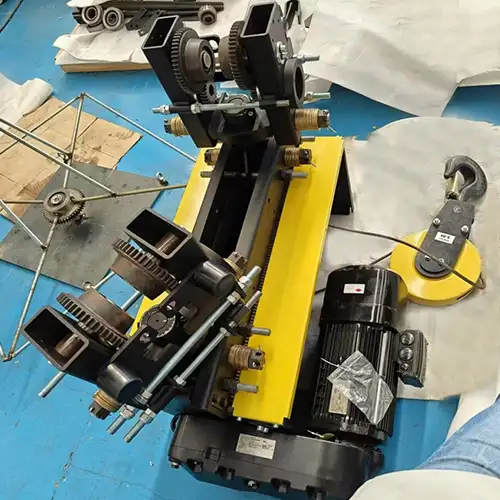
Electric Monorail Trolley Hoist: Monorail Chain &Wire Rope Hoists
Electric monorail trolley hoists for sale, available in monorail chain hoist & monorail wire rope hoist designs for industrial various applications.
Category: Overhead Hoist
Your Trusted Monorail Hoist and Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Electric Monorail Trolley Hoists: Monorail Chain Hoist & Monorail Wire Rope Hoist Options
Electric monorail trolley hoists for sale, available in monorail chain hoist & monorail wire rope hoist designs for industrial various applications.
Overview of Electric Monorail Trolley Hoists
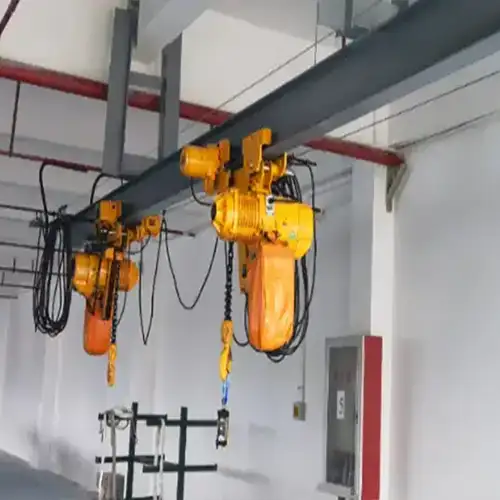
Electric monorail trolley hoists are specialized lifting devices designed to transport heavy loads along a single rail system. They consist of a trolley that moves on the rail, allowing for efficient horizontal movement alongside vertical lifting capabilities. The primary purpose of these hoists is to enhance material handling in various industrial environments, enabling workers to lift and transport items safely and quickly. Their design promotes flexibility in tight spaces, making them ideal for use in warehouses, manufacturing plants, and construction sites.
In the field of material handling, efficiency and safety are paramount. Electric monorail trolley hoists play a vital role in achieving these objectives. They streamline operations by facilitating smooth and controlled lifting and moving of heavy objects, which reduces the risk of worker injuries and minimizes damage to materials. Their adaptability makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from lifting automotive parts in factories to moving equipment in warehouses. Additionally, these hoists contribute to overall productivity by minimizing downtime and enhancing workflow, ultimately leading to increased operational efficiency.
This guide will explore the differences between monorail chain hoists and monorail wire rope hoists. Each type has unique features that make it suitable for specific applications. Monorail chain hoists are known for their lightweight design and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for lighter loads and less demanding environments. In contrast, monorail wire rope hoists are engineered for heavier lifting and are favored in construction and heavy industry due to their robustness and durability. Understanding these differences will empower you to make informed decisions based on your specific lifting requirements.
Hot Sale Capacities and Their Significance
The capacity of a hoist is one of the most critical factors to consider when selecting equipment for your operations. This guide will highlight the most popular capacities, including 1 ton, 2 ton, and 3 ton options, and discuss their relevance in various industrial contexts. Choosing the right capacity ensures that the hoist can safely handle the intended loads without compromising performance. Furthermore, understanding the significance of hot sale capacities will help you identify the best options for your needs, whether you're lifting lightweight materials or managing heavy-duty applications.
Basics of Electric Monorail Trolley Hoists
Components of Electric Monorail Trolley Hoists
Hoist Mechanism (Motor, Gearbox, et)
The hoist mechanism serves as the heart of an electric monorail trolley hoist, comprising several essential components:
- Motor: The motor powers the hoist by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is crucial to choose a motor with sufficient horsepower to match the lifting capacity required for your applications. The motor's efficiency and performance directly affect the hoist's overall functionality.
- Gearbox: The gearbox is responsible for reducing the motor's speed while increasing torque, which enables the hoist to lift heavy loads efficiently. Selecting the appropriate gear ratio is vital, as it impacts the desired lifting speed and the weight of the load. A well-matched gearbox ensures smooth operation and maximizes lifting performance.
- Brake System: A reliable braking system is essential for ensuring safety during hoisting operations. The brake system prevents the accidental lowering of loads and provides precise control during both lifting and lowering. Various braking technologies, such as electric, mechanical, or regenerative brakes, may be utilized based on the specific application requirements.
- Lifting Mechanism: This includes chains or wire ropes that attach to the load, facilitating the vertical lifting process. Selecting the right material for the lifting mechanism is critical for durability, load capacity, and operational efficiency. Regular inspections and maintenance of the lifting mechanism help ensure safe and effective operation.
Trolley Design (Fixed, Adjustable)
The trolley is the component that moves along the rail system, allowing the hoist to transport loads horizontally. There are two primary types of trolley designs:
- Fixed Trolley: This design is rigid and best suited for applications where the load needs to move along a predetermined path. It offers enhanced stability and is often used in environments with fixed layouts, such as assembly lines or dedicated workstations. Fixed trolleys are straightforward to install and maintain, making them a reliable choice for consistent operations.
- Adjustable Trolley: This design allows the hoist to be repositioned along the rail, making it ideal for applications that require flexibility. Adjustable trolleys are particularly beneficial in facilities with changing layouts or varying load sizes. They enhance versatility by enabling users to optimize the hoist's functionality based on operational needs, allowing for efficient material handling in dynamic environments.
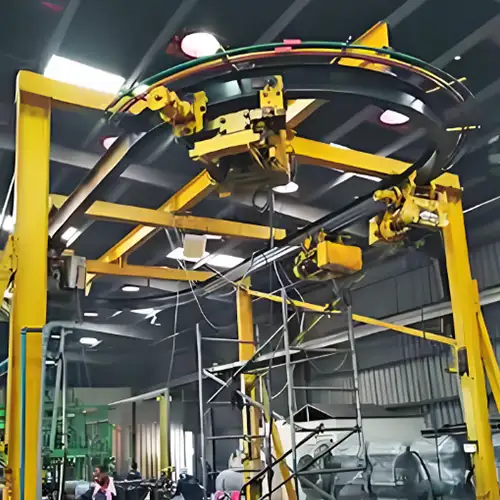
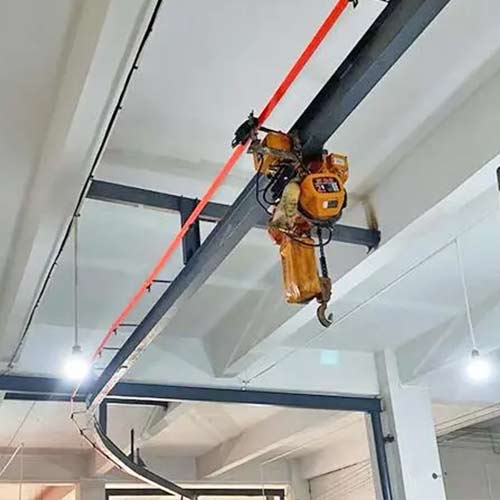
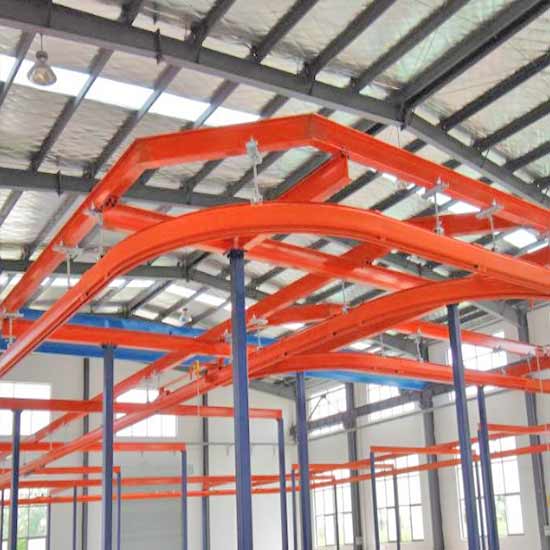
Rail System (Curved and Straight Options)
The rail system supports the trolley and hoist mechanism, facilitating the smooth movement of loads. There are two primary configurations:
- Straight Rails: Straight rails are straightforward and best suited for linear movement along a fixed path. They provide stability and are easier to install in warehouses and production facilities with long aisles. Straight rail systems can accommodate heavier loads, making them suitable for many industrial applications.
- Curved Rails: Curved rails allow for more complex movement paths and are beneficial in facilities where space is limited or where maneuvering around obstacles is necessary. Curved rails enhance operational efficiency by enabling the hoist to navigate tight corners and complex layouts. When designing the rail system, it is important to consider the specific movement patterns required in your facility to ensure optimal performance.
How Electric Monorail Trolley Hoists Work on Monorails ( Curved and Straight)
Electric monorail trolley hoists are designed to efficiently lift and move loads along a rail system, whether it be straight or curved. The functionality and effectiveness of these hoists depend on several factors, including the rail configuration, power source, and control mechanisms.
Special Design Considerations for Curved and Straight Rails
When operating on straight rails, the design of the monorail trolley hoist is relatively straightforward, focusing primarily on maximizing load capacity and ensuring smooth operation along the length of the rail. However, curved rails introduce specific challenges that require special design considerations:
- Trolley Design: For curved rail systems, the trolley must be equipped with special wheels or rollers that can navigate the curvature without losing stability. The design may include flexible couplings or pivoting mechanisms to accommodate changes in angle while maintaining load integrity.
- Rail Alignment: Proper alignment and installation of curved rails are critical. Any misalignment can cause increased wear on the trolley wheels and may affect the hoist's operational efficiency. It's essential to ensure that curves are engineered according to the hoist specifications to avoid any operational hazards.
- Safety Margins: Curved tracks can affect load stability, especially when traveling at speed. Manufacturers often recommend specific speed limits when operating on curved rails to prevent tipping or loss of control.
- Weight Distribution: The load must be balanced when traveling on curved rails. Unevenly distributed loads can shift and destabilize the hoist, potentially leading to accidents. Operators should be trained to ensure proper load placement.
Power Source and Operation
Electric monorail trolley hoists typically operate using standard electrical power, with the choice between AC or DC motors based on application requirements. Key elements of their operation include:
- Activation: When the hoist is activated, the motor powers a gearbox that drives the lifting mechanism—either a chain or a wire rope. The choice of lifting mechanism often depends on the specific load requirements and operational context.
- Control Mechanisms: Operators control the hoist through a pendant or remote control system, allowing for precise movements of the load. Safety features, including overload protection and limit switches, are integrated into the system to enhance safe operation.
Load Lifting and Control Mechanisms
The lifting process begins with the operator engaging the control mechanism, which activates the hoist motor. The lifting mechanism raises the load off the ground using various control options:
- Manual Control: Operators can manually control the lifting and movement of loads via pendant controls, ideal for straightforward applications that require precision in load positioning.
- Automated Control: Advanced applications may utilize automated controls, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs). These systems allow for pre-set lifting sequences and synchronization with other machinery, thereby enhancing overall productivity.
- Variable Speed Control: Many electric hoists come equipped with variable speed control options, enabling operators to adjust lifting and lowering speeds according to load size and operational requirements. This feature promotes safety and accuracy during load handling, particularly in complex environments.
Key Considerations for Operators
When operating electric monorail trolley hoists on both straight and curved rails, operators should keep the following points in mind:
- Training: Ensure that operators are adequately trained in the specifics of operating hoists on curved rails, particularly regarding speed limitations and load balancing.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections of the hoist and rail system to identify potential wear or misalignment. This proactive approach helps maintain safety and efficiency.
- Environmental Factors: Be aware of how environmental conditions (such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and potential exposure to chemicals) may impact hoist operation and maintenance needs.
Types of Monorail Trolley Hoists
Monorail Chain Hoists
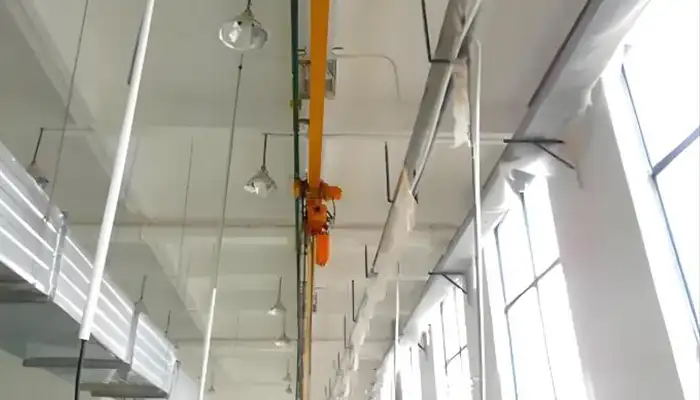

monorail chain hoist on straight rail

monorail chain hoist on curved rail

European style monorail chain hoist on straight rail
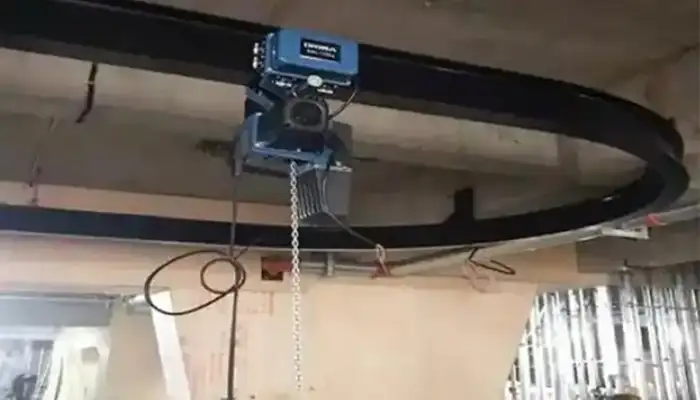

European style monorail chain hoist on curved rail
Design and Construction
Monorail chain hoists are engineered for both reliability and efficiency, featuring a robust design. The hoisting mechanism typically includes a high-strength steel chain, ensuring a secure grip on loads and resistance to wear and tear.
- Hoisting Chain: Made from grade 80 or higher steel, these chains provide enhanced durability.
- Housing: The hoist is encased in protective housing, typically constructed from high-quality materials like steel or aluminum, which offers resistance to environmental factors.
- Trolley System: Many monorail chain hoists come equipped with a trolley that can be either fixed or adjustable, allowing for smooth horizontal movement along the rail.
Key Features and Benefits
Monorail chain hoists offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in various industries.
- Lightweight and Cost-effective: These hoists are generally lighter than their wire rope counterparts, facilitating easier installation and mobility. Their cost-effective nature appeals to businesses operating on a budget.
- Ease of Maintenance: Chain hoists require less maintenance than other types, as the chain is straightforward to lubricate and replace. This simplicity translates into lower operational costs over time.
Typical Applications
Due to their versatility, monorail chain hoists find applications in various industries.
- Manufacturing: They are commonly employed for assembly line operations, moving components efficiently between workstations.
- Automotive Assembly: Ideal for lifting parts and assemblies in automotive production, they contribute to a more streamlined workflow.
- Maintenance: Frequently used in maintenance and repair operations, chain hoists provide the flexibility and maneuverability necessary for effective operations.
Case Studies Showcasing Successful Implementations
Several companies have successfully implemented monorail chain hoists, experiencing significant operational improvements.
- Automobile Manufacturing Plant: A leading automotive manufacturer replaced older equipment with monorail chain hoists, resulting in a 20% increase in productivity and reduced cycle times for vehicle assembly.
- Warehouse Operations: A distribution center adopted monorail chain hoists for loading and unloading heavy pallets, significantly improving overall efficiency due to the ease of maintenance and lower operating costs.
Monorail Wire Rope Hoists
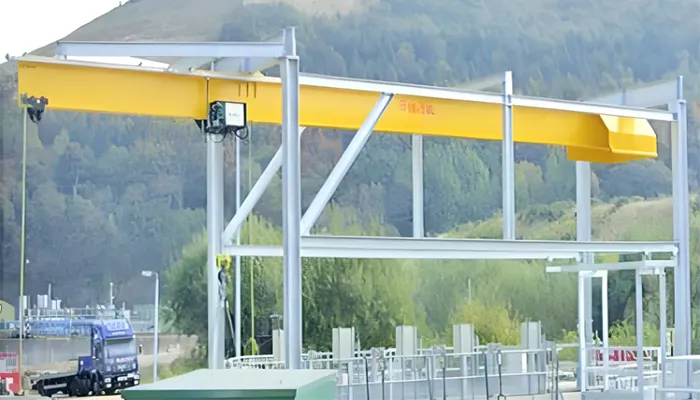

European style monorail wire rope hoist on straight rail

European style monorail wire rope hoist on curved rail

monorail wire rope hoist on straight rail

monorail wire rope hoist on curved rail
Design and Construction
Monorail wire rope hoists are designed for strength and efficiency, incorporating several key components.
- Wire Rope: Comprised of multiple strands of steel wire twisted together, wire ropes are engineered for high tensile strength and flexibility, making them suitable for handling heavy loads.
- Drum and Sheave System: These hoists utilize a drum to wind the wire rope and sheaves to guide the rope, allowing for smooth lifting and lowering operations.
- Heavy-Duty Housing: The housing is typically reinforced to withstand harsh conditions, making wire rope hoists well-suited for demanding environments.
Key Features and Benefits
Monorail wire rope hoists offer a range of features that make them ideal for various heavy-duty applications.
- High Strength and Durability: Capable of handling significantly heavier loads compared to chain hoists, wire rope hoists are built to last, with components designed to endure rigorous use.
- Better for Heavy Lifting and Outdoor Use: The robustness of wire rope hoists makes them suitable for outdoor applications, such as construction sites, where exposure to the elements is a concern.
Typical Applications
Monorail wire rope hoists are widely employed in industries that demand heavy lifting capabilities.
- Construction: These hoists are crucial for lifting heavy materials like steel beams and concrete blocks, facilitating quick and efficient operations on construction sites.
- Heavy Industries: Industries such as shipbuilding and machinery manufacturing rely on wire rope hoists to move heavy parts and equipment safely and efficiently.
Case Studies Highlighting Effective Usage
Several successful implementations of monorail wire rope hoists illustrate their effectiveness in various industries.
- Construction Project: A large construction firm utilized monorail wire rope hoists to lift steel girders during a skyscraper project. This implementation reduced the time required for each lift by 30%, leading to significant cost savings and improved safety records.
- Shipbuilding Yard: A shipyard replaced older lifting systems with wire rope hoists to manage heavy components during the ship assembly process. This upgrade resulted in a 25% increase in production efficiency due to faster turnaround times.
Hot Sale Capacities of Monorail Hoists
Overview of Common Capacities
1 ton, 2 ton, 3 ton Monorail Hoists
- 1 ton Monorail Hoists: These hoists are among the most popular choices for light to moderate lifting tasks. Commonly used in warehouses, small workshops, and assembly lines, they provide sufficient capacity for moving smaller loads efficiently.
- 2 ton Monorail Hoists: A step up in capacity, 2 ton hoists are ideal for slightly heavier applications, including light industrial tasks and medium-duty lifting in manufacturing. They are versatile and can handle a range of loads, from machinery components to materials in stock rooms.
- 3 ton Monorail Hoists: Often used in settings requiring moderate lifting capability, such as automotive repair shops and construction sites, these hoists are effective for various general-purpose applications, enabling the safe movement of heavier components.
Higher Capacity Options (5 Tons, 10 Tons, et)
- 5 ton Monorail Hoists: Suitable for more demanding environments, 5 ton hoists are frequently employed in construction and heavy industrial settings where larger equipment or materials need to be lifted. They provide robust performance for high-volume lifting tasks.
- 10 ton and Above: Hoists with capacities of 10 tons or more are essential for heavy-duty applications in industries such as shipbuilding, large-scale manufacturing, and logistics. These hoists can handle massive loads, ensuring safe and efficient operation in challenging environments.
Factors Affecting Hoist Capacity Selection
Load Type and Weight (Static vs. Dynamic Loads)
When selecting a hoist, it's crucial to consider the nature of the load. Static loads, which remain stationary while being lifted, typically allow for lower capacity ratings. These loads are more stable, making it easier for the hoist to maintain control during lifting. In contrast, dynamic loads—those that may shift or move during lifting—require more robust hoists to account for potential fluctuations in weight distribution. Dynamic loads can introduce additional stresses, making it essential to select a hoist with appropriate capacity and safety features.
Frequency and Duration of Use (Daily, Occasional)
The expected frequency of use also impacts hoist selection. For daily operations, it's advisable to choose a hoist with a higher capacity and durability to withstand constant use. Frequent lifting can lead to wear and tear, so investing in a more robust hoist can enhance longevity. On the other hand, for occasional lifting tasks, a lower capacity hoist may suffice, provided it meets the load requirements for those specific instances. Understanding the usage pattern can help determine the necessary capacity and features.
Environmental Conditions (Temperature, Humidity, Outdoor vs. Indoor)
Environmental factors play a significant role in hoist performance and longevity. For instance, hoists used in outdoor settings must be rated for exposure to elements like rain, dust, and humidity. These conditions can impact the materials and components of the hoist, potentially leading to corrosion or failure if not properly rated. In contrast, indoor environments might have more controlled conditions, allowing for a wider range of hoist options. Additionally, extreme temperatures can affect material performance, so it's essential to consider hoists designed for specific environmental conditions. Selecting a hoist suited to its operating environment ensures reliable performance and extends its life
Special Cases for Capacity Consideration
Applications Involving Unusual Loads (Irregular Shapes, Fragile Items)
When dealing with unusual loads, such as irregularly shaped or fragile items, it's vital to select a hoist that provides precise control and stability. Irregular shapes can create challenges during lifting due to their unpredictable balance and weight distribution. To address these issues, using specialized lifting attachments, such as cradles or slings, can enhance the hoist's ability to handle awkward loads. This approach ensures safe lifting while minimizing the risk of damage to the materials being moved. Additionally, operators should be trained in best practices for handling fragile items to avoid accidents during lifting operations.
Industry-Specific Requirements (Food Processing, Automotive Manufacturing)
Different industries may have specific requirements that significantly influence hoist selection. For instance, in the food processing industry, hoists often need to adhere to stringent hygiene standards. This may include using materials that are easy to clean, resistant to corrosion, and designed to prevent contamination. Such features are critical in maintaining food safety and quality.
Similarly, in automotive manufacturing, hoists may need to accommodate heavier parts, such as engines and chassis components, which can weigh several tons. In this context, hoists should incorporate robust safety features, including overload protection and emergency stop functions, to ensure the safety of both workers and equipment. Understanding these industry nuances is essential for making the right choice, as it allows for the selection of a hoist that meets specific operational and safety needs.
Comparison of Monorail Chain Hoists and Monorail Wire Rope Hoists
Performance Metrics
Lifting Speed and Efficiency
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Monorail chain hoists generally offer moderate lifting speeds, which makes them suitable for a variety of general-purpose applications. While they provide reliable performance for light to medium loads, they may not match the rapid lifting capabilities found in wire rope hoists. Their operational speed is often adequate for tasks where time is not a critical factor, such as routine lifting in smaller workshops or warehouses.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: These hoists are known for their superior lifting speeds, making them ideal for applications that require quick and efficient load handling. The efficient design of wire rope hoists allows for rapid operation, which is crucial in busy industrial environments where minimizing downtime is essential. Their capability to lift heavier loads quickly enhances overall productivity, especially in high-demand settings.
Load Stability and Handling
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Chain hoists provide decent stability for lighter loads, but caution is required when lifting heavier or awkwardly shaped items. Users often need to be vigilant about potential load sway during operation, which can lead to safety risks or inefficient lifting processes. Proper load handling techniques and additional stabilization measures may be necessary in challenging scenarios.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: Wire rope hoists excel in load stability due to their robust wire rope design. This construction minimizes sway and enhances precision when handling heavy and irregularly shaped loads. Their design makes them a preferred choice in demanding lifting scenarios, such as construction sites or manufacturing plants, where load stability is paramount to ensuring safety and efficiency.
Cost Analysis
Initial Purchase Costs vs. Long-Term Maintenance
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Chain hoists typically have a lower initial purchase price, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. However, the long-term maintenance costs can vary significantly depending on usage frequency and environmental factors, such as exposure to moisture or chemicals. While they may save money upfront, their overall cost-effectiveness could diminish with heavy use.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: While wire rope hoists require a higher upfront investment, they often lead to lower maintenance costs over time due to their durable construction and efficiency. This balance makes them more cost-effective in the long run, particularly in high-use applications where reliability and performance are critical. The initial investment can be offset by the reduced need for repairs and replacements.
Total Cost of Ownership for Different Hoist Types
Analyzing the total cost of ownership for both hoist types involves considering multiple factors: purchase price, maintenance, downtime, and operational efficiency. While chain hoists may seem cheaper initially, wire rope hoists often prove to be more economical over time. Their longevity and performance capabilities in demanding environments can lead to lower operational costs and higher return on investment.
Maintenance and Durability
Frequency and Complexity of Maintenance Tasks
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Maintenance tasks for chain hoists are typically straightforward and involve regular inspections and lubrication. However, the frequency of these tasks can increase with heavy usage or exposure to harsh environments. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure smooth operation and longevity, especially in applications where hoists are subjected to continuous use.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: These hoists may require more specialized maintenance, including periodic checks of the wire rope and its integrity. While maintenance can be more complex, the overall durability of wire rope hoists often means less frequent servicing. Their robust design minimizes wear and tear, which can translate to longer service intervals and reduced maintenance time.
Longevity and Reliability in Harsh Environments
- Monorail Chain Hoists: While chain hoists are reliable for general applications, they may experience wear and tear in environments with high humidity or exposure to corrosive materials, affecting their lifespan. Ensuring appropriate protective measures, such as coatings or housing, can help extend their usability in such conditions.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: Designed for heavy-duty use, wire rope hoists are generally more resilient in harsh conditions. Their superior resistance to corrosion and wear makes them well-suited for environments where other hoists might fail. The robust design ensures reliable performance, even in demanding settings, making them ideal for industrial applications where longevity is essential.
Safety Features and Standards
Compliance with Industry Safety Regulations
Both monorail chain hoists and wire rope hoists must comply with industry safety standards, such as those set by OSHA and ANSI. These regulations ensure safe operation and provide guidelines for the design and maintenance of lifting equipment. Compliance not only enhances safety but also protects operators and minimizes liability for employers.
Emergency Stop Functions and Overload Protection
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Many chain hoists come equipped with emergency stop features and overload protection mechanisms, which are essential for safe operation. However, users must ensure that these systems are regularly tested to confirm their functionality, as failure to do so can pose significant safety risks.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: Typically, wire rope hoists feature advanced safety systems, including automatic overload protection and emergency stop functions that activate under stress. These safety features enhance user confidence and minimize the risk of accidents, making wire rope hoists a safer option for heavy lifting applications.
User Experience and Feedback
Testimonials from Industry Users
Users of both monorail chain hoists and wire rope hoists frequently share their experiences regarding performance, reliability, and efficiency. Testimonials often highlight the user-friendly nature of chain hoists for basic applications, while praising the exceptional performance of wire rope hoists in heavy-duty situations. Many users emphasize the importance of selecting the right hoist based on their specific operational needs.
Common Concerns and Praises
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Users appreciate the lower cost and ease of maintenance associated with chain hoists but sometimes express concerns about load stability during lifting. Feedback often suggests a need for better handling solutions in challenging applications, indicating areas for potential improvement in design or training.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: Many users praise wire rope hoists for their durability, lifting speed, and overall performance. However, some concerns may arise regarding their higher initial investment and more complex maintenance needs. Despite these issues, users tend to recommend wire rope hoists for heavy lifting and demanding applications due to their performance and reliability.
This detailed comparison provides a thorough understanding of the differences between monorail chain hoists and monorail wire rope hoists, addressing performance, cost, maintenance, safety features, and user feedback.
Performance Metrics
Lifting Speed and Efficiency
- Monorail Chain Hoists: These hoists typically offer moderate lifting speeds, often ranging from 5 to 10 meters per minute. This makes them suitable for general-purpose applications, such as assembly lines and light lifting tasks. While they provide reliable performance for light to medium loads (up to approximately 10 tons), their lifting speed may not match the rapid capabilities of wire rope hoists, which can be a limitation in high-demand settings.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: Known for their faster lifting speeds, typically around 10 to 20 meters per minute, wire rope hoists excel in applications that require quick load handling, such as in automotive assembly or heavy manufacturing. Their efficient design allows for swift operation, making them ideal for busy industrial environments where time and productivity are crucial factors.
Load Stability and Handling
- Monorail Chain Hoists: While chain hoists offer decent stability for lighter loads, they may require additional care when lifting heavier or awkwardly shaped items. Users need to be particularly attentive to load sway during operation, as chain design can lead to greater movement and potential instability, especially in high winds or confined spaces.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: These hoists provide superior load stability due to their robust wire rope design, which minimizes sway and enhances precision when handling heavy and irregularly shaped loads. The structural integrity of wire rope hoists ensures consistent performance, making them the preferred choice in demanding lifting scenarios such as construction sites and industrial facilities where precision is paramount.
Cost Analysis
Initial Purchase Costs vs. Long-Term Maintenance
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Generally, chain hoists have a lower initial purchase price, making them attractive for budget-conscious buyers. However, their long-term maintenance costs can vary depending on usage frequency and environmental factors, such as exposure to moisture or corrosive materials. While they are cost-effective for light-duty applications, frequent maintenance may increase overall costs.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: Wire rope hoists may require a higher upfront investment, typically due to their more complex design and robust construction. However, they often lead to lower maintenance costs over time due to their durability and efficiency. This balance makes them cost-effective in the long run, particularly in high-use applications where reliability is critical.
Total Cost of Ownership for Different Hoist Types
Analyzing the total cost of ownership for both hoist types involves considering several factors:
- Purchase Price: Initial investment required for the equipment.
- Maintenance Costs: Ongoing costs associated with upkeep.
- Downtime: Potential costs incurred during maintenance periods.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficiency in energy consumption and performance.
While chain hoists might seem cheaper initially, wire rope hoists often prove to be more economical due to their longevity, reduced maintenance frequency, and superior performance capabilities.
Maintenance and Durability
Frequency and Complexity of Maintenance Tasks
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Maintenance tasks for chain hoists are typically straightforward, involving regular inspections, lubrication of chains and gears, and checking for wear. However, the frequency of these tasks can increase with heavy usage or exposure to harsh environments, necessitating more frequent attention.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: These hoists may require more specialized maintenance, including periodic checks of the wire rope for fraying, kinks, or corrosion, and the inspection of mechanical components. While maintenance can be more complex, the durability of wire rope hoists often means less frequent servicing overall, translating to lower operational disruptions.
Longevity and Reliability in Harsh Environments
- Monorail Chain Hoists: While chain hoists are generally reliable for general applications, they may experience wear in environments with high humidity or exposure to corrosive materials. Regular maintenance is essential to mitigate potential damage and ensure longevity.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: Designed for heavy-duty use, wire rope hoists are often more resilient in harsh conditions. Their superior resistance to corrosion, along with their robust design, ensures reliable performance, even in demanding settings such as outdoor construction sites and chemical processing facilities.
Safety Features and Standards
Compliance with Industry Safety Regulations
Both types of hoists must comply with industry safety standards, such as those set by OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute). These regulations ensure safe operation and provide guidelines for the design, installation, and maintenance of lifting equipment. Regular training and safety assessments are essential to adhere to these standards.
Emergency Stop Functions and Overload Protection
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Many chain hoists come equipped with emergency stop features and overload protection mechanisms, which are essential for safe operation. However, users must ensure that these systems are regularly tested and maintained to avoid failures during critical lifting operations.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: Typically, wire rope hoists feature advanced safety systems, including automatic overload protection and emergency stop functions that activate under stress. These safety features enhance user confidence and minimize the risk of accidents, making them suitable for high-stakes lifting scenarios.
User Experience and Feedback
Testimonials from Industry Users
Users of both monorail chain hoists and wire rope hoists often share their experiences regarding performance, reliability, and efficiency. Testimonials frequently highlight the user-friendly nature of chain hoists for basic applications, praising their simplicity and ease of use. In contrast, wire rope hoists are often celebrated for their exceptional performance in heavy-duty situations, where reliability and speed are critical.
Common Concerns and Praises
- Monorail Chain Hoists: Users appreciate the lower cost and ease of maintenance but sometimes express concerns about load stability during lifting operations. Feedback often suggests a need for better handling and stability features in challenging applications, such as lifting unevenly shaped loads.
- Monorail Wire Rope Hoists: Many users praise wire rope hoists for their durability and speed, noting their ability to handle heavy loads efficiently. However, some concerns may arise regarding their higher initial investment and more complex maintenance needs. Overall, users tend to recommend wire rope hoists for heavy lifting and demanding applications due to their superior performance and reliability.
Buying Tips for Electric Monorail Hoists
Key Considerations Before Purchase
Assessing Specific Application Requirements
Before purchasing an electric monorail hoist, it's essential to evaluate your specific application needs thoroughly. Consider factors such as:
- Types of Loads: Determine the weight and shape of the loads you will be handling. This assessment will guide you in choosing a hoist with the appropriate capacity and features.
- Lifting Height: Identify the maximum height you need the hoist to reach. This factor can influence the design and configuration of the hoist.
- Frequency of Use: Consider how often the hoist will be operated. For frequent use, investing in a more robust, high-speed hoist may be beneficial, whereas occasional use may allow for more economical options.
These parameters will help you select the most suitable hoist for your operations, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Evaluating Total Cost of Ownership
The purchase price is just one aspect of the total cost of ownership. Analyze potential ongoing costs, including:
- Maintenance: Factor in the costs associated with routine inspections, repairs, and replacements over the hoist's lifespan.
- Energy Consumption: Consider the efficiency of the hoist and how it will affect your operational costs.
- Repair Needs: Assess how often you might need repairs based on the manufacturer's reputation and warranty conditions.
A cheaper initial investment might lead to higher long-term expenses if the hoist requires frequent servicing or has lower efficiency. Evaluate the expected lifespan and reliability of the hoist to ensure you're making a sound financial decision.
Questions to Ask Suppliers
Warranty and Support Options
Inquire about the warranty provided with the hoist, including:
- Duration: How long is the warranty valid?
- Coverage Specifics: What does the warranty cover? Are there exclusions?
A robust warranty can protect your investment and provide peace of mind. Additionally, ask about the support options available post-purchase. Ensure the supplier offers responsive customer service and technical support for troubleshooting or repairs.
Customization Possibilities Based on Needs
Different applications may require customized solutions. Discuss with suppliers the possibility of tailoring the hoist to fit your specific operational needs. Consider adjustments in:
- Lifting Capacity: Ensure the hoist can handle your heaviest loads.
- Speed: Depending on your workflow, you may need a hoist with adjustable speeds.
- Control Systems: Discuss options for remote operation, safety features, and ergonomic controls.
Customization can enhance the hoist's effectiveness in your unique environment, improving productivity and safety.
Importance of Trial and Demonstration
Requesting On-Site Demonstrations or Trials
Whenever possible, request an on-site demonstration of the hoist before making a purchase. Seeing the hoist in action will provide valuable insights into its performance and suitability for your operations. A hands-on demonstration allows you to assess its lifting speed, stability, and ease of use in your specific working environment.
Testing Load Capacity and Functionality Before Purchasing
Ensure that the hoist can handle the specific loads you plan to lift. During the trial, test its load capacity by lifting weights that mimic your typical operational loads. Pay attention to how smoothly and reliably the hoist operates under these conditions. This real-world testing is crucial to validate that the hoist meets your performance expectations and is suitable for your operational demands.
Installation and Maintenance
Installation Guidelines for Electric Monorail Trolley Hoists
Site Preparation and Safety Precautions
Site Assessment: Before installation, a thorough assessment of the installation area is crucial. Ensure that the ceiling or supporting structure can accommodate the hoist's weight and the loads it will lift. Check for sufficient headroom and clearance to facilitate safe operation.
Safety Measures: Establish a safety zone around the installation site to protect workers from potential hazards. All personnel involved in the installation should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including hard hats, gloves, and safety glasses. Training in safety protocols is essential to ensure that everyone is aware of the risks and procedures.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Mounting the Rails: Begin by installing the rail system according to the manufacturer's specifications. It's essential to ensure the rails are level and securely anchored to support the hoist's weight. Use the appropriate hardware and fasteners to secure the rails effectively.
Hoist Installation: Once the rails are mounted, attach the trolley hoist to the rail system. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines closely to ensure proper alignment and functionality. Be meticulous in making all electrical connections safely and in accordance with local codes.
Testing: After installation, conduct a thorough test run of the hoist. Lift a load within the hoist's capacity to verify smooth operation and stability. Pay close attention for any unusual noises or vibrations during this test and make necessary adjustments as needed.
Maintenance Best Practices for Longevity and Performance
Regular Inspection Schedules
Establish a routine inspection schedule to regularly assess the condition of the hoist and its components. Critical parts such as the motor, gears, chain, and rail system should be checked for wear and tear. Inspections are recommended at least once a month, or more frequently if the hoist is subjected to heavy usage.
Documenting inspection findings is vital for tracking performance over time and identifying any recurring issues that may require attention.
Lubrication and Parts Replacement
Ensure that all moving parts are properly lubricated to minimize friction and wear. Adhere to the manufacturer's recommendations regarding lubrication intervals and the types of lubricant to use.
Regular checks and timely replacement of worn or damaged parts—such as chains, ropes, and brakes—are necessary to maintain safe and efficient operation. Keeping a stock of critical replacement parts can significantly reduce downtime during repairs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying and Resolving Operational Problems
Common issues that may arise include uneven lifting, unusual noises, or failure to operate. Start troubleshooting by checking the power supply and ensuring all electrical connections are secure.
If the hoist is lifting unevenly, inspect the load distribution and verify that the hoist is correctly aligned on the rail. For any abnormal noises, check for loose components or insufficient lubrication.
Resources for Assistance and Repairs
Maintain contact information for the manufacturer or supplier for technical support and warranty service. They can provide valuable assistance in diagnosing problems and offering repair solutions.
Consider training personnel in basic troubleshooting and maintenance techniques to empower them to address minor issues independently. Keeping a maintenance manual on hand can also aid in resolving common problems effectively.
This section outlines comprehensive guidance on the installation and maintenance of electric monorail trolley hoists, emphasizing safety protocols, best practices, and troubleshooting strategies to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we explored the crucial aspects of Electric Monorail Trolley Hoists, specifically focusing on the differences between monorail chain hoists and wire rope hoists. Key findings include:
- Design and Construction: Both types of hoists have unique design elements that cater to various lifting requirements. Chain hoists are lightweight and cost-effective, ideal for lighter loads, while wire rope hoists provide higher strength and durability for heavier lifting tasks.
- Hot Sale Capacities: Common capacities range from 1 ton to 10 tons, and selecting the right capacity is essential based on load type, usage frequency, and environmental conditions. Specialized applications require careful consideration of the unique demands they impose on the hoist.
- Performance Comparison: A thorough analysis of performance metrics reveals that lifting speed, load stability, maintenance needs, and cost considerations are critical factors that influence a buyer's decision. Safety features, including compliance with industry standards, are paramount for ensuring operational safety.
Final Recommendations for Choosing the Right Electric Monorail Trolley Hoist
When selecting an electric monorail trolley hoist, consider the following recommendations:
- Assess Specific Needs: Identify your specific lifting requirements, including load weight, size, and frequency of use. Choose a hoist that matches your operational demands while allowing for potential future expansion.
- Evaluate Supplier Options: Research various suppliers to compare not only initial costs but also warranty terms, support services, and customization options. A reliable supplier will offer valuable insights and assistance tailored to your application.
- Test Before You Buy: Whenever possible, request demonstrations or trials of the hoists you are considering. This hands-on approach allows you to evaluate the hoist's performance in your operational environment and ensure it meets your expectations.
- Prioritize Safety Features: Ensure that the hoist adheres to the latest safety standards and includes essential safety features such as overload protection, emergency stop functions, and user-friendly controls.
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights into electric monorail trolley hoists and assisted you in making informed decisions. Should you have any questions or require further assistance, please do not hesitate to reach out. Our team is committed to supporting your needs, whether it involves product inquiries, customization requests, or guidance on installation and maintenance.
Investing in the right hoist will enhance your material handling efficiency and contribute to a safer working environment. We look forward to fostering a productive partnership and supporting your future lifting needs!
Main Projects
Related Products
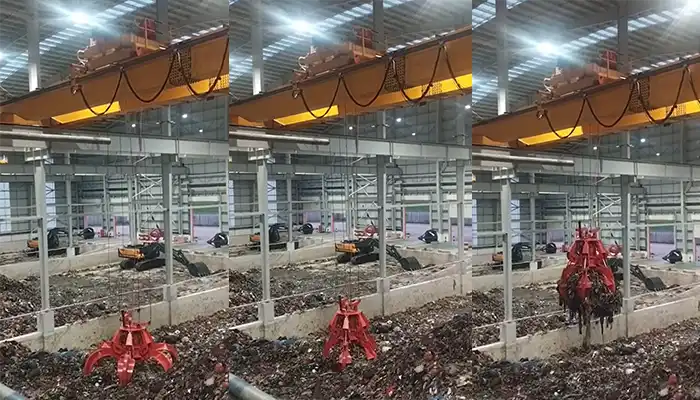

Supplied three grab bucket crane kits to Indonesia, enhancing garbage handling efficiency with high load capacity and reliable performance.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch