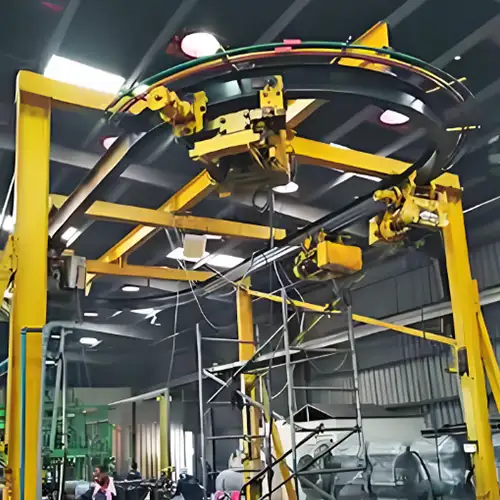
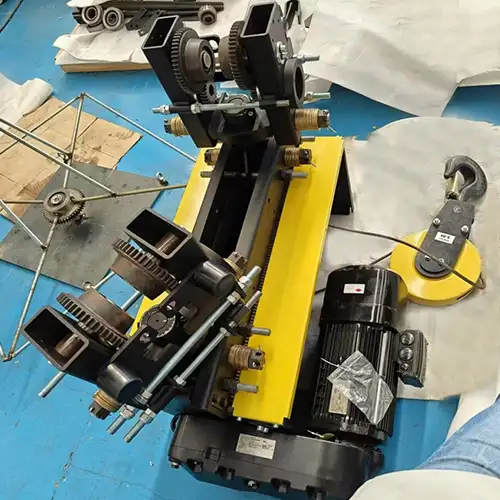
Overhead Monorail Cranes and Their Applications
Overhead monorail cranes streamline material handling, offering efficient movement in manufacturing, assembly lines & warehousing, enhancing productivity.
Category: Overhead Hoist
Your Trusted Overhead Crane Manufacturer & Supplier
Overhead Monorail Cranes and Their Applications
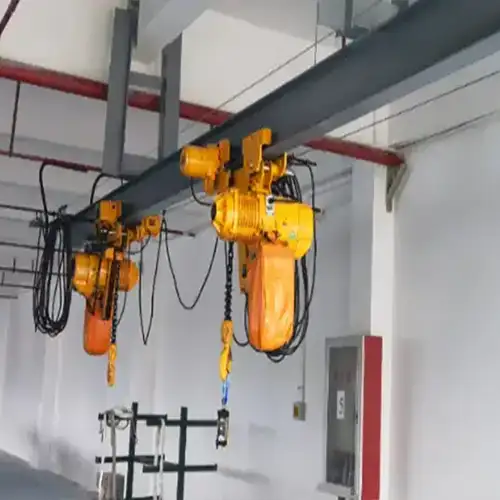
Overhead monorail cranes are a type of material handling system used in industrial environments to efficiently transport and position heavy loads along a fixed path. Unlike traditional overhead bridge cranes, which have two parallel runways with a bridge spanning between them, monorail cranes operate on a single girder or rail mounted directly overhead.
Monorail cranes consist of a hoist trolley that runs along the monorail beam, supported by a gantry structure or ceiling-mounted supports. They are designed to move loads horizontally within a facility, typically in a straight line or along a curved track, providing versatile and controlled movement of materials.
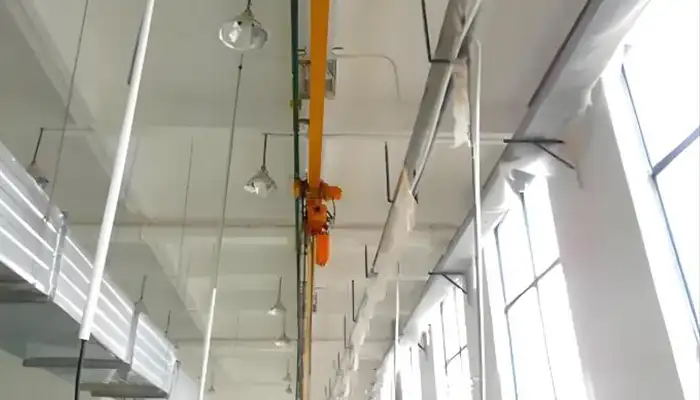

Overhead Monorail Cranes with Straight Track for Sale
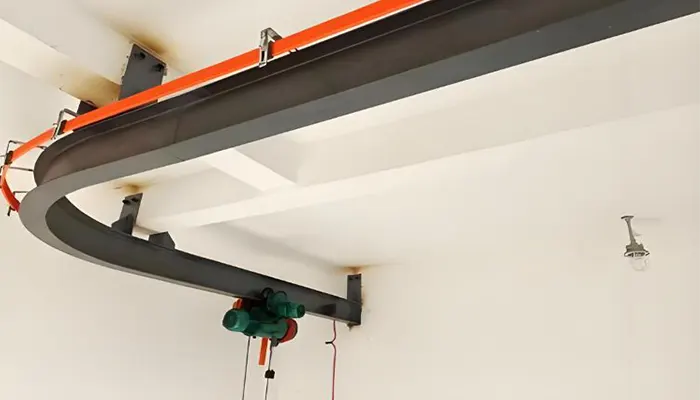

Overhead Monorail Cranes with curved and round track for sale
Advantages Over Other Crane Types
- Space Utilization: Monorail cranes are ideal for facilities with limited floor space as they operate overhead, leaving the ground level clear for other operations such as production or storage. This compact design maximizes the usable workspace within the facility.
- Flexibility and Maneuverability: Due to their single rail design, monorail cranes can navigate tight spaces and follow complex paths, making them suitable for applications where precise load positioning is required. They are often used in assembly lines, machining centers, and warehouses to streamline workflows.
- Cost Efficiency: Compared to overhead bridge cranes, monorail systems are typically more cost-effective to install and maintain, especially in smaller work areas or when integrating with existing structures. They offer a lower initial investment and reduced operating costs over their lifespan.
- Safety and Ergonomics: Monorail cranes improve workplace safety by reducing manual handling risks and enhancing ergonomics for operators. They enable efficient load movement without the need for heavy lifting by personnel, minimizing the potential for injuries and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Customization Options: Modern monorail crane systems can be customized with various hoist and trolley configurations, speed controls, and automation features to suit specific operational requirements. This adaptability makes them versatile for handling diverse loads and adapting to changing production demands.
- Environmental Benefits: By optimizing material flow and reducing energy consumption compared to alternative handling methods, monorail cranes contribute to environmental sustainability initiatives within industrial settings.
Overall, overhead monorail cranes offer a reliable and efficient solution for material handling needs in manufacturing, logistics, and other industrial sectors, providing substantial benefits in space utilization, flexibility, cost efficiency, and safety. Their design versatility and operational advantages make them a preferred choice for optimizing workflow processes and enhancing productivity in modern industrial environments.
Components of Overhead Monorail Crane Systems
Overview of Monorail Hoist Crane Catalogue
An overhead monorail crane system consists of several key components that work together to facilitate efficient material handling operations within industrial environments. Understanding these components and their functions is essential for designing, installing, and maintaining a reliable crane system.
Key Components and Their Functions
Monorail Beam or Girder:
- Function: The monorail beam serves as the track along which the hoist trolley moves. It is typically mounted overhead and supports the weight of the hoist and the load it carries.
- Types: Monorail beams can be straight or curved, depending on the layout and operational requirements of the facility.
Hoist Trolley:
- Function: The hoist trolley is mounted on the monorail beam and moves horizontally to position the hoist hook or other lifting device above the load.
- Types: Hoist trolleys can be manual, electric, or pneumatic, offering different levels of automation and lifting capacities.
Hoist Unit:
- Function: The hoist unit is responsible for lifting and lowering loads. It is typically equipped with a motor, brake system, and lifting mechanism (such as chain or wire rope) to handle varying load capacities.
- Types: Hoist units come in various configurations, including single-speed, dual-speed, and variable-speed options, to accommodate different load handling requirements.
End Trucks:
- Function: End trucks support the hoist trolley and allow it to travel along the monorail beam. They include wheels or rollers that run along the beam track, providing smooth movement and stability.
- Types: End trucks may be manually operated or motorized, depending on the size and weight of the loads being transported.
Electrical Controls and Power Supply:
- Electrical controls manage the operation of the crane system, including hoist movement, speed adjustments, and safety features. They also ensure proper power distribution to the hoist and trolley components.
- Components: Control panels, pendant stations, limit switches, and emergency stop devices are essential electrical components that enhance operational safety and efficiency.
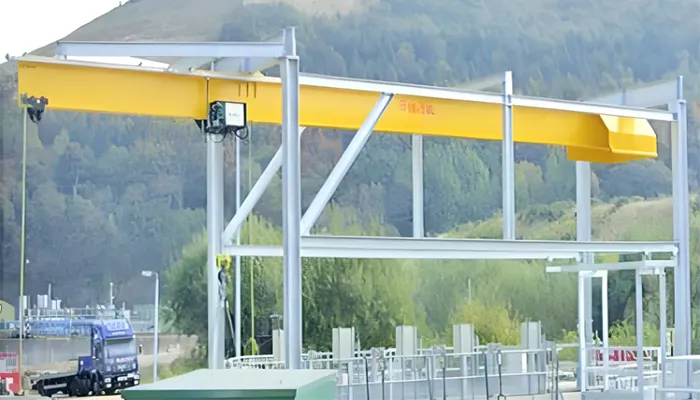
Support Structures:
- Function: Support structures, such as gantry frames or ceiling-mounted supports, provide stability and structural integrity to the monorail crane system. They are designed to withstand the weight of the crane components and the loads they carry.
- Installation Considerations: Support structures must be securely anchored or mounted to the building structure to ensure safe and reliable crane operation.
Safety Features:
- Function: Safety features are critical for protecting personnel and equipment during crane operations. They include overload protection devices, collision avoidance systems, and emergency stop controls to prevent accidents and equipment damage.
- Compliance: Monorail crane systems must adhere to industry safety standards and regulations, ensuring compliance with workplace safety guidelines.
Understanding these components and their functions is essential for designing a monorail crane system that meets specific operational requirements and safety standards. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of these components contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of overhead monorail crane systems in industrial applications.
Types and Capacities of Overhead Monorail Cranes
Overhead monorail cranes come in various types and capacities to suit different industrial applications, offering versatility and efficiency in material handling operations. The types and capacities helps in selecting the right crane system for specific operational needs.
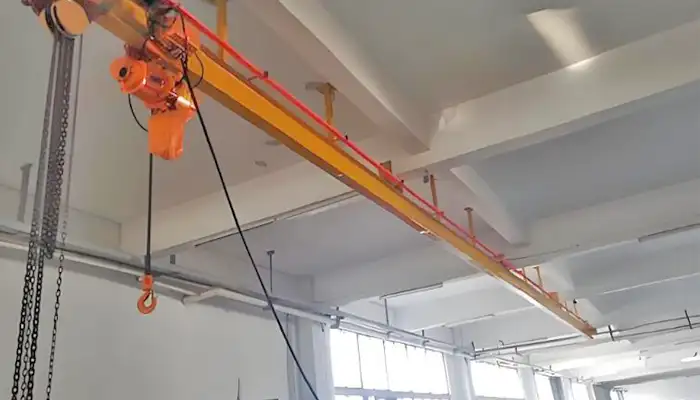

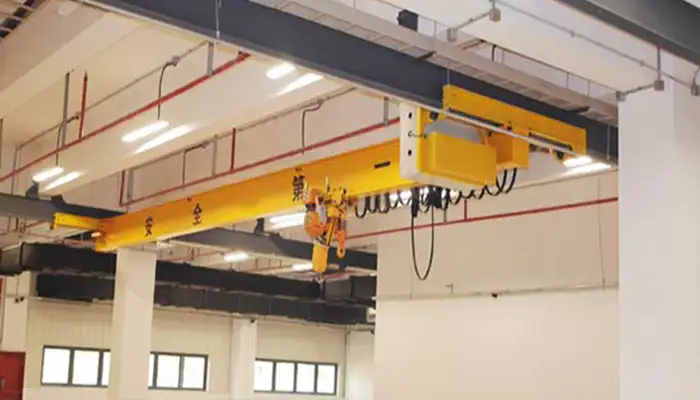
Overhead Monorail Cranes with Straight Monorails:
- Description: These cranes feature a straight monorail beam that runs in a linear path along the designated track.
- Advantages: Ideal for applications requiring linear movement of loads with minimal curves. - Simplifies load positioning and enhances operational efficiency in straight-line production processes.
- Applications: Commonly used in assembly lines, production floors, and warehouses where straightforward material handling is essential.
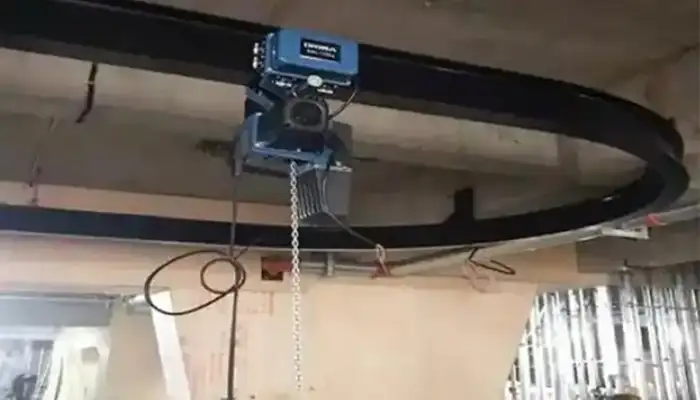

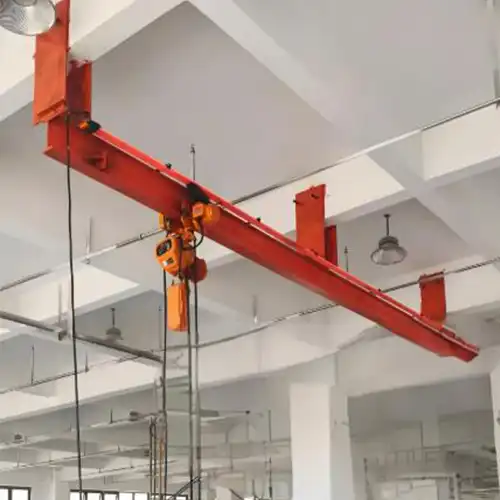
Overhead Monorail Cranes with Curved Monorails:
- Description: Curved monorail cranes incorporate curved sections in the monorail track to navigate around obstacles or follow specific production layouts.
- Advantages: Facilitates flexible load movement around corners and irregularly shaped work areas. - Optimizes space utilization by adapting to complex production floor layouts.
- Applications: Suitable for facilities with limited space or complex layouts, such as automotive assembly lines, foundries, and machining centers.
Specifications of monorail cranes encompass a range of key details that define their capabilities and suitability for various industrial applications. Here are the typical specifications to consider:
Specifications of Monorail Cranes:
Load Capacity:
- Range: Monorail cranes are available in various load capacities, ranging from light-duty options handling as low as 0.5 tons (500 kilograms) to heavy-duty models capable of lifting loads exceeding 50 tons or more.
- Determinants: The load capacity is determined by factors such as the structural design of the crane, the hoisting mechanism, and the intended application within the industrial environment.
Span Length:
- Definition: Span length refers to the distance between support structures or mounting points of the monorail beam.
- Variability: Span lengths can vary widely depending on the specific requirements of the facility, ranging from a few meters to over 30 meters for larger industrial applications.
- Considerations: Longer spans may require additional support structures or special engineering considerations to ensure structural integrity and safe operation.
Hoisting Speed and Control:
- Speed Options: Monorail cranes offer different hoisting speeds to accommodate varying load handling requirements. Options include single-speed, dual-speed, or variable-speed mechanisms.
- Control Mechanisms: Controlled via pendant stations, radio remote controls, or integrated with automated systems for precise load handling and positioning.
- Precision: High-speed options enable efficient material flow and rapid positioning of loads, while variable-speed controls provide flexibility for handling delicate or complex operations.
Bridge and Trolley Speeds:
- Bridge Speed: Refers to the speed at which the hoist trolley moves along the monorail beam.
- Trolley Speed: Indicates the speed at which the entire crane system can traverse horizontally across the span.
- Customization: Adjustable speeds can be tailored to specific operational needs, enhancing productivity and optimizing workflow efficiency.
Environmental Considerations:
- Operating Conditions: Monorail cranes are designed to operate in various environmental conditions, including temperature extremes, humidity, and corrosive atmospheres.
- Material Selection: Components such as monorail beams and structural supports are often constructed from durable materials like steel or aluminum alloys to withstand harsh environments and ensure long-term reliability.
Safety Features:
- Essential Components: Include overload protection devices, emergency stop buttons, limit switches, and collision avoidance systems.
- Compliance: Monorail crane systems adhere to industry safety standards and regulations to ensure safe operation and protect personnel and equipment from potential hazards.
Control Systems and Automation:
- Integration: Cranes may integrate with advanced control systems for automation, allowing for seamless operation and coordination with other industrial processes.
- Remote Access: Remote monitoring and control capabilities enable operators to manage crane operations from a safe distance, enhancing overall safety and operational efficiency.
Understanding these specifications is crucial for selecting the appropriate monorail crane system that meets specific load handling requirements, operational environment conditions, and safety standards within industrial settings. Each specification parameter contributes to the crane's overall performance, efficiency, and reliability in material handling operations.
Hot Sale Capacities of Overhead Monorail Cranes:
Hot Sale Capacities of Overhead Monorail Cranestypically refer to the most commonly purchased or in-demand load capacities within the market. These capacities are often dictated by industrial needs, operational requirements, and the types of applications where monorail cranes are frequently employed. Here are some typical "hot sale" capacities:
2 Ton Overhead Monorail Cranes: Widely used in light to moderate industrial applications. Ideal for assembly lines, workshops, and small-scale manufacturing environments where precision handling of loads up to 2 tons is required.
5 Ton Overhead Monorail Cranes: Popular choice for medium-duty industrial operations. - Commonly found in manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and production lines where heavier loads up to 5 tons need to be lifted and maneuvered.
10 Ton Overhead Monorail Cranes: Heavy-duty applications demanding robust lifting capacities. Suitable for industries such as steel mills, foundries, and heavy equipment manufacturing, where handling substantial loads up to 10 tons is routine.
These capacities represent the most frequently sought-after options in the market due to their versatility, reliability, and ability to meet a wide range of industrial lifting requirements. Choosing the appropriate capacity depends on factors such as the weight of the loads to be handled, operational environment, and specific application needs within the facility.
Selection Considerations:
- Load Characteristics: Choose a monorail crane system based on the weight and dimensions of the loads to be handled, ensuring that the crane's capacity matches operational requirements.
- Span and Reach: Consider the span and reach required for the crane to cover the entire work area effectively without obstruction, optimizing material flow and operational efficiency.
- Operational Environment: Assess environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and corrosive elements to select crane components and materials that withstand specific operating conditions.
- Automation and Control Options: Evaluate automation features such as variable speed controls, remote operation capabilities, and integration with existing industrial automation systems to enhance productivity and safety.
Understanding the types and capacities of overhead monorail cranes enables informed decision-making in selecting the right crane system to meet production goals, enhance workflow efficiency, and ensure safe material handling operations in industrial settings.
Applications in Industrial Settings
Typical Industrial Uses of Overhead Monorail Cranes
Overhead monorail cranes play a crucial role in various industrial settings, offering efficient and controlled material handling solutions. Here are some typical applications where these cranes are widely utilized:
Manufacturing Facilities:
- Assembly Lines: Monorail cranes are used to transport components, sub-assemblies, and finished products along production lines. They facilitate smooth and continuous workflow by ensuring timely delivery of materials to assembly stations.
- Machining and Fabrication: Cranes assist in moving raw materials, workpieces, and tools between machining centers and workstations, enhancing productivity and reducing manual handling.
Warehousing and Distribution Centers:
- Inventory Management: Monorail cranes are employed for efficient loading and unloading of goods, optimizing storage space utilization and streamlining logistics operations.
- Order Picking: They enable quick retrieval and transport of items within warehouses, supporting order fulfillment processes with minimal downtime.
Automotive Industry:
- Production Plants: Monorail cranes aid in handling vehicle components such as engines, chassis, and body panels during assembly. They ensure precise positioning and alignment of parts to meet quality standards and production schedules.
- Maintenance Facilities: Used for lifting and transporting heavy automotive parts and equipment for maintenance and repair tasks, improving operational efficiency and safety.
Heavy Equipment Manufacturing:
- Foundries and Forges: Cranes assist in handling molten metal, molds, and finished castings in foundry operations. They withstand high temperatures and rugged environments while ensuring reliable material flow and production continuity.
- Steel Mills: Monorail cranes play a critical role in handling steel coils, billets, and finished products across various stages of steel manufacturing processes, from melting to rolling and finishing operations.
Examples in Manufacturing, Warehousing, and Assembly Lines
- Manufacturing: A textile factory uses monorail cranes to transport rolls of fabric between cutting, sewing, and packaging stations, optimizing workflow and reducing labor costs.
- Warehousing: A distribution center employs monorail cranes to move heavy pallets of goods from storage racks to loading docks efficiently, minimizing product handling time and maximizing storage capacity.
- Assembly Lines: An electronics manufacturer integrates monorail cranes to transport circuit boards and electronic components along the assembly line, ensuring precision and consistency in product assembly.
These examples illustrate the versatility and practical applications of overhead monorail cranes across diverse industrial sectors, enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and overall productivity in material handling operations.
Load Handling and Efficiency
Typical Loads Handled in Workshops and Factories
Overhead monorail cranes are designed to handle a wide range of loads within workshops and factories, catering to diverse industrial applications. Here are some typical loads that are commonly handled:
- Raw Materials: Monorail cranes transport raw materials such as steel bars, aluminum sheets, and plastic pellets from storage areas to production lines or processing stations.
- Components and Sub-Assemblies: They move components and sub-assemblies between workstations on assembly lines, ensuring timely and accurate assembly of products.
- Finished Products: Cranes are used to lift and transport finished products, including machinery parts, consumer goods, and packaged items, for storage or shipment.
- Heavy Equipment: In heavy industries like automotive and aerospace, monorail cranes handle heavy equipment components, such as engines, chassis frames, and aircraft fuselages, during manufacturing and assembly processes.
- Specialized Loads: They also handle specialized loads such as coils in steel mills, molds in foundries, and fragile items in manufacturing facilities requiring delicate handling.
Efficiency and Productivity Gains
- Reduced Handling Time: Monorail cranes streamline material handling operations by reducing the time and effort required for manual lifting and transport. This efficiency minimizes downtime and increases overall production output.
- Improved Workflow: By automating repetitive tasks, monorail cranes optimize workflow processes in workshops and factories. They ensure consistent material flow, eliminate bottlenecks, and enhance operational continuity.
- Space Optimization: Operating overhead, monorail cranes maximize floor space utilization in crowded work areas. They free up valuable ground space for other activities such as production operations or additional storage.
- Enhanced Safety: Automated features and precise control systems improve workplace safety by reducing the risk of accidents associated with manual material handling. Safety mechanisms such as overload protection and collision avoidance systems further mitigate risks.
- Cost Efficiency: Monorail cranes contribute to cost savings by minimizing labor costs associated with manual handling, optimizing energy consumption through efficient operation, and reducing maintenance expenses with durable components and reliable performance.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: With customizable configurations and adaptable designs, monorail cranes accommodate changing production needs and evolving manufacturing processes. They support scalability and adaptability in dynamic industrial environments.
Overall, overhead monorail cranes enhance efficiency, productivity, and safety in workshops and factories by facilitating smooth material flow, optimizing space utilization, and reducing operational costs. Their role in handling diverse loads and improving workflow efficiency makes them indispensable in modern industrial operations.
Overhead Monorail Cranes Comparison with Overhead Bridge Cranes
Differences in Design and Functionality
Design:
- Overhead Monorail Cranes: These cranes operate on a single rail or beam, typically mounted overhead and supported by ceiling-mounted or gantry structures. They move along a straight or curved path and are designed for linear material handling within a specific area.
- Overhead Bridge Cranes: Also known as gantry cranes, these cranes have two parallel runways with a bridge spanning between them. The bridge supports a hoist and trolley mechanism that moves horizontally across the span, allowing for versatile movement and coverage across a broader workspace.
Flexibility and Maneuverability:
- Monorail Cranes: Monorail cranes excel in applications requiring precise linear movement of loads along a fixed path. They are suitable for facilities with limited space or complex layouts where straight-line movement is essential.
- Bridge Cranes: Bridge cranes offer greater versatility in material handling as they can cover a larger area with the ability to move loads not only horizontally along the runway but also vertically through lifting and lowering operations. This makes them suitable for handling loads across expansive manufacturing or warehouse environments.
Load Capacity and Reach:
- Monorail Cranes: Typically used for lighter to medium-duty applications, handling loads ranging from a few hundred kilograms to several tons depending on the design and configuration.
- Bridge Cranes: Designed for heavier loads, bridge cranes can lift significantly larger capacities, often exceeding 100 tons or more. They are preferred for heavy-duty industrial operations requiring robust lifting capabilities.
Installation and Space Utilization:
- Monorail Cranes: Installation of monorail systems is generally simpler and requires less structural support compared to bridge cranes. They optimize vertical space by operating overhead, leaving the ground level clear for other activities.
- Bridge Cranes: Installing bridge cranes involves constructing support structures for the parallel runways and bridge assembly. They occupy more floor space but offer the advantage of covering larger work areas with efficient load handling capabilities.
Advantages of Overhead Monorail Cranes in Specific Applications
- Space Efficiency: Monorail cranes maximize vertical space utilization, making them ideal for facilities with limited floor space or congested layouts. They allow for efficient material handling without obstructing ground-level operations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Due to their simpler design and installation requirements, monorail cranes often entail lower initial costs compared to bridge cranes. They offer a cost-effective solution for smaller-scale material handling needs.
- Precision Handling: Monorail cranes excel in applications requiring precise load positioning and movement along a designated path. They ensure accurate alignment and placement of materials, enhancing production quality and efficiency.
- Safety and Ergonomics: Operating overhead, monorail cranes minimize the risk of ground-level accidents and improve ergonomic conditions for operators. They reduce manual lifting and handling tasks, contributing to a safer work environment.
- Adaptability and Customization: Monorail crane systems can be customized with various hoist configurations, speed controls, and automation features to meet specific operational requirements. This adaptability supports diverse industrial applications and evolving production demands.
In summary, while overhead bridge cranes offer broader coverage and higher load capacities suitable for heavy-duty operations, overhead monorail cranes provide advantages in space efficiency, cost-effectiveness, precision handling, safety, and customization options. Choosing between the two types depends on the specific operational needs, space constraints, and material handling requirements of the industrial facility.
Overhead Monorail Cranes Comparison with Ceiling-Mounted Overhead Bridge Cranes

Overhead Monorail Cranes
Differences in Design and Functionality
Design:
- Overhead Monorail Cranes: These cranes operate on a single rail or beam that is typically mounted overhead, supported by ceiling-mounted structures or gantry systems. They move along a straight or curved path and are designed for linear material handling within a specific area or production line.
- Ceiling-Mounted Bridge Cranes: Also known as overhead bridge cranes, these cranes have two parallel runways mounted on the ceiling or elevated structures. A bridge spans across these runways, supporting a hoist and trolley mechanism that provides both horizontal movement along the runways and vertical lifting capability.
Flexibility and Coverage:
- Monorail Cranes: Monorail cranes are suited for applications requiring linear movement of loads along a fixed path. They offer precise control over load positioning and are ideal for facilities with restricted floor space or where straight-line movement is critical.
- Ceiling-Mounted Bridge Cranes: Ceiling-mounted bridge cranes provide extensive coverage across larger work areas due to their dual runway configuration. They offer versatile movement capabilities, including lateral travel and vertical lifting, making them suitable for handling loads across expansive manufacturing or warehouse environments.
Load Capacity and Handling:
- Monorail Cranes: Typically used for lighter to medium-duty applications, monorail cranes can handle loads ranging from a few hundred kilograms to several tons, depending on the crane's design and configuration.
- Ceiling-Mounted Bridge Cranes: Designed for heavier loads, ceiling-mounted bridge cranes have higher lifting capacities, often exceeding 100 tons or more. They are preferred for heavy-duty industrial operations that require robust lifting and precise load positioning capabilities.
Installation and Structural Requirements:
- Monorail Cranes: Installation of monorail systems is generally simpler and requires less structural support compared to ceiling-mounted bridge cranes. They optimize vertical space utilization and can be integrated into existing building structures more easily.
- Ceiling-Mounted Bridge Cranes: Installing ceiling-mounted bridge cranes involves constructing support structures for the parallel runways and bridge assembly, which requires significant overhead space and structural reinforcement. They occupy more floor space but provide substantial lifting capacity and operational flexibility.
Advantages of Overhead Monorail Cranes in Specific Applications
- Space Efficiency: Monorail cranes maximize vertical space utilization by operating overhead, leaving the ground level clear for other activities. They are ideal for facilities with limited floor space or where maintaining clear ground access is crucial.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Due to their simpler design and installation requirements, monorail cranes often entail lower initial costs compared to ceiling-mounted bridge cranes. They offer a cost-effective solution for smaller-scale material handling needs without compromising on efficiency.
- Precision Handling: Monorail cranes excel in applications requiring precise load positioning and movement along a designated path. They ensure accurate alignment and placement of materials, enhancing production quality and operational efficiency.
- Safety and Ergonomics: Operating overhead, monorail cranes minimize the risk of ground-level accidents and improve ergonomic conditions for operators. They reduce manual lifting and handling tasks, contributing to a safer work environment and reducing potential injuries.
- Adaptability and Customization: Monorail crane systems can be customized with various hoist configurations, speed controls, and automation features to meet specific operational requirements. This adaptability supports diverse industrial applications and allows for integration with existing production processes seamlessly.
In summary, while ceiling-mounted bridge cranes offer extensive coverage and higher load capacities suitable for heavy-duty operations, overhead monorail cranes provide advantages in space efficiency, cost-effectiveness, precision handling, safety, and customization options. Choosing between the two types depends on the specific operational needs, space constraints, and material handling requirements of the industrial facility.
Here's a comparison table between Overhead Monorail Cranes and Ceiling-Mounted Overhead Bridge Cranes:
Comparison Table: Overhead Monorail Cranes vs. Ceiling-Mounted Overhead Bridge Cranes
| Feature | Overhead Monorail Cranes | Ceiling-Mounted Overhead Bridge Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single rail or track system suspended from the ceiling | Bridge structure with one or more girders supported from the ceiling |
| Movement | Hoist and trolley move along a single rail or track, providing linear movement | Bridge structure allows for longitudinal and lateral movement across the span |
| Support | Suspended from the ceiling, typically using hangers or brackets | Supported by the ceiling structure directly or through hangers |
| Applications | Ideal for linear material handling along a fixed path, suitable for assembly lines and production processes | Versatile for handling heavy loads, larger areas, and complex material handling tasks in industrial environments |
| Load Capacity | Typically lighter loads compared to bridge cranes, suitable for lighter to moderate applications | Higher load capacities, suitable for heavy industrial applications requiring robust lifting capabilities |
| Space Utilization | Maximizes floor space, minimally obstructive | Requires overhead space for the bridge structure and movement, may limit floor space utilization |
| Flexibility | Limited to linear paths, less versatile compared to bridge cranes | Offers versatile movement capabilities across larger areas and varied material handling scenarios |
| Installation Complexity | Generally simpler installation due to single rail or track system | More complex installation requiring structural considerations for bridge mounting and span |
| Cost | Cost-effective solution for specific linear material handling needs | Higher initial cost due to complex structure and heavier load capacity |
| Maintenance | Easier maintenance due to simpler design and fewer components | Requires regular maintenance of bridge structure, rails, and trolley system |
| Ideal Use Cases | Straight-line material transport in confined spaces | Heavy industrial applications, large-scale material handling, and production environments requiring versatile crane movement |
Summary:
- Overhead Monorail Cranes are efficient for linear material handling along fixed paths, maximizing floor space and suitable for lighter to moderate loads.
- Ceiling-Mounted Overhead Bridge Cranes offer versatile movement capabilities across larger areas and are ideal for heavy industrial applications requiring robust lifting and complex material handling.
Choosing between these crane types depends on specific operational requirements, space constraints, load capacities, and the complexity of material handling tasks within industrial environments.
Overhead Monorail Cranes Comparison with Floor-Mounted Monorail Cranes
Differences in Design and Functionality
Design:
- Overhead Monorail Cranes: These cranes operate on a single rail or beam that is mounted overhead, typically supported by ceiling-mounted structures or gantry systems. They move along a straight or curved path and are designed for linear material handling within a specific area or production line.
- Floor-Mounted Monorail Cranes: Floor-mounted monorail cranes have their rail or beam installed at ground level, often supported by columns or freestanding structures. They move along the floor and are designed to cover linear paths or specific work zones within a facility.
Flexibility and Coverage:
- Overhead Monorail Cranes: Overhead monorail cranes provide efficient material handling solutions while maximizing vertical space utilization. They are suitable for facilities with limited floor space or where maintaining clear ground access is essential. These cranes offer precise control over load positioning and movement, ideal for straight-line material flow.
- Floor-Mounted Monorail Cranes: Floor-mounted monorail cranes are versatile in covering linear paths along the ground. They offer flexibility in layout and can be configured to cover different areas within a facility without the need for overhead support structures. However, they occupy floor space and may require additional clearance for ground-level operations.
Load Capacity and Handling:
- Overhead Monorail Cranes: Typically used for lighter to medium-duty applications, overhead monorail cranes can handle loads ranging from a few hundred kilograms to several tons, depending on their design and configuration. They are efficient for repetitive material handling tasks with controlled movement overhead.
- Floor-Mounted Monorail Cranes: Designed for similar load capacities as overhead monorail cranes, floor-mounted versions offer ground-level accessibility and can handle loads with ease across different points within a facility. They are suitable for applications where direct ground access is preferred or where overhead installation is impractical.
Installation and Structural Requirements:
- Overhead Monorail Cranes: Installation of overhead systems involves mounting the rail or beam overhead, which requires sufficient ceiling height and structural support. They are integrated into building structures and may require planning for crane clearances and operational pathways.
- Floor-Mounted Monorail Cranes: Installation of floor-mounted systems involves setting up support columns or freestanding structures along the ground level. They are easier to install and require less structural modification compared to overhead installations, making them more flexible for various facility layouts.
Advantages of Overhead Monorail Cranes in Specific Applications
- Space Efficiency: Overhead monorail cranes maximize vertical space utilization by operating overhead, leaving the ground level clear for other activities. They are ideal for facilities with limited floor space or where maintaining clear ground access is crucial.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Due to their simpler design and installation requirements, overhead monorail cranes often entail lower initial costs compared to floor-mounted versions. They offer a cost-effective solution for smaller-scale material handling needs without compromising on efficiency.
- Safety and Ergonomics: Operating overhead, monorail cranes minimize the risk of ground-level accidents and improve ergonomic conditions for operators. They reduce manual lifting and handling tasks, contributing to a safer work environment and reducing potential injuries.
- Precision Handling: Overhead monorail cranes excel in applications requiring precise load positioning and movement along a designated path. They ensure accurate alignment and placement of materials, enhancing production quality and operational efficiency.
- Adaptability and Customization: Overhead monorail crane systems can be customized with various hoist configurations, speed controls, and automation features to meet specific operational requirements. This adaptability supports diverse industrial applications and allows for seamless integration with existing production processes.
In summary, while floor-mounted monorail cranes offer flexibility in ground-level accessibility and layout configuration, overhead monorail cranes provide advantages in space efficiency, cost-effectiveness, precision handling, safety, and customization options. Choosing between the two types depends on the specific operational needs, space constraints, and material handling requirements of the industrial facility.
Comparison Table: Overhead Monorail Cranes vs. Floor-Mounted Monorail Cranes

Overhead Monorail Cranes
| Feature | Overhead Monorail Cranes | Floor-Mounted Monorail Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Mounted on the ceiling, suspended using hangers or brackets | Mounted on the floor, supported by columns or pillars |
| Movement | Hoist and trolley move along a single rail or track system suspended from the ceiling | Hoist and trolley move along a single rail or track system mounted on the floor |
| Space Utilization | Maximizes floor space, minimal obstruction | Requires floor space for the rail or track system, may obstruct floor operations |
| Flexibility | Limited to linear paths, less versatile compared to floor-mounted systems | Provides linear movement flexibility within the operational area |
| Applications | Suitable for applications requiring overhead movement efficiency | Ideal for environments where floor space is ample and linear material handling is needed |
| Load Capacity | Typically lighter loads, suited for lighter to moderate applications | Capable of handling moderate to heavy loads, depending on the design and structure |
| Maintenance | Easier maintenance due to simpler access to components suspended from the ceiling | Requires maintenance of floor-mounted tracks or rails, as well as support columns or pillars |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective due to simpler installation compared to bridge cranes | May be more cost-effective in terms of installation and maintenance, depending on the facility layout and load requirements |
| Ideal Use Cases | Maximizing overhead space, suitable for confined spaces | Where floor space allows for efficient material handling operations with linear movement capabilities |
Summary:
- Overhead Monorail Cranes maximize floor space and are suitable for applications requiring overhead movement efficiency.
- Floor-Mounted Monorail Cranes provide flexibility in linear movement within the operational area and are ideal where floor space is ample.
Choosing between these crane types depends on specific operational needs, space constraints, load capacities, and the layout of the facility.
Installation and Maintenance of Overhead Monorail Cranes
Installation Process and Considerations
Installation Process:
- Site Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the facility to determine suitable locations for mounting the monorail beam or rail. Consider factors such as ceiling height, structural integrity of mounting points, and clearances required for crane operation.
- Structural Requirements: Ensure that the building structure can support the weight of the crane system, including the rail or beam, hoist mechanism, and any additional equipment such as motor drives and control systems.
- Mounting and Assembly: Install support brackets or columns for ceiling-mounted systems or freestanding supports for floor-mounted systems. Securely mount the monorail beam or rail along the designated path, ensuring alignment and levelness for smooth crane operation.
- Electrical and Control Setup: Connect electrical wiring for power supply to the crane, hoist, and control panel. Install control stations and ensure proper functionality of safety features such as limit switches and emergency stop controls.
Considerations:
- Clearance and Accessibility: Ensure adequate clearance around the crane's path to prevent obstruction during operation. Plan for maintenance access points and emergency escape routes as per safety regulations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhere to local codes, standards, and regulations governing crane installation, including load capacity ratings, electrical safety requirements, and structural stability.
Maintenance Best Practices for Longevity
Regular Inspections:
- Visual Inspections: Conduct routine visual inspections of the entire crane system, including the rail or beam, hoist mechanism, trolley, and electrical components. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage that may affect performance.
- Functional Checks: Test the operation of controls, limit switches, emergency stops, and safety features to ensure they are functioning correctly. Verify load capacity indicators and ensure they align with operational requirements.
Lubrication and Cleaning:
- Lubrication Schedule: Follow manufacturer recommendations for lubricating moving parts such as wheels, bearings, gears, and rails. Use appropriate lubricants to reduce friction and wear, extending the lifespan of components.
- Cleaning Procedures: Keep the crane system and components clean from dust, debris, and contaminants that can affect performance. Use compressed air or vacuum cleaning methods to maintain optimal operating conditions.
Component Maintenance:
- Hoist Mechanism: Inspect and maintain hoist chains, ropes, hooks, and lifting mechanisms regularly. Replace worn-out components promptly to prevent operational hazards or breakdowns.
- Electrical System: Check wiring, connections, and electrical components for signs of wear or damage. Ensure grounding and insulation integrity to prevent electrical faults or short circuits.
Structural Integrity:
- Rail or Beam Inspection: Monitor the condition of the monorail beam or rail for signs of deformation, cracks, or corrosion. Address structural issues promptly to maintain safe and reliable crane operation.
- Support Structures: Inspect ceiling-mounted supports or columns for stability and alignment. Ensure they can withstand operational stresses and environmental conditions without compromising safety.
Operator Training and Safety: Provide regular training for crane operators on safe operating procedures, emergency protocols, and equipment maintenance practices. Promote a culture of safety awareness to prevent accidents and ensure workplace safety.
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintenance Logs: Maintain detailed records of inspections, maintenance activities, repairs, and component replacements. Use these records to track equipment performance, identify recurring issues, and plan for future maintenance needs.
Case Studies and Examples of Overhead Monorail Cranes
Overhead monorail cranes have been successfully implemented in various industries, demonstrating their effectiveness in improving operational efficiency, safety, and productivity. Here are some real-world applications and success stories:
Automotive Manufacturing:
- Application: A leading automotive manufacturer integrated overhead monorail cranes into their assembly line to handle heavy components such as engine blocks and chassis frames.
- Benefits: The cranes facilitated precise positioning of parts during assembly, reducing production cycle times and improving overall product quality. They also enhanced workplace safety by minimizing manual handling and reducing the risk of accidents.
Food Processing Industry:
- Application: A food processing plant installed overhead monorail cranes to transport bulk ingredients and finished products between processing stages and storage areas.
- Benefits: The cranes streamlined material flow, ensuring timely delivery of ingredients for production and efficient distribution of finished goods. They met stringent hygiene standards and improved operational hygiene by minimizing floor contact and contamination risks.
Steel Manufacturing:
- Application: In a steel mill, overhead monorail cranes were used to transport heavy steel coils and billets across production lines and storage yards.
- Benefits: The cranes optimized material handling processes, reducing handling time and labor costs associated with moving large and heavy loads. They also supported continuous production flow, enhancing throughput and operational efficiency.
Warehouse and Distribution Centers:
- Application: Large warehouses and distribution centers utilize overhead monorail cranes for efficient loading and unloading of palletized goods and containers.
- Benefits: The cranes maximize vertical space utilization, allowing for high-density storage and retrieval operations. They enable rapid order fulfillment, reducing order processing times and improving inventory management efficiency.
Benefits Realized by Businesses
- Increased Productivity: Businesses experience significant productivity gains with overhead monorail cranes due to streamlined material handling processes, reduced cycle times, and improved workflow efficiency.
- Cost Savings: By minimizing manual labor and optimizing operational processes, businesses achieve cost savings in labor expenses, operational downtime, and maintenance costs associated with equipment wear and tear.
- Improved Safety: Overhead monorail cranes enhance workplace safety by reducing the risk of accidents related to manual lifting, material handling errors, and ergonomic strains on workers.
- Flexibility and Scalability: The modular design and customizable configurations of monorail crane systems allow businesses to adapt quickly to changing production demands and facility layouts.
- Enhanced Quality Control: Precise load positioning and controlled movement capabilities of monorail cranes contribute to improved product quality and consistency in manufacturing and assembly processes.
- Compliance and Standards: Businesses benefit from meeting regulatory compliance standards and industry-specific requirements related to material handling and workplace safety.
These case studies and examples highlight the diverse applications and tangible benefits of overhead monorail cranes across different industries. Businesses leveraging these crane systems can achieve operational excellence, improve competitiveness, and drive sustainable growth through enhanced efficiency and performance.
Conclusion
Recap of Advantages and Applications
Overhead monorail crane systems represent a versatile and efficient solution for various industrial material handling needs. Throughout this guide, we have explored their key advantages and diverse applications:
Advantages:
- Space Efficiency: Maximizes vertical space utilization, ideal for facilities with limited floor space.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower initial costs and operational expenses compared to other crane types.
- Precision Handling: Ensures accurate load positioning and movement along designated paths.
- Safety: Minimizes risks associated with manual handling through automated operations.
- Flexibility: Customizable configurations to adapt to specific operational requirements.
Applications:
- Manufacturing: Enhances assembly line efficiency and product quality.
- Warehousing: Optimizes storage and retrieval operations in distribution centers.
- Heavy Industries: Supports handling of large and heavy loads in steel mills and automotive plants.
- Food Processing: Maintains hygiene standards while facilitating efficient material flow.
Final Considerations for Implementing Monorail Crane Systems
Implementing overhead monorail crane systems involves careful planning and consideration of several factors:
- Operational Needs: Assess specific material handling requirements, including load capacities, movement patterns, and workflow integration.
- Space and Layout: Evaluate available space and facility layout to determine the most suitable crane configuration—ceiling-mounted, freestanding, or floor-mounted.
- Safety and Compliance: Ensure compliance with safety regulations and standards for crane installation, operation, and maintenance.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to assess the financial viability and return on investment of installing monorail crane systems.
- Maintenance Planning: Establish a proactive maintenance schedule and practices to maximize crane performance, reliability, and longevity.
By leveraging the advantages of overhead monorail crane systems and tailoring their implementation to specific operational needs, businesses can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, safety, and overall productivity. These systems not only optimize material handling processes but also contribute to operational excellence and competitive advantage in today's dynamic industrial landscape.
Related Products
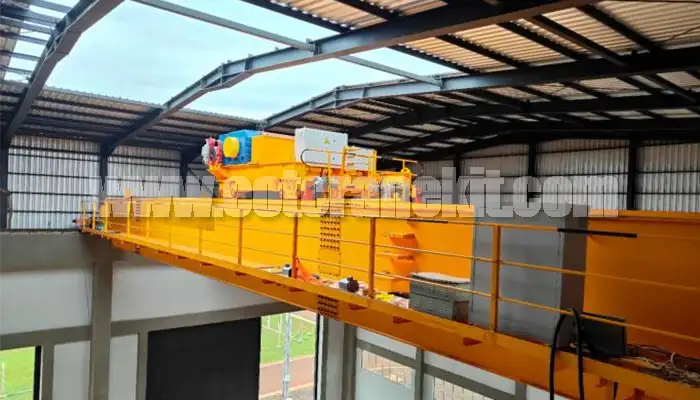

Latest project
150 Ton Overhead Crane Installation Feedback – Paraguay Case
QDX 150 ton overhead crane in action in Paraguay. Installation photos, video, and client feedback show performance, safety, and heavy-lifting efficiency.
Free consultation to Confirm Parameters & Specifications and Get
Latest Crane Price & Crane Rate.
- Types of overhead cranes : _______?
- Optional: Overhead travelling crane, goliath gantry crane,Slewing jib crane, Single girder or double girder crane,small portable crane or kbk crane, etc.
- Capacity of overhead crane: _______?
- Optional: 0.25ton, 0.5 ton, 1 ton, 2 ton, 3ton, 5 ton, 10 ton,15ton, 20ton, 25 ton, 30ton,35ton, up to 550ton, etc.
- Crane span & lifting height : _______?
- Crane travelling length : _____?
- Control of overhead crane:_______?
- Optional: pendant/ remote/cabin control
- Voltage supply of overhead crane:_____?
- Eg,: 380V50/60HZ,3Phase or others,etc.
- Application/usage of crane:_______?
- Eg,: Steel mill, ,injection mold, cement,stone, concrete,granite, general manufacturing, etc.
Just leave a message via the contact form and our hoist and crane engineer will contact you with in 24working hours.
Get In Touch