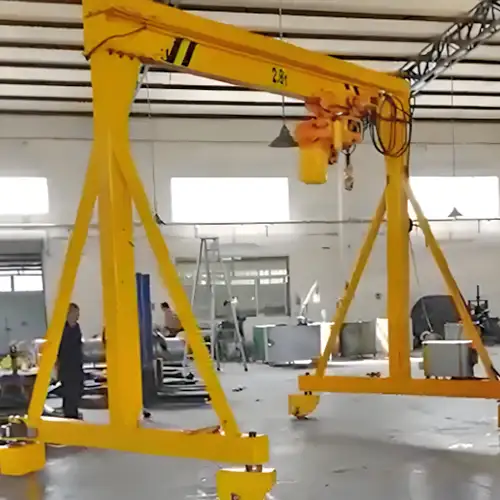
Die Handling Crane & Mold Handling Crane
Overview of Mold and Die Handling in Various Industries
Mold and die handling is crucial in industries like plastics, automotive, metalworking, and rubber manufacturing. In these sectors, molds and dies are used to shape and form products, and they come in different sizes, weights, and materials. Handling these molds properly is essential to ensure smooth production, reduce risk, and protect the equipment.
- Plastics Industry: Molds create plastic parts for products like containers, automotive parts, and consumer goods.
- Automotive Industry: Large molds and dies are used for body panels, engine components, and other heavy-duty parts.
- Metalworking Industry: Dies are used for forging and stamping large metal parts.
- Rubber Industry: Molds shape products like tires, seals, and rubber components.
Each mold or die is different in weight, shape, and size, which is why it's important to choose the right lifting equipment to ensure safe and efficient handling.
Importance of Selecting the Right Mold Lifting Crane
Selecting the right mold lifting crane is key to maintaining both safety and efficiency during mold handling. Using the wrong lifting equipment can cause damage to the molds, increase the risk of injuries, and lead to production delays. On the other hand, choosing the right crane ensures that molds are lifted securely, positioned accurately, and transported without issues, improving overall productivity and lowering costs.
Key points about choosing the right crane:
- Safety: Reduces the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Precision: Ensures accurate positioning of molds.
- Efficiency: Helps maintain a smooth, continuous workflow.
Using cranes that are designed for mold and die handling minimizes the risk of damaging molds or components and keeps the workplace safe for operators.
Types of Molds and Dies That Require Lifting Equipment
There are several types of molds and dies, and each one requires different lifting equipment based on its size, weight, and shape. Here are some common types:
- Injection Molds: Used in the plastics industry, these can range from small to large in size and require precise lifting.
- Die Casting Molds: Found in metalworking, these molds are heavy and often large, requiring high-capacity cranes.
- Stamping Dies: Used in the automotive and metal industries for shaping metal sheets, these dies can be large and heavy.
- Blow Molding Dies: Used for producing hollow plastic products, these molds are often delicate and need careful handling.
- Compression Molds: Common in rubber manufacturing, these molds handle large, bulky items and require heavy-duty lifting.
- Extrusion Dies: Used for creating continuous shapes like pipes and profiles, these molds need to be moved carefully.
Each type of mold has its own specific lifting requirements to ensure safety and minimize damage. Some molds are small and lightweight, while others are large, heavy, and complex. The right lifting crane will be selected based on these factors to ensure smooth and efficient mold handling.
Die Lifting Equipment for Different Molds Handling
Injection Molds
Key Characteristics, Typical Weights, and Dimensions:
- Injection molds are typically made from steel or aluminum and have a complex, multi-part design.
- Weight: Ranges from 50 kg to 2,000 kg (110 lbs to 4,400 lbs).
- Dimensions: Generally compact, varying from a few centimeters to several meters in size, depending on the molded part.
Typical Applications:Plastics industry: Molding parts for automotive components, consumer goods, medical devices, and containers.
Lifting Requirements and Mould Handling Equipment:
- Requires precision lifting to avoid damage.
- Recommended lifting equipment: Small overhead cranes, jib cranes, or hoists (1-ton to 5-ton capacity).
- Vacuum lifters or electric hoists are often used for intricate or delicate molds.
Die Casting Molds
Key Characteristics, Typical Weights, and Dimensions:
- Made from high-strength steel, designed to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures.
- Weight: Ranges from 1,000 kg to 10,000 kg (2,200 lbs to 22,000 lbs).
- Dimensions: Larger than injection molds, typically several meters in size.
Common Uses:Metalworking: Used for casting metal parts in industries like automotive (engine blocks, cylinder heads), aerospace, and heavy machinery.
Lifting Considerations:
- Requires heavy-duty lifting equipment due to the high weight.
- Recommended lifting equipment: Overhead cranes or gantry cranes with capacities from 5 tons to 15 tons.
- Spreader beams or lifting tongs are used for even weight distribution.
Stamping Dies
Features, Weight Ranges, and Sizes:
- Used in metalworking to shape metal sheets under high pressure.
- Weight: Ranges from 500 kg to 25,000 kg (1,100 lbs to 55,000 lbs).
- Dimensions: Can range from small dies for parts like brackets to large dies for automotive body panels.
Common Industries and Applications:Primarily used in automotive manufacturing for producing body parts, structural elements, and chassis components.
Lifting Needs:
- Stamping dies are heavy and require precision lifting to avoid misalignment.
- Recommended lifting equipment: Overhead cranes or gantry cranes with capacities from 5 tons to 50 tons.
- Lifting beams or slings are often used to ensure even load distribution.
Blow Molding Dies
Typical Weight, Dimensions, and Uses:
- Blow molding dies are used for producing hollow plastic products such as bottles, containers, and other packaging.
- Weight: Ranges from 100 kg to 5,000 kg (220 lbs to 11,000 lbs).
- Dimensions: Sizes vary from small, portable molds to large-scale production molds.
Unique Lifting Challenges and Solutions:
- Blow molding molds are often fragile and hollow, requiring careful handling to avoid damage.
- Recommended lifting equipment: Overhead cranes with electric hoists, vacuum lifters, or jib cranes (1-ton to 5-ton capacity).
- Vacuum lifters are commonly used to lift delicate, lightweight molds without direct contact.
Compression Molds
Characteristics, Size Range, and Common Applications:
- Used for molding thermosetting plastics and rubber products, these molds are larger and robust to handle high-pressure molding.
- Weight: Ranges from 500 kg to 15,000 kg (1,100 lbs to 33,000 lbs).
