective communication and emergency preparedness, played a key role in preventing accidents and ensuring smooth operations. Lessons from past incidents emphasized the need for clear procedures and regular safety drills.
These experiences underscore the importance of careful planning, training, and maintenance in the successful operation of wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes in confined spaces.
Conclusion
In summary, ensuring safety when operating wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes in confined spaces involves adhering to several key protocols and best practices. Pre-operation safety checks are crucial for identifying potential issues before use, while proper training and certification are essential for equipping operators with the necessary skills and knowledge. Effective load handling procedures, including securing loads and calculating load limits, help maintain safe crane operations.
Best practices include thorough workspace evaluation to assess space constraints and hazards, maintaining clear communication and coordination among team members, and preparing for emergencies with well-developed response plans. Identifying and mitigating common hazards, such as limited clearance and electrical or mechanical issues, further enhances safety and operational efficiency.
Ensuring safety in confined spaces requires a proactive approach and a commitment to following established safety standards. Regular maintenance, operator training, and adherence to safety protocols are integral to mitigating risks and maintaining a safe working environment. By addressing potential hazards and implementing effective safety measures, operators can navigate the challenges of confined spaces with confidence and efficiency.
It is essential for all personnel involved in operating wall-mounted cantilever jib cranes in confined spaces to strictly adhere to safety standards and regulations. Continuous education and professional guidance play a critical role in staying up-to-date with best practices and advancements in safety protocols. Seek out expert advice and training to ensure compliance with safety requirements and to enhance the overall safety and effectiveness of crane operations.
Related Products

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch