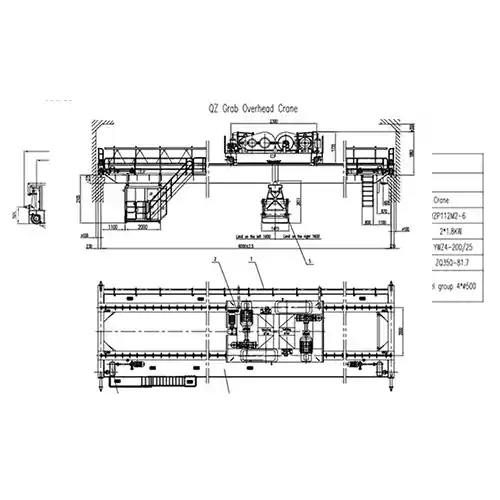
Electric Overhead Cranes for Sale, All Types of Electric Cranes
All types of electric motorized travelling cranes for sale, electric overhead cranes, electric gantry cranes & electric jib cranes for sale, good price.
Category: Overhead Crane for Your Use
Your Trusted Electric Overhead Bridge Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Types of Electric Cranes & Electric Motorized Cranes for Sale
Electric Overhead Cranes, Electric Gantry Cranes & Electric Jib Cranes for Sale Good Price
Electric cranes are material handling machines used to lift, move, and position heavy loads in various industrial settings. They are powered by electricity, either from the grid or onboard batteries, eliminating the need for traditional fuel sources like diesel or gasolin The primary components of an electric crane include the main structure (bridge, boom, or jib), electric motors, lifting mechanisms (hoists or winches), and controls.
Electric Overhead Crane:
Description and Working Principle:
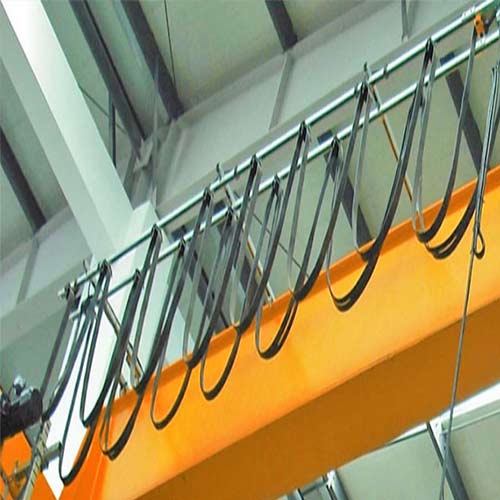
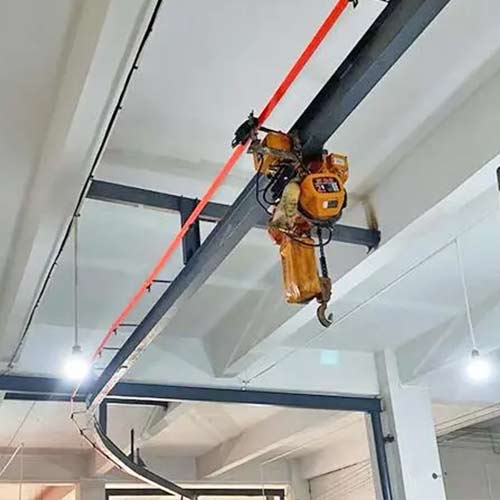
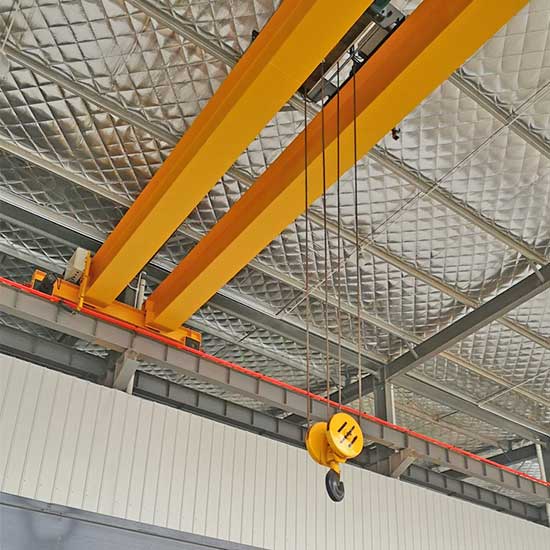
Electric Overhead Cranes, also known as electric overhead traveling cranes (EOT cranes), are prominent industrial lifting machines. These cranes operate by moving horizontally along tracks installed on an overhead structure, typically composed of beams or girders. The electric overhead crane configuration includes a bridge, end trucks, and a trolley. The bridge spans the width of the working area and moves along the elevated runway tracks. The trolley, equipped with a hoist, travels horizontally along the bridge, facilitating efficient material handling.
Electric overhead cranes come in various designs, such as single girder, double girder, and underslung configurations. Single girder electric overhead cranes feature one primary girder, while double girder electric overhead cranes boast two parallel girders. Underslung electric overhead cranes have the main girder mounted below the overhead structur
Components and Structure:
- Bridge: The bridge, also referred to as the crane girder, forms the horizontal beam supporting the trolley and facilitates movement along the overhead runway tracks.
- End Trucks: Positioned at either end of the bridge, the end trucks house the wheels responsible for smooth travel along the runway rails.
- Trolley: The trolley, integral to the electric overhead crane, carries the hoist and the load, enabling horizontal movement along the bridge using wheels or rollers.
- Hoist: A crucial lifting mechanism, the hoist is often an electric wire rope or chain hoist, attached to the trolley. It performs the task of lifting and lowering heavy loads.
Applications and Industries:
Electric overhead cranes serve diverse industries due to their exceptional versatility and capability to handle substantial loads. These cranes find applications in various sectors, including:
- Steel Plants: Electric overhead cranes are indispensable for handling heavy steel coils, ingots, and other materials in steel manufacturing facilities.
- Warehouses: They efficiently move and store heavy goods within warehouses and distribution centers.
- Construction Sites: Electric overhead cranes aid in the safe lifting and transportation of construction materials and equipment on construction sites.
- Automotive Industry: They play a vital role in the assembly and movement of automobile parts during the manufacturing process.
- Manufacturing: Electric overhead cranes are integral to multiple manufacturing processes, including machine shops and assembly lines.
- Ports and Shipping: Large electric overhead cranes are employed at ports for loading and unloading containers from ships.
- Foundries: Electric overhead cranes are essential for handling molten metal and heavy casting molds in foundries.
Electric overhead cranes are highly esteemed for their exceptional load-bearing capacity, precise movements, and ability to cover vast areas, making them indispensable for efficient material handling across diverse industrial settings.
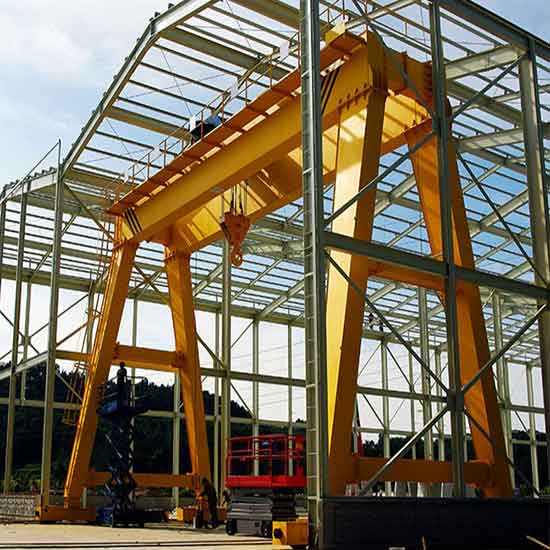
Electric Gantry Crane:
Overview and Design:
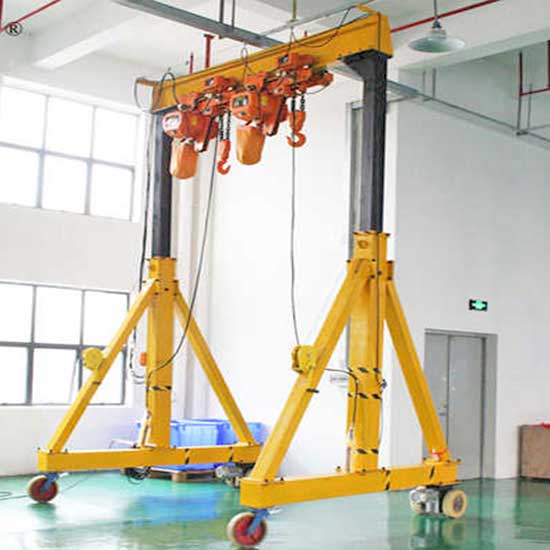
Electric Gantry Cranes are versatile lifting machines designed to move materials and heavy loads both indoors and outdoors. They are equipped with legs or supporting structures that straddle the load, allowing for flexibility in positioning and lifting. Gantry cranes can be electrically powered, eliminating the need for conventional fuel sources and reducing emissions.
Types (Rubber-tired, Rail-mounted) and Applications:
Rubber-tired Gantry Crane (RTG Crane):
- Overview: RTG cranes are equipped with rubber tires, enabling them to move efficiently on solid ground without the need for rails. They are commonly used in container terminals, intermodal yards, and storage areas.
- Applications: RTG cranes are ideal for handling containers, loading and unloading trucks, and arranging containers in stacks.
Rail-mounted Gantry Crane (RMG Crane):
- Overview: RMG cranes run on rails, providing more stability and precision during movement. They are widely used in container yards and rail terminals.
- Applications: RMG cranes are suitable for high-density container storage, precise positioning of containers, and handling intermodal cargo.
Types of Portable Electric Gantry Cranes and Applications:
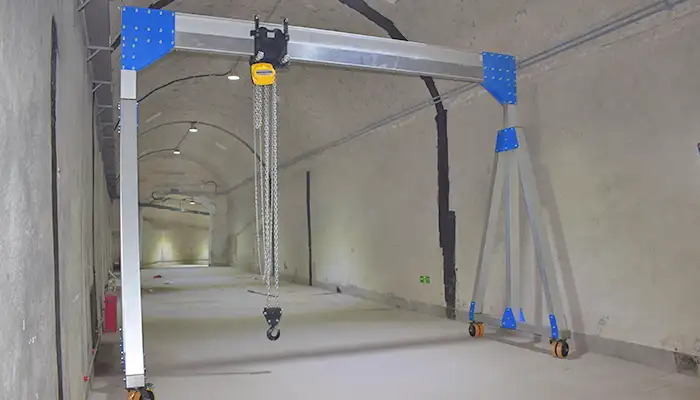
Adjustable Height Portable Gantry Crane:
- Overview: This type of portable gantry crane is designed with adjustable height, allowing it to be easily adapted to different lifting tasks and spaces.
- Applications: Adjustable height portable gantry cranes are commonly used in workshops, maintenance, and small-scale material handling.
Aluminum Portable Gantry Crane:
- Overview: These gantry cranes are made of lightweight aluminum, making them easy to move and position. They are suitable for lighter lifting requirements.
- Applications: Aluminum portable gantry cranes are used in workshops, laboratories, and applications where a lightweight, mobile lifting solution is neede
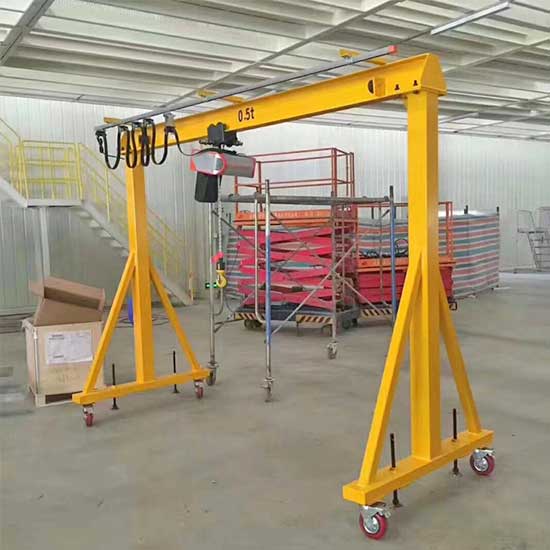
A-frame Portable Gantry Crane:
- Overview: The A-frame design provides stability and strength, making it suitable for heavy lifting tasks.
- Applications: A-frame portable gantry cranes are commonly used in construction sites, warehouses, and areas where there is a need for occasional heavy lifting.
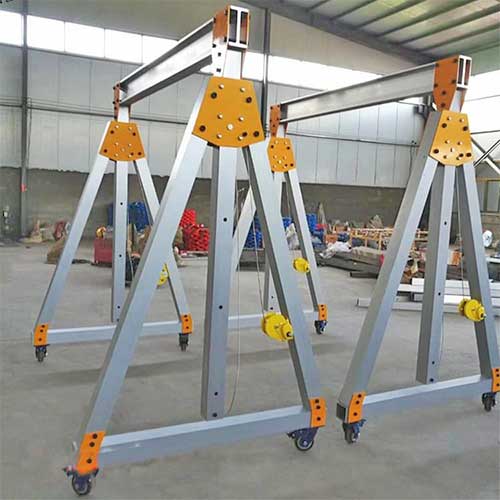
Adjustable Span Portable Gantry Crane:
- Overview: This type of portable gantry crane has an adjustable span, allowing it to accommodate various load widths.
- Applications: Adjustable span portable gantry cranes are used in applications where the distance between the legs needs to be adjusted to handle different-sized loads.