- Dimensions: Vary based on the application, from small rubber seals to large automotive components.
Lifting Needs for Thermosetting Plastic or Rubber Products:
- Compression molds require heavy-duty lifting equipment to handle the high pressure and robust materials used.
- Recommended lifting equipment: Overhead cranes or gantry cranes (5-ton to 20-ton capacity).
- Lifting tongs or custom lifting beams ensure the mold is lifted evenly, preventing distortion or damage.
Extrusion Dies
Size, Weight, and Shape:
- Extrusion dies are used to create continuous shapes like pipes, profiles, and sheets by forcing material through a mold.
- Weight: Ranges from 200 kg to 10,000 kg (440 lbs to 22,000 lbs).
- Dimensions: Typically long and thin, tailored to the desired product (e.g., pipes, rods, sheets).
Unique Requirements for Handling Continuous Shapes:
- Extrusion dies are often long and require precise, balanced handling to prevent bending or distortion.
- Recommended lifting equipment: Overhead cranes, gantry cranes, or jib cranes with vacuum lifters or spreader beams.
- Custom lifting setups ensure even weight distribution along the length of the die.
Summary of Key Considerations for Lifting Molds and Dies
Each type of mold or die has unique characteristics that affect its lifting requirements. The right lifting equipment is essential for ensuring safety, precision, and efficiency. Understanding the weight, dimensions, and fragility of molds and dies helps in selecting the appropriate lifting crane and accessories. Whether handling small, delicate injection molds or large, heavy die casting molds, selecting the right crane and lifting solution is crucial to maintaining a safe and productive work environment.
Overhead Cranes for Die Handling and Automotive Stamping
Overhead cranes solutions & rigging for dies & molds handling and automotive stamping. Cost-effective die handling crane & mold handling crane for sale.
In automotive press workshops, the pressing molds are required to be transported, overturned or replaced. For mould handling, there are types of overhead cranes are available such as,single girder overhead crane and double girder overhead crane,jib cranes, portable gantry crane and other other process cranes to meet various lifting requirements and applications.
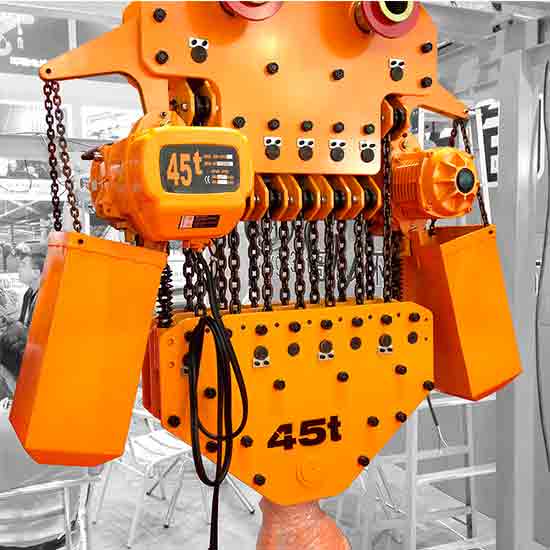
Electric chain hoists mounted on hook, lug, manual or electric hoist trolley for types of electric chain hoist cranes with capacity of 500kg, 5 ton, 10 ton, 32 ton.
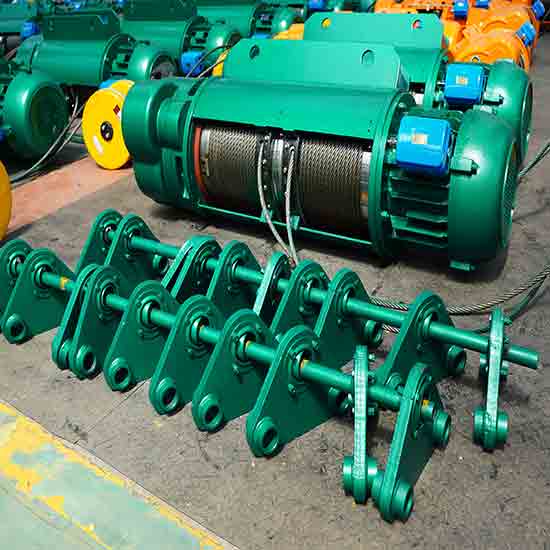

Types of wire rope hoists designs for overhead hoist cranes- explosion-proof cable hoist, low profile wire hoist & single & double girder hoists for your hoist cranes.
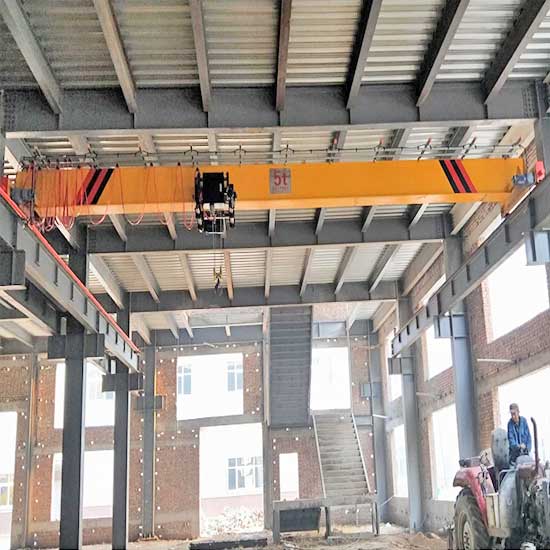

European standard overhead hoist crane, Small overhead crane:European single girder overhead cranes, compact FEM hoist crane design, small & light overhead hoist crane.
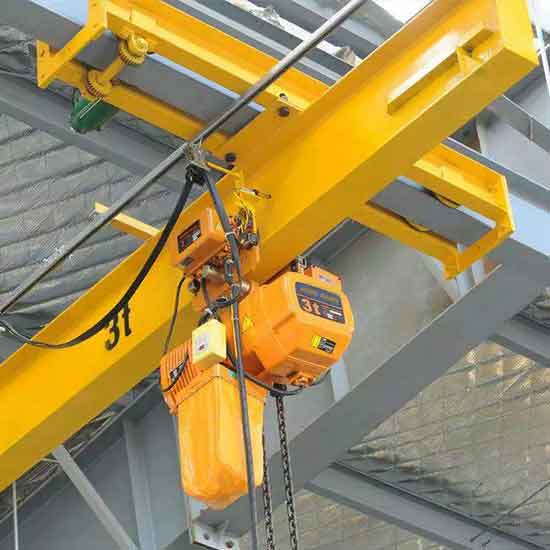

1 ton -10 ton underhung bridge crane, light single girder overhead crane design, suspended on overhead roof, free floor space, economical underhung crane.
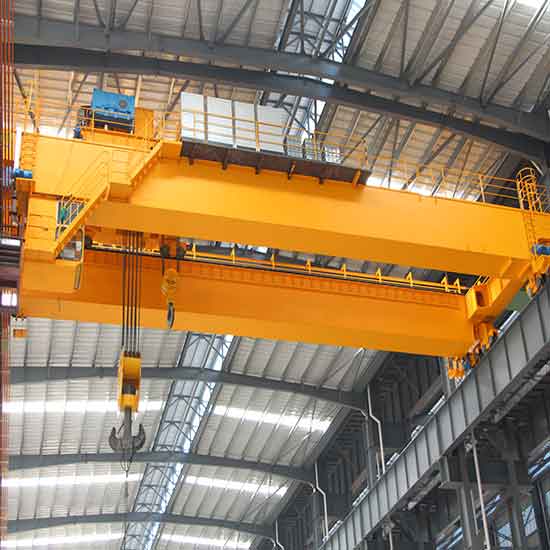

FEM/ DIN open winch bridge crane-European standard double girder overhead crane with open winch trolley, your heavy duty winch crane up to 320 ton.
Single Girder Overhead Cranes with lifting capacity from 1 ton to 20 ton are widely adopted to improve your working efficiency and help to make the best use of your space and save your investment on plant construction due to the features of light weight and small wheel pressure, easy installation and operation, etc. Single girder overhead cranes with process crane designs are available to meet your particular automobile industrial application.
Heavy duty double girder overhead cranes with configurations of hoist trolley crane or open winch cranes are frequently used in stamping workshops and press working of the automobile factory and plants for handling loads with weight above 32 ton. Process cranes for your specific industrial applications in press plants operated by the automotive industry.The process overhead travelling crane system can ensure that the required tools are stored and supplied to the press lines timely and safely.
Double girder overhead crane with duel hoists are most widely selected when mold overturning is required during die maintenance. When the molds are required to be turned over, double hoist cranes enable the wire rope be turned at certain angle, which is defined by the wire rope length and space between two hooks.
Benefits and Applications for Large or Heavy Molds:
- Overhead cranes are ideal for lifting large, heavy, and complex molds such as die casting molds, compression molds, and large stamping dies.
- They are highly effective in manufacturing environments like the automotive, metalworking, and plastics industries, where molds require precise handling and large lifting capacities.
Recommended Lifting Capacities and Configurations:
- Lifting capacities: Ranges from 5 tons to 100 tons or more, depending on the size and weight of the mold.
- Common configurations: Double girder and single girder overhead cranes.Double girder cranes: Ideal for handling heavy molds over long distances, offering greater stability.Single girder cranes: Suitable for lighter molds and more compact work areas.
Key Features for Safe Mold Handling:
- Load limiters to prevent overloads and ensure safe lifting.
- Tandem lifting capabilities for distributing the weight of larger molds evenly.
- Anti-sway systems to minimize load swing and maintain precise positioning.
- Variable speed control for smooth, controlled movements, which is essential for delicate mold handling.

Single girder overhead crane for material handling in plastic injection workshop and maintenance workshop

Top running overhead cranes for plastic workshop storages and material handling
Small Overhead Crane for Mold & Die Handling, Economical Steel Beam Crane, Light I beam Crane
Gantry Cranes
Advantages for Heavy-Duty Lifting and Mold Transport Across Large Spaces:
- Gantry cranes are ideal for large, heavy molds that need to be moved across a wide area. They are often used in manufacturing plants, warehouses, or outdoor environments.
- Perfect for lifting die casting molds, large stamping dies, and extrusion dies, gantry cranes allow flexibility in transporting molds over large distances.
Customization Options for Load Handling and Mobility:
- Adjustable span and height: These cranes can be customized to fit specific mold sizes and lift heights, making them suitable for various applications.
- Mobile gantry cranes: These cranes are mounted on wheels or rails, providing high mobility for mold handling across large factory floors or outdoor spaces.
Typical Lifting Capacities:
- Gantry cranes typically offer 5-ton to 50-ton lifting capacities, but they can be designed to handle even heavier loads based on the project requirements.
2 Ton Gantry Crane with Portable Crane Design for Light Mold Handling
Jib Cranes
Ideal for Confined Spaces and Precision Handling:
- Jib cranes are compact, versatile, and often used in environments where space is limited. They are ideal for precision lifting of smaller molds, such as injection molds, blow molds, and small stamping dies.
- They can be installed in tight spaces like workshops, assembly areas, or next to machines for efficient local handling.
Lifting Capacities and Applications for Smaller Molds:
- Lifting capacity: Typically ranges from 500 kg to 5 tons.
- Applications: Best suited for lighter molds or parts that require frequent handling in confined spaces. Common in the plastics, automotive, and electronics industries.
Key Features:
- Articulating arms: Provide flexibility for reaching into tight spaces.
- Rotating or swiveling capabilities: Allow for precise, controlled positioning of molds without additional space requirements.
- Electric or manual hoists: For easy lifting and lowering of molds.
2 Ton Jib Crane for Mold & Die Handling, Economical Small Jib Crane for Efficient Die Handling
Electric Hoists and Chain Hoists
Applications in Vertical Lifting and Precise Positioning:
- Electric hoists and chain hoists are frequently used in vertical lifting of molds, particularly for molds that need to be moved vertically within a confined space (e.g., for installation into presses or other equipment).
- These hoists are used to provide precise control when lifting smaller molds or positioning large molds in a specific location.
Typical Load Capacities and Motorized Options:
- Electric hoists: Typically have lifting capacities ranging from 500 kg to 5 tons. They are motorized and can be operated by remote controls for ease of use.
- Chain hoists: These are commonly used for heavier lifting needs, ranging from 500 kg to 20 tons. They are available in both manual and electric configurations, allowing for flexibility depending on the mold handling needs.
Key Features:
- Precision controls: For exact positioning and smooth lifting.
- Electric motor-driven hoists: Provide fast lifting speeds and consistent power for vertical mold movements.
- Chain hoists: Suitable for heavier lifting when precise positioning is needed.
Choosing the right type of mold lifting crane and equipment is essential for ensuring safe, efficient, and precise handling of molds in various industries. Each type of lifting equipment offers distinct benefits:
- Overhead cranes are ideal for handling heavy and large molds.
- Gantry cranes excel in moving molds across large spaces, with the flexibility for customization.
- Jib cranes are perfect for confined spaces and precision handling of smaller molds.
- Electric and chain hoists are suited for vertical lifting and precise positioning, making them ideal for mold installations.
Typical Capacity of Mold lifting Cranes
The capacity of cranes used for mold handling depends on the size, weight, and type of mold or die being handled. Here are some typical crane capacities that are commonly used in mold handling across various industries:
Light Duty Molds (Small Molds, Dies, and Tooling)
Typical Weight Range:50 kg to 2,000 kg (110 lbs to 4,400 lbs)
Crane Capacity:
- 1-ton to 5-ton cranes (Overhead Cranes, Jib Cranes, and Hoists)
- Suitable for small molds and dies used in plastics, rubber, or smaller metalworking operations.
Applications:
- Handling small injection molds, small stamping dies, and blow molding molds.
Recommended Crane Types:
- Overhead Cranes: For small molds and dies in manufacturing environments where precise lifting is necessary.
- Jib Cranes: Ideal for lifting small molds in confined spaces or for tool changing operations.
- Chain Hoists / Electric Hoists: For vertical lifting and precise handling.
Medium Duty Molds (Standard Molds and Dies)
Typical Weight Range:2,000 kg to 10,000 kg (4,400 lbs to 22,000 lbs)
Crane Capacity:
- 5-ton to 15-ton cranes (Overhead Cranes, Gantry Cranes, and Electric Hoists)
- These cranes handle medium-sized molds used in industries such as automotive, die casting, and heavy plastics molding.
Applications:
- Handling larger die casting molds, compression molds, and medium-sized stamping dies.
Recommended Crane Types:
- Overhead Cranes: For high-capacity lifting in large facilities, used for handling molds, dies, and heavy tooling.
- Gantry Cranes: Ideal for outdoor or large manufacturing spaces where mobility is important.
- Electric Hoists: Suitable for lifting and positioning molds with high precision.
- Vacuum Lifters: For delicate or complex molds that require non-contact handling.
Heavy Duty Molds (Large and Complex Molds, Dies)
Typical Weight Range:10,000 kg to 50,000 kg (22,000 lbs to 110,000 lbs)
Crane Capacity:
- 15-ton to 50-ton cranes (Overhead Cranes, Gantry Cranes, and Specialized Hoists)
- These are used for handling large molds, such as those used in automotive manufacturing or die casting industries.
Applications:
- Handling large automotive molds, heavy die casting molds, or large stamping dies.
- Used in facilities with large mold-making operations, such as for automotive parts, large appliances, and industrial equipment.
Recommended Crane Types:
- Double Girder Overhead Cranes: For heavy-duty lifting and handling of large, high-precision molds and dies.
- Gantry Cranes: For large molds that need to be moved across extensive spaces.
- Vacuum Lifters: For larger molds that are too heavy for manual lifting, especially for intricate shapes or delicate materials.
- Custom Lifting Beams or Spreader Bars: For ensuring even load distribution and safety when handling oversized or awkwardly shaped molds.
Ultra-Heavy Duty Molds (Massive Molds, Dies, and Specialized Tooling)
Typical Weight Range:50,000 kg to 150,000 kg (110,000 lbs to 330,000 lbs)
Crane Capacity:
- 50-ton to 100-ton cranes (Heavy Duty Overhead Cranes, Specialized Gantry Cranes)
- Used for very large, heavy molds, often found in industries such as aerospace, large metal manufacturing, and heavy casting.
Applications:
- Handling large-scale industrial molds, large die casting molds for engine blocks, aerospace components, or large structural parts.
Recommended Crane Types:
- Heavy Duty Double Girder Overhead Cranes: For the heaviest molds in large manufacturing plants with high lifting capacities.
- Custom Gantry Cranes: For moving exceptionally heavy molds in large spaces or over long distances.
- Crawler Cranes: When molds need to be moved over rugged terrain or in outdoor spaces.
Extreme Duty Molds (Specialized Molds for High-Temperature or Corrosive Environments)
Typical Weight Range:100,000 kg and above (220,000 lbs and above)
Crane Capacity:
- 100-ton to 500-ton cranes (Super Heavy Duty Overhead Cranes, Custom Gantry Cranes, and Floating Cranes)
- These are typically used for the most demanding applications, such as handling molds in high-temperature or hazardous environments.
Applications:
- Handling very large, heavy molds in steel production, aerospace, or military applications, where high strength, precision, and safety are critical.
Recommended Crane Types:
- Super Heavy Duty Overhead Cranes: Designed for extremely heavy molds that need specialized handling in challenging environments.
- Heavy Duty Gantry Cranes: Used for both indoor and outdoor handling of large molds and dies.
- Floating Cranes: In marine environments, for handling ultra-heavy molds used in shipbuilding or offshore applications.
Factors Affecting Crane Selection for Mold Handling
- Mold Weight: The primary factor in determining the crane's lifting capacity. Always ensure that the crane can handle at least 10-15% more than the mold's weight to account for dynamic forces during lifting.
- Mold Size and Shape: Larger molds or molds with complex shapes may require specialized attachments or spreader beams to ensure safe handling and even weight distribution.
- Precision Handling: For small or delicate molds, precision lifting equipment such as hoists, vacuum lifters, or jib cranes may be necessary.
- Space Constraints: The facility layout plays a role in selecting between overhead cranes, gantry cranes, or jib cranes, depending on headroom and space availability.
- Environmental Factors: For molds in harsh environments (high temperatures, corrosive substances), cranes with heat-resistant components, corrosion protection, and other specialized features may be required.
The crane capacity required for mold handling varies significantly based on the weight and size of the molds, as well as the precision and environmental conditions of the workspace. Selecting the appropriate crane ensures safe, efficient, and reliable mold handling, reducing the risk of damage to molds, injuries, and operational downtime. Always choose a crane with a slightly higher lifting capacity than the mold's weight to provide an added safety margin.
Die Dandling Cranes and How to Ensure Precisie Handling
Die handling cranes, also known as die transfer cranes or die handling overhead cranes, are specialized lifting equipment used to handle heavy dies in various manufacturing processes. These cranes are commonly found in industries such as automotive, aerospace, metalworking, and plastic manufacturing, where large and heavy dies need to be moved between workstations, storage areas, and production machines.
To ensure precision handling of dies, several factors need to be considered:
- Design and Capacity Die handling cranes should be designed with the specific die dimensions and weight in mind. The crane's capacity should exceed the weight of the heaviest die to be handled to ensure safe and efficient lifting.
- Hoist and Lifting Mechanism The crane's hoist and lifting mechanism should provide smooth and controlled movements. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) can help achieve precise lifting and lowering speeds, reducing the risk of sudden movements that could damage the dies.
- Load Balancing Proper load balancing is crucial to ensure that the weight of the die is evenly distributed on the crane's lifting mechanism. Imbalanced loads can cause instability and potentially lead to accidents or damage to the dies.
- Control Systems Advanced control systems, such as radio remote controls or pendant controls with fine speed adjustments, allow operators to have precise control over the crane's movements. This enables the crane to handle dies with accuracy, especially in tight spaces.
- Safety Features Die handling cranes should be equipped with safety features, including limit switches and overload protection systems. Limit switches prevent the crane from overtraveling, while overload protection prevents the crane from lifting loads beyond its capacity, ensuring safe operations.
- Specialized Lifting Attachments The use of specialized lifting attachments, such as die lifters or custom-designed lifting devices, can improve precision handling. These attachments securely hold the dies during lifting and transfer operations, reducing the risk of unintended movements or damage.
- Operator Training Proper training of crane operators is essential for precision handling. Operators should be familiar with the crane's controls, safety features, and proper procedures for lifting and transferring dies.
- Regular Maintenance Regular maintenance and inspections of the crane are essential to ensure that it operates smoothly and accurately. Any signs of wear, malfunction, or misalignment should be promptly addressed to maintain precision handling.
- Automation and Robotics In some advanced manufacturing settings, automation and robotics can be integrated into die handling processes to achieve even higher levels of precision and efficiency.
By considering these factors and ensuring that the die handling crane is designed, maintained, and operated properly, precision handling of dies can be achieved. This not only improves safety but also contributes to smoother production processes, reducing downtime, and ensuring the longevity of valuable dies used in manufacturing.
Key Considerations When Choosing Mold Lifting Equipment
Weight and Size of the Mold/Die
Determining Lifting Capacity:
- The first step in selecting the right lifting equipment is determining the weight and size of the mold or die.
- For light molds (e.g., injection molds, blow molds), lifting capacities from 1 ton to 5 tons are typically sufficient.
- For heavier molds (e.g., die casting molds, stamping dies), cranes with 5 tons to 50 tons or more lifting capacity are necessary, depending on the size and weight.
Types of Cranes for Light vs. Heavy Molds:
- Light Molds:Jib cranes, electric hoists, or small overhead cranes (1-ton to 5-ton capacity) are ideal for precise handling of smaller, delicate molds.
- Heavy Molds:Heavy-duty overhead cranes, gantry cranes, and semi-gantry cranes are recommended for larger, heavier molds that require more substantial lifting power.These cranes often need additional attachments, such as spreader beams or lifting tongs, to ensure an even load distribution.
Precision and Handling Requirements
Importance of Precision for Delicate or Complex Molds:
- Many molds, such as injection molds and blow molds, can be delicate or intricate, requiring high precision during lifting. Mishandling can cause misalignment, damage, or even complete mold failure.
- Molds for high-precision parts (e.g., in the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries) require careful handling to avoid scratches, misalignment, or surface damage.
Recommended Lifting Equipment for Accuracy:
- Vacuum Lifters: Ideal for handling delicate molds and preventing direct contact with the mold surface.
- Electric Hoists: Provide precise control over lifting, ideal for small molds where accuracy is crucial.
- Jib Cranes: Offer flexibility and maneuverability for small-to-medium-sized molds, ensuring precise positioning.
Work Environment Factors
Impact of Space Constraints, Temperature, and Environmental Conditions:
- Space: Limited workspace can impact the crane's lifting ability and movement. In tight spaces, compact cranes or jib cranes are ideal.
- Temperature: Extreme heat or cold conditions can affect both the mold and lifting equipment. High temperatures can make cranes overheat, while low temperatures can cause metal embrittlement.
- Corrosive Environments: Molds and dies used in marine, chemical, or food processing industries are susceptible to corrosion. Anti-corrosion coatings or stainless steel cranes may be necessary.
Choosing Equipment Based on Conditions:
Compact Cranes: When space is a constraint, cranes with smaller footprints (e.g., jib cranes or portable gantry cranes) are better suited for confined environments.
Environment-Specific Cranes:
- For high temperatures, high-temperature-rated cranes or cranes with heat-resistant components are recommended.
- For corrosive environments, stainless steel cranes or cranes with special anti-corrosion coatings ensure longevity and safe operation.
Safety Features
Safety Standards and Features:
Lifting heavy molds comes with inherent risks, making it crucial to select lifting equipment with the right safety features to protect operators and the equipment itself.
Essential Safety Features:
- Load Limiters: Prevent overloading by automatically halting crane movement once the safe load limit is reached.
- Over-Speed Protection: Prevents the crane from moving too quickly, which can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
- Emergency Stop Functions: Allows operators to stop the crane immediately in case of malfunction or unsafe conditions.
Handling Hazardous or High-Temperature Molds:
- Hazardous Materials: If molds involve toxic or hazardous materials, explosion-proof hoists or flameproof lifting equipment are necessary.
- High-Temperature Molds: Special cranes designed to handle high-temperature materials (e.g., die casting molds) should be equipped with temperature-resistant components to avoid heat damage.
When choosing mold lifting equipment, several factors need to be carefully considered to ensure the right crane is selected for the job:
- Weight and Size: Ensure the crane has the correct lifting capacity for the mold's weight and size, with appropriate equipment for light or heavy molds.
- Precision and Handling: Delicate molds require equipment that provides precision handling, such as vacuum lifters and electric hoists.
- Work Environment: Environmental conditions like temperature, space constraints, and corrosive environments should influence the selection of cranes with the proper features (e.g., heat resistance or compact design).
- Safety: Ensure the crane meets safety standards, with features like load limiters, over-speed protection, and emergency stops, particularly when handling hazardous materials or high-temperature molds.
Selecting the appropriate mold lifting equipment is crucial for maintaining safety, efficiency, and precision in mold handling operations.
Customized Mold Handling Cranes Projects for Your Reference
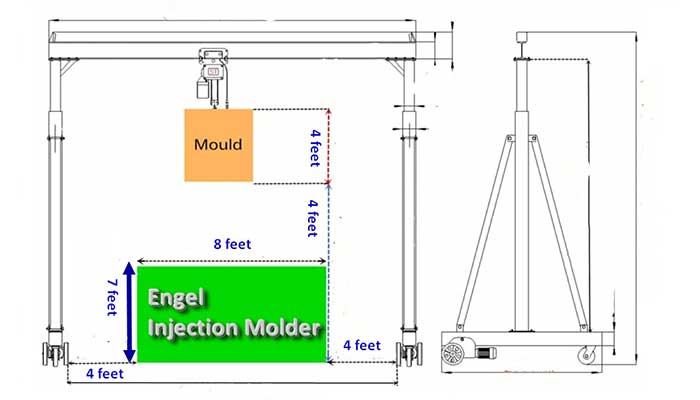
Portable A frame gantry crane 10 ton for coffe capsule mold handling
- Types of Cranes:Portable A Frame Gantry Crane 10 Ton
- Date of Placing Order: 2021-09-22
- Date of delivery :30 Days after payment
- Transportation :By sea , container.
- Payment: TT
- Destination port:DDU, delviery to the workshop of the client, the designated address
- Destination country:Canada
- Backgroud of 10 ton A frame cranes for injection die handling
The 10-ton gantry crane will be used for injection mold handling in a coffee capsule manufacturing facility in Canada. In terms of multi-cavity mold design and production for the making of coffee capsules made of biodegradable plastic, Mold & dies at the forefront of the industry. The 10 ton A frame crane is required to improve injection mold exchanging efficiency and safety.
Light Mold Handling
2 Ton Jib Crane Application in Small Mold Handling in Thailand
Low Headroom Gantry Crane 5 Ton for Plastic Injection Mold Handling
5 Ton Telescoping Gantry Crane for Loading Mold to Truck Kuwait
Variable Speed Gantry Crane 5 Ton for Mold Handling High Precision
Heavy Mold Handling
Gantry Cranes 10 Ton for Prefabricated Cable Trench Mold Handling
10 Ton A Frame Crane, Small 10 Ton Portable A frame crane for Mold Hoisting
European Style 15 Ton Overhead Bridge Crane for Blow Mold Handling
Mold Handling 40 Ton Bridge Crane in Automobile Parts Factory USA
Overhead Crane 3 Ton to 50 Ton for Mold Table Material Handling in Precasting
Gantry Cranes & Overhead Cranes for Large Formworks & Concrete Molds Handling
How to Select the Right Mold Lifting Crane for Your Needs
1. Assessing Mold/Die Characteristics
Evaluate Size, Weight, Shape, and Fragility to Determine the Ideal Lifting Equipment
When selecting a lifting crane, it's essential to first assess the mold or die characteristics:
- Size and weight: Determine if the mold is heavy or large. This will help guide the lifting capacity and type of crane required.
- Shape: Irregularly shaped molds may require cranes with special attachments or configurations for stable lifting.
- Fragility: Delicate molds, like blow molding dies or injection molds, require cranes that can handle them without causing damage.
Case Studies on Selecting Cranes for Different Types of Molds
- Heavy die casting molds might require overhead cranes with high lifting capacities (e.g., 30 tons or more), as they are often bulky and need precise positioning.
- Injection molds or blow molding dies, which are more delicate, may require vacuum lifters or jib cranes for non-contact lifting and accurate positioning in confined spaces.
2. Facility Requirements
Choosing Based on Facility Layout, Available Headroom, and Space Constraints
- Consider the facility layout when choosing a crane. The crane should be able to move freely within the space without obstructing other operations or equipment.
- Headroom is crucial; ensure that the crane's height fits within the available vertical space without affecting overhead clearance.
- For narrow spaces or areas with limited headroom, a jib crane or gantry crane may be more suitable.
Choosing Between Permanent and Portable Crane Systems
- Permanent systems: Fixed installations like overhead cranes provide high reliability and efficiency for high-volume mold handling.
- Portable systems: Mobile gantry cranes or jib cranes are more flexible, allowing you to move the crane between workstations or even across different locations within the facility. These are ideal for low-volume or temporary setups.
3. Load Handling and Precision Needs
Aligning Crane Selection with the Level of Precision Required for Handling Specific Molds and Dies
- For molds requiring high precision (e.g., injection molds, blow molds), choose a crane system that offers fine control over lifting and movement. Cranes with variable speed controls and soft-start features ensure smooth lifting without jolting or swinging.
Using Tools Like Spreader Beams, Lifting Beams, and Custom Attachments for Improved Handling
- Spreader beams and lifting beams help evenly distribute the weight of larger or awkwardly shaped molds, ensuring that they are lifted safely and stably.
- Custom attachments like vacuum lifters, clamps, and grippers can be added to the crane to meet the specific requirements of handling delicate or intricate molds.
4. Maintenance and Durability
Selecting Equipment That Minimizes Downtime and Is Easy to Maintain
- Opt for crane systems that are designed for low-maintenance and easy repairs. Look for features like self-lubricating systems or quick-change parts to reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
- Regular inspection and maintenance schedules are essential for extending the crane's lifespan and ensuring consistent performance.
Ensuring Long-Term Durability, Especially for High-Use Applications or Harsh Environments
- For high-use environments or harsh conditions (e.g., extreme heat, corrosive environments), choose cranes with durable materials and anti-corrosion coatings.
- Cranes used in environments like die casting plants or metalworking should be designed to withstand frequent use and harsh operating conditions, ensuring minimal wear and tear.
5. Safety and Compliance
Ensuring the Crane Meets Industry Safety Standards
- Ensure that the crane is designed and certified according to industry safety standards, such as the CE marking or ISO certification.
- Verify that the crane complies with local regulations and standards specific to your industry to ensure safety and legal compliance.
Understanding the Role of Safety Devices Like Overload Protection, Anti-Sway Mechanisms, and Emergency Stops
- Overload protection: Prevents accidents by limiting the weight the crane can lift, ensuring it doesn't exceed its rated capacity.
- Anti-sway mechanisms: Minimize load swing and help the operator maintain control, which is especially useful when lifting large or heavy molds.
- Emergency stop functions: Allow operators to stop the crane immediately in the event of an emergency, reducing the risk of accidents and mold damage.
Selecting the right mold lifting crane involves evaluating the mold characteristics, understanding the facility requirements, ensuring precision and load handling, maintaining equipment durability, and ensuring safety compliance. By considering each of these factors, you can select the most appropriate crane system that meets your operational needs, reduces downtime, and improves overall safety and efficiency in mold handling.
Best Practices for Efficient Mold Handling
Proper Rigging and Lifting Techniques
Techniques for Safe Rigging to Avoid Damage or Accidents
- Proper rigging is essential for safe and efficient mold handling. It involves the use of correct rigging hardware, such as slings, shackles, and hooks, to secure the mold or die during the lifting process.
- Ensure that the rigging gear is rated for the weight of the mold and is in good condition. Always inspect the rigging equipment for signs of wear or damage before use.
- Avoid overloading: Never exceed the rated lifting capacity of the crane or rigging gear. This can lead to accidents, equipment failure, or mold damage.
- For irregularly shaped molds, use lifting beams or spreader beams to ensure balanced lifting and prevent tipping or swinging.
Best Practices for Lifting Large and Heavy Molds
- When handling large or heavy molds, always use a team of operators if necessary. Ensure that the load is properly distributed, and avoid sudden movements to reduce the risk of accidents.
- Slow and steady lifting: Move the load slowly and smoothly to prevent sudden jerks or swings, which could damage both the crane and the mold.
- Use taglines or guiding ropes when handling large molds to help control the load during lifting, especially in tight or confined spaces.
- Ensure proper load balance by confirming that the mold is centered and evenly distributed before lifting to avoid tipping or misalignment during the lifting process.
Routine Maintenance and Inspections
Importance of Regular Checks on Lifting Equipment to Ensure Safe Operation
- Regular maintenance is critical to ensure that your mold lifting equipment operates smoothly and safely. Without proper upkeep, wear and tear can cause malfunctions, increasing the risk of accidents and downtime.
- Create a maintenance schedule based on the frequency of use and environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity). Regular inspections should check for signs of wear, corrosion, and stress on key parts like cables, pulleys, and hoists.
Key Areas for Maintenance (Hoists, Ropes, Controls, etc.)
- Hoists: Regularly inspect the motors, gears, and brakes for signs of wear or damage. Check the lifting chains or ropes for fraying or stretching, which could compromise the lifting capacity.
- Ropes and Cables: Ensure that the ropes or cables used for lifting are in good condition and free from frays or kinks. Replace any damaged ropes immediately to prevent accidents.
- Controls: Ensure that the control systems (whether manual or automated) are functioning correctly. Test the emergency stop function and other safety features regularly to ensure proper response in case of emergencies.
- Crane structure: Inspect the crane framework, rails, and trolley systems for signs of stress, cracks, or misalignment. Routine checks will ensure the crane operates efficiently and safely under all conditions.
Operator Training and Safety Protocols
Providing Adequate Training for Operators to Ensure They Understand Equipment Functions and Safety Procedures
- Training is crucial for operators to safely and efficiently handle mold lifting equipment. All operators should be certified and thoroughly trained in crane operation, rigging, and safety protocols.
- Training should include familiarizing operators with specific crane models, load capacities, lifting techniques, and safety devices. Operators should also be trained to identify potential hazards and take appropriate action to mitigate risks.
- Hands-on training is essential, as it allows operators to practice lifting and handling molds in a controlled environment before working with actual molds in production settings.
Creating a Safety Culture Around Mold Handling
- Encourage a safety-first mentality across the entire operation by providing regular safety refresher courses for operators, maintenance personnel, and other relevant staff.
- Implement clear safety protocols for mold handling, including rules for inspections, emergency responses, and communication between operators and support staff.
- Regularly review and update safety guidelines to ensure they align with the latest industry standards and reflect any changes in equipment, materials, or operating conditions.
- Promote teamwork and ensure that workers understand the importance of clear communication during mold handling. Use signaling or walkie-talkies to help guide lifting operations and ensure smooth coordination.
Quick Checklist for Selecting the Right Mold Lifting Crane
Mold and Die Characteristics
Weight:
- Choose a crane with the appropriate lifting capacity based on the mold's weight.
- Light Molds: If handling smaller molds (up to 5 tons), electric hoists or jib cranes are ideal for precision.
- Heavy Molds: For large, heavy molds (above 10 tons), overhead cranes or gantry cranes are better suited due to their higher load capacity.
Size:
- Compact Molds: If space is limited, a jib crane or a light-duty gantry crane might be suitable for smaller molds.
- Large Molds: For molds requiring large operational space, a double girder overhead crane or a heavy-duty gantry crane is better for handling oversized molds efficiently.
Fragility:For delicate or intricate molds, vacuum lifters or electric hoists with precise control are ideal to avoid damaging the mold.
Shape:If the mold has an unusual or complex shape, spreader beams or custom lifting attachments may be required to ensure safe handling and avoid stress on the mold.
Industrial Sector Needs
Plastics Industry:
- Injection Molds and Blow Molding Dies are common in this sector.
- Recommended Cranes: Overhead cranes with precise controls (e.g., electric hoists) or gantry cranes for larger molds.
- Cranes should have high lifting capacities (up to 20 tons) to handle heavy molds, but they must also be able to provide fine control to prevent mold damage.
Automotive Industry:
- Stamping Dies and Injection Molds are typical for this industry.
- Recommended Cranes: Overhead cranes with high lifting capacity (up to 30 tons) and gantry cranes for heavy-duty mold transport across large facilities.
- Jib cranes may be useful in confined spaces for precision handling of smaller molds.
Metalworking:
- Die Casting Molds and Extrusion Dies are common in this sector.
- Recommended Cranes: Heavy-duty overhead cranes and gantry cranes (up to 50 tons or more) are often required to handle large, heavy molds with rough surfaces.
- Anti-corrosion coatings and heat-resistant features may be needed for molds exposed to high temperatures or harsh chemicals.
Rubber Industry:
- Compression Molds are frequently used to form rubber products.
- Recommended Cranes: Overhead cranes with high lifting capacity and electric hoists with precise control for handling heavy and often large compression molds.
- The cranes should also be durable enough to handle high-temperature molds.
Food Processing:
- Typically involves smaller molds for forming food products.
- Recommended Cranes: Jib cranes or light-duty gantry cranes are suitable for small mold handling.
- Equipment should also be easy to clean and comply with food safety regulations.
Precision and Handling Requirements
Precision Handling:
- If your molds require high precision, opt for electric hoists or vacuum lifters for delicate, smaller molds. These provide fine control, minimizing the risk of damage during lifting.
- Jib cranes offer excellent flexibility for precise, localized handling of smaller molds in confined spaces.
Heavy Load Handling:
- For large, heavy molds, a double girder overhead crane or a gantry crane is more appropriate due to their ability to handle high loads and span wide areas.
Facility Considerations
- Space Constraints:In smaller factories or production areas, jib cranes are ideal as they can fit into tight spaces and are easy to maneuver.For larger facilities with more expansive mold handling needs, overhead cranes or gantry cranes are better suited to handle large loads across broad areas.
- Headroom:Check the available headroom for lifting the mold. If the headroom is limited, a low-profile gantry crane or a single girder overhead crane may be needed to maximize vertical space.
- Mobility:If molds need to be moved across different areas within a facility, consider portable gantry cranes or mobile jib cranes for flexibility and ease of relocation.
Environmental Factors
Temperature and Corrosive Conditions:
- For molds exposed to high heat (e.g., die casting), select cranes with heat-resistant motors and anti-corrosion coatings.
- Explosion-proof hoists or cranes may be necessary in environments with hazardous materials or explosive risks.
Outdoor or Heavy-Duty Needs:
- Gantry cranes are typically used in outdoor environments, especially in construction or steel industries, as they can withstand harsher conditions.
Maintenance and Durability
- For long-term use, consider the crane's maintenance needs and durability in high-use environments.
- Cranes with easy access for maintenance, durable materials, and minimal downtime will ensure reliable operation in industries like automotive or metalworking.
By considering these factors specific to your industry and mold handling needs, you can select the ideal mold lifting crane for your production line, ensuring safe, efficient, and precise handling in your facility.
Safety Features
- Look for load limiters, emergency stop buttons, and anti-sway systems to ensure safe lifting and operation, especially when handling heavy or delicate molds.
- Over-speed protection and motion control features are essential for ensuring mold handling is done within safe operational limits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the best lifting equipment for handling small, delicate molds?
For handling small, delicate molds, vacuum lifters or electric hoists with precise control are often the best options. Vacuum lifters offer non-contact lifting, reducing the risk of damage to the mold's surface. Jib cranes with manual or electric hoists are also ideal for precision handling in confined spaces. They provide control and accuracy, making them suitable for lifting smaller, more intricate molds without damaging them.
How do I know if my overhead crane can handle the required weight and size of the mold?
To ensure that your overhead crane can handle the required weight and size of the mold, you need to check the crane's load capacity and span. The crane's load rating must exceed the weight of the mold, including any accessories such as lifting beams or hooks. Additionally, you must confirm the crane's lift height and space clearance to ensure the mold can be lifted and transported without obstruction. If unsure, consult with a crane expert or manufacturer to verify that your crane meets the specific requirements of your molds.
What are the safety features I should look for when selecting mold lifting equipment?
When selecting mold lifting equipment, prioritize the following safety features:
- Load limiters: Prevent overloading by automatically stopping the crane if it exceeds its rated capacity.
- Emergency stop functions: Allow operators to quickly halt operations in case of malfunction or emergency.
- Over-speed protection: Ensures that the crane moves at a safe speed and prevents rapid, uncontrolled lifting or lowering.
- Anti-sway mechanisms: Reduce load swinging during operation, improving control and stability.
- Safety guards and rails: Protect operators from accidental contact with the lifting equipment or mold.
- Inspection and monitoring systems: Include systems that allow real-time monitoring of load weights and crane performance, ensuring safe operations at all times.
By ensuring that these safety features are integrated into the lifting equipment, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with mold handling and maintain a safe working environment.
Conclusion
Summary of the Importance of Selecting the Correct Mold Lifting Crane
Selecting the right mold lifting crane is essential for ensuring safe and efficient operations in industries that handle large, heavy, or delicate molds and dies. Choosing the correct crane ensures that the lifting process is carried out with precision, minimizing risks such as mold damage, equipment failure, or accidents. It also plays a crucial role in optimizing productivity by ensuring smooth, timely, and secure handling of molds and dies.
Final Recommendations for Assessing Your Mold Handling Needs
When selecting a mold lifting crane, it is important to assess:
- Mold Characteristics: Evaluate the weight, size, fragility, and shape of the molds and dies you handle to determine the appropriate lifting capacity and crane type.
- Work Environment: Consider space constraints, temperature conditions, and any hazardous or corrosive environments that may influence crane selection.
- Precision Needs: Choose equipment that ensures the required level of precision, especially for intricate or delicate molds.
- Safety and Compliance: Ensure that the lifting equipment meets relevant safety standards and is equipped with necessary safety features like load limiters and emergency stop functions.
How Making the Right Choice in Equipment Can Lead to Increased Efficiency, Safety, and Reduced Downtime
Investing in the right mold lifting crane not only enhances the safety of the operation by preventing accidents and ensuring safe handling but also improves efficiency by reducing lifting times and ensuring a smoother workflow. The right equipment minimizes downtime caused by equipment failures, offering long-term reliability and performance. By selecting the appropriate crane and handling equipment, businesses can achieve higher productivity, reduced mold damage, and lower maintenance costs, ultimately contributing to a safer, more efficient work environment.
Get Your Customized Overhead Cranes
As a reliable partner to the automotive industry, we are able to supply types of industrial crane solutions and services for the materials handling and in-house logistics along the entire value chain. Contact us to get the industry crane system for your specific application in the automotive industry.
On buying overhead crane, the following main parameters are needed:
- Types of overhead crane: Single girder or double girder overhead crane? Top running or underlusng crane?
- Lifting capacity of overhead crane : Ultimate load lifting capacity= ____tons.
- Span of overhead crane span: distance between the railway center = ____ meters.
- Lifting height of overhead crane : height of lifting from the ground to the lift center (Hook) = ____ meters.
- Crane track length of overhead crane _______m
- Crane track required (to be installed on existing supports): ØCrane track length _______m ,ØSupport spacing _______m
- Overhead crane use/application: ____________________________________
- Control methods of overhead crane : Remote control / Cabin control /Panel control
- Frequency = ____.
- Voltages = ____.
How much does an overhead crane cost to buy? Send us an inquiry via the below form to get an overhead crane solution to lift your loads and relief your burden! Send an overhead crane inquiry to get your latest eot crane price now!