Electric gantry cranes, with their diverse configurations and applications, offer efficient and cost-effective solutions for lifting and material handling requirements in a variety of industries. Their electric power source, combined with different designs and types, makes them suitable for both indoor and outdoor lifting operations.
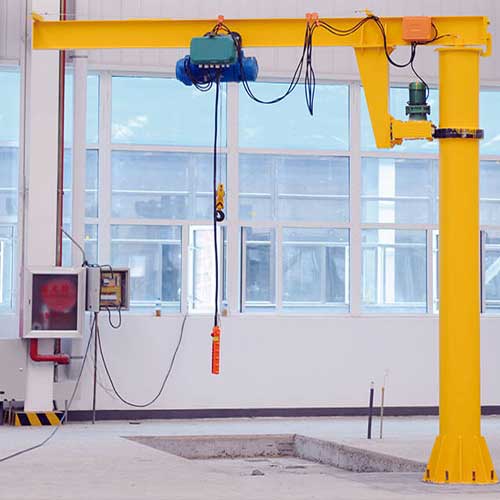
Electric Jib Crane:
Structure and Components:
Electric Jib Cranes are specialized lifting devices with a horizontal jib or boom that extends from a vertical support. They are designed to rotate and pivot, allowing for easy material handling within a limited are The key components of an electric jib crane include:
- Jib or Boom: The jib is the horizontal arm of the crane that extends from the vertical support. It provides the reach for lifting and moving loads.
- Vertical Support: The vertical support structure is the central column or post that holds the jib crane in place and provides stability during operation.
- Hoist: The hoist is the lifting mechanism, typically an electric chain hoist or wire rope hoist, mounted on the ji It handles the lifting and lowering of loads.
- Rotation Mechanism: Electric jib cranes have a rotating mechanism that enables the jib to rotate, allowing for easy positioning of loads.
- Control System: The control system includes buttons or levers that the operator uses to control the hoist's movements and rotation.
Types (Wall-mounted, Floor-mounted, Articulating):

Wall-mounted Electric Jib Crane

Floor-mounted Electric Jib Crane

Articulating Electric Jib Crane
Wall-mounted Jib Crane:
- Overview: Wall-mounted jib cranes are attached to a wall or support structure, saving valuable floor space and providing a wide range of motion.
- Applications: They are commonly used in workstations, assembly lines, and areas with limited floor spac
Floor-mounted Jib Crane:
- Overview: Floor-mounted jib cranes are installed directly on the floor, offering stability and flexibility in positioning.
- Applications: Floor-mounted jib cranes are suitable for applications where wall mounting is not feasible, such as outdoor areas or in open spaces within manufacturing facilities.
Articulating Jib Crane (also known as Articulated Jib Crane):
- Overview: Articulating jib cranes have an additional joint or elbow in their boom, providing enhanced maneuverability and reach.
- Applications: They are commonly used in tight spaces, assembly lines, and maintenance tasks where precise positioning is require
Usages in Manufacturing and Maintenance:
Electric jib cranes serve a variety of purposes in manufacturing and maintenance settings:
- Manufacturing: They are employed in assembly lines to lift and move components during the production process, increasing efficiency and reducing manual handling.
- Maintenance: Electric jib cranes are used for equipment maintenance, allowing technicians to lift and position heavy machinery for repairs or inspections.
- Material Handling: They aid in the efficient movement of raw materials, workpieces, and finished products within manufacturing facilities.
- Welding and Fabrication: Electric jib cranes assist in positioning workpieces for welding and fabrication processes, enhancing precision and worker safety.
Electric jib cranes offer a compact and versatile lifting solution for various industries, enabling efficient material handling and improved workflow in manufacturing and maintenance applications.
Key Features of Electric Cranes
Electric Power Source:
The power supply requirements for an electric crane can vary depending on the type, size, and specific features of the cran Generally, electric cranes require a stable and reliable power source to ensure safe and efficient operation. Here are some key considerations regarding power supply requirements:
- Electrical Voltage and Frequency: Most electric cranes are designed to operate on standard electrical voltages and frequencies used in the region where they are installe Common voltages include 230V, 400V, 460V, or 690V, and the frequency is typically either 50 Hz or 60 Hz. The specific voltage and frequency requirement will be indicated on the crane's nameplate or user manual.
- Power Capacity: The power capacity of the crane's electric motors and other electrical components must match the rated capacity of the cran The power capacity should be sufficient to handle the maximum load that the crane is designed to lift.
- Three-Phase Power: Electric cranes usually require a three-phase power supply, as they often use three-phase electric motors for their main lifting and traveling functions. Three-phase power is more efficient and allows for smoother operation compared to single-phase power.
- Power Quality: The power supply should meet certain quality standards to ensure the crane's safe and reliable operation. This includes consistent voltage levels, low harmonic distortion, and minimal voltage fluctuations.
- Power Source Stability: Electric cranes require a stable power supply system to prevent issues such as voltage drops, which can lead to motor malfunctions and potential accidents. Voltage fluctuations can also cause damage to electrical components.
- Power Cable and Connections: Adequate power cables and connections must be provided to deliver electricity from the power source to the crane's electrical system. These cables should be appropriately sized to handle the current and voltage requirements.
- Emergency Power Supply: In some critical applications, such as emergency response scenarios or specific industrial processes, electric cranes might require a backup power supply like an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or an emergency generator to ensure operation during power outages.
It is essential to consult the crane's manufacturer or a qualified electrical engineer to determine the specific power supply requirements for a particular electric crane model. Compliance with these requirements will not only ensure the safe operation of the crane but also optimize its performance and prolong its lifespan. Additionally, local electrical codes and regulations should be adhered to during installation and operation to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Advantages of Electric Crane: Electricity vs. Conventional Fuel:Electric cranes are powered by electricity, whereas conventional cranes often rely on conventional fuel sources like diesel or gasolin The use of electricity as the primary power source offers several advantages over traditional fuel-powered cranes:
- Reduced Emissions: Electric cranes produce lower emissions compared to their conventional counterparts. This reduction in emissions contributes to improved air quality and helps combat environmental pollution.
- Noise Reduction: Electric cranes operate more quietly than conventional cranes running on combustion engines. This reduction in noise pollution is especially beneficial in urban areas and noise-sensitive environments.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric cranes are generally more energy-efficient than conventional cranes. They convert electrical energy into mechanical work with higher efficiency, resulting in less energy wastage and lower operating costs.
- Sustainable Energy Sources: By using electricity as their power source, electric cranes can be powered by various sustainable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydroelectric power. This aligns with the global shift toward renewable energy and sustainable practices.
Environmental Benefits:
Electric cranes offer several significant environmental benefits:
- Lower Carbon Footprint: As electric cranes produce fewer emissions, they contribute to a lower carbon footprint, helping to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many countries and regions have strict regulations regarding emissions and environmental impact. Electric cranes help companies comply with these regulations and reduce potential fines or penalties.
- Eco-Friendly Operations: Electric cranes promote eco-friendly operations, making them an attractive choice for environmentally conscious industries and companies aiming to be more sustainabl
- Noise Pollution Reduction: The quieter operation of electric cranes helps minimize noise pollution in surrounding areas, contributing to a better quality of life for nearby residents and workers.
By harnessing the benefits of electricity as a clean and sustainable power source, electric cranes play a vital role in advancing eco-friendly and efficient lifting solutions for various industries, making them a preferred choice in modern material handling operations.
Industrial power supply of electric crane in different countries
The industrial power supply for electric cranes varies from country to country due to differences in electrical standards, voltage, and frequency. Here are some common industrial power supply configurations for electric cranes in different regions:

4 Types of Crane Power Supply Lines for Overhead Cranes
- Joint-free tight wire (6mm²-35mm²)- solid copper conductors
- Single conductor slide wire (200-2000 amps) - aluminum alloy conductors
- Festoon cable system (C type steel track)
- Tri-Bar/Four-Bar slide wire- solid copper conductor (10mm²-70mm²)
North America:
- United States and Canada: 480V, 3-phase, 60 Hz
Europe:
- European Union: 400V, 3-phase, 50 Hz
- United Kingdom: 400V, 3-phase, 50 Hz
Asia:
- China: 380V or 400V, 3-phase, 50 Hz
- Japan: 200V, 3-phase, 50 Hz or 60 Hz (dual frequency)
- India: 415V, 3-phase, 50 Hz
Australia and New Zealand:
- Australia: 415V, 3-phase, 50 Hz
- New Zealand: 400V, 3-phase, 50 Hz
South America:
- Brazil: 380V or 440V, 3-phase, 60 Hz
Africa:
- South Africa: 380V, 3-phase, 50 Hz
Drive Systems and Controls of Electric Cranes and Electric Overhead Cranes:
Electric Motor Technology:
Electric cranes are equipped with advanced electric motor technology, which plays a crucial role in their efficient operation and precise control. Key aspects of electric motor technology in electric cranes include:
- AC (Alternating Current) Motors: AC motors are commonly used in electric cranes due to their high efficiency, reliability, and ease of control. They allow smooth and continuous motion, making them ideal for various crane applications.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): VFDs are electronic devices used to control the speed of AC motors by varying the frequency of the supplied power. VFDs enable stepless speed control, allowing the crane to operate at different speeds based on the load requirements.
- Hoisting Motors: Electric cranes utilize specialized hoisting motors, such as electric wire rope hoists or chain hoists, to lift and lower heavy loads. These motors are designed for high torque and precise positioning.
- Traveling Motors: Traveling motors are responsible for moving the crane along the runway or tracks. They offer smooth acceleration, deceleration, and travel speed control.
Variable Speed Control:
Variable speed control is a critical feature in electric cranes, offering several advantages in terms of efficiency, safety, and load handling capabilities:
- Precise Positioning: Variable speed control allows for precise positioning of loads, especially when operating in confined spaces or near obstacles.
- Smooth Operation: The ability to control the crane's speed smoothly ensures gentle starts and stops, reducing stress on the crane's structure and components.
- Energy Efficiency: Variable speed control helps optimize energy usage by adjusting the crane's speed to match the load requirements. It reduces unnecessary energy consumption and operating costs.
- Load Sway Reduction: Electric cranes equipped with variable speed control can minimize load sway during lifting and positioning, enhancing safety and operator comfort.
Remote Control and Automation:
Modern electric cranes often come equipped with remote control systems and automation features, offering numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Safety: Remote control allows operators to control the crane from a safe distance, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring better visibility of the lifting operation.
- Increased Productivity: Automation features enable pre-programmed crane movements, optimizing lifting sequences and reducing the time required to complete tasks.
- Precision and Consistency: Automation ensures consistent and repeatable crane movements, enhancing precision and reducing the likelihood of human errors.
- Real-time Monitoring: Remote control systems often provide real-time data on the crane's performance and health, allowing for proactive maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Integration with IoT (Internet of Things): Advanced electric cranes can be integrated with IoT platforms, enabling data-driven insights for predictive maintenance and process optimization.
The combination of advanced electric motor technology, variable speed control, and remote control and automation features makes electric cranes and electric overhead cranes highly efficient, safe, and adaptable solutions for modern material handling requirements.
Safety Features of Electric Motor Cranes:
Overload Protection:
Overload protection is a critical safety feature in electric motor cranes that prevents the crane from attempting to lift loads beyond its rated capacity. When the load exceeds the safe working load (SWL), the overload protection system automatically stops the lifting operation or alerts the operator, preventing potential accidents or damage to the cran This safety feature helps maintain the structural integrity of the crane and ensures safe lifting practices.
Limit Switches and Sensors:
Electric motor cranes are equipped with limit switches and sensors at various critical points to monitor and control the crane's movements. These safety devices help prevent the crane from overtravel or colliding with obstacles, improving overall safety during crane operation. Types of limit switches and sensors used in electric motor cranes include:
- Hoisting Limit Switch: Monitors the upper and lower limits of the lifting motion to prevent the hook or load from hitting the boom or the groun
- Travel Limit Switch: Ensures the crane stops at predetermined points along the runway or track, preventing it from traveling beyond safe zones.
- Slewing Limit Switch: Monitors the rotation of the jib or boom and prevents over-rotation, avoiding potential collisions or damag
- Anti-Collision Sensors: Installed on larger cranes working in proximity, these sensors detect other cranes or structures to prevent collisions.
Emergency Stop Mechanism:
An emergency stop (E-stop) mechanism is a crucial safety feature that allows the operator to halt all crane movements immediately in emergency situations. When activated, the E-stop disengages power to all motors, bringing the crane to a complete stop. It is typically a prominent red button or lever located on the crane's control panel or remote control unit. The emergency stop mechanism ensures swift and decisive action in case of any potential danger, protecting personnel, loads, and equipment.
Safety is paramount in crane operations, and these safety features in electric motor cranes contribute to accident prevention, protect personnel and assets, and promote safe lifting practices. Regular maintenance and proper training for crane operators further enhance the safe and efficient operation of electric motor cranes.
Lifting Mechanisms and Hoists of Electric Cranes
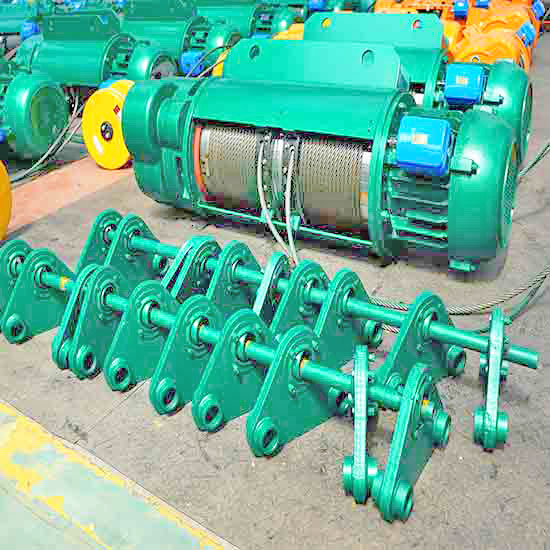

Wire rope hoists are commonly used lifting mechanisms in electric cranes. They consist of a spool or drum around which a steel wire rope is woun The wire rope is connected to a hook or other lifting attachment. When the hoist's motor is activated, it winds the wire rope onto the drum, lifting the loa Wire rope hoists are known for their strength, durability, and ability to handle heavy loads with eas They are widely used in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and material handling.
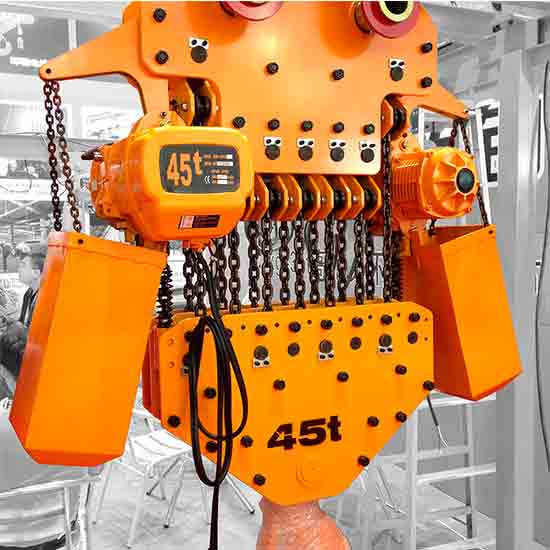
Electric chain hoists utilize a chain as their lifting mechanism. The chain is wound around a chain wheel, which is driven by an electric motor. Electric chain hoists are known for their compact design, precise lifting, and ease of installation. They are often preferred in applications where precise load positioning is critical, such as in assembly lines and workshop settings. Electric chain hoists come in various load capacities to suit different lifting requirements.

Electric crane winches are lifting mechanisms used in certain types of electric cranes, such as gantry cranes and overhead cranes. These winches consist of a motor-driven drum around which the wire rope is woun The motor's power allows the winch to raise and lower heavy loads with control and precision. Electric crane winches are commonly used in industries that require heavy lifting, like construction, shipyards, and material yards.
Hook, Magnet, and Grab Attachments:
Electric cranes are equipped with various lifting attachments to handle different types of loads. These attachments include:

Hook: The standard lifting attachment found on most electric cranes. It is used for lifting loads that can be securely hooked onto the crane's hoist.
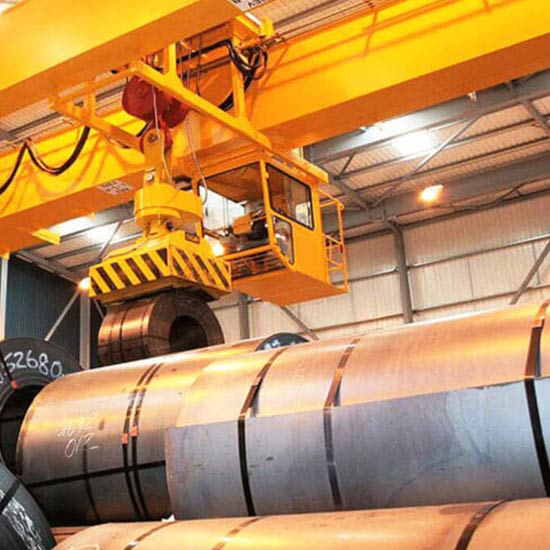

Magnet for electric mangetic crane : Magnetic lifting attachments are used to handle ferrous materials, such as steel plates or beams. They offer a convenient and efficient way to lift and transport magnetic materials without the need for slings or hooks.
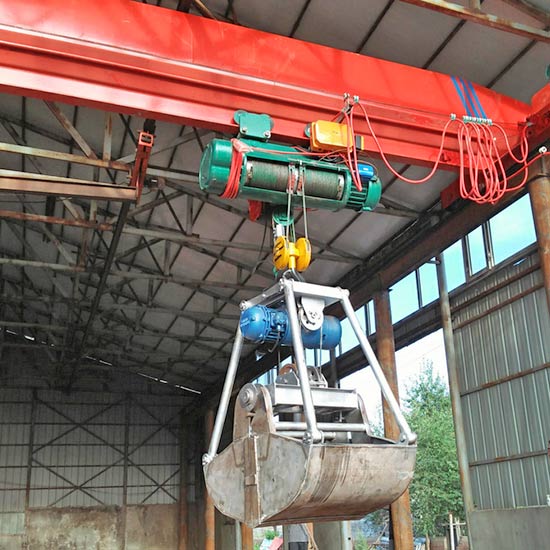

Grab for Electric Grab Overhead Crane: Grab attachments are used for bulk material handling, such as sand, gravel, or grain. They are designed to grasp and release the material, making them ideal for applications in mining, construction, and waste management.
The selection of the appropriate lifting mechanism and attachment depends on the specific requirements of the lifting task and the type of load to be handle These diverse lifting mechanisms and hoists enable electric cranes to efficiently lift, move, and position loads in various industries, contributing to enhanced productivity and safety in material handling operations.
Applications of Electric Cranes
Material Handling:
Industrial Warehouses:
Electric cranes play a vital role in industrial warehouses, facilitating the movement and storage of goods and materials. They are used to load and unload heavy pallets, containers, and other items from trucks and storage racks. Electric overhead cranes and electric gantry cranes are commonly employed in warehouses to optimize material handling processes, ensuring efficient storage and retrieval of goods.
Construction Sites:
Electric cranes are indispensable in construction sites for lifting and positioning heavy building materials, machinery, and equipment. They aid in the assembly of steel structures, concrete panels, and pre-fabricated elements. Tower cranes, mobile cranes, and rough-terrain cranes are common types of electric cranes used in construction, contributing to increased productivity and safety on the job sit
Manufacturing Plants:
Manufacturing plants utilize electric cranes to streamline production processes. Electric jib cranes are often used on assembly lines for precise material positioning and transfer. Electric overhead cranes are employed for heavy-duty tasks like moving large machinery and finished products within the production facility. The efficiency and versatility of electric cranes contribute to improved productivity and workflow in manufacturing operations.
Port Operations:
Container Handling:
Ports are major users of electric cranes, particularly rubber-tired gantry (RTG) cranes and rail-mounted gantry (RMG) cranes, for container handling. These cranes are responsible for loading and unloading containers from ships and stacking them in the container yar Electric cranes enable rapid and efficient container transfers, essential for smooth port operations.
Bulk Cargo Handling:
Electric cranes equipped with grab attachments are commonly used in ports to handle bulk cargoes, such as coal, ores, grains, and other loose materials. Grab cranes efficiently load and unload bulk cargo from ships, barges, or conveyor systems, ensuring an uninterrupted flow of goods in and out of the port.
Mining and Heavy Industries:
Mining Operations:
In mining, electric cranes are utilized for material handling in open-pit mines, underground mines, and mineral processing facilities. Electric overhead cranes and electric gantry cranes are used to transport heavy equipment, minerals, and overburden, contributing to increased operational efficiency and safety.
Steel Industry:
The steel industry relies heavily on electric cranes for various tasks, such as moving raw materials, handling molten metal in foundries, and transporting steel coils and finished products. Electric cranes are essential in steel manufacturing, ensuring smooth material flow and efficient production processes.
Electric cranes find diverse applications in numerous industries, providing efficient, safe, and reliable solutions for material handling and lifting tasks. Their versatility and adaptability make them indispensable for modern industrial operations, contributing to increased productivity and reduced manual labor.
Electric Cranes for Ports and Container Handling:
Shipyard Operations:
Electric cranes play a crucial role in shipyard operations, providing essential lifting capabilities to support shipbuilding, repair, and maintenance tasks. These cranes are designed to handle heavy loads and equipment required in shipyard operations. Key applications of electric cranes in shipyards include:
- Ship Assembly: Electric gantry cranes and overhead cranes are used to lift and position large sections of the ship during the assembly process. They facilitate precise alignment and fitting of ship components.
- Ship Launching: Specialized electric cranes are employed to support the launching process of newly constructed ships, carefully lowering the vessel into the water.
- Ship Repairs: Electric cranes assist in lifting and transporting heavy ship parts, such as engines and propellers, during repair and maintenance activities.
Loading and Unloading Containers:
Electric cranes, particularly rubber-tired gantry (RTG) cranes and rail-mounted gantry (RMG) cranes, are extensively used for container handling in ports. These cranes are specifically designed to efficiently load and unload containers from ships and stack them in the container yar Key functions of electric cranes in container handling include:
- Container Stacking: Electric cranes stack containers in orderly rows and columns within the container yard, optimizing storage space and facilitating easy retrieval when neede
- Intermodal Transfer: Electric cranes transfer containers between different modes of transportation, such as ships, trucks, and trains, enabling seamless intermodal logistics.
- Productivity and Throughput: Electric cranes significantly improve port productivity and throughput by reducing vessel turnaround times and enhancing the overall efficiency of container operations.
- Safety and Precision: Electric cranes offer precise control, ensuring safe and accurate container movements even in confined port areas.
- Automation and Integration: Advanced electric cranes can be integrated into port management systems, allowing for automation and real-time tracking of container movements, optimizing operational efficiency.
Electric cranes are indispensable for port and container handling operations, enabling ports to handle large volumes of cargo efficiently, supporting global trade, and contributing to the smooth flow of goods around the worl Their ability to handle heavy loads with precision and reliability makes them essential equipment in modern port infrastructur
Electric Cranes for the Automotive Industry:
Vehicle Assembly Lines:
Electric cranes are extensively used in the automotive industry to facilitate the assembly of vehicles on production lines. These cranes play a vital role in handling heavy components and subassemblies during the vehicle manufacturing process. Key applications of electric cranes in vehicle assembly lines include:
- Engine Installation: Electric cranes lift and position engines onto the vehicle chassis, ensuring precise alignment and attachment during the assembly process.
- Body-in-White (BIW) Handling: Electric cranes assist in moving the vehicle's body shell through the various stages of assembly, including welding and joining operations.
- Door and Hood Installation: Cranes are used to lift and place doors, hoods, and other large body panels onto the vehicle, ensuring proper alignment and fit.
- Installation of Interior Components: Electric cranes help with the installation of interior components, such as seats, dashboard, and steering wheel, ensuring efficient and accurate assembly.
Parts Handling:
Electric cranes are essential for handling automotive parts in various stages of production and logistics. They offer precise and efficient material handling solutions for the automotive industry. Key applications of electric cranes in parts handling include:
- Warehousing: Electric overhead cranes are used in automotive parts warehouses to load and unload pallets, racks, and containers, ensuring timely delivery to assembly lines.
- Foundries and Forges: Electric cranes are used to handle raw materials, molds, and casting components in foundries and forging operations.
- Paint Shops: Cranes assist in moving vehicle bodies and parts through the paint shop, ensuring smooth and precise material flow during the painting process.
- Logistics and Distribution: Electric cranes are employed in logistics centers and distribution hubs to load and unload automotive parts from trucks and containers, facilitating efficient distribution to dealerships and assembly plants.
Electric cranes in the automotive industry contribute to improved productivity, enhanced safety, and streamlined manufacturing processes. Their ability to handle heavy loads and perform precise movements makes them indispensable equipment for automakers, ensuring the smooth and efficient production of vehicles and automotive components.
Electric Cranes for Foundries and Metallurgy:
Handling Molten Metal:
Electric cranes are essential in foundries and metallurgical plants for handling molten metal during various stages of metal production. Foundries deal with high-temperature molten metal, which requires specialized equipment capable of withstanding extreme heat. Key applications of electric cranes in handling molten metal include:
- Ladle Handling: Electric cranes equipped with ladle attachments are used to lift and transport ladles filled with molten metal from the furnace to the casting are They ensure safe and controlled pouring of molten metal into molds.
- Tundish Handling: In continuous casting processes, electric cranes handle tundishes (containers holding molten metal) to supply a continuous flow of molten metal into casting molds.
- Crucible Handling: Electric cranes are employed to handle crucibles containing molten metal during various melting and alloying processes.
- Scrap Charging: Electric cranes facilitate the loading of scrap metal into melting furnaces, ensuring efficient and controlled charging of materials.
Heavy Casting Applications:
Foundries and metallurgical plants often deal with heavy casting applications that require robust lifting equipment capable of handling substantial loads. Electric cranes are used for various heavy casting tasks, including:
- Mold Handling: Electric cranes lift and position heavy casting molds to receive molten metal during the casting process.
- Finished Product Handling: Cranes are used to lift and transport heavy castings to cooling areas, inspection stations, and subsequent processing stages.
- Ingot Handling: In metallurgical plants, electric cranes handle heavy ingots, which are large metal blocks produced by casting molten metal into molds.
- Anode and Cathode Handling: In the production of metals like aluminum, electric cranes assist in handling anodes and cathodes used in electrolytic processes.
Electric cranes in foundries and metallurgy are designed for extreme conditions, including high temperatures, heavy loads, and harsh environments. Their ability to operate reliably in these challenging settings is essential for ensuring the efficient and safe handling of molten metal and heavy casting operations. These cranes contribute significantly to the metal production process, improving productivity and maintaining a high level of safety for workers and equipment.
Electric Crane for Shipbuilding:
Lifting and Positioning Ship Components:
Electric cranes play a vital role in shipbuilding yards by lifting and positioning various ship components during the construction process. Shipbuilding involves handling heavy and oversized materials, and electric cranes are specifically designed to handle these challenging tasks. Key applications of electric cranes in shipbuilding include:
- Hull Assembly: Electric gantry cranes and overhead cranes are used to lift and position large sections of the ship's hull during the construction process. These cranes ensure precise alignment and welding of hull components.
- Installation of Superstructure: Electric cranes assist in lifting and placing the superstructure onto the ship's hull, including accommodation blocks, bridges, and navigation equipment.
- Engine and Propulsion System Installation: Cranes are used to lift and position ship engines, propellers, and other propulsion systems into their designated spaces.
- Equipment Installation: Electric cranes handle various shipboard equipment, including cargo handling machinery, winches, and communication systems, ensuring proper installation.
- Outfitting and Finishing: Electric cranes assist in outfitting the ship with furnishings, interior components, and finishing touches before its launch.
Electric cranes in shipbuilding contribute to the efficient assembly and construction of ships, ensuring precise positioning of components and enhancing the overall productivity of shipyards.
Electric Overhead Crane for Maintenance and Repair:
Machinery and Equipment Handling:
Electric overhead cranes are widely used in maintenance and repair facilities to handle machinery, equipment, and heavy components. These cranes offer flexibility and versatility in lifting and moving heavy loads, making them ideal for maintenance applications. Key applications of electric overhead cranes in maintenance and repair include:
- Equipment Maintenance: Electric overhead cranes are used to lift and transport machinery and equipment for inspection, repair, and servicing.
- Component Replacement: Cranes assist in removing and replacing heavy components, such as engines, motors, and gearboxes, during maintenance procedures.
- Conveyor Systems Maintenance: Electric overhead cranes facilitate maintenance work on conveyor systems by lifting conveyor belts, rollers, and other components.
- Plant Shutdown and Turnaround: During planned plant shutdowns or turnarounds, electric overhead cranes help with dismantling and reassembling equipment for maintenance purposes.
- Spare Parts Handling: Cranes assist in loading and unloading spare parts and supplies in maintenance workshops and storage areas.
Electric overhead cranes provide a safe and efficient means of handling heavy machinery and equipment during maintenance and repair operations, minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth plant maintenance processes.
Electric Overhead Crane for Maintenance and Operational Considerations:
Regular Inspections and Checks:
To ensure the safe and efficient operation of electric overhead cranes, regular inspections and checks are essential. These inspections help identify potential issues and prevent accidents. Key considerations for regular inspections and checks include:
- Daily Pre-Operational Checks: Before each shift, the crane operator should perform a pre-operational check, examining critical components like brakes, hoist ropes, hooks, and limit switches.
- Periodic Inspections: Conduct regular and thorough inspections at specified intervals, as recommended by the manufacturer and relevant safety standards. These inspections may involve examining the electrical system, mechanical components, and structural integrity.
- Load Testing: Periodically conduct load testing to verify the crane's lifting capacity and ensure it meets safety standards and load rating requirements.
Lubrication and Maintenance of Components:
Proper lubrication and maintenance of crane components are crucial for their longevity and reliable performanc Key considerations for lubrication and maintenance include:
- Lubrication Schedule: Follow a regular lubrication schedule for critical components such as bearings, gears, and wire ropes. Proper lubrication minimizes wear and reduces friction, extending the life of moving parts.
- Inspection of Wire Ropes: Regularly inspect wire ropes for signs of wear, corrosion, or damag Replace worn or damaged ropes promptly to avoid accidents.
- Brakes and Motors: Ensure that brakes and motors are functioning correctly and adjust them if necessary. Faulty brakes can lead to unsafe conditions during operation.
- Electrical System: Regularly inspect the electrical system, including cables, connections, and controls, to identify and rectify any issues affecting the crane's performanc
Operator Training and Safety Guidelines:
Operator training and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for the safe operation of electric overhead cranes. Key considerations for operator training and safety guidelines include:
- Certified Operators: Ensure that only certified and trained operators operate the electric overhead cran Proper training includes understanding the crane's controls, load limits, and safety procedures.
- Safety Procedures: Provide clear and comprehensive safety guidelines to crane operators. These guidelines should cover safe load handling, emergency procedures, and the proper use of safety devices like limit switches and emergency stop mechanisms.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators and workers in the vicinity of the crane should wear appropriate PPE, such as hard hats, safety glasses, and high-visibility vests, to minimize the risk of injuries.
- Load Capacity Awareness: Ensure that operators are aware of the crane's load capacity and never exceed the specified limits to prevent overloading accidents.
Proper maintenance, regular inspections, and comprehensive operator training are essential for maintaining the safety and operational efficiency of electric overhead cranes. Following these considerations helps prevent accidents, reduce downtime, and prolong the service life of the cran
Future Trends in Electric Crane Technology:
Advancements in Electric Motor Technology:
As technology continues to evolve, advancements in electric motor technology will have a significant impact on electric cranes' performance and capabilities. Some future trends in electric motor technology for cranes include:
- High-Efficiency Motors: Development of more efficient electric motors with improved power-to-weight ratios and reduced energy losses will enhance the overall energy efficiency of electric cranes.
- Direct Drive Motors: Direct drive motors eliminate the need for complex transmission systems, reducing maintenance requirements and improving crane reliability and performanc
- Permanent Magnet Motors: Permanent magnet motors offer higher power density and improved performance, leading to increased lifting capacities and better control of loads.
- Regenerative Braking: Implementation of regenerative braking systems will enable electric cranes to recover and reuse energy during braking, further improving energy efficiency.
Increasing Energy Efficiency:
Energy efficiency will remain a critical focus in the future of electric crane technology. Several trends will contribute to improved energy efficiency:
- Hybrid Power Systems: Integration of hybrid power systems, combining electric and alternative power sources (g., battery, solar, or hydrogen), will reduce reliance on grid electricity and promote sustainable energy usag
- Smart Power Management: Advanced power management systems will optimize crane power consumption based on load requirements and operational conditions, further reducing energy wastag
- Energy Storage Solutions: Advancements in energy storage technologies, such as high-capacity batteries, will enable efficient energy storage and on-demand power supply for electric cranes.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Adoption of eco-friendly materials in crane construction will contribute to reduced weight and energy consumption, making cranes more energy-efficient.
These future trends in electric crane technology will shape the crane industry, leading to safer, more efficient, and sustainable material handling solutions, meeting the evolving demands of various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an electric crane, and how does it work?
An electric crane is a type of material handling equipment powered by electricity. It uses electric motors to lift, lower, and move heavy loads. Electric cranes typically consist of a hoist, trolley, and bridge, with the bridge moving along rails or beams to cover a specific are When activated, the electric motor drives the hoist and trolley, allowing the crane to perform lifting and positioning tasks.
What are the main types of electric cranes and their differences?
The main types of electric cranes include Electric Overhead Traveling Cranes (EOT Cranes), Electric Gantry Cranes, and Electric Jib Cranes. EOT cranes are mounted on overhead runways and are suitable for heavy-duty applications. Gantry cranes have legs that straddle the workspace and are used in outdoor environments or areas with limited headroom. Jib cranes have a rotating arm and are ideal for precise material handling in confined spaces.
How is the power supply for electric cranes determined in different countries?
The power supply for electric cranes is determined based on the electrical standards and regulations of each country. In most cases, electric cranes can be designed to operate on the standard electrical supply available in that country, which is usually AC power at various voltage and frequency levels.
What are the key features and components of an electric crane?
Key features of electric cranes include precise control, safety measures, and energy efficiency. The main components of an electric crane are the hoist, trolley, bridge, electric motor, wire ropes or chains, control panel, and safety devices like limit switches and emergency stop mechanisms.
How do you control an electric crane? Is remote control available?
Electric cranes can be controlled through a control panel located on the crane or through remote control units. The operator uses buttons or levers to control the movement of the crane, including lifting, lowering, and traversing. Remote control allows operators to control the crane from a distance, providing flexibility and improved visibility during operation.
What are the safety measures in place to prevent accidents with electric cranes?
Electric cranes have several safety features, including overload protection, limit switches to prevent overtravel, emergency stop mechanisms, and anti-collision devices. Operators are also required to undergo proper training and follow safety guidelines to minimize the risk of accidents.
How much weight can an electric crane lift?
The lifting capacity of an electric crane varies depending on the crane's design, configuration, and siz Electric cranes can lift loads ranging from a few hundred kilograms to several hundred tons.
What are the typical applications of electric cranes in various industries?
Electric cranes are used in a wide range of industries, including construction, manufacturing, warehouses, ports, mining, and automotiv They are employed for material handling, assembly, loading and unloading, and other heavy lifting tasks.
How do I select the right electric crane for my specific needs?
Selecting the right electric crane depends on factors such as the required lifting capacity, the working environment, the available space, and the specific application. It's essential to consult with a qualified crane supplier or engineer to determine the most suitable crane for your needs.
How often should an electric crane be inspected and maintained?
Electric cranes should undergo regular inspections and maintenance as per the manufacturer's recommendations and relevant safety standards. Daily pre-operational checks, periodic inspections, and scheduled maintenance are essential to ensure safe and reliable crane operation.
Can electric cranes be used in hazardous environments, such as explosive atmospheres?
Electric cranes can be designed to meet specific hazardous environment requirements, such as those found in explosive atmospheres or flammable environments. Explosion-proof or spark-resistant features can be incorporated to make the crane safe for such applications.
What are the maintenance requirements and costs associated with electric cranes?
The maintenance requirements and costs for electric cranes depend on the crane's type, usage, and working conditions. Regular maintenance and proper lubrication of components are essential to ensure the crane's longevity and reliable operation.
Are there any energy-efficient features or technologies used in electric cranes?
Yes, electric cranes can incorporate energy-efficient features such as regenerative braking, direct drive motors, and smart power management systems to optimize energy usage and reduce operating costs.
Can electric cranes be used in outdoor environments, exposed to weather conditions?
Yes, electric cranes can be designed for outdoor us Outdoor electric cranes may have additional protective features to withstand weather conditions, such as weather-resistant enclosures and corrosion-resistant materials.
What are the limitations of electric cranes compared to other types of cranes?
Electric cranes may have limitations regarding their power supply, lifting capacity, and operating environment compared to other types of cranes, such as hydraulic or diesel-powered cranes. However, advancements in technology continue to bridge these gaps.
Can an existing crane be converted to an electric crane?
Converting an existing crane to an electric crane is possible in some cases, depending on the crane's design and condition. However, it requires careful engineering and evaluation by qualified professionals
All in all,
Electric cranes offer numerous advantages over conventional cranes, making them indispensable in modern material handling operations. Key advantages include:
- Environmental Friendliness: Electric cranes produce zero emissions at the point of use, contributing to a cleaner and greener environment compared to cranes powered by conventional fuels.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric cranes are highly energy-efficient, thanks to advancements in electric motor technology, regenerative braking, and smart power management systems.
- Precise Control: Electric cranes provide smooth and precise control over load movements, ensuring safe and accurate material handling.
- Safety Features: Electric cranes are equipped with advanced safety features like overload protection, limit switches, and emergency stop mechanisms, enhancing operational safety.
- Low Operating Costs: With fewer moving parts and reduced maintenance requirements, electric cranes offer cost-effective long-term operation and ownership.
Growing Importance in Modern Industries:
Electric cranes are becoming increasingly important in modern industries due to their versatility and efficiency. From construction and manufacturing to ports and logistics, electric cranes play a crucial role in streamlining operations and meeting the growing demands of global trade and production. Their ability to handle heavy loads, adapt to various applications, and incorporate automation and IoT technologies positions them as essential tools in the material handling landscap
Prospects for Further Development and Implementation:
The future of electric crane technology holds great promise, with ongoing advancements in electric motor technology, integration of IoT and automation, and increasing energy efficiency. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, electric cranes will become even more prevalent, contributing to reduced carbon footprints and improved operational efficiency. The development of autonomous and remotely controlled cranes, along with the incorporation of alternative power sources, will further revolutionize material handling operations.
In conclusion, electric cranes have emerged as innovative and eco-friendly solutions for modern material handling challenges. With their myriad advantages, growing importance in various industries, and prospects for further development and implementation, electric cranes will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of industrial operations, driving efficiency, safety, and sustainability forwar
Main Projects
Related Products
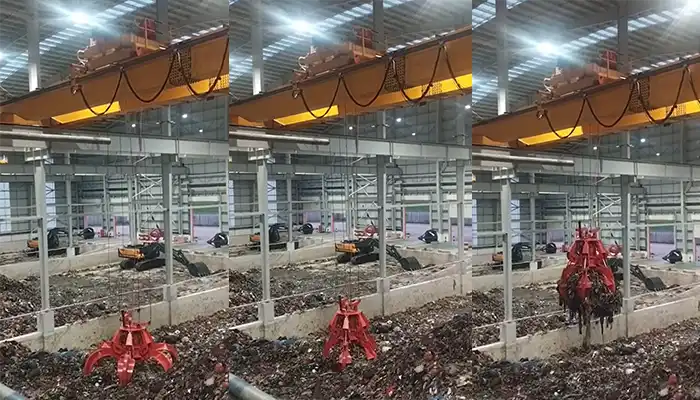

Supplied three grab bucket crane kits to Indonesia, enhancing garbage handling efficiency with high load capacity and reliable performance.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch